How to Prevent and Cure Zinc Deficiency in Your Plants
Table of Contents
Zinc Deficiency in Plants: Understanding the Importance of Zinc
Zinc is an essential micronutrient for plants, playing a critical role in various physiological processes. It is involved in the synthesis of proteins, enzymes, and chlorophyll, as well as in the regulation of growth and development. Without adequate levels of zinc, plants can suffer from a range of issues, ultimately impacting their overall health and productivity.

One particular importance of zinc lies in its role in photosynthesis. Zinc is a vital component of the enzyme carbonic anhydrase, which facilitates the conversion of carbon dioxide into the organic compounds that fuel plant growth. Additionally, zinc is involved in the synthesis of auxins, a class of plant hormones that regulate cell elongation and differentiation. These hormones are crucial for root development, nutrient uptake, and overall plant growth. Without sufficient zinc, plants may exhibit stunted growth, decreased root development, and reduced photosynthetic efficiency.
Signs of Zinc Deficiency in Plants: Identifying the Problem Early
Zinc deficiency in plants is a common problem that can lead to significant negative impacts on plant growth and overall health. Identifying the signs of zinc deficiency early is crucial for effective intervention and to prevent further damage. One of the primary signs of zinc deficiency in plants is stunted growth. Plants lacking zinc may appear stunted, with smaller leaves and shorter stems compared to healthy plants. This stunted growth can be particularly noticeable in young plants that are still developing.
Another sign of zinc deficiency is interveinal chlorosis, which is the yellowing of the tissue between the veins of leaves. This occurs because zinc is essential for the synthesis of chlorophyll, the pigment responsible for the green color in plants. Without adequate zinc, plants are unable to produce chlorophyll effectively, resulting in yellowing leaves with green veins. Furthermore, zinc deficiency can also manifest as leaf distortion, where leaves may curl or become misshapen. This distortion occurs due to the disruption of normal growth processes in the absence of zinc.

It is important to note that the signs of zinc deficiency can vary depending on the plant species and its nutrient requirements. Therefore, gardeners need to familiarize themselves with the specific signs of zinc deficiency in the plants they are cultivating. By identifying these signs early on, gardeners can take appropriate measures to rectify the deficiency and ensure healthy plant growth.
Soil Testing: Assessing Zinc Levels in Your Soil
When it comes to growing healthy and thriving plants, understanding the nutrient levels in your soil is crucial. One important nutrient that plays a key role in the growth and development of plants is zinc. Assessing the zinc levels in your soil through regular soil testing is an essential step to ensure that your plants have adequate access to this vital element.
Soil testing provides valuable information about the availability of zinc in your soil, helping you determine whether your plants are at risk of zinc deficiency. Zinc deficiency can lead to stunted growth, reduced yields, and increased susceptibility to diseases and pests. By assessing the zinc levels in your soil, you can identify potential deficiencies early on and take necessary measures to address them. Soil testing not only helps you understand the current zinc status of your soil but also enables you to track changes over time, allowing for adjustments in your fertilization and management practices.

To assess the zinc levels in your soil accurately, it is recommended to consult with a professional soil testing laboratory. These labs utilize specialized techniques and equipment to measure the concentration of zinc in your soil sample. The results of the soil test will provide you with valuable insights into the actual zinc content in your soil, allowing you to make informed decisions regarding fertilizer applications and soil amendments. Through regular soil testing, you can effectively monitor and manage the zinc levels in your soil, ensuring optimal nutrient availability for your plants and maximizing their growth and productivity.
Improving Soil Health: Enhancing Zinc Availability for Plants
Enhancing zinc availability for plants is a crucial aspect of improving soil health. Zinc is an essential micronutrient required for plant growth and development. When the levels of zinc in the soil are limited, plants may exhibit signs of deficiency, such as stunted growth, yellowing of leaves, and reduced crop yields.
To enhance zinc availability in the soil, it is important to focus on improving soil fertility and structure. One effective method is to incorporate organic matter, such as compost or well-rotted manure, into the soil. Organic matter improves soil structure, water-holding capacity, and nutrient retention, ultimately aiding in the release of zinc for plant uptake.



Another strategy to enhance zinc availability is by maintaining optimal soil pH levels. The pH of the soil affects the solubility and availability of nutrients, including zinc. Most plants thrive in slightly acidic to neutral pH ranges, which is typically between 6 and 7. Regular soil testing can help you monitor the pH levels and adjust them accordingly through the addition of soil amendments, such as lime to raise pH or elemental sulfur to lower pH.
Furthermore, the use of zinc-rich fertilizers can be beneficial in ensuring sufficient zinc supply to plants. These fertilizers contain a higher concentration of zinc and can be applied directly to the soil or via foliar sprays. However, it is important to apply fertilizers at the recommended rates to avoid excess zinc accumulation, which can be detrimental to plant health.
Improving soil health and enhancing zinc availability is an ongoing process that requires regular monitoring and maintenance. By implementing these practices, you can create an environment that provides ample zinc for your plants, ensuring their optimal growth and productivity. So remember, take care of your soil, and your plants will thank you with abundant harvests.
Choosing Zinc-Rich Fertilizers: Nourishing Your Plants
Choosing the right fertilizer for your plants is crucial to ensure they receive the necessary nutrients for optimal growth and health. When it comes to addressing zinc deficiency in plants, selecting zinc-rich fertilizers can make a significant difference. Zinc is an essential micronutrient that plays a vital role in various plant functions, such as enzyme activation, photosynthesis, and hormone regulation.


To nourish your plants adequately, consider opting for fertilizers specifically formulated with high zinc content. These fertilizers are designed to provide a concentrated dose of this micronutrient, effectively replenishing any deficiencies. Look for fertilizers that clearly state their zinc content on the packaging, ensuring you can meet the recommended zinc levels for your plants. This will help promote healthy growth, improve overall plant vigor, and enhance resistance to diseases and pests.
In addition to considering zinc content, it’s essential to keep in mind the overall nutrient balance of the fertilizer to avoid over-fertilization or imbalances. Zinc is just one piece of the nutrient puzzle, and a well-rounded fertilizer that incorporates a range of essential nutrients will help ensure your plants receive comprehensive nourishment. Consulting with a knowledgeable gardening expert or referring to reputable agricultural sources can aid in selecting the right fertilizer formulation tailored to your plant’s specific needs.
Organic Sources of Zinc: Natural Ways to Boost Zinc Levels
Organic sources of zinc provide gardening enthusiasts with natural ways to boost zinc levels in their plants. These sources not only promote environmentally friendly practices but also contribute to overall plant health. One organic source of zinc is compost, which is rich in various nutrients, including zinc. By incorporating compost into the soil, gardeners can enhance zinc availability for their plants, ensuring optimal growth and development.
Another organic source of zinc is manure from animals such as cattle, poultry, or horses. Manure contains essential minerals, including zinc, which can be released into the soil as it decomposes. Applying well-aged manure to the garden beds or mixing it into the potting mix can supply plants with the necessary zinc levels. Additionally, gardeners can consider using organic fertilizers specifically formulated to enrich the soil with zinc. These fertilizers, made from natural ingredients such as bone meal or seaweed extracts, offer a convenient and sustainable approach to boost zinc levels in plants.
By turning to organic sources of zinc, gardeners can effectively enhance the nutrient content in their soils and provide their plants with the necessary elements for optimal growth. Not only do organic practices support sustainable gardening, but they also contribute to the overall health and well-being of plants, allowing gardening enthusiasts to enjoy thriving gardens and bountiful harvests. Would you like to learn more about other organic practices and botanical recommendations for boosting plant health?
Optimal pH Levels: Balancing Soil Acidity for Zinc Uptake
Maintaining optimal pH levels in the soil is crucial for ensuring efficient zinc uptake by plants. Zinc availability is greatly influenced by soil acidity, with pH levels playing a significant role in determining the availability of this essential nutrient.

Most plants prefer slightly acidic to neutral pH levels, around 6.0 to 7.0, for optimal growth and nutrient uptake. However, when the soil becomes too acidic or alkaline, it can hinder the plant’s ability to absorb zinc effectively. In acidic soils with a pH below 6.0, zinc tends to become less available to plants, leading to deficiencies. On the other hand, in alkaline soils with a pH above 7.3, zinc availability decreases, resulting in reduced uptake by plants.
Achieving the optimal pH level for zinc uptake requires balancing soil acidity. This can be accomplished through the addition of various soil amendments. For acidic soils, the application of agricultural lime or dolomite can help raise the pH level, making zinc more available to plants. Conversely, adding organic matter like compost or well-decomposed manure to alkaline soils can help lower the pH, promoting better zinc uptake. Regular soil testing is essential to monitor pH levels and make appropriate adjustments to maintain a suitable environment for zinc absorption.
Avoiding Excess Zinc: Ensuring Proper Nutrient Balance
Excessive zinc in the soil can have detrimental effects on plant health. While zinc is an essential nutrient for plants, too much of it can lead to toxicity and imbalance in nutrient uptake. To ensure proper nutrient balance and avoid excess zinc, gardeners and farmers need to take certain precautions.
First and foremost, it is crucial to conduct regular soil testing to determine the zinc levels in your soil. This will help you understand the existing zinc content and avoid over-application of zinc fertilizers. Soil testing can be done through various methods, including using home testing kits or sending samples to a laboratory for analysis. By monitoring the soil’s zinc levels, you can make informed decisions on whether or not to add additional Levels Balancing Soil Acidity for Zinc Uptake
Additionally, proper crop rotation can help prevent zinc depletion in the soil. Different plant species have varying nutrient requirements, and rotating crops can help maintain a balanced nutrient profile in the soil. This practice also reduces the risk of excess zinc accumulation in the long term. Don’t forget to consider the pH levels of your soil, as zinc availability is influenced by soil acidity. Regularly monitoring the pH levels and adjusting them as needed can contribute to optimal zinc uptake by plants.
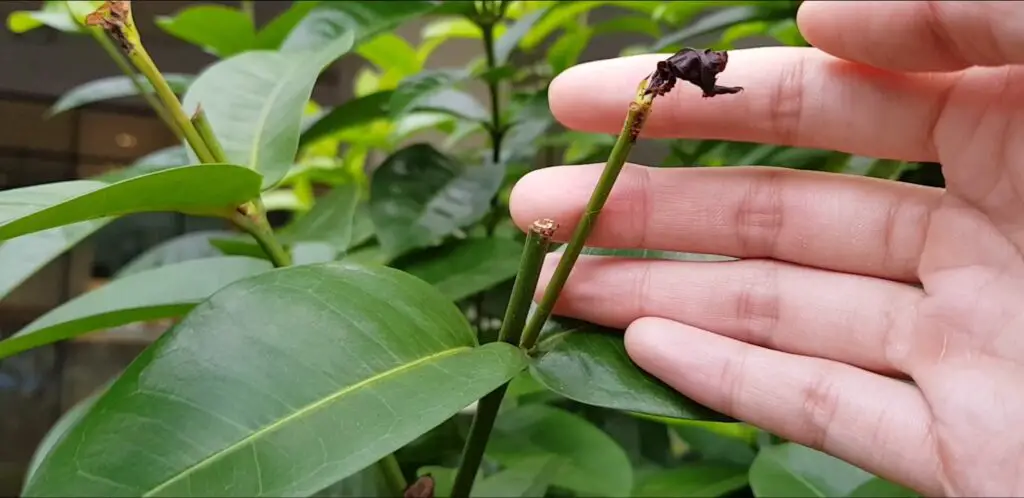


Avoiding excess zinc is vital to ensure proper nutrient balance in plants. Through soil testing, crop rotation, and pH level management, gardeners and farmers can maintain a healthy and thriving garden or farm, promoting optimal plant growth and overall plant health.
• Regular soil testing is crucial to determine the zinc levels in your soil and avoid over-application of zinc fertilizers.
• Soil testing can be done through home testing kits or by sending samples to a laboratory for analysis.
• Monitoring the soil’s zinc levels allows informed decisions on whether or not to add additional zinc supplements to plants.
• Proper crop rotation helps prevent zinc depletion in the soil and maintains a balanced nutrient profile.
• Different plant species have varying nutrient requirements, so rotating crops is essential for overall soil health.
• Consider the pH levels of your soil as it influences zinc availability. Adjusting pH levels as needed contributes to optimal zinc uptake by plants.
• Avoiding excess zinc ensures proper nutrient balance and promotes healthy plant growth.
Applying Zinc Fertilizers: Techniques for Effective Application
When it comes to applying zinc fertilizers, several techniques can ensure effective application and maximize zinc uptake by plants. One important technique is to apply the fertilizer in a band or strip, close to the root zone of the plants. This allows for direct contact between the roots and the zinc, facilitating absorption. Additionally, it is recommended to avoid mixing zinc fertilizers with other nutrients, as this can lead to nutrient antagonism and reduce zinc availability. Instead, it is best to apply zinc fertilizers separately, either before planting or during the growing season, ensuring that the zinc is evenly distributed in the soil.


Another technique that can enhance zinc uptake is the use of slow-release zinc fertilizers. These formulations are designed to release zinc gradually over time, providing a steady supply of nutrients to plants. This not only improves nutrient efficiency but also reduces the risk of zinc leaching or runoff, minimizing environmental impact. It is important to follow the instructions provided by the manufacturer regarding the application rates and methods for these slow-release fertilizers. Overall, utilizing these techniques for applying zinc fertilizers can greatly enhance the availability and uptake of zinc by plants, promoting healthier growth and higher yields.
Foliar Sprays: Enhancing Zinc Absorption through Leaves
Foliar sprays are an effective method for enhancing zinc absorption in plants, providing a targeted approach to deliver this essential nutrient directly to the leaves. By applying a foliar spray containing zinc, plants can bypass any soil deficiencies or limitations and rapidly take up zinc through their foliage. This method is particularly beneficial for plants that exhibit signs of zinc deficiency, as it allows for a quick response in addressing their nutritional needs.
One of the main advantages of foliar sprays is the efficient uptake of zinc by plant leaves. Unlike the roots, which are responsible for absorbing nutrients from the soil, the leaves have specialized cells called stomata that facilitate the absorption of nutrients directly from the spray solution. This allows for a more rapid and direct uptake of zinc, bypassing any potential barriers or limitations in the soil. Moreover, the ability of foliar sprays to enhance zinc absorption is further improved when applied during times when the stomata are open, such as early in the morning or in the evening, when the relative humidity is higher. The increased humidity helps to keep the stomata open, allowing for better nutrient absorption.
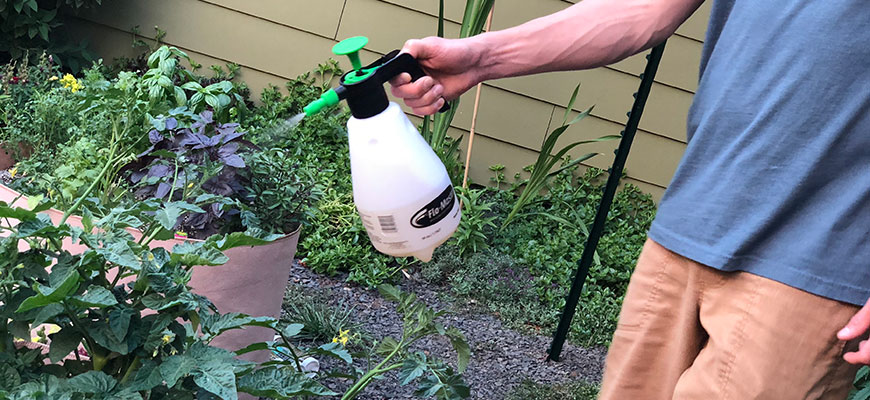


In addition to providing a targeted and efficient method of zinc delivery, foliar sprays also offer flexibility in adjusting zinc levels as needed. By observing the plant’s response and monitoring its zinc status, adjustments can be made to the spray concentration or frequency of application. This allows for precise control over the amount of zinc applied, minimizing the risk of over-application and potential toxicity. It is important, however, to follow recommended application rates and guidelines to ensure optimal results and avoid any negative effects on plant health.
Overall, foliar sprays provide a valuable tool for enhancing zinc absorption in plants, particularly those showing signs of deficiency. With their ability to circumvent soil limitations and deliver zinc directly to the leaves, these sprays offer an effective approach to address nutritional needs and promote healthy plant growth. However, it is important to note that foliar sprays should not be the sole method of zinc supplementation, as addressing soil deficiencies and maintaining proper nutrient balances remain crucial for long-term plant health. By incorporating foliar sprays into a comprehensive zinc management program, gardeners and growers can maximize nutrient uptake and ensure optimal plant performance.
Crop Rotation: Preventing Zinc Depletion in the Soil
Crop rotation is a widely recognized practice in agriculture that offers numerous benefits for plant health and soil fertility. When it comes to preventing zinc depletion in the soil, implementing a well-planned crop rotation strategy can be highly effective. By rotating crops, gardeners can help break the cycle of continuous zinc uptake by specific plant species and reduce the risk of depleting zinc levels in the soil.
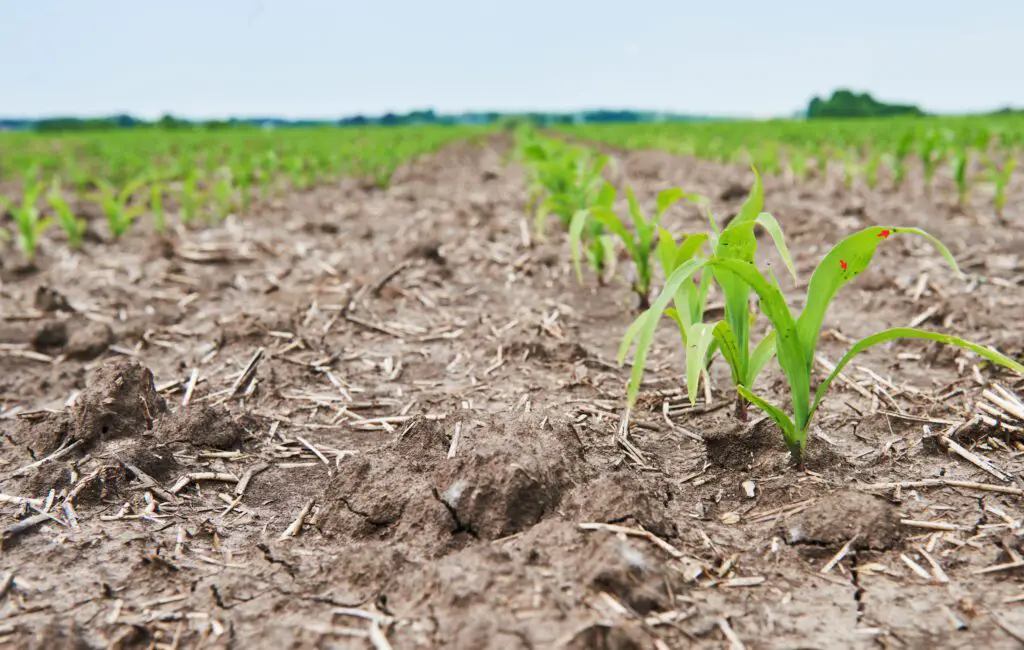


One key aspect to consider when implementing crop rotation for zinc depletion prevention is selecting plant species that have varying zinc demands and nutrient uptake patterns. By alternating between crops with high and low zinc requirements, gardeners can minimize the risk of depleting zinc levels in the soil. For instance, choosing leguminous plants such as beans or peas as one rotation option can be beneficial, as they can fix atmospheric nitrogen, reducing the dependency on added fertilizer and minimizing the depletion of soil zinc levels. Additionally, incorporating cover crops like rye or clover can further support soil health and maintain a balance of nutrients, including zinc, throughout the rotation cycle.
Zinc Supplements: Additional Support for Zinc-Deficient Plants
Zinc supplements can provide valuable support for plants that are experiencing a deficiency in this essential nutrient. When a plant lacks sufficient zinc, it can lead to stunted growth, reduced fruiting or flowering, and overall poor plant health. Zinc plays a crucial role in various physiological processes, including enzyme activity, hormone regulation, and chlorophyll production.
One effective way to address zinc deficiency is through the application of zinc sulfate or zinc chelates as foliar sprays or soil amendments. These supplements are readily absorbed by plants and provide an immediate boost of zinc uptake. Research has shown that foliar sprays, in particular, can enhance plant growth and yield by improving zinc absorption through the leaves. However, it is important to carefully follow the recommended application rates to avoid the risk of excess zinc, which can lead to toxicity and negatively impact plant health. In combination with other strategies for improving soil health and enhancing zinc availability, zinc supplements can provide the additional support needed to overcome zinc deficiency and promote optimal plant growth.
Regular Monitoring: Evaluating Zinc Levels and Plant Health
Regular monitoring of zinc levels is crucial for evaluating plant health and ensuring optimal growth. By regularly assessing zinc levels in the soil and in plant tissues, gardeners can identify early signs of zinc deficiency and take necessary actions to rectify the situation. This proactive approach not only prevents yield loss but also promotes overall plant health and vitality.
There are various methods for monitoring zinc levels, depending on the desired accuracy and convenience. Soil testing is commonly used to assess the amount of zinc available for plant uptake. This can be done through laboratory analysis or portable testing kits, which provide quick and reliable results. Additionally, plant tissue analysis can be conducted to directly measure the zinc content in different parts of the plant. This helps in identifying any potential nutrient limitations and adjusting fertilization practices accordingly. regular monitoring allows gardeners to respond promptly and effectively to any zinc deficiencies, ensuring that plants are receiving the necessary nutrients for optimal growth and productivity.
How can I determine if my plants are suffering from zinc deficiency?
Look for signs such as stunted growth, yellowing or discoloration of leaves, and reduced fruit or flower production.
How can I test the zinc levels in my soil?
Soil testing is the most accurate way to assess zinc levels. You can send a soil sample to a laboratory or use a home soil testing kit.
Are there any natural ways to increase zinc levels in the soil?
Yes, you can enhance zinc availability for plants by improving soil health through organic matter additions, such as compost or manure.
What fertilizers should I choose to provide sufficient zinc for my plants?
Look for zinc-rich fertilizers that contain a balanced blend of nutrients, or choose fertilizers specifically formulated to address zinc deficiency.
Can I boost zinc levels in my plants using organic sources?
Yes, organic sources of zinc, such as zinc sulfate or zinc oxide, can be used to naturally increase zinc levels in the soil.
How does soil acidity affect the uptake of zinc by plants?
Maintaining optimal pH levels in the soil is essential for proper zinc uptake by plants. Adjust soil acidity if necessary to ensure efficient absorption.
Is it possible to provide too much zinc to plants?
Yes, excess zinc can be harmful to plants and disrupt the balance of nutrients. It is important to avoid over-application of zinc fertilizers.
What are the best techniques for applying zinc fertilizers to plants?
Apply zinc fertilizers evenly and at the recommended rates. Incorporate them into the soil before planting or use foliar sprays for effective absorption.
How can crop rotation prevent zinc depletion in the soil?
Rotating crops helps prevent the continuous extraction of zinc from the soil by different plant species, reducing the risk of depletion.
Are there any additional supplements available to support zinc-deficient plants?
Yes, there are zinc supplements specifically designed to provide additional support and address severe zinc deficiency in plants.
How often should I monitor zinc levels and plant health?
Regular monitoring is crucial to evaluate zinc levels and plant health. It is recommended to test soil and inspect plants periodically throughout the growing season.







