Tomato Germination: Unlocking the Secrets
Table of Contents
Understanding the Science behind Tomato Germination
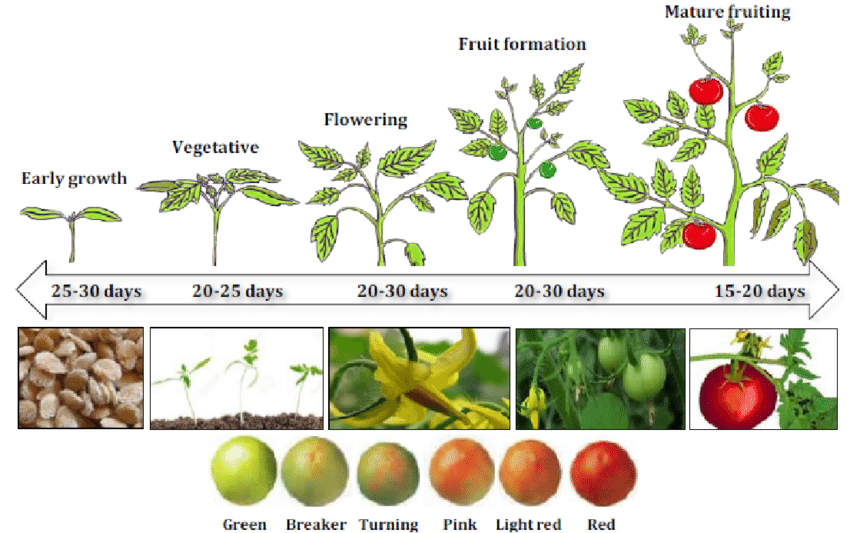
The process of germinating tomato seeds is a fascinating journey that involves intricate scientific mechanisms. Understanding the science behind tomato germination can greatly enhance your gardening skills and increase your chances of success. Tomato seeds, like all plant seeds, contain a dormant embryo surrounded by a protective seed coat. When the seed is exposed to favorable conditions, a series of biochemical reactions are triggered, leading to the awakening of the seed and the commencement of germination.
One crucial factor in tomato seed germination is water absorption. As the seed hydrates, enzymes within the embryo become activated, initiating the breakdown of stored food reserves. These reserves provide the essential energy and nutrients required for the seedling’s growth and development. Additionally, water absorption also leads to the reactivation of the seed’s metabolism, including DNA replication and protein synthesis. This metabolic reawakening is essential for the seed to resume its physiological processes and start growing into a healthy tomato plant.
Another significant aspect of tomato seed germination is the role of temperature. Tomato seeds have a specific temperature range within which they germinate optimally. Generally, a temperature range of 20-30°C (68-86°F) is ideal for most tomato varieties. At lower temperatures, the metabolic activities slow down, prolonging the germination process. On the other hand, higher temperatures can hamper germination, leading to low seedling vigor and poor growth. Achieving the right temperature balance during germination is crucial for ensuring the successful emergence of tomato seedlings.
The Importance of Proper Seed Selection for Successful Germination
Proper seed selection is essential for successful germination of tomato seeds. As a gardener, hydroponics expert, botanist, and agronomist, I understand the significance of choosing the right seeds to ensure healthy and vigorous plants. Selecting high-quality tomato seeds not only increases the chances of successful germination but also plays a crucial role in determining the overall growth and productivity of the tomato plants.
When selecting tomato seeds, it is important to consider factors such as variety, maturity, disease resistance, and viability. Different varieties of tomatoes offer varying characteristics, including taste, color, size, and shape. It is crucial to choose a variety that suits your specific needs and growing conditions. Additionally, selecting seeds from disease-resistant varieties can help minimize the risk of plant diseases and increase the chances of a successful harvest. Finally, checking the viability of the seeds ensures that you are starting with seeds that are capable of germination.
By investing the time and effort in properly selecting tomato seeds, gardeners can set themselves up for success right from the start. With the right seeds in hand, they can proceed to create an optimal germination environment and effectively nurture their tomato plants throughout their growth cycle. So, be sure to choose the best seeds for your needs and give your tomatoes the best chance at success.
Here’s a table highlighting The Importance of Proper Seed Selection for Successful Germination:
| Aspect | Importance |
|---|---|
| Quality Seeds | High-quality seeds are the foundation of a healthy crop. They ensure uniform maturity, endurance in adverse conditions, and genetic purity. Improved varieties lead to higher yields and stronger, disease-resistant seedlings with well-developed root systems. |
| Adaptation to Local Conditions | Choosing seeds adapted to the local climate and soil conditions is crucial. These seeds thrive better, resist diseases, and cope with pests specific to the region. |
| Disease Resistance | Disease-free seeds prevent the transmission of seed-borne diseases, safeguarding crop health and productivity. |
| Even Sowing | Proper seed distribution during sowing ensures optimal plant spacing, adequate sunlight, and efficient resource utilization. Traditional hand sowing or machine-assisted drilling methods can achieve this. |
| Water Absorption | Adequate water is essential for germination. Some seeds require significant hydration relative to their dry weight. |
Remember, the right seed selection can significantly impact crop yield, quality, and overall success in agriculture.
Preparing the Ideal Germination Environment for Tomato Seeds
To ensure successful germination of tomato seeds, it is crucial to create the ideal environment that promotes healthy growth and development. The germination process is influenced by various factors, including temperature, humidity, and light exposure. By carefully controlling these variables, you can give your tomato seeds the best chance of thriving.
First and foremost, maintaining an optimal temperature is vital for tomato seed germination. Most tomato varieties require a temperature range of 70-85°F (21-29°C) for successful sprouting. To achieve this, you can use a heating mat or place the seeds in a warm area of your home. Additionally, it is essential to monitor the temperature to ensure it remains within the ideal range throughout the germination period.
Another critical aspect is providing adequate moisture without drowning the seeds. Before sowing, make sure to moisten the germination medium, often a seed-starting mix or sterile potting soil, to the appropriate level. Overly wet or dry conditions can prevent germination or lead to seed rot. It is recommended to cover the container with a clear plastic dome or wrap it with plastic wrap to maintain humidity levels. However, it is crucial to periodically check and adjust the humidity by either removing the plastic covering or misting the soil surface.
Lastly, proper lighting conditions are crucial for successful tomato seed germination. Although tomato seeds do not require light to germinate, they need ample light once they have sprouted. Providing 12-14 hours of light per day, either through natural sunlight or artificial grow lights, will help seedlings develop sturdy stems and healthy foliage. Ensuring that light is evenly distributed and adequately reaching all the seedlings is essential for uniform growth.
By carefully preparing the ideal germination environment for tomato seeds with a focus on temperature, moisture, and light, you can enhance the chances of successful germination and set your plants up for healthy growth.

Exploring the Different Germination Methods for Tomato Seeds
One of the most important aspects of successfully germinating tomato seeds is choosing the right method. There are several different germination methods that gardeners can explore, each with its own advantages and disadvantages. One common method is sowing seeds directly in the ground, which allows the seeds to experience natural conditions and environmental cues. This method can be ideal for gardeners who have ample space and time to allow the seeds to grow at their own pace. Another popular method is starting seeds indoors, either in pots or trays. This method provides more control over the growing environment, allowing gardeners to adjust factors such as temperature, light, and humidity to optimize germination. Indoor germination is particularly beneficial for those in regions with shorter growing seasons or colder temperatures. Hydroponic systems are another option for germinating tomato seeds, providing a soil-less environment where seeds are placed in a nutrient-rich water solution. This method is gaining popularity for its efficiency and ability to conserve water, making it ideal for urban gardeners or those with limited gardening space. By exploring these different germination methods, gardeners can find the approach that suits their needs and conditions best, ultimately increasing their chances of successful tomato seed germination.
In addition to the various germination methods available, gardeners should also consider the specific requirements of tomato seeds for optimal germination. Tomatoes generally prefer warm temperatures for germination, with the ideal range being between 70-80°F (21-27°C). Providing a consistent temperature within this range can significantly enhance germination rates. Light is another crucial factor to consider, as tomatoes require sufficient light to trigger germination. Placing seeds in a brightly lit area or providing supplemental light through grow lights or fluorescent lamps can promote better germination. Moisture is essential as well, but it is crucial to strike a balance as excessive moisture can lead to seed rot or fungal growth. Proper watering techniques, such as misting or bottom watering, can help maintain the right moisture levels without drowning the seeds. By understanding and implementing these key factors in germination methods, gardeners can embark on their journey to healthy and robust tomato plants.
Choosing the Right Soil Mix for Tomato Germination
One of the crucial factors to consider when germinating tomato seeds is choosing the right soil mix. The soil used for tomato germination plays a significant role in providing the necessary nutrients, supporting root development, and retaining moisture.
Ideally, a well-draining soil mix is essential for tomato germination. When the soil retains too much water, it can lead to root rot and hinder the growth of healthy seedlings. On the other hand, soil that drains quickly may leave the seeds vulnerable to drying out. Striking the right balance is crucial for optimum germination success.
A recommended soil mix for tomato germination consists of equal parts of a high-quality potting mix and perlite. This combination provides the necessary nutrients while ensuring adequate drainage and moisture retention. The potting mix provides the organic matter needed to support seedling growth, and the perlite aids in aeration and prevents soil compaction. Moreover, adding compost or well-rotted manure to the mix can further enrich the soil with essential nutrients.
It’s important to note that using garden soil alone is not advisable for germinating tomato seeds. Garden soil may contain pathogens or pests that can harm the delicate seedlings. Additionally, it may not have the optimal texture and nutrient composition needed for successful germination.
By selecting the right soil mix for tomato germination, garden enthusiasts can give their seeds the best chance to develop into healthy and robust seedlings. Ultimately, this careful attention to the soil’s composition helps lay the foundation for a thriving tomato garden.

The Role of Temperature and Light in Tomato Seed Germination
Tomato seed germination is a delicate process that is greatly influenced by the surrounding temperature and light conditions. Temperature plays a critical role in determining the speed and success of germination. Tomato seeds generally require a consistent temperature range of 70 to 85 degrees Fahrenheit (21 to 29 degrees Celsius) for optimal germination. Higher temperatures can lead to faster germination, but they also pose the risk of seedling stress and reduced vigor.
Light is another important factor for tomato seed germination. Unlike some other plant species, tomato seeds do not require light for the germination process itself. They germinate perfectly well in complete darkness. However, once the seedling emerges from the soil, it needs sufficient light for proper growth and development. Tomatoes are considered “phototropic,” meaning they have a natural inclination to grow towards light sources. This response enables them to maximize their exposure to light for effective photosynthesis and healthy foliage production. Providing ample light to tomato seedlings helps prevent them from becoming leggy and weak, ensuring robust growth and sturdy stems.
Understanding the role of temperature and light in tomato seed germination is essential for achieving successful outcomes. By maintaining the ideal temperature range during germination and providing adequate light once the seedlings emerge, gardeners can promote healthy growth and optimize the chances of a bountiful tomato harvest.
Watering Techniques and Timing for Optimal Tomato Germination
Watering techniques and timing play a crucial role in ensuring optimal tomato germination. Proper hydration is essential for the seeds to absorb water and activate the germination process. However, overwatering can lead to excess moisture, which may cause the seeds to rot or develop fungal infections.
To achieve the perfect balance, it is recommended to water tomato seeds immediately after sowing. This initial watering provides the moisture necessary for the seeds to initiate germination. Afterward, it is important to monitor the moisture level in the soil regularly. A good way to assess whether watering is required is by checking the top inch of soil. If it feels dry, it’s time to water, but if it’s still moist, it’s best to wait.
When watering tomato seeds, it is crucial to avoid using excessive force that could disrupt the soil and damage the delicate germinating seeds. Gentle watering, either by using a misting spray or a gentle shower head attachment, ensures a uniform distribution of moisture without causing any harm. Additionally, it is important to note that watering should be done at the soil level and not directly on the leaves, as wet foliage may increase the chances of fungal diseases.
Determining the right watering frequency can be challenging, as it depends on various factors such as temperature, humidity, and soil type. In general, the goal is to maintain consistent moisture levels throughout the germination period. Keeping the soil slightly damp but not waterlogged is ideal. Remember, it’s always better to underwater than to overwater, as tomato seeds have the ability to withstand short periods of dryness but are highly sensitive to excessive moisture.
By following these watering techniques and timing guidelines, you can provide the optimal conditions for successful tomato germination.
Overcoming Common Challenges in Tomato Germination
Tomato germination can sometimes present challenges even for experienced gardeners. However, with the right knowledge and techniques, these obstacles can be overcome to ensure successful germination. One common challenge is poor seed quality, which can lead to low germination rates or even seed failure. To overcome this challenge, it is crucial to select high-quality seeds from reputable sources. Look for seeds that have been tested and treated for diseases, as this can greatly improve germination success.
Another challenge to be aware of is improper moisture levels. Insufficient moisture can lead to delayed or uneven germination, while excessive moisture can cause fungal diseases and rotting of the seeds. To overcome this challenge, it is essential to strike the right balance by providing adequate moisture without overwatering. Regularly monitor the moisture levels in the germination medium and adjust watering accordingly. Using a spray bottle or mister to water the seeds can help prevent overwatering and ensure even moisture distribution.
Temperature fluctuations can also pose a challenge to tomato germination. Tomatoes are warm-season plants and require consistent warmth to germinate successfully. Cold temperatures can significantly delay germination or even prevent it altogether. To overcome this challenge, provide a consistently warm environment for the seeds. Using a seedling heat mat or placing the germination container near a heat source can help maintain optimal temperatures for germination.
By addressing these common challenges, gardeners can increase their chances of successful tomato germination. However, it is important to remember that germination can still vary depending on the specific tomato variety and growing conditions. Monitoring the progress of the germination process closely and making necessary adjustments will ultimately lead to healthy and vigorous tomato seedlings.
The Significance of Seed Scarification for Tomato Germination
Seed scarification is a technique that is gaining popularity among tomato gardeners due to its significant impact on germination success. Scarification involves intentionally damaging the seed coat to facilitate moisture absorption and promote faster and more uniform germination. This is particularly important for tomato seeds, as they have a naturally tough outer coating that can prevent water from penetrating and reaching the embryo.
Scarification can be done in several ways, including mechanical methods such as rubbing the seeds between sandpaper or using a file to lightly scratch the surface. Chemical scarification is another option, where the seeds are soaked in a diluted sulfuric acid or hydrogen peroxide solution for a short period to break down the seed coat. Whichever method is chosen, it is crucial to handle the seeds with care to prevent damaging the delicate embryo inside.
By scarifying tomato seeds, gardeners can significantly improve germination rates and shorten the time it takes for the seeds to sprout. This method is particularly beneficial for older or hard-to-germinate seeds, as it helps overcome dormancy and ensures higher success rates. Additionally, scarification can also contribute to more uniform germination, resulting in plants of similar size and vigor, which leads to more consistent crop production. The significance of seed scarification in tomato germination cannot be understated, making it a valuable technique for gardeners seeking optimal results.
Enhancing Germination Success with Tomato Seed Priming Techniques
Tomato seed priming techniques are an effective way to enhance germination success and promote strong seedling development. Seed priming involves pre-treating tomato seeds to optimize conditions for germination, providing them with the necessary moisture and nutrients to kickstart the process. This technique has been widely utilized by professional growers and gardening enthusiasts to improve germination rates and overall plant health.
One commonly used method of tomato seed priming is osmopriming. Osmopriming involves soaking the seeds in a solution of chemicals, such as potassium nitrate or calcium chloride, for a specific duration. The osmotic potential created by these solutions allows water to penetrate the seed coat, initiating hydration and metabolic activities. This process stimulates enzyme activation and the production of essential proteins, increasing the seed’s ability to germinate quickly and uniformly.
Another popular priming technique is hormonal priming. This method involves treating tomato seeds with plant growth regulators like gibberellic acid or kinetin. These hormones play a crucial role in seed development and germination by regulating hormonal balances, promoting cell division, and breaking dormancy. Hormonal priming has been proven to enhance the speed and uniformity of germination in tomato seeds, leading to stronger and healthier seedlings.
Overall, employing tomato seed priming techniques can significantly improve germination success and ultimately lead to a more successful growing season. By providing the seeds with optimal conditions for growth and development, gardeners can increase their chances of achieving healthy and robust tomato plants. Stay tuned for the next section, where we will explore different techniques for identifying and managing seed dormancy in tomato seeds.
Identifying and Managing Seed Dormancy in Tomato Seeds
Seed dormancy is a natural mechanism that prevents the immediate germination of seeds, ensuring that they have the best chance of survival in unfavorable conditions. Tomato seeds can also exhibit dormancy, which can cause frustration for gardeners eager to see sprouts emerge. Identifying seed dormancy is important for managing it effectively and promoting successful germination.
There are various factors that can contribute to seed dormancy in tomato seeds, including genetic traits and environmental conditions. Some tomato varieties have naturally dormant seeds, while others may develop dormancy due to environmental factors such as temperature or moisture levels. To identify seed dormancy, it is essential to understand the specific requirements of the tomato variety you are working with. This can involve researching the seed characteristics and consulting reputable sources or seed suppliers to gather information on germination requirements such as optimal temperature and moisture conditions.
Once seed dormancy has been identified, there are several strategies that gardeners can employ to manage it and promote germination. Scarification, which involves gently scratching or nicking the seed coat, can help break dormancy and improve germination rates. This can be done using a file or sandpaper, being careful not to damage the embryo within the seed. Another technique is stratification, which mimics the natural process of exposure to cold temperatures to initiate the germination process. This can be achieved by placing the tomato seeds in a damp paper towel or vermiculite and refrigerating them for a specific period, usually around 2 to 4 weeks. By understanding and implementing these management techniques, gardeners can overcome seed dormancy and achieve successful germination of tomato seeds.
The Impact of pH Levels on Tomato Seed Germination
Maintaining the appropriate pH levels is crucial for successful tomato seed germination. pH is a measure of the acidity or alkalinity of a substance, and it greatly influences the availability of essential nutrients for plant growth. Tomatoes prefer slightly acidic soil, with a pH range of 6.0 to 6.8, for optimal germination and subsequent growth.
If the pH levels are too high or too low, it can negatively affect the availability and absorption of vital nutrients, stunting the germination process. A pH that is too high, indicating alkaline soil, can result in nutrient deficiencies, particularly in iron, manganese, zinc, and copper. Conversely, when the pH is too low, indicating acidic soil, it can inhibit the availability of calcium, magnesium, and phosphorus.
To ensure the ideal pH levels for tomato seed germination, it is recommended to test the soil using a pH meter or a soil testing kit. If the pH is not within the desired range, adjustments can be made by adding amendments. Lime or wood ash can be added to raise the pH, while sulfur or peat moss can be incorporated to lower it. Always follow the product instructions and consider the specific needs of your tomato variety when making pH adjustments.
Maintaining the appropriate pH levels is just one of the many crucial factors that contribute to successful tomato seed germination. In the following sections of this article, we will delve into other equally important aspects such as seed selection, germination environment, temperature and light requirements, watering techniques, and troubleshooting tips. Together, these elements form the foundation for a successful germination process and pave the way for healthy tomato seedlings to flourish.
Nutritional Requirements for Healthy Tomato Seed Germination
Tomato seed germination is a crucial phase in the growth of healthy tomato plants. To ensure successful germination, it is important to provide the seeds with the nutritional requirements they need. Nutrients play a vital role in nourishing the tiny seedlings, enabling them to develop strong root systems and robust growth.
One of the key nutritional requirements for tomato seed germination is nitrogen. Nitrogen is an essential element for plant growth, as it aids in the development of proteins and enzymes necessary for cellular processes. To provide an adequate nitrogen supply, gardeners can use nitrogen-rich fertilizers or incorporate organic materials, such as compost or aged manure, into the soil. This will ensure that the seeds have access to the necessary nitrogen levels to support their early growth.
In addition to nitrogen, phosphorus is another crucial nutrient for healthy tomato seed germination. Phosphorus plays a vital role in energy transfer within the plant, promoting root development and facilitating the transfer of nutrients from the soil. To provide sufficient phosphorus, gardeners can add phosphorus-rich fertilizers, such as rock phosphate, to the soil or use composts and manures that contain higher levels of phosphorus. By adequately supplying phosphorus during the germination phase, gardeners can help the seeds establish strong root systems, setting the stage for successful growth.
In the quest for healthy tomato seed germination, it is important to remember that nourishing the seeds with the right balance of nutrients is essential. Providing adequate nitrogen and phosphorus will give the seeds the foundation they need to develop into vigorous seedlings. By focusing on the nutritional requirements and ensuring their fulfillment, gardeners can set their tomato seeds on the path to success.
Certainly! Here’s a table outlining the nutritional requirements for healthy tomato seed germination:
| Nutrient | Role |
|---|---|
| 1. Nitrogen | Essential for leaf growth, flower development, and overall plant vigor. |
| 2. Phosphorus | Crucial for root development, energy transfer, and fruit production. |
| 3. Potassium | Aids in water regulation, disease resistance, and enzyme activation. |
| 4. Calcium | Supports cell wall structure and prevents blossom end rot. |
| 5. Magnesium | Necessary for chlorophyll production and photosynthesis. |
| 6. Sulfur | Vital for protein synthesis and overall plant health. |
Remember, providing a balanced nutrient mix ensures robust tomato seed germination and healthy seedlings!
The Role of Air Circulation in Tomato Germination
Air circulation plays a vital role in the germination of tomato seeds. Adequate airflow is crucial for ensuring the overall health and successful germination of tomato seeds. When seeds are sown, they require oxygen to respire and release energy for germination. Proper air circulation allows for the exchange of gases, ensuring a sufficient supply of oxygen and the removal of carbon dioxide.
Insufficient air circulation can lead to a buildup of moisture around the seeds, creating a damp and stagnant environment that promotes the growth of harmful organisms. Poor air circulation can also result in the accumulation of heat, leading to high temperatures that can be detrimental to seed germination. Additionally, limited airflow can impede the dispersal of volatile compounds released by germinating seeds, which may inhibit the germination process.
To ensure favorable air circulation during tomato seed germination, it is essential to provide adequate spacing between seeds or seedlings. This allows for better air movement and reduces the likelihood of seedlings competing for resources. Proper spacing also prevents the accumulation of excess moisture and reduces the risk of fungal diseases. Utilizing tools such as fans or natural airflow from windows or ventilation systems can further enhance air circulation in indoor growing environments.
In conclusion, maintaining proper air circulation is essential for successful tomato seed germination. By ensuring a steady supply of oxygen, removing excess moisture, and facilitating the dispersal of volatile compounds, adequate airflow helps create an optimal germination environment. Gardening enthusiasts should prioritize this aspect of seed germination to maximize their chances of achieving healthy and vigorous tomato seedlings.
Recognizing and Preventing Seedling Diseases during Tomato Germination
Seedling diseases during tomato germination can often lead to poor germination rates and weak, susceptible plants. It is important for gardeners to be able to recognize the signs of seedling diseases and take appropriate measures to prevent their occurrence. One common seedling disease is damping-off, caused by various fungal pathogens such as Pythium and Rhizoctonia. Damping-off typically manifests as the sudden wilting and collapse of young seedlings, often at the soil line. To prevent damping-off, it is crucial to ensure seedlings are grown in a clean and sanitized environment. This can be achieved by using sterile germination trays, providing adequate air circulation, and avoiding overwatering. Additionally, treating seeds with fungicide prior to germination can further reduce the risk of damping-off.
Troubleshooting Tips for Failed Tomato Germination Attempts
When it comes to successfully germinating tomato seeds, sometimes things don’t go according to plan. If you’ve experienced failed attempts in tomato germination, don’t be discouraged. There are several common issues that can hinder the germination process, but with a little troubleshooting, you can overcome these challenges and increase your chances of success.
One common problem is improper soil moisture. Tomato seeds require consistent moisture to germinate, but excessive watering can lead to rot or fungal diseases. On the other hand, allowing the soil to dry out can prevent the seeds from absorbing the necessary moisture for germination. To ensure proper moisture levels, it’s important to find a balance. Regularly check the soil with your finger to gauge its moisture content and adjust your watering routine accordingly.
Another issue that may be hindering your tomato germination is incorrect temperature. Tomato seeds thrive in warm temperatures, typically between 70-85°F (21-29°C). If the temperature is too low, germination may be slow or fail altogether. Consider using a heating mat or placing your seed tray in a warm location, such as near a sunny window or on top of a refrigerator. Providing a consistent source of warmth can greatly improve the chances of successful germination.
By addressing these two common issues of soil moisture and temperature, you can troubleshoot and improve your tomato germination success rate. Next, we will explore other potential challenges and offer further tips to help you achieve optimal results. Remember, patience and perseverance are key, and with the right techniques, you’ll soon be on your way to a flourishing tomato garden.
Watch the below video for more information.
Why are my tomato seeds not germinating?
There could be several reasons for failed tomato germination, such as improper seed selection, inadequate germination environment, incorrect soil mix, unsuitable temperature and light conditions, improper watering techniques, seed dormancy, or nutrient deficiencies.
How can I select the right tomato seeds for successful germination?
It is important to choose high-quality tomato seeds from a reputable source. Look for seeds that are fresh, disease-free, and specifically meant for germination.
What is the ideal germination environment for tomato seeds?
Tomato seeds require a warm and moist environment for germination. Maintain a temperature between 70-80°F (21-27°C), provide adequate moisture, and ensure proper air circulation.
What are the different methods for germinating tomato seeds?
There are several germination methods for tomato seeds, including direct sowing in the garden, starting seeds indoors in seed trays or pots, or using seedling plugs or peat pellets.
What type of soil mix should I use for tomato germination?
Use a well-draining soil mix that is rich in organic matter. A recommended mix is a combination of peat moss, perlite, and vermiculite.
How important is the role of temperature and light in tomato seed germination?
Temperature and light play a crucial role in tomato seed germination. Maintain a suitable temperature range and provide sufficient light for germination to occur successfully.
What are the common challenges in tomato germination and how can I overcome them?
Common challenges include seed dormancy, improper watering techniques, nutrient deficiencies, and seedling diseases. Follow the troubleshooting tips mentioned in the article to overcome these challenges.
What is seed scarification and how does it help tomato germination?
Seed scarification is a process of breaking or weakening the seed coat to enhance germination. It can be done by lightly sanding or nicking the seed coat, allowing water and air to penetrate, thus promoting germination.
What is tomato seed priming and how does it improve germination success?
Tomato seed priming involves pre-soaking seeds in water or a nutrient solution to kickstart germination. This technique helps overcome seed dormancy and promotes faster and more uniform germination.
How can I identify and manage seed dormancy in tomato seeds?
Seed dormancy can be identified by extended germination time or lack of germination. To manage it, you can try scarification, stratification (exposing seeds to cold temperatures), or using seed priming techniques.
How do pH levels affect tomato seed germination?
Tomato seeds prefer slightly acidic to neutral soil with a pH level between 6.0-7.0. Extreme pH levels can hinder germination and nutrient uptake, so it’s important to maintain the appropriate pH range.
What are the nutritional requirements for healthy tomato seed germination?
Tomato seeds require a balanced supply of essential nutrients such as nitrogen, phosphorus, and potassium for successful germination. Using a fertilizer specifically formulated for seedlings can help meet these requirements.
How does air circulation contribute to tomato germination?
Proper air circulation is important during germination as it helps prevent the growth of mold or fungi that can damage seedlings. Good air movement also helps in the exchange of gases and prevents excessive humidity.
How can I recognize and prevent seedling diseases during tomato germination?
Look out for signs of damping-off, fungal infections, or other seedling diseases. To prevent them, maintain a clean and sterile germination environment, avoid overwatering, ensure proper air circulation, and use disease-resistant tomato varieties if available.
What troubleshooting tips can I follow if my tomato germination attempts fail?
The article provides several troubleshooting tips for failed tomato germination attempts, including checking seed quality, adjusting germination environment, trying different germination methods, addressing watering techniques, managing seed dormancy, and addressing nutrient deficiencies.

Nicole Burke is a dynamic writer at SouthElMonteHydroponics, fueled by her passion for horticulture and environmental sustainability. Armed with a degree in Environmental Science from a renowned institution, Nicole’s expertise lies in hydroponic gardening, organic farming, and biodiversity conservation. Her insatiable curiosity and love for nature drive her to explore innovative techniques in hydroponics, seeking to revolutionize the way we grow crops in urban environments. Nicole’s writing reflects her deep commitment to promoting eco-conscious practices and fostering a deeper connection between humans and the natural world. Through her engaging storytelling, she inspires others to embrace sustainable living and harness the power of hydroponics for a greener future.






