Urine as Fertilizer: Is It a Myth or a Valid Method?
“Ever wondered if your morning trip to the bathroom could actually benefit your garden? Turns out, the answer might surprise you. Yes, we’re talking about using urine as fertilizer. But before you cringe or dismiss the idea altogether, let’s dive into the science behind it. Is it just a quirky gardening trend, or is there some genuine merit to it?
In this blog, we’ll separate fact from fiction and explore whether urine as fertilizer is a legitimate method for boosting plant growth. So, grab your gardening gloves and let’s debunk this age-old myth together. Spoiler alert: you might rethink flushing next time! Ready to uncover the truth? Let’s get started.”
Table of Contents
Urine as Fertilizer: Is It a Myth or a Valid Method?
The use of urine as fertilizer is a topic that has gained increasing attention in recent years. While some may view it as a myth or unconventional practice, there is scientific evidence to suggest that urine can indeed be a valid method of fertilizing plants.

Historical Use of Urine as Fertilizer:
- Ancient civilizations like the Romans and Egyptians utilized urine for soil enhancement.
- Recognition of its value dates back centuries, highlighting its effectiveness in enhancing soil fertility.
Scientific Studies and Composition Analysis:
- Recent studies have analyzed urine composition, revealing essential nutrients.
- Nitrogen, phosphorus, and potassium are among the key nutrients found in urine, crucial for plant growth.
Promising Results for Plant Growth:
- Research indicates urine’s potential as a sustainable alternative to conventional fertilizers.
- Presence of vital nutrients suggests urine’s effectiveness in supporting healthy plant development.
Further Exploration and Understanding:
- Examining research supporting urine’s viability as a fertilizer is crucial.
- Understanding optimal application methods enhances effectiveness and efficiency.
Addressing Concerns and Perspectives:
- Evaluating health, safety, and environmental impacts is essential.
- Cultural and legal perspectives provide additional insight into urine’s use as a fertilizer.
Review of “Human Urine as a Fertilizer”
I recently read “Human Urine as a Fertilizer” and found it to be an enlightening resource. The book provides comprehensive information on the benefits of using human urine as a fertilizer, supported by scientific research and studies. It offers practical tips on how to collect, dilute, and apply urine to plants, making it an eco-friendly and cost-effective alternative to traditional chemical fertilizers.
The environmental benefits of recycling urine and reducing waste are well highlighted, making it a compelling read for those interested in sustainable gardening practices. However, the topic may be culturally sensitive for some readers, and practical application can be challenging, especially in managing odor and ensuring proper handling to avoid contamination.
Overall, the book is a valuable guide for those open to exploring unconventional yet effective methods in gardening.
Scientific Backing: Cites studies and research to support the claims.
Practical Tips: Offers practical advice on collection, dilution, and application.
Environmental Benefits: Highlights the eco-friendly aspects of urine recycling.
Cost-Effective: Promotes a low-cost alternative to chemical fertilizers.
Application Challenges: Practical implementation may be challenging for some gardeners.
Odor Concerns: Potential issues with odor management.
Health Precautions: Requires careful handling to avoid contamination.
Limited Appeal: May not be appealing to those skeptical about unconventional methods.
The Historical Perspective: Exploring the use of urine as fertilizer throughout history
Throughout history, urine has been utilized as a natural and readily available fertilizer in various cultures around the world.
- Ancient Civilizations:
- Romans and Egyptians recognized urine’s value in promoting healthier crops and improving soil fertility.
- Utilized urine due to its high concentration of essential nutrients, including nitrogen, phosphorus, and potassium.
2. Medieval Europe:
- Urine was considered a valuable commodity for farmers and collected in public urinals.
- Continued for centuries as a practice to enhance crop yields in agriculture and horticulture.
3. Knowledge Transfer:
- The understanding of urine’s fertilizing properties was passed down through generations.
- Widespread use in farming communities as a sustainable and natural fertilizer.
4. Circular Economy Principles:
- Aligns with the principles of a circular economy, where waste products are transformed into resources.
- Urine was not seen as waste but as a valuable resource to be recycled back into the soil.
5. Resourcefulness of Ancestors:
- Highlights the ingenuity and resourcefulness of ancient agricultural societies.
- Demonstrates their ability to recognize and utilize natural, locally available resources for agricultural purposes.
6. Modern Relevance:
- Provides a historical case for exploring the viability and potential benefits of urine as a fertilizer in modern agriculture.
- Raises questions about sustainable and eco-friendly practices in contemporary farming.
The historical use of urine as fertilizer showcases the practical wisdom of past societies in harnessing natural resources for agricultural productivity and emphasizes the potential sustainability of such practices in today’s agricultural landscape.
Understanding the Composition: Analyzing the components of urine that make it potentially beneficial for plants
Urine is a complex liquid that contains various components that can potentially benefit plants.
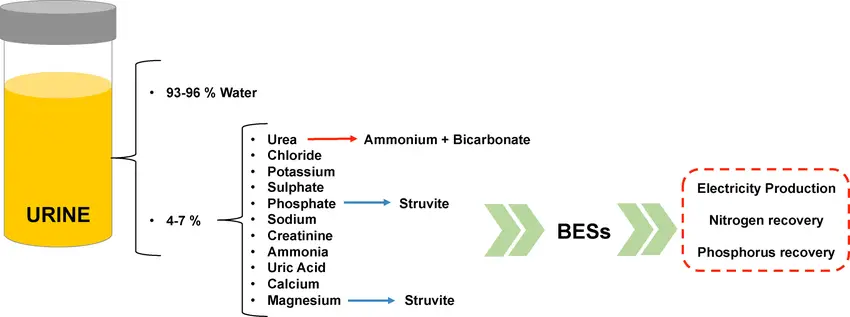
- Nitrogen Content:
- Urine is rich in nitrogen, which is an essential nutrient for plant growth.
- Nitrogen is crucial for the formation of proteins, enzymes, and chlorophyll, vital for plant functioning.
- Other Essential Nutrients:
- Urine also contains phosphorus and potassium, which are important for plant development.
- Phosphorus plays a crucial role in energy transfer and helps in the formation of DNA and cell membranes.
- Potassium is involved in water regulation, photosynthesis, and overall plant health.
- Organic Matter:
- Urine contains organic matter, which contributes to the overall fertility of the soil and promotes robust plant growth.
By using urine as a fertilizer, plants can readily absorb and utilize these essential nutrients, leading to healthy and robust growth.
Nurturing Nutrients: Investigating the presence of essential nutrients in urine and their potential role in plant growth
Urine, often deemed as a waste product, may surprise many with its potential as a fertilizer. Its composition comprises an array of essential nutrients that can nurture plant growth.
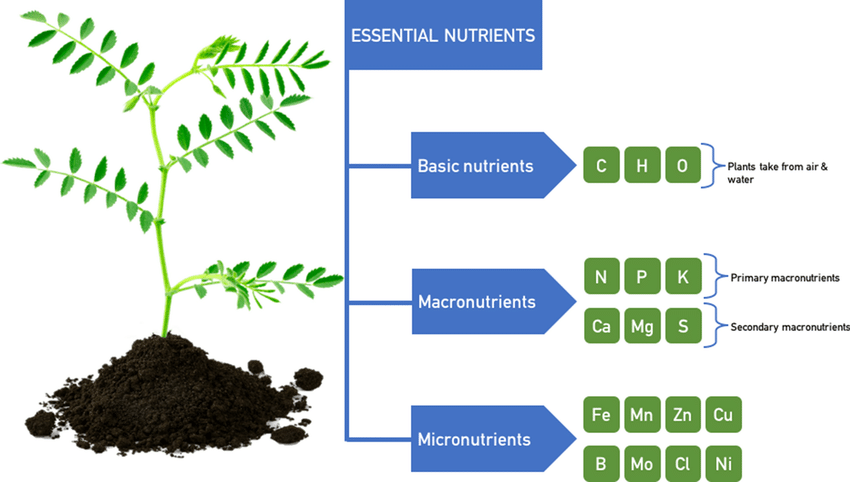
Nitrogen:
- Acts as a vital nutrient for plants, promoting leafy growth.
- Aids in the development of healthy stems and roots.
Phosphorus and Potassium:
- Crucial macronutrients found in urine.
- Support robust flowering, fruit production, and overall plant vitality.
Other Essential Elements:
- Smaller quantities of calcium, magnesium, and sulfur present in urine.
- Serve as building blocks for plant structure and metabolic processes.
Potential Benefits for Gardeners and Farmers:
- Valuable resource for enhancing soil nutrient content.
- Promotes plant health and vitality.
Considerations for Optimal Plant Growth:
- Proportions and ratios of nutrients must be considered.
- Further research needed to understand nutrient dynamics for maximum efficacy.
The Science Behind it: Examining the scientific research supporting the use of urine as a viable fertilizer
Urine has long been considered a potential fertilizer, and recent scientific research is shedding light on its efficacy. Several studies have shown that urine contains significant amounts of nitrogen, phosphorus, and potassium, which are essential nutrients for plant growth. In fact, the nitrogen in urine is typically three times higher than that found in most commercial fertilizers.
- Nutrient Content:
- Fertilizer Value:
- Environmental Impact:
- Optimal Application Rates and Methods:
- Long-term Effects:
By highlighting these points, the potential of urine as a fertilizer is emphasized, along with the need for further research to ensure its effective and sustainable use in agriculture.
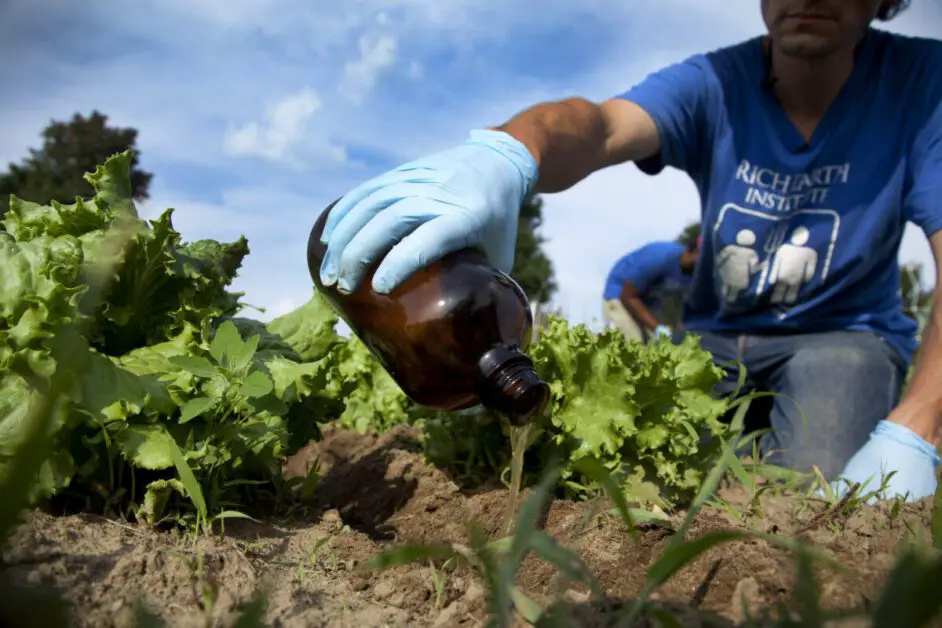
Effective Application: Exploring different methods and techniques for applying urine as fertilizer in a safe and efficient manner
When it comes to applying urine as a fertilizer, there are a few different methods and techniques that can be used to ensure safe and efficient application.

Dilution with Water:
- Helps reduce the concentration of potentially harmful compounds in urine.
- Ensures a more balanced nutrient mixture for plants.
Composting:
- Organic gardening option involves composting urine before application.
- Combining urine with organic materials like leaves or straw promotes decomposition.
- Resulting compost enriches soil and supports plant growth.
Timing and Frequency:
- Application during the growing season is recommended.
- Plants are actively taking up nutrients during this time, optimizing absorption.
- Minimizes nutrient loss through leaching.
Frequency Considerations:
- Apply urine sparingly to avoid over-fertilization.
- Excessive nutrients can adversely affect plant health and the environment.
Implementation of Methods:
- Understanding and implementing these techniques maximizes the benefits of urine as a fertilizer.
- Minimizes potential risks to plant health and the environment.
Review of EZ-Straw Mulch
I recently used EZ-Straw Mulch in my garden, mixing it with urine fertilizer to enhance soil fertility and moisture retention. Here’s my experience:
The straw was easy to apply and came clean and processed, free from seeds and unwanted debris. This made it perfect for my garden as I didn’t have to worry about introducing any weeds. When mixed with urine fertilizer, it worked exceptionally well to improve soil health, ensuring that my plants received consistent moisture and nutrients.
One of the standout features was its effectiveness in controlling soil erosion. It kept the soil in place even during heavy rains, which was a significant advantage. The straw is biodegradable, so it naturally breaks down and enriches the soil over time.
However, I did notice that the coverage was a bit less than I expected. For larger areas, I had to use multiple bales. Additionally, because the straw is lightweight, I had to make sure it was adequately secured to prevent it from being blown away by strong winds. There was also a bit of initial dust when I first applied it, but this was a minor inconvenience.
Overall, EZ-Straw Mulch proved to be a valuable addition to my gardening routine. It helped maintain soil moisture and added beneficial organic matter, enhancing the overall health of my garden. While it may be a bit pricier and require careful handling, the benefits it provided were well worth it.
- Easy to Apply: Comes in a convenient bale that is simple to spread.
- Clean and Processed: Free from seeds and other unwanted debris.
- Improves Soil Moisture: Helps retain moisture in the soil, reducing the need for frequent watering.
- Erosion Control: Effective in preventing soil erosion.
- Biodegradable: Breaks down naturally, enriching the soil.
- Coverage: The coverage area may be less than expected, requiring multiple bales for larger areas.
- Lightweight: Can be blown away by strong winds if not secured properly.
- Initial Dust: Some users report dust when first applying it.
- Cost: Slightly more expensive compared to bulk straw.
- Packaging: The bale can be difficult to reseal if not all the straw is used at once.
Health and Safety Concerns: Addressing potential risks associated with using urine as fertilizer and how to mitigate them
When considering the use of urine as a fertilizer, it is important to address potential health and safety concerns that may arise.

- Pathogen Risk:
- Nutrient Imbalance:
- Urine contains valuable nutrients like nitrogen, phosphorus, and potassium, but it may not provide a balanced blend of essential elements required for optimal plant growth.
- Nutrient imbalances can lead to deficiencies or toxicities, negatively impacting plant health.
- Regular monitoring of soil nutrient levels and supplementation with additional fertilizers or amendments as needed can help mitigate this risk.
Furthermore, proper dilution and application techniques should be employed to ensure that urine is used in appropriate amounts to avoid nutrient overload. By addressing these concerns and implementing appropriate safety measures, the use of urine as fertilizer can be a viable and sustainable option for gardening enthusiasts.
Environmental Impact: Evaluating the environmental implications of using urine as a sustainable alternative to conventional fertilizers
As more people embrace sustainable practices in gardening and agriculture, the use of urine as a fertilizer has gained attention for its potential environmental benefits.
Urine serves as a sustainable alternative to synthetic fertilizers.
Reduces the use of synthetic chemicals and their harmful effects on ecosystems.
Unlike synthetic fertilizers, urine is a natural and easily accessible resource.
Can be sourced and applied to crops without producing harmful byproducts.
Urine as fertilizer supports closed-loop systems.
Waste is recycled and repurposed instead of being discarded.
Reduces the need for energy-intensive manufacturing and transportation.
Cuts down on carbon emissions associated with conventional fertilizer production.
Reduction in carbon emissions helps combat climate change.
Preserves the health of the planet by minimizing environmental impact.
Thorough evaluation of environmental impacts is crucial.
Ensures efficacy and sustainability of urine as a fertilizer in various agricultural systems.
Community Involvement: Discussing the potential for urine collection and recycling initiatives in local communities
In recent years, there has been growing interest in the potential for urine collection and recycling initiatives in local communities as a means to promote sustainability and reduce dependence on conventional fertilizers. Urine, which is rich in nitrogen, phosphorus, and potassium, contains valuable nutrients that can benefit plants when properly processed and applied.
To address the potential concerns regarding odor control, hygiene, and the safe handling of urine in community urine collection programs, follow these key points:
- Odor Control:
- Hygiene:
- Safe Handling:
- Community Involvement:
- Infrastructure:
By addressing these concerns, community urine collection programs can effectively promote sustainable agricultural practices and contribute to a more sustainable future.
The table explain more about community involvement in discussing the potential for urine collection and recycling initiatives in local communities
| Consideration | Description |
| Community Education | Raise awareness about the benefits of urine recycling as a sustainable fertilizer. |
| Establish Collection Points | Implement designated collection points or home urine-diversion systems for convenient use. |
| Odor Control Measures | Address concerns about odors by incorporating effective odor control measures. |
| Hygiene Guidelines | Develop and communicate clear hygiene guidelines for safe urine collection and handling. |
| Infrastructure Planning | Ensure proper infrastructure for urine collection, storage, and transport to processing sites. |
| Processing and Treatment | Establish safe and effective methods for processing urine to make it suitable for agricultural use. |
| Community Gardens and Projects | Collaborate with local community gardens and urban farming projects for utilizing recycled urine. |
| Regulatory Compliance | Ensure compliance with local regulations and standards related to waste and fertilizer use. |
| Community Engagement and Participation | Encourage active participation and engagement from community members in urine recycling initiatives. |
Cultural Perspectives: Investigating cultural attitudes and practices surrounding the use of urine as fertilizer in different regions
Cultural attitudes towards the use of urine as fertilizer vary considerably across different regions, reflecting the diverse beliefs, traditions, and practices associated with agriculture and gardening.
Cultural Acceptance and Tradition:
- Urine as a natural fertilizer has been embraced in various cultures, especially in Asia and Africa.
- Traditional and sustainable farming practice spanning centuries, providing essential nutrients and enhancing soil fertility.
Cultural Practices and Collection Methods:
- Cultural practices have developed around the collection and application of urine.
- In regions like Nepal, specially designed containers in public toilets facilitate sanitary urine collection.
- Collected urine is often diluted with water before application to crops, preventing root burn while ensuring nutrient uptake.
Rituals and Customs:
- Some cultures have specific rituals or customs associated with urine as fertilizer.
- Reinforces the cultural significance and acceptance of urine as a valuable agricultural resource.
Legal Considerations: Examining any regulations or restrictions that may exist regarding the use of urine as a fertilizer
When considering the use of urine as a fertilizer, it is important to understand the legal considerations that may exist.

Regulatory Considerations:
- Regulations and restrictions may govern the use of urine as fertilizer.
- Varied depending on region and influenced by factors like public health and environmental impact.
Guidelines and Permits:
- Specific guidelines or permits may be required for the use of urine as fertilizer.
- Ensures safe and appropriate application, considering factors like pathogens and contaminants.
Treatment Requirements:
- Some jurisdictions may mandate treatment of urine before use to reduce pathogens or contaminants.
- Ensures safety and minimizes potential risks to human health and the environment.
Application Limits:
- Restrictions on the amount of urine applied to a given area may exist.
- Prevents over-application and potential negative impacts on soil and ecosystems.
Handling and Storage Protocols:
- Specific protocols for handling and storing urine may be in place.
- Aimed at preventing any adverse effects on surrounding ecosystems and water bodies.
It is important for gardeners and agriculturalists to familiarize themselves with local regulations and guidelines before utilizing urine as a fertilizer. By adhering to these rules, practitioners can ensure that their use of urine as a fertilizer is not only effective in nourishing plants but also in compliance with legal requirements that protect public health and the environment.
Alternative Uses: Highlighting other potential applications for urine, such
Urine, though primarily associated with waste elimination, holds potential for various alternative uses beyond fertilizing plants.
- Biofuel Production:
- Urine contains high levels of urea, a nitrogen-rich compound that can be converted into ammonia.
- Ammonia can be transformed into hydrogen gas, an essential component in the production of clean and renewable energy.
- This approach offers a sustainable source of fuel while addressing waste management challenges by utilizing a readily available resource.
- Eco-Friendly Brick Making:
- Traditional clay bricks require significant amounts of energy to produce, contributing to carbon emissions.
- Urine can be incorporated into the brick-making process, with the ammonia acting as a binding agent that enables the formation of solid structures.
- By replacing some clay content with urine, the energy consumption and environmental impact of brick manufacturing can be significantly reduced.
- This approach provides a sustainable alternative and promotes a more circular economy, where waste products are transformed into valuable resources.
These innovative applications of urine demonstrate the potential to harness waste as a resource, contributing to the development of sustainable energy solutions and eco-friendly construction materials.
Learn more about the Urine as Fertilizer is the given video:
FAQ
Can urine be used for anything other than fertilizer?
Yes, urine can have various alternative uses such as producing biofuels, generating electricity, and as a source of clean water through purification processes.
Are there any legal regulations regarding the use of urine as a fertilizer?
The regulations regarding the use of urine as a fertilizer can vary depending on the region and country. It is important to check with local authorities or agricultural agencies to ensure compliance with any applicable regulations.
What are some potential health and safety concerns associated with using urine as fertilizer?
While urine is generally considered safe for use as fertilizer, there are some health and safety considerations to keep in mind. These include the risk of bacterial contamination, potential exposure to harmful chemicals or medications present in the urine, and proper handling and storage to prevent any potential odor or hygiene issues.
How can urine be applied as a fertilizer in a safe and efficient manner?
Urine can be applied as a fertilizer through various methods such as diluting it with water before application, using specialized urine-diverting toilets or systems, or incorporating it into composting processes. It is important to follow recommended guidelines and best practices to ensure safe and effective application.
What are the environmental implications of using urine as a sustainable alternative to conventional fertilizers?
Using urine as a fertilizer can have positive environmental impacts by reducing the reliance on synthetic fertilizers, conserving water resources, and minimizing nutrient pollution in water bodies. Additionally, it can contribute to closing the nutrient loop and promoting a more circular economy.
Are there any initiatives in local communities for urine collection and recycling?
Yes, there are various urine collection and recycling initiatives in some communities, particularly in areas where sustainable agriculture practices are prioritized. These initiatives often involve the installation of urine-diverting toilets, community-based urine collection systems, and educational programs to promote the benefits of urine recycling.
How do cultural attitudes and practices differ regarding the use of urine as fertilizer?
Cultural attitudes and practices surrounding the use of urine as fertilizer can vary across different regions. Some cultures have a long history of using urine in agriculture, while others may have taboos or reservations about its use. Understanding and respecting local cultural perspectives is important when promoting urine as a sustainable fertilizer.
Can urine be used as fertilizer for all types of plants?
Urine can be used as fertilizer for a wide variety of plants, including vegetables, fruits, flowers, and even certain trees. However, it is important to consider the specific nutrient requirements of each plant and adjust the urine application accordingly to avoid over-fertilization or nutrient imbalances.
How does urine contribute to plant growth and development?
Urine contains essential nutrients like nitrogen, phosphorus, and potassium, which are vital for plant growth and development. These nutrients are readily absorbed by plants, promoting healthy root development, leaf growth, and overall plant vigor.
Can urine be used as a fertilizer in organic farming?
Yes, urine can be used as a fertilizer in organic farming, as long as it is derived from natural sources without the use of synthetic substances. However, it is important to ensure that the urine used in organic farming meets the relevant organic certification standards and guidelines.

Studied Agricultural Engineering-Plant Protection at University of California, Davis.
Head of Content writing team at Southelmontehydroponics.com









