Blood Meal Fertilizer: How to Use It to Improve Your Soil
Table of Contents
Understanding the Benefits of Blood Meal Fertilizer for Soil Enrichment
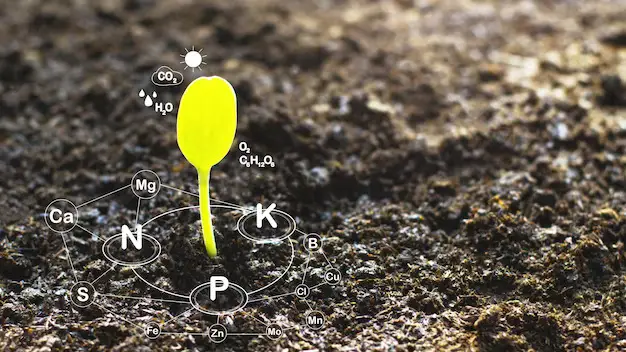
Blood meal fertilizer is a powerful soil amendment that offers numerous benefits for soil enrichment. One of its key advantages is its high nitrogen content, which can greatly improve the growth and development of plants. Nitrogen is an essential nutrient for plants, playing a crucial role in photosynthesis, the production of chlorophyll, and overall plant metabolism. By supplying plants with a readily available source of nitrogen, blood meal fertilizer promotes lush vegetation and vibrant green leaves.

In addition to its nitrogen content, blood meal fertilizer also contains other important nutrients like phosphorus and potassium. These nutrients are vital for various aspects of plant growth and development, including root formation, flower and fruit production, and resistance to diseases and pests. The presence of these essential nutrients in blood meal fertilizer makes it an excellent choice for improving soil fertility and ensuring healthy plant growth. Moreover, blood meal fertilizer is known for its slow-release properties, which release the nutrients gradually over time, providing a sustained source of nourishment for plants. This not only benefits the plants but also helps to reduce nutrient runoff, minimizing the risk of water pollution.
Identifying the Nutritional Components of Blood Meal Fertilizer
Blood meal fertilizer is a highly valuable source of nutrients for plants, particularly nitrogen. Nitrogen is one of the essential macronutrients that plants require for healthy growth and development. In fact, it plays a crucial role in various essential plant processes, including photosynthesis, protein synthesis, and the formation of chlorophyll.
The main nutritional component of blood meal fertilizer is nitrogen in the form of ammonium and amino acids. It typically contains a high nitrogen content, usually ranging from 10% to 14%. This makes it one of the most concentrated sources of nitrogen available for plant fertilization. Additionally, blood meal fertilizer also contains smaller amounts of other vital nutrients such as phosphorus and potassium. While the levels of these nutrients may vary depending on the source and processing method, blood meal generally provides a balanced nutrient profile that can benefit a wide range of plants.
This table outlines the nutritional components typically found in blood meal fertilizer:
| Nutritional Component | Description |
|---|---|
| Nitrogen (N) | Blood meal is primarily a nitrogen-rich fertilizer, containing a high percentage of organic nitrogen. |
| Phosphorus (P) | Generally low in phosphorus content, although some variations might contain trace amounts. |
| Potassium (K) | Contains negligible potassium (potash) content. |
| Amino Acids | Contains various amino acids, which break down slowly, providing a sustained nitrogen release. |
| Trace Minerals | May contain trace amounts of micronutrients like iron, zinc, and calcium, beneficial for plants. |
| Organic Matter | Blood meal contributes organic matter to the soil, improving its structure and microbial activity. |
The nitrogen content in blood meal fertilizer is released slowly into the soil through natural microbial activity, providing plants with a consistent and prolonged supply of this essential nutrient. This slow-release characteristic makes blood meal fertilizer particularly suitable for plants that have high nitrogen requirements, such as leafy greens, vegetables, and fruiting plants. However, it is important to note that excessive application of blood meal can lead to nitrogen burn or other nutrient imbalances in the soil. Therefore, proper dosage and careful monitoring of soil conditions are necessary to ensure optimal results.
Assessing Soil Conditions: Is Blood Meal Fertilizer Suitable for Your Garden?
Assessing the soil conditions before applying any type of fertilizer is essential for ensuring optimal plant growth and health. When considering whether blood meal fertilizer is suitable for your garden, it is important to evaluate key factors such as the current nutrient levels, pH balance, and the specific needs of your plants.

One factor to consider when assessing soil conditions is the nutrient composition of the soil. Blood meal fertilizer is known for its high nitrogen content, which is essential for promoting healthy foliage growth. However, if your soil already contains high levels of nitrogen, applying blood meal can lead to an imbalance in nutrients. It is recommended to conduct a soil test to determine the current nutrient levels and identify any deficiencies or excesses that may exist. This will help you determine whether your soil would benefit from the addition of nitrogen-rich blood meal fertilizer.
Another aspect to consider is the pH level of your soil. Blood meal fertilizer is acidic in nature, and it can lower the pH of the soil over time. If your soil already has a low pH, applying blood meal can further decrease the acidity level, which may not be suitable for certain plants that prefer more alkaline conditions. Conversely, if your soil has a high pH, the acidic properties of blood meal can help balance the pH and create a more favorable environment for plant growth. A pH test will provide valuable information about the acidity or alkalinity of your soil, allowing you to make informed decisions about the suitability of blood meal fertilizer for your garden.
By assessing the nutrient levels and pH balance of your soil, you can make an informed decision about whether blood meal fertilizer is suitable for your garden. Understanding the specific needs of your plants and taking into account factors such as nitrogen levels and pH will help you create an optimal soil environment for healthy and thriving vegetation. In the next section, we will explore the necessary steps to prepare your soil before applying blood meal fertilizer, ensuring a successful integration into your gardening routine.
Preparing Your Soil: Steps to Take Before Applying Blood Meal Fertilizer

Preparing your soil before applying blood meal fertilizer is vital to ensure optimal results and the health of your plants. Here are some key steps to follow before incorporating this nutrient-rich fertilizer into your garden:
1. Soil Testing: Begin by conducting a thorough soil test to determine its pH level and nutrient composition. This step is crucial as it helps you understand the specific needs of your soil and identify any deficiencies or imbalances. Use a reputable soil testing kit or consult with a local agricultural extension service for accurate results.
2. Adjusting pH Levels: Blood meal fertilizer performs best in slightly acidic to neutral soil with a pH range of 6.0 to 7.0. If your soil’s pH deviates from this range, make the necessary adjustments by adding lime to raise pH or sulfur to lower it. This ensures that your soil is in the optimal range for nutrient uptake and utilization by plants.
3. Organic Matter Incorporation: Enhancing the organic matter content in your soil is essential for its overall fertility and structure. Prior to applying blood meal fertilizer, consider adding compost, well-rotted manure, or other organic materials to improve soil moisture retention, drainage, and nutrient-holding capacity. Spreading a layer of organic matter and working it into the top few inches of soil will gradually release nutrients and create a favorable environment for plant growth.
By following these essential steps, you will set the stage for a successful blood meal fertilizer application while promoting a healthy and nutrient-rich soil ecosystem for your plants to thrive. Taking the time to prepare your soil adequately will maximize the efficacy of this organic fertilizer and contribute to the overall success of your gardening endeavors. Stay tuned for further guidance on the application process and dos and don’ts to ensure optimal results.
Applying Blood Meal Fertilizer: Dos and Don’ts for Optimal Results
Dos:
1. Test the soil: Before applying blood meal fertilizer, it is essential to test your soil to ensure it requires the additional nutrients provided by the fertilizer. Soil testing kits can easily be purchased and will provide you with valuable information about your soil’s pH levels, nutrient deficiencies, and overall composition. By conducting a soil test, you can accurately determine the appropriate dosage of blood meal fertilizer needed for optimal results.
2. Follow dosage instructions: Blood meal fertilizer is highly concentrated in nitrogen, which can burn plants if used excessively. It is crucial to follow the dosage instructions provided by the manufacturer to prevent any harm to your plants. Applying too much blood meal fertilizer can result in nitrogen toxicity and may inhibit the growth and development of your plants. Be cautious and use the recommended amount based on your soil test results.
Don’ts:
1. Don’t apply blood meal to plants in bloom: Blood meal releases its nutrients slowly over time. Applying it to plants that are already blooming may lead to an imbalance in nutrient uptake and disrupt their natural growth cycle. It is best to apply blood meal fertilizer during the early stages of plant growth or before the flowering phase to ensure a balanced nutrient release for optimal results.
2. Don’t use blood meal fertilizer on nitrogen-sensitive plants: Some plants are more sensitive to high nitrogen levels, such as legumes, strawberries, and onions. These plants may experience adverse effects if blood meal fertilizer is applied. It is essential to research which plants are sensitive to high nitrogen levels and avoid using blood meal on them. Alternatively, consider using alternative organic fertilizers or adjusting the dosage accordingly to avoid any potential damage to your plants.
The Role of Nitrogen in Blood Meal Fertilizer and Soil Health
Nitrogen plays a crucial role in blood meal fertilizer and its impact on soil health. As one of the three primary macronutrients necessary for plant growth, nitrogen is essential for the development of healthy foliage and promotes overall plant vitality.

In blood meal fertilizer, nitrogen exists in the form of protein. This protein is derived from the blood of animals, typically byproduct from the meat industry. As blood meal breaks down in the soil, the nitrogen becomes readily available to plants, aiding in the formation of amino acids, enzymes, and chlorophyll.
The availability of nitrogen in blood meal fertilizer is particularly beneficial for leafy green vegetables and crops that require a boost in foliage growth. Furthermore, nitrogen also helps promote root development and enhances the plants’ ability to take up other essential nutrients from the soil. The inclusion of blood meal fertilizer in your garden can invigorate plant growth and contribute to the overall health and vigor of your plants.
• Nitrogen is a primary macronutrient necessary for plant growth
• Blood meal fertilizer contains nitrogen in the form of protein derived from animal blood
• The breakdown of blood meal releases nitrogen, aiding in the formation of amino acids, enzymes, and chlorophyll
• Leafy green vegetables and crops that require foliage growth benefit from the availability of nitrogen in blood meal fertilizer
• Nitrogen also promotes root development and enhances nutrient uptake from the soil
• Including blood meal fertilizer in your garden can promote overall plant health and vigor
Enhancing Plant Growth: How Blood Meal Fertilizer Promotes Lush Vegetation
Blood meal fertilizer is a highly effective means of enhancing plant growth and promoting lush vegetation in your garden. This natural fertilizer is derived from dried blood, usually from cattle or poultry slaughterhouses. Its high nitrogen content, typically ranging from 11% to 15%, makes it a valuable nutrient source for plants.
Nitrogen is an essential element for plant growth, playing a critical role in the development of chlorophyll and proteins. Chlorophyll is responsible for the green color of plants and is vital for photosynthesis, the process by which plants convert sunlight into energy. The increased availability of nitrogen through blood meal fertilizer encourages the production of chlorophyll and promotes strong, healthy leaf growth. Additionally, nitrogen is necessary for the synthesis of proteins, enzymes, and other essential compounds that contribute to overall plant vigor and vitality.
Incorporating blood meal fertilizer into your gardening routine can significantly contribute to the lushness and vibrancy of your plants. This natural source of nitrogen encourages robust and vigorous growth, resulting in larger foliage, more abundant flowering, and increased fruit production. Whether you’re tending to a flower garden, a vegetable patch, or a crop field, the application of blood meal fertilizer can provide the necessary nutrients to support optimal plant development. However, it is crucial to consider soil conditions, plant requirements, and proper application techniques to achieve the best results. In the following section, we will explore the dos and don’ts of applying blood meal fertilizer for optimal plant growth.
Improving Soil Fertility: Other Ways Blood Meal Fertilizer Benefits Your Garden
Blood meal fertilizer is not only effective in improving soil fertility, but it also offers various other benefits for your garden. One of the key advantages of using blood meal fertilizer is its ability to enhance the overall nutrient content of the soil. Blood meal is rich in nitrogen, which is an essential element for plant growth and development. Nitrogen promotes the formation of proteins, enzymes, and chlorophyll, all of which are crucial for healthy plant growth and vibrant foliage.
In addition to nitrogen, blood meal fertilizer also contains other essential nutrients that are beneficial for soil fertility. These include phosphorus, potassium, and trace elements like iron, copper, and zinc. The presence of these nutrients helps to maintain a balanced nutrient profile in the soil, ensuring that your plants have access to all the necessary elements for optimal growth. By enriching the soil with these vital nutrients, blood meal fertilizer can significantly improve the fertility of your garden, leading to healthier plants and higher yields.
Addressing Common Concerns: Misconceptions and Precautions with Blood Meal Fertilizer
Blood meal fertilizer is a popular choice among gardeners for its numerous benefits in enriching the soil. However, there are some common concerns and misconceptions that need to be addressed to ensure its safe and effective usage. One common misconception is that blood meal fertilizer attracts pests, particularly carnivorous insects. While it is true that blood meal has a strong odor that might attract some insects, it is important to note that properly applied blood meal does not pose a significant risk of pest infestation. In fact, the smell of blood meal usually dissipates once the fertilizer is incorporated into the soil.
Another concern often raised is the potential for burning or damaging plants when using blood meal fertilizer. Blood meal is indeed a potent source of nitrogen, and excessive application can lead to nitrogen burn. However, as long as the recommended dosage is followed, blood meal can significantly enhance plant growth without causing harm. It is crucial to carefully read and adhere to the instructions provided by the manufacturer to avoid any negative effects. Additionally, for young or delicate plants, it is advisable to apply blood meal in smaller quantities or consider diluting it with compost or other organic matter to reduce the risk of nitrogen burn. By being mindful of proper dosage and considering the specific needs of different plants, gardeners can enjoy the benefits of blood meal fertilizer without encountering any issues.
Maximizing the Long-Term Effects: Tips for Incorporating Blood Meal Fertilizer
To maximize the long-term effects of blood meal fertilizer in your garden, there are a few key tips to keep in mind. First and foremost, it’s important to apply the fertilizer at the appropriate time and in the correct amounts. Blood meal fertilizer is high in nitrogen, so using too much can result in excessive leaf growth and potentially damage your plants. Conversely, using too little may not provide the desired benefits.
Here’s a table outlining tips for effectively incorporating blood meal fertilizer into gardening practices:
| Tip | Description |
|---|---|
| Soil Testing | Conduct soil tests to determine existing nutrient levels before applying blood meal. |
| Application Rate | Follow recommended application rates specified on the blood meal fertilizer packaging. |
| Avoid Over-application | Overuse can lead to excessive nitrogen levels, potentially causing harm to plants. |
| Incorporation Method | Mix blood meal thoroughly into the soil surface to ensure even distribution. |
| Watering After Application | Water the soil after application to help activate the fertilizer and prevent nitrogen burn. |
| Frequency of Application | Apply blood meal sparingly and intermittently, as it’s a slow-release fertilizer. |
| Consider Plant Needs | Assess the specific needs of plants; some may require higher nitrogen, while others may not. |
| Timing | Apply blood meal during the growing season when plants have increased nutrient demands. |
| Monitor Plant Response | Observe plant growth and appearance; adjust fertilizer application based on plant response. |
Another tip is to ensure proper incorporation of the blood meal fertilizer into the soil. This can be achieved by mixing it thoroughly with the top few inches of soil or by utilizing irrigation methods to help distribute the nutrients evenly. By properly incorporating the fertilizer, you can ensure that the nitrogen and other vital nutrients are readily available to your plants for uptake.
Additionally, it’s crucial to regularly monitor and maintain the pH levels of your soil when using blood meal fertilizer. High levels of nitrogen can lead to a decrease in soil pH over time, which may negatively impact plant health. To counteract this, consider conducting regular soil testing and adjusting the pH as needed by adding amendments such as lime.
Incorporating organic matter, such as compost or well-rotted manure, alongside blood meal fertilizer can also enhance its effectiveness. Organic matter improves soil structure, enhances nutrient retention, and promotes beneficial microbial activity, all of which contribute to healthier, more productive plants in the long run.
Lastly, be mindful of the environmental impact of blood meal fertilizer usage. While it offers significant benefits for plant growth, it’s important to use it responsibly and in accordance with recommended guidelines to prevent nutrient runoff and potential harm to nearby water sources. By following these tips and using blood meal fertilizer judiciously, you can maximize its long-term effects and reap the benefits of healthier, more vibrant plants in your garden.
Understanding the Environmental Impact of Blood Meal Fertilizer Usage
Blood meal fertilizer is a popular choice for gardeners looking to enrich their soil and promote healthy plant growth. However, it is important to consider the environmental impact of its usage. While blood meal is a natural and organic fertilizer, its production has certain implications that need to be taken into account.
One of the main concerns regarding the environmental impact of blood meal fertilizer usage is its source – animal byproducts. Blood meal is typically derived from the slaughterhouse industry, where the blood of animals is collected and processed into a fine powder. The production of blood meal raises questions about sustainability and ethical considerations, as it is directly connected to the meat industry.
Want to know more, here’s what can help you?
Additionally, the transportation of blood meal fertilizer can contribute to greenhouse gas emissions and energy consumption. The process of collecting and distributing blood meal from slaughterhouses to garden centers or individual users requires transportation, which often relies on fossil fuels. This transportation contributes to the overall carbon footprint associated with blood meal fertilizer. Gardeners should be aware of these environmental considerations and explore alternative options or use blood meal sparingly and judiciously to minimize its impact.
In conclusion, understanding the environmental impact of blood meal fertilizer usage is crucial for responsible gardening practices. By considering the source of blood meal and the transportation involved, gardeners can make informed decisions about its usage and explore alternative soil enhancement options that are more sustainable. Taking a holistic approach to gardening ensures that we not only nourish our plants but also care for the environment in a responsible manner.
Alternatives to Blood Meal Fertilizer: Exploring Other Soil Enhancement Options
As a gardening enthusiast, you may be familiar with blood meal fertilizer as a popular soil enhancement option. However, it’s always beneficial to explore other alternatives to find the best fit for your garden’s specific needs. In this section, we will delve into some other soil enhancement options that can provide similar benefits to blood meal fertilizer.
1. Compost: Composting is a natural and cost-effective way to enrich your soil with organic matter. By decomposing organic materials such as kitchen scraps, leaves, and grass clippings, you can create nutrient-rich compost that improves soil structure and fertility. Additionally, compost helps retain moisture, encourages beneficial microbial activity, and reduces the risk of soil erosion.
2. Bone meal: Similar to blood meal, bone meal is a slow-release fertilizer derived from animal bones. It is particularly high in phosphorus, which plays a crucial role in promoting root development, flowering, and fruiting. Bone meal also contains calcium and trace minerals, contributing to overall soil health and plant nutrition. It can be an excellent alternative for gardeners seeking to enhance bloom production in flowering plants or strengthen root systems in young seedlings.
By considering alternatives like compost and bone meal, you can tailor your soil enhancement approach to your garden’s specific requirements. Experimenting with different options and combinations can help you discover the most effective solution for promoting healthy plant growth and maximizing your garden’s potential.
Troubleshooting: Common Issues and Solutions with Blood Meal Fertilizer Application
Common Issues with Blood Meal Fertilizer Application
When using blood meal fertilizer in your garden, you may encounter a few common issues that require troubleshooting. One issue that gardeners often face is the strong odor associated with blood meal fertilizer. This distinctive smell can be off-putting, especially if you are using the fertilizer in an enclosed space or near living areas. To mitigate this issue, it is important to apply the fertilizer sparingly and avoid using excessive amounts. Additionally, consider applying the fertilizer on a day with favorable weather conditions, such as when there is a light breeze to help disperse the odor.
Another common issue is the potential for nitrogen burn, which occurs when too much nitrogen is applied to the plants. Blood meal fertilizer is high in nitrogen, and if used in excessive quantities, it can cause leaf discoloration and burning, stunting the growth of your plants. To prevent nitrogen burn, it is crucial to follow the recommended application rates provided by the manufacturer. If you notice signs of nitrogen burn, such as yellowing or browning leaves, reduce the amount of blood meal fertilizer used and water your plants thoroughly to dilute the nitrogen concentration in the soil.
Expert Insights: Tips and Advice from Gardeners Who Use Blood Meal
As gardening enthusiasts, we always strive to maximize the benefits of any fertilizer we use. In this section, we will provide you with insights from experienced gardeners who have successfully incorporated blood meal fertilizer into their gardening routines.
Firstly, seasoned gardener Mary Thompson shares her advice on the dosage of blood meal fertilizer. She recommends following the package instructions carefully and starting with a smaller amount to avoid overfeeding your plants. Mary explains, “It’s crucial to strike a balance. Too little blood meal won’t provide enough nutrients, while too much can burn the plants. Start with a teaspoon per square foot and gradually increase the dosage if needed.”
Watch this video to learn more!
On the other hand, Jim Reynolds, a hydroponics expert, emphasizes the importance of soil testing before applying blood meal fertilizer. He states, “Knowing your soil composition and pH level is crucial. Blood meal is acidic, so if your soil is already acidic, it may not be suitable for your garden. Conduct a soil test to determine your soil’s pH and adjust it accordingly.” Jim recommends using agricultural limestone to raise the pH level if required.
These insights from experienced gardeners emphasize the significance of proper dosage and soil testing when using blood meal fertilizer. By understanding and implementing their advice, you can ensure optimal results in enhancing your soil’s fertility and promoting healthy plant growth.
Is blood meal fertilizer safe for pets and children?
Blood meal fertilizer should be used with caution around pets and children, as it can be attractive to them due to its smell. Ingestion of blood meal can cause stomach upset and may be toxic in large quantities. It is best to keep pets and children away from treated areas until the fertilizer has been thoroughly watered into the soil.
Can blood meal fertilizer attract pests or wildlife to my garden?
Blood meal fertilizer has a strong odor that may attract wildlife, such as raccoons or deer, to your garden. To prevent this, it is recommended to apply the fertilizer evenly and bury it slightly in the soil to reduce the smell. Additionally, using companion plants or natural pest deterrents can help keep pests away from your garden.
Can blood meal fertilizer be used on all types of plants?
While blood meal fertilizer is beneficial for many plants, it may not be suitable for all types. Some plants, such as legumes, are naturally high in nitrogen and may not require additional nitrogen from blood meal. It is important to research the specific needs of your plants and consult gardening resources or experts to determine if blood meal is appropriate for your garden.
How often should blood meal fertilizer be applied?
The frequency of blood meal fertilizer application depends on the specific needs of your plants and the condition of your soil. In general, it is recommended to apply blood meal fertilizer once or twice during the growing season. However, it is important to monitor your plants and soil regularly to determine if additional applications are necessary.
Can blood meal fertilizer be used in organic gardening?
Yes, blood meal fertilizer can be used in organic gardening as it is derived from animal waste. However, it is important to ensure that the blood meal you are using is certified organic and free from any synthetic additives or chemicals. Organic gardening practices also involve considering the overall health of the soil ecosystem and using sustainable fertilization methods.
How soon can I harvest vegetables after applying blood meal fertilizer?
The time it takes to harvest vegetables after applying blood meal fertilizer varies depending on the specific crop and the amount of blood meal used. In general, it is recommended to wait at least two to four weeks before harvesting leafy greens and at least four to six weeks for fruits or root vegetables. It is important to follow the specific recommendations for each plant variety and monitor for any signs of nutrient burn or excessive nitrogen levels.

Pallavi Gupta is a burgeoning writer at SouthElMonteHydroponics, blending her passion for data analysis with a keen interest in biotechnology. Currently pursuing a Bachelor’s in Biotechnology at Amity University, Pallavi delves into the intricacies of life sciences while gaining hands-on experience in the exciting world of data analysis. Her unique background provides a fresh perspective on hydroponic farming, as she explores the intersection of biotechnology and sustainable agriculture. Through her writing, Pallavi aims to bridge the gap between data-driven insights and innovative farming practices, inspiring others to harness technology for a greener future.