Garden Soil Nutrient Testing: How to Test and Analyze Your Soil Quality and Fertility for Your Plants
Table of Contents
Understanding the Importance of Soil Testing for Successful Gardening
Soil testing is an essential step for any gardener looking to achieve successful results. By analyzing the composition and nutrient levels of your soil, you can gain valuable insights into its health and fertility. This information allows you to make informed decisions about which amendments and fertilizers to use, ultimately maximizing the growth and productivity of your garden.
One of the primary reasons why soil testing is crucial is because it helps identify nutrient deficiencies. Nutrients such as nitrogen (N), phosphorus (P), and potassium (K) are vital for plant growth, and their availability in the soil directly impacts the health and development of your garden. Without proper knowledge of the nutrient levels in your soil, you may unknowingly deprive your plants of the elements they need, leading to stunted growth, poor yields, or even plant death.
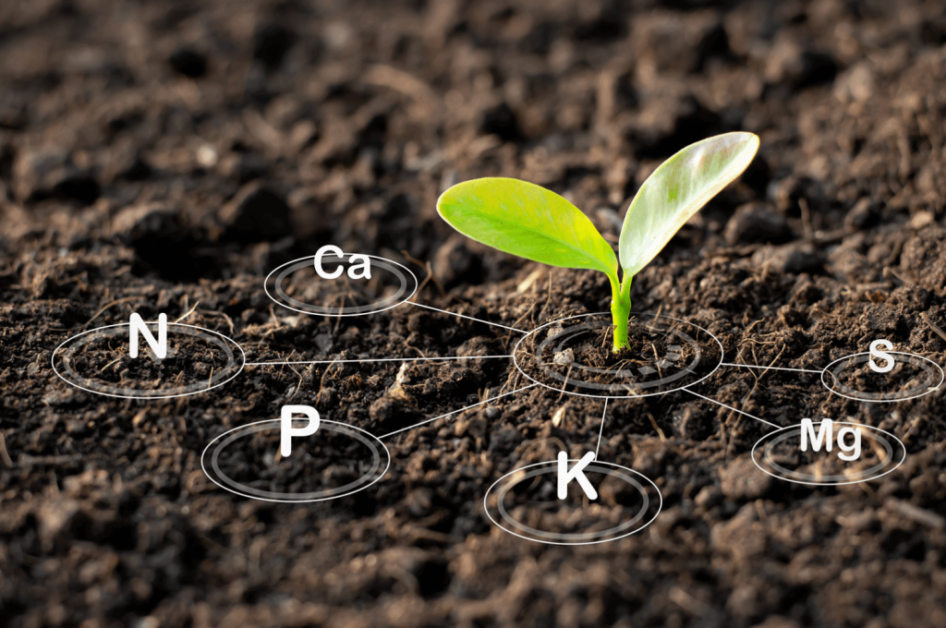

Moreover, soil testing provides valuable insights into the pH level of your soil. pH is a measure of how acidic or alkaline the soil is, and different plants have different pH requirements. Testing your soil’s pH allows you to determine whether it is too acidic or too alkaline for your desired plants. By adjusting the pH to the optimal range, you can create a favorable environment for root development and nutrient uptake, ensuring the overall well-being of your garden.
In summary, soil testing is an important practice for successful gardening as it enables you to understand the nutrient composition and pH level of your soil accurately. Armed with this knowledge, you can make informed decisions about fertilizer application and soil amendments, creating an optimal environment for your plants to thrive. In the next section, we will explore the common signs of nutrient deficiencies in plants, further underscoring the significance of soil testing in gardening.
Identifying Common Signs of Nutrient Deficiency in Plants
Nutrient deficiency in plants can lead to various visible signs that indicate the lack of essential elements required for their optimal growth and development. By understanding and recognizing these common signs, gardeners can take appropriate measures to address nutrient deficiencies and ensure healthy plant growth.
One common sign of nutrient deficiency is chlorosis, which is characterized by yellowing of the leaves. This is often an indication of a lack of essential nutrients such as nitrogen, magnesium, or iron. Nitrogen deficiency, for example, can cause the older leaves to turn yellow while the veins remain green. On the other hand, magnesium deficiency can lead to interveinal chlorosis, where the leaf veins remain green while the areas between them turn yellow. Iron deficiency can cause yellowing of the young leaves, as iron is necessary for the production of chlorophyll.
Another sign of nutrient deficiency is stunted growth. When plants do not have an adequate supply of nutrients, they may experience slower growth and smaller overall size. This can be observed in the form of shorter stems, smaller leaves, and reduced flower or fruit production. For instance, phosphorus deficiency can lead to stunted root development, resulting in poor nutrient absorption and impaired growth. Calcium deficiency, on the other hand, may cause stunted shoot growth and weak stems.
Recognizing these common signs of nutrient deficiency in plants is crucial for gardeners to diagnose and address the underlying nutrient imbalances. Proper identification and timely intervention can help ensure the health and vitality of plants, promoting successful gardening endeavors.
Types of Soil Tests Available for Assessing Soil Quality and Fertility
Soil testing is a crucial step in assessing the quality and fertility of your garden soil. There are several types of soil tests available that can provide valuable insights into the composition and health of the soil.
One commonly used soil test is the pH test, which measures the acidity or alkalinity of the soil. This is important because different plants thrive in different pH levels. For example, most vegetables prefer a slightly acidic soil with a pH level between 6.0 and 7.0. By testing the pH of your soil, you can determine if it needs to be adjusted to create an optimal environment for your plants.
Another type of soil test is the nutrient test, which analyzes the levels of essential nutrients in the soil. These nutrients, such as nitrogen, phosphorus, and potassium, are essential for plant growth and development. By knowing the nutrient levels in your soil, you can determine if any deficiencies or imbalances exist and take appropriate steps to address them. This may involve adding organic matter, such as compost or manure, or applying specific fertilizers to meet the plants’ nutritional needs.

In addition to pH and nutrient tests, there are also tests available to assess the presence of contaminants in the soil, such as heavy metals or pesticides. These tests are especially important if you are gardening in an urban area or suspect that the soil may have been contaminated. By identifying any potential contaminants, you can take steps to mitigate their effects and ensure the safety of your plants and those consuming the produce.
By utilizing various types of soil tests, you can gain a comprehensive understanding of your soil’s quality and fertility. This knowledge allows you to make informed decisions regarding soil amendments, fertilizers, and other practices necessary for successful gardening. Remember that soil testing should be an ongoing process as soil conditions can change over time, and regular testing will help you maintain a healthy and thriving garden.
Step-by-Step Guide to Collecting Soil Samples for Testing
Collecting soil samples for testing is a crucial step in understanding the health and fertility of your garden soil. By following a step-by-step guide, you can ensure that your samples are representative of the entire area you wish to test, providing accurate results for informed decision-making.
First, start by determining the areas you want to test. It’s essential to divide your garden into different zones, especially if you have distinct plant types or varying soil conditions. For each zone, identify the specific crops or plants you’re interested in analyzing, as this will help you tailor your soil amendments and fertilization strategies. Next, equip yourself with the necessary tools, including a spade or shovel, a clean bucket, and a soil probe or auger, depending on your preference and the depth of sampling required.
When collecting the soil samples, it’s important to gather representative soil from different locations within each zone. Begin by removing any surface debris or vegetation to expose the bare soil. Dig a small hole or pit in the designated location, ensuring that you go to the appropriate depth for your plant’s root zone. For most garden plants, a depth of six to eight inches is sufficient. Use the soil probe or auger to collect a vertical sample from the side of the hole, taking care to avoid any contamination. Repeat this process in several spots within the zone, and remember to mix the collected soil in the clean bucket, thoroughly homogenizing it.
Taking the time to collect soil samples properly ensures that you obtain accurate and representative data on the soil’s nutrient levels, pH, and other essential properties. Armed with this information, you can make informed decisions about fertilization, soil amendments, and plant selection, ultimately leading to healthier, more productive gardens. So, follow these steps diligently, and get ready to unlock the secrets hidden beneath the surface of your soil.
Selecting the Right Soil Testing Laboratory for Accurate Results
Ensuring accurate results from soil testing is crucial for gardeners who want to make informed decisions about their plant nutrition. Selecting the right soil testing laboratory is an important step in this process. When choosing a laboratory, it is essential to consider factors such as reputation, accreditation, and the range of services offered.
One important criterion to consider is the reputation of the soil testing laboratory. Look for a laboratory that has established itself as a trusted authority in the field. Check if the laboratory has a track record of providing reliable and accurate results to their clients. Reading customer reviews and testimonials can provide valuable insights into the laboratory’s performance and customer satisfaction levels.
Accreditation is another vital consideration. Look for laboratories that have been accredited by relevant industry organizations or regulatory bodies. Accreditation ensures that the laboratory follows strict quality control measures and adheres to recognized standards. By selecting an accredited laboratory, you can have confidence in the accuracy and reliability of the results they provide.

Additionally, it is essential to assess the range of services offered by the laboratory. Consider whether they offer comprehensive testing for all the essential nutrients and soil properties that you need for your particular gardening needs. Some laboratories may specialize in certain types of tests or cater to specific crops or gardening methods. Choose a laboratory that can meet your specific requirements and provide you with complete and detailed information about your soil’s condition.
By carefully considering the reputation, accreditation, and range of services offered by a soil testing laboratory, gardeners can ensure that they receive accurate and dependable results. These results will serve as the foundation for making informed decisions about soil amendments, fertilizers, and other strategies to optimize plant health and productivity. Remember, selecting the right laboratory is an investment in the success of your gardening endeavors, and it is worth taking the time to find the most suitable option.
Interpreting Soil Test Reports: What the Numbers Mean
Soil test reports provide valuable insights into the quality and fertility of your soil, helping you understand its nutrient content and pH levels. Interpreting these reports is crucial for making informed decisions about fertilization and soil management in order to promote optimal plant health and growth.
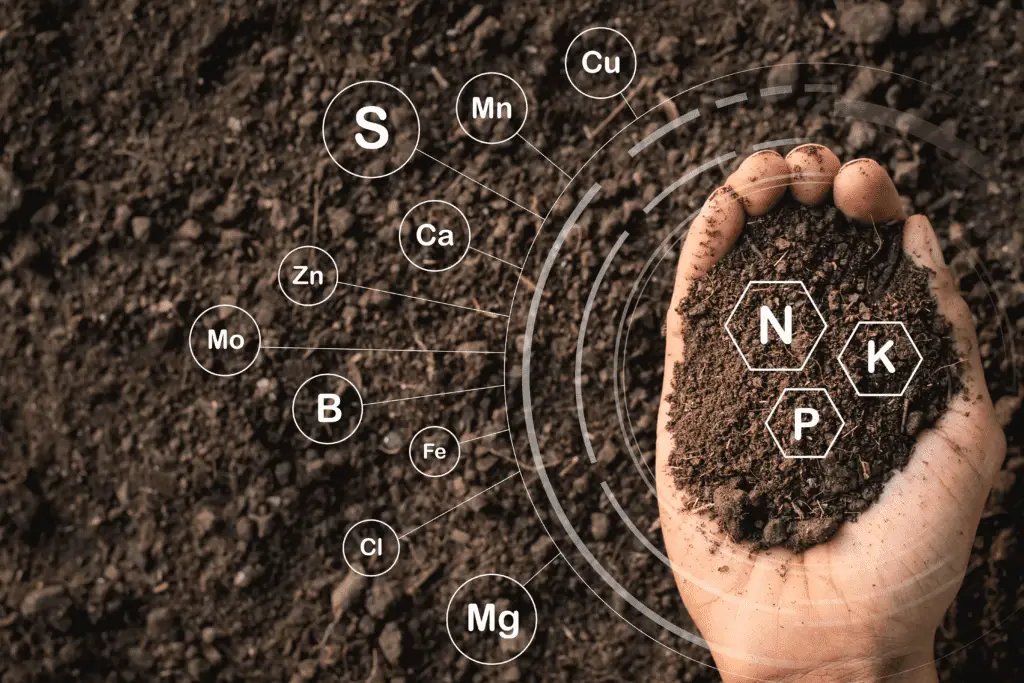
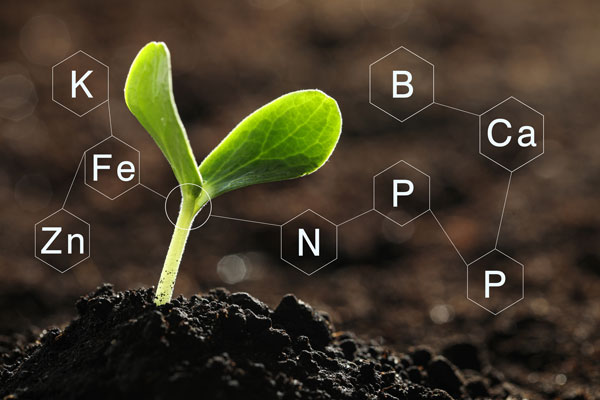
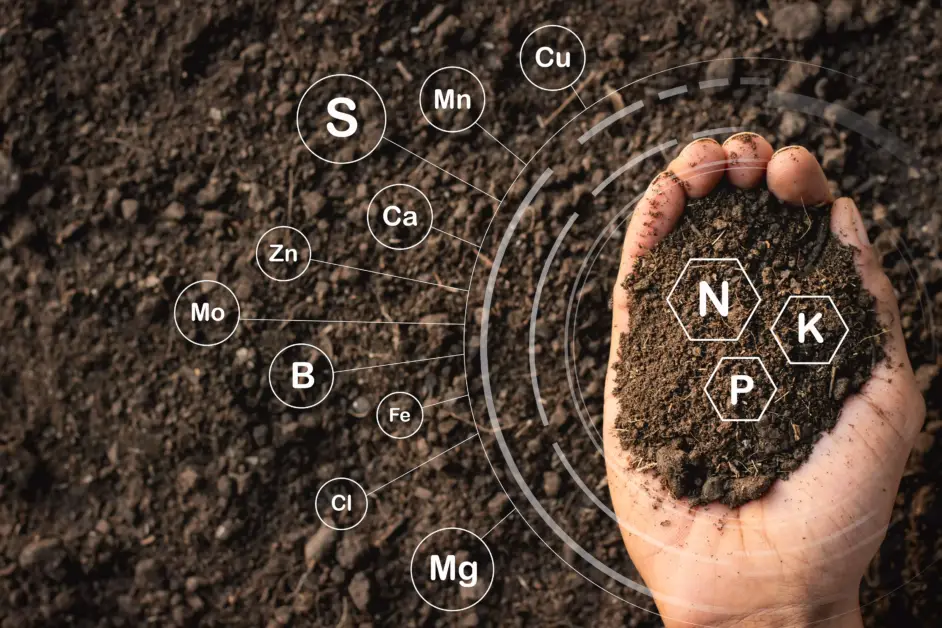
One of the key aspects of interpreting soil test reports is understanding the numbers and units used to represent various nutrient levels. Each nutrient is typically presented as a part per million (ppm) measurement. The report will include the levels of essential macronutrients such as nitrogen (N), phosphorus (P), and potassium (K), as well as secondary macronutrients like calcium (Ca), magnesium (Mg), and sulfur (S). The availability of micronutrients like iron (Fe), manganese (Mn), zinc (Zn), copper (Cu), boron (B), and molybdenum (Mo) may also be included. These numbers indicate the concentration of each nutrient present in the soil and provide the basis for adjusting fertilizer applications to meet specific plant requirements.
In addition to nutrient levels, soil test reports also include pH values, which indicate the acidity or alkalinity of the soil. The pH scale ranges from 0 to 14, with values below 7 indicating acidity and values above 7 indicating alkalinity. Most plants prefer a slightly acidic to neutral pH range of 6.0 to 7.5. If the pH deviates from this range, it can impact nutrient availability to plants. Therefore, understanding the pH value reported in your soil test can help you determine if adjustments are needed to create optimal growing conditions for your plants.
Essential Nutrients for Plant Growth and How to Measure Them
Proper nutrition is key for the healthy growth and development of plants. Just as humans require essential nutrients for optimal health, plants also rely on certain elements to thrive. These essential nutrients for plants can be broadly categorized into two groups: macronutrients and micronutrients.
Macronutrients, as the name suggests, are required by plants in large quantities. These include nitrogen (N), phosphorus (P), and potassium (K), commonly referred to as N-P-K. Nitrogen is essential for leaf and stem growth, phosphorus promotes strong root development, and potassium aids in overall plant health and disease resistance.
Micronutrients, on the other hand, are needed in smaller amounts but are equally important for plants. Examples of micronutrients include iron (Fe), manganese (Mn), zinc (Zn), copper (Cu), and boron (B). Although micronutrients are required in lesser quantities, their deficiency can have a significant impact on plant growth and yield.
Determining the availability and adequacy of these essential nutrients in the soil is crucial to ensure proper plant nutrition. This is where soil testing plays a vital role. By assessing the nutrient levels in the soil through laboratory analysis, gardeners can identify any deficiencies or imbalances and take appropriate action to rectify them. Soil testing also helps to prevent over-fertilization, which can lead to environmental issues and wastage of resources.
Adjusting Soil pH: Balancing Acidity and Alkalinity for Optimal Plant Health
Maintaining the proper pH level of your soil is essential for optimal plant health and successful gardening. The pH scale ranges from 0 to 14, with 7 being considered neutral. A pH level below 7 indicates acidic soil, while a pH above 7 indicates alkaline soil. Different plants thrive in different pH conditions, and adjusting your soil’s pH can greatly impact their growth and overall health.
Acidity or alkalinity affects the availability of essential nutrients in the soil. When soil is too acidic or alkaline, certain nutrients may become locked up and inaccessible to plants. For example, acidic soil can cause an imbalance of aluminum and manganese, negatively impacting plant growth. On the other hand, alkaline soil can limit the availability of essential nutrients like iron and phosphorus. By adjusting the pH of your soil to the appropriate range for your plants, you can create an ideal environment for their growth and development.
There are several methods to adjust soil pH, depending on whether you need to make it more acidic or alkaline. Adding organic matter such as compost, peat moss, or leaf mulch can help to increase acidity. On the other hand, adding materials like limestone or wood ash can help to raise pH levels. It is important to note that adjusting soil pH is not a one-time fix, as pH levels can change over time. Regular soil testing and monitoring will help you maintain the optimal pH range for your plants, ensuring they receive the nutrients they need to thrive. In the next section, we will explore the different types of soil tests available to assess soil quality and fertility, which can further guide your efforts in adjusting soil pH.
Organic vs. Synthetic Fertilizers: Pros and Cons for Soil Health
Organic and synthetic fertilizers are two commonly used options for enhancing soil fertility in gardening. Both have their advantages and disadvantages, making it important to understand their pros and cons when considering their impact on soil health.
Organic fertilizers, derived from natural sources such as animal manure, compost, and plant residues, have several benefits for soil health. Firstly, they provide a slow-release of nutrients, ensuring a steady supply of essential elements for plants over an extended period. Additionally, organic fertilizers improve soil structure and increase its ability to retain water, promoting better root development and reducing the risk of nutrient leaching. Moreover, organic fertilizers promote the growth of beneficial organisms in the soil, such as earthworms and beneficial bacteria, which contribute to overall soil health and nutrient cycling.

However, organic fertilizers also have some drawbacks to consider. Due to their slow-release nature, they may not provide an immediate nutrient boost when plants need it the most. Moreover, the nutrient composition of organic fertilizers can vary, making it a bit challenging to determine precise nutrient ratios for targeted plant needs. Additionally, organic fertilizers may contain pathogens or weed seeds, requiring proper handling and application techniques to avoid any adverse effects. Despite these limitations, organic fertilizers are considered environmentally-friendly and sustainable options, aligning well with the principles of organic gardening and sustainability.
Improving Soil Fertility: Techniques for Enhancing Nutrient Content
Soil fertility plays a crucial role in the success of any gardening endeavor. To enhance the nutrient content of your soil and promote healthy plant growth, there are several proven techniques that you can employ. One effective method is the addition of organic matter such as compost, manure, or mulch. These materials provide a rich source of essential nutrients, improve soil structure, and enhance water retention capabilities. Incorporating compost and organic matter into your soil not only enriches its fertility but also promotes the growth of beneficial microorganisms that contribute to overall soil health.
Another technique for enhancing nutrient content in soil is through the application of suitable fertilizers. Before applying any fertilizers, it is essential to conduct a soil test to determine the specific nutrient requirements of your plants. A soil test will analyze the current nutrient levels in your soil, allowing you to make informed decisions regarding fertilizer types and quantities. Organic fertilizers derived from natural sources like animal waste and plant materials offer slow-release nutrients that are less likely to harm the environment. On the other hand, synthetic fertilizers provide a quick nutrient boost but require careful application to prevent overloading the soil. By understanding your soil’s nutrient deficiencies and utilizing appropriate fertilizers, you can effectively enhance the nutrient content and fertility of your soil, leading to vibrant and healthy plant growth.
Next, you may want to explore other techniques such as crop rotation, cover cropping, and intercropping. These practices involve strategically planting different crops in rotation to maximize nutrient uptake and minimize depletion. Crop rotation helps break pest and disease cycles, improve organic matter content, and enrich soil fertility naturally. Cover cropping involves sowing certain plants that are known for their ability to fix nitrogen and improve soil structure. Intercropping refers to growing different crops together in the same area, allowing for efficient utilization of resources and complementary nutrient needs. By implementing these techniques, you can optimize your soil’s nutrient balance and boost overall fertility, leading to thriving and resilient plants.
Note: It is important to consult with local experts or agricultural extension services to determine the most suitable techniques for your specific soil type and gardening conditions.
Soil Amendments: Understanding the Role of Compost, Manure, and Mulch
Soil Amendments: Understanding the Role of Compost, Manure, and Mulch
In the world of gardening, soil amendments play a crucial role in maintaining soil fertility and promoting healthy plant growth. Among the various types of amendments available, compost, manure, and mulch are popular choices for many gardeners. These organic materials not only help improve the overall quality of the soil but also provide essential nutrients that plants need to thrive.
Compost, often referred to as “black gold” by gardeners, is a nutrient-rich organic matter that results from the decomposition of plant and animal waste. When added to the soil, compost enhances its structure, improves water retention, and promotes beneficial microbial activity. It also acts as a slow-release fertilizer, gradually releasing nutrients into the soil, ensuring a steady supply for plant uptake. Compost can significantly increase the organic matter content of the soil, which is crucial for maintaining its overall health and fertility.
Manure, another valuable soil amendment, is a rich source of essential nutrients that are necessary for plant growth. It is primarily derived from animal waste and can be obtained from various sources such as cows, horses, chickens, and rabbits. When properly aged and composted, manure becomes a safe and effective soil amendment. It adds organic matter to the soil, improves its structure, and releases nutrients such as nitrogen, phosphorus, and potassium. However, it is important to use well-rotted manure to avoid the risk of introducing harmful pathogens to the garden.
Mulch, on the other hand, is a protective layer applied to the soil surface to conserve moisture, suppress weed growth, and regulate soil temperature. It can be made from a variety of materials, including shredded leaves, straw, wood chips, or grass clippings. Mulching not only helps retain soil moisture by preventing evaporation but also acts as a natural weed suppressant, reducing the need for excessive manual weeding or herbicide use. Additionally, as organic mulch breaks down over time, it contributes organic matter to the soil, improving its fertility.
When it comes to incorporating soil amendments into your garden, it is essential to consider the specific requirements of your plants and the existing condition of your soil. Each amendment offers unique benefits to the soil and plants, and understanding their individual roles will help you make informed decisions to achieve optimal garden health. So, let’s explore how to effectively use these soil amendments to unlock the full potential of your garden and cultivate thriving plants.
Best Practices for Soil Testing and Fertilizer Application in Different Seasons
Soil testing is a crucial step in maintaining healthy and productive gardens throughout the year. By understanding the best practices for soil testing and fertilizer application in different seasons, gardeners can optimize their plant growth and ensure the efficient use of nutrients.
In warmer seasons such as spring and summer, it is recommended to conduct soil testing before planting and apply fertilizers accordingly. This helps determine the nutrient levels and pH of the soil, allowing gardeners to make informed decisions about the types and quantities of fertilizers to use. Additionally, regular soil testing throughout the growing season can help monitor nutrient depletion and adjust fertilizer application to meet the plants’ changing needs.
In cooler seasons like fall and winter, soil testing becomes equally important. As plants enter a dormant phase, it is an ideal time to collect soil samples and assess nutrient levels. By analyzing the results, gardeners can identify any nutrient deficiencies or imbalances that need to be addressed before the next growing season. This allows for appropriate amendments and fertilizers to be applied well in advance, giving the soil ample time to develop and improve before the plants are ready to thrive again in the spring.
By following these best practices for soil testing and fertilizer application in different seasons, gardeners can ensure that their plants receive the necessary nutrients and maintain optimal health throughout the year. Understanding the specific needs of the soil and adapting fertilization strategies accordingly will ultimately lead to more successful and bountiful gardens.
• Conduct soil testing before planting in spring and summer seasons
• Regularly test soil throughout the growing season to monitor nutrient depletion
• Adjust fertilizer application based on soil test results to meet changing plant needs
• Collect soil samples and assess nutrient levels during fall and winter seasons
• Address any nutrient deficiencies or imbalances identified in soil tests before next growing season
• Apply appropriate amendments and fertilizers well in advance for optimal soil development
and improvement
• Adapting fertilization strategies according to specific soil needs will lead to more successful gardens.
Monitoring Soil Health: Regular Testing and Maintenance for Sustainable Gardening.
Regular testing and maintenance of soil health is crucial for sustainable gardening. By monitoring the condition of your soil, you can identify any potential deficiencies or imbalances in nutrients, pH levels, and organic matter. This helps you understand the specific needs of your plants and take appropriate steps to ensure their optimal growth.
Soil testing provides valuable insights into the composition of your soil, allowing you to make informed decisions about fertilization and amendments. Through the analysis of soil samples, you can determine the levels of essential nutrients such as nitrogen, phosphorus, and potassium, as well as secondary and micronutrients. This information enables you to apply fertilizers and soil amendments accurately, avoiding unnecessary supplementation or potential nutrient imbalances. Additionally, regular testing helps you assess the pH level of your soil, which is crucial as it affects nutrient availability to plants. By monitoring and adjusting soil pH, you can create an environment that promotes the healthy growth of your plants.
How often should I test my soil for nutrient levels?
It is recommended to test your soil at least once every three years to ensure optimal nutrient levels for your plants.
Can I test my soil myself or should I hire a professional?
While there are DIY soil testing kits available, it is generally recommended to hire a professional soil testing laboratory for accurate and reliable results.
What are the essential nutrients for plant growth?
Essential nutrients for plant growth include nitrogen, phosphorus, potassium, calcium, magnesium, and various micronutrients such as iron, zinc, and manganese.
How can I adjust the pH of my soil?
To adjust soil pH, you can add lime to raise the pH or sulfur to lower it. The amount needed will depend on your soil type and desired pH level.
What are the pros and cons of organic and synthetic fertilizers?
Organic fertilizers are derived from natural sources and improve soil health over time, but they can be slower to release nutrients. Synthetic fertilizers provide immediate nutrients but can harm soil health if overused.
What are some techniques for improving soil fertility?
Techniques for enhancing soil fertility include adding organic matter such as compost or manure, practicing crop rotation, and using cover crops to improve nutrient content.
How do soil amendments like compost, manure, and mulch affect soil health?
Soil amendments improve soil structure, water retention, and nutrient availability. Compost and manure add organic matter, while mulch helps conserve moisture and control weeds.
Is soil testing and fertilizer application different for each season?
Yes, soil testing and fertilizer application should consider the specific needs of plants in different seasons. For example, fall is often a good time to test soil before adding nutrients for the next growing season.
How does regular soil testing contribute to sustainable gardening?
Regular soil testing allows gardeners to identify nutrient deficiencies, adjust pH levels, and make informed decisions about soil amendments and fertilizer application. This promotes healthy plant growth and reduces the risk of nutrient runoff and environmental pollution.

Pallavi Gupta is a burgeoning writer at SouthElMonteHydroponics, blending her passion for data analysis with a keen interest in biotechnology. Currently pursuing a Bachelor’s in Biotechnology at Amity University, Pallavi delves into the intricacies of life sciences while gaining hands-on experience in the exciting world of data analysis. Her unique background provides a fresh perspective on hydroponic farming, as she explores the intersection of biotechnology and sustainable agriculture. Through her writing, Pallavi aims to bridge the gap between data-driven insights and innovative farming practices, inspiring others to harness technology for a greener future.








You really make it seem really easy together with your presentation but I to find this topic to be really something that I feel I would by no means understand. It seems too complicated and very wide for me. I’m taking a look forward for your subsequent post, I¦ll attempt to get the hold of it!
Wow! Thank you! I constantly wanted to write on my website something like that. Can I take a fragment of your post to my website?