Red Clover Plant: Soil-Improving Cover Crop
Benefits of Using Red Clover as a Cover Crop
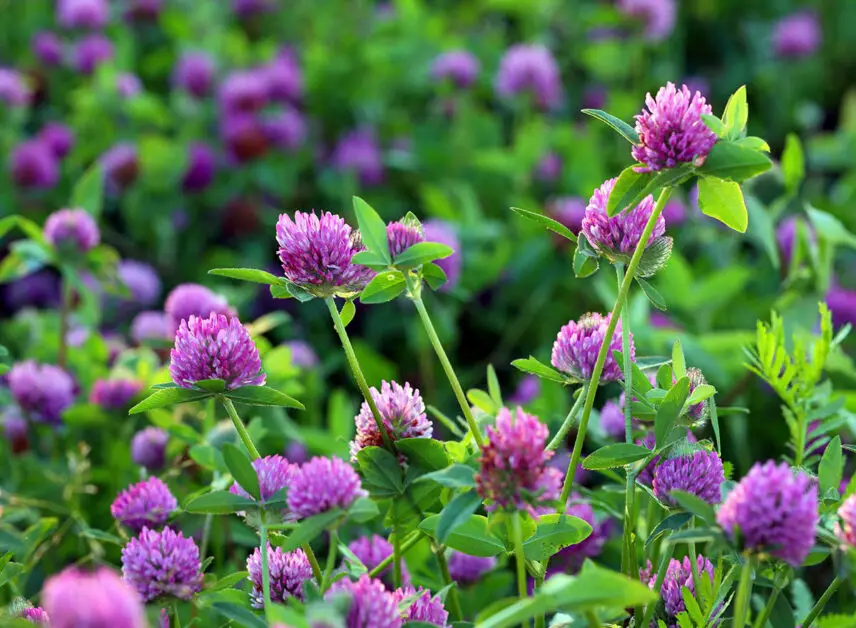
Red clover, known scientifically as Trifolium pratense, is a versatile cover crop that brings numerous benefits to agricultural ecosystems. One of the key advantages of using red clover is its ability to fix atmospheric nitrogen into the soil, enriching it for subsequent crops. This process not only reduces the need for synthetic fertilizers but also promotes healthier plant growth and increased crop yields. Additionally, red clover’s deep root system helps improve soil structure by enhancing drainage, reducing erosion, and increasing water retention, leading to better overall soil health and productivity.
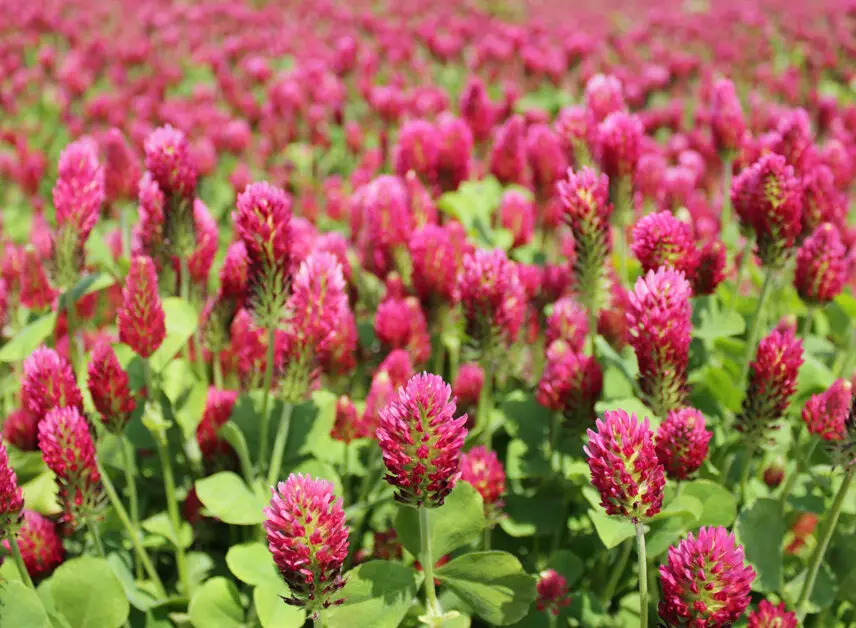

Moreover, red clover acts as a natural weed suppressor, inhibiting the growth of unwanted plants and reducing the need for herbicides. By outcompeting weeds for nutrients and space, red clover effectively minimizes weed pressure in fields, creating a more favorable environment for cash crops to thrive. This eco-friendly approach to weed management not only saves time and money for farmers but also contributes to sustainable agricultural practices that benefit the environment in the long term.
Ideal Growing Conditions for Red Clover
Red clover, known scientifically as Trifolium pratense, thrives under specific growing conditions that are essential for its optimal development. This versatile legume is favored for its ability to fix nitrogen in the soil, making it a valuable cover crop in sustainable farming practices. Red clover performs best in well-drained soils with a neutral pH level ranging from 6.0 to 7.0. The plant requires full sun for at least six hours a day to promote healthy growth and flowering.
Additionally, red clover appreciates a cool and moist environment, making it well-suited for regions with mild temperatures and consistent rainfall. It can tolerate some shade but produces more vigorous growth in sunny locations. The plant’s deep taproot system allows it to access nutrients in the soil efficiently, contributing to its resilience and ability to thrive in various conditions. Understanding and providing these ideal growing conditions can help gardeners and farmers harness the full potential of red clover as a beneficial cover crop.
The table below shows the conditions for red clover growth:
| Ideal Growing Conditions for Red Clover | Description |
|---|---|
| Temperature | Thrives in cool to moderate climates; optimal temperature range is 15-25°C (59-77°F). |
| Sunlight | Prefers full sun but can tolerate partial shade, especially in hotter climates. |
| Soil Type | Well-drained loamy soils with good fertility and pH between 6.0 and 7.0 are ideal. |
| Moisture | Requires consistent moisture; not tolerant of drought but can tolerate short periods of waterlogging. |
| pH Level | Prefers slightly acidic to neutral soils; optimal pH range is 6.0 to 7.0. |
| Fertilization | Generally does not require additional fertilization if grown in fertile soils, but benefits from phosphorus and potassium if soil levels are low. |
| Companion Plants | Grows well with grasses such as ryegrass and legumes like alfalfa. |
How Red Clover Improves Soil Quality
Red clover is a highly beneficial cover crop that plays a crucial role in improving soil quality. One significant way in which red clover enhances soil health is through its ability to fix atmospheric nitrogen into a form that plants can readily use. As a legume, red clover forms a symbiotic relationship with nitrogen-fixing bacteria in its roots, converting nitrogen gas into a more accessible form that enriches the soil. This process not only boosts soil fertility but also reduces the need for synthetic nitrogen fertilizers, thereby promoting environmentally friendly agriculture practices.
Furthermore, red clover’s deep root system helps break up compacted soils and improve overall soil structure. The extensive root network of red clover enhances soil aeration, water infiltration, and nutrient cycling, creating a more hospitable environment for beneficial soil organisms. By fostering a healthier soil ecosystem, red clover contributes to increased crop yields, disease resistance, and overall sustainability in agricultural systems.
The Role of Red Clover in Nitrogen Fixation
Red clover, scientifically known as Trifolium pratense, plays a crucial role in nitrogen fixation, making it a valuable cover crop for enhancing soil fertility. Through a symbiotic relationship with Rhizobia bacteria present in its root nodules, red clover has the unique ability to convert atmospheric nitrogen into a plant-usable form. This process, known as nitrogen fixation, not only benefits the red clover plant itself but also enriches the soil with nitrogen, making it available for other neighboring plants.
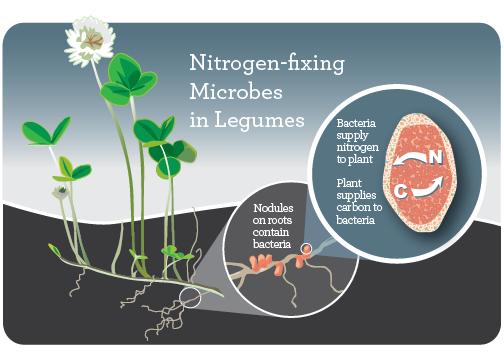
By harnessing the power of nitrogen fixation, red clover contributes to sustainable agricultural practices by reducing the need for synthetic fertilizers, which can have detrimental effects on the environment. Additionally, the nitrogen-fixing ability of red clover helps promote healthier plant growth, increase crop yields, and improve overall soil health. Farmers and gardeners alike can leverage the natural nitrogen fixation capabilities of red clover to enhance the productivity and sustainability of their land, paving the way for a more eco-friendly approach to agriculture.
Managing Red Clover in Crop Rotation
Crop rotation is a key aspect of successful farming practices, and integrating red clover into this strategy can offer a range of benefits for soil health and crop productivity. Red clover is known for its ability to fix nitrogen, which can help reduce the need for synthetic fertilizers in subsequent crops. When incorporating red clover into your crop rotation plan, it’s important to consider its growth characteristics and timing to maximize its soil-improving capabilities.
As a legume, red clover has the unique ability to form a symbiotic relationship with nitrogen-fixing bacteria, allowing it to take nitrogen from the air and convert it into a form that can be easily used by plants. This makes red clover an excellent choice for improving soil fertility and structure, particularly in rotations with nitrogen-demanding crops. By strategically managing the timing of red clover planting and termination within your crop rotation schedule, you can harness its nitrogen-fixing potential to optimize soil health and crop yields.
Red Clover’s Impact on Soil Structure
Red Clover’s deep root system plays a crucial role in improving soil structure by enhancing aeration and drainage. The extensive root network of Red Clover helps break up compacted soil, promoting better water infiltration and reducing the likelihood of soil erosion. As the roots penetrate the ground, they create channels that allow air and moisture to reach deeper soil layers, fostering a healthy environment for soil organisms.

Moreover, Red Clover’s ability to accumulate nutrients and organic matter in the soil further contributes to enhancing soil structure. The decomposition of Red Clover residues adds valuable organic material to the soil, increasing its overall fertility and improving its ability to retain moisture. By incorporating Red Clover into crop rotation systems, farmers can harness its soil-enhancing properties to promote long-term soil health and productivity.
Choosing the Right Variety of Red Clover for Your Soil
Red clover comes in various varieties that are suited to different soil types and growing conditions. Choosing the right variety of red clover for your soil is essential to maximize its benefits as a cover crop. For example, the Ladino variety is known for its high forage quality and adaptability to a wide range of soil types, making it a popular choice for livestock forage systems. On the other hand, the Medium Red variety thrives in well-drained soils and is commonly used for soil improvement and erosion control.
When selecting a red clover variety, consider factors such as soil pH, drainage, and intended use to ensure optimal performance. Conducting a soil test can help determine the pH level and nutrient content of your soil, guiding you in choosing the most suitable red clover variety. Additionally, consulting with local agricultural extension services or seed suppliers can provide valuable insights on the best varieties for your specific growing conditions. By selecting the right red clover variety, you can enhance soil fertility, suppress weeds, and improve overall crop yields in an environmentally sustainable manner.
Best Practices for Planting Red Clover as a Cover Crop
When it comes to planting red clover as a cover crop, following best practices is essential to maximize its benefits for soil health and crop production. Firstly, ensure that the soil pH is within the optimal range of 6.0 to 7.0, as red clover thrives in slightly acidic to neutral conditions. Prepare a well-drained seedbed free of weeds and compacted soil to promote successful establishment of red clover seeds. Planting depth should be shallow, ideally between ¼ to ½ inch, to encourage quick germination and early growth.
After planting, ensure adequate moisture for germination by irrigating if needed, but be cautious of overwatering which can lead to seed rot. Consider inoculating the red clover seeds with the appropriate rhizobia strain to enhance nitrogen-fixing capabilities. To promote strong root development, avoid grazing or cutting the red clover too early in its growth stage. Monitoring the growth progress and adjusting management practices accordingly will help achieve optimal results when utilizing red clover as a cover crop.
The Importance of Incorporating Red Clover into Your Soil Management Plan
Incorporating Red Clover into your soil management plan can have numerous benefits for your overall crop health and soil quality. Red clover is known for its ability to fix nitrogen from the atmosphere into a form that plants can use, reducing the need for synthetic fertilizers. By planting red clover as a cover crop in between cash crops, you can improve soil structure, reduce erosion, and suppress weed growth naturally. This can ultimately lead to better yields and healthier soil for future growing seasons.
Furthermore, red clover’s deep root system helps to break up compacted soil, allowing for better water infiltration and root penetration by subsequent crops. The incorporation of red clover into your soil management plan can also enhance biodiversity in your fields, attracting beneficial insects and improving microbial activity in the soil. Overall, by strategically including red clover in your farming practices, you can reap the long-term rewards of improved soil health and sustainable agriculture.
How Red Clover Suppresses Weeds in Fields
Red clover is a versatile cover crop that not only improves soil health but also helps in weed suppression in fields. One of the ways red clover achieves this is by outcompeting weeds for resources like sunlight, water, and nutrients. The dense foliage of red clover shades out emerging weed seedlings, preventing them from establishing and growing effectively. This natural weed-suppressing ability of red clover reduces the need for herbicides, making it an eco-friendly option for weed management in agricultural fields.

Additionally, red clover produces compounds called coumarin and phenolic acids, which can inhibit the germination and growth of certain weed species. These allelopathic properties of red clover contribute to its weed-suppressing capabilities, further enhancing its role as a sustainable and effective cover crop for weed management. By incorporating red clover into crop rotations or as a living mulch, farmers can not only improve soil quality but also reduce weed pressure in their fields, promoting healthier and more productive agricultural systems.
Maximizing the Soil-Improving Benefits of Red Clover
Maximizing the soil-improving benefits of red clover requires strategic planning and attention to detail. To enhance the nitrogen-fixing capabilities of this cover crop, consider planting red clover in conjunction with a legume inoculant to promote symbiotic relationships with nitrogen-fixing bacteria. Additionally, rotating red clover with other cash crops can help break pest and disease cycles, while also improving soil structure and nutrient availability. By carefully managing the timing of planting and termination of red clover, you can ensure optimal soil health benefits and maximize its impact on your agricultural ecosystem.
Moreover, incorporating red clover residues into your soil through proper decomposition techniques, such as tillage or mulching, can further enhance organic matter content and microbial activity. Utilizing red clover as a green manure cover crop in between cash crop plantings can also contribute to weed suppression and erosion control, ultimately leading to a more sustainable and productive farming system. By implementing these practices effectively, you can harness the full potential of red clover in enriching your soil and promoting long-term agricultural vitality.
Here is a table that shows soil improving benefits of red clover:
| Soil-Improving Benefits of Red Clover | Description |
|---|---|
| Nitrogen Fixation | Fixes atmospheric nitrogen into soil, enhancing fertility and reducing the need for synthetic fertilizers. |
| Organic Matter Addition | Adds organic matter, improving soil structure, moisture retention, and nutrient availability. |
| Soil Erosion Control | Dense root system binds soil particles, reducing erosion and providing ground cover. |
| Weed Suppression | Vigorous growth outcompetes weeds, aiding in weed control. |
| Soil pH Regulation | Slightly alkaline effect can balance soil pH, enhancing nutrient availability. |
| Biodiversity Enhancement | Attracts beneficial insects, promoting ecosystem biodiversity. |
| Green Manure | Acts as green manure when tilled into soil, enriching it with nutrients. |
| Drought Tolerance | Exhibits some drought tolerance, maintaining soil stability and productivity. |
| Improved Microbial Activity | Promotes beneficial microbial activity, aiding in nutrient cycling and soil health. |
Potential Challenges of Using Red Clover as a Cover Crop
One potential challenge of using red clover as a cover crop is its slow establishment compared to other cover crops. Red clover can take several weeks to establish a strong root system, making it vulnerable to competition from weeds during the early stages of growth. This slow start may require diligent weed management practices to ensure the red clover can successfully outcompete unwanted vegetation and thrive in the field.
Another challenge with using red clover as a cover crop is its sensitivity to grazing pressure, especially in pastures where livestock may have access. Overgrazing can significantly reduce red clover stands, limiting the crop’s ability to fix nitrogen and provide soil-enhancing benefits. Proper management practices, such as rotational grazing or limiting grazing during critical growth stages, are essential to maintain a healthy red clover cover crop and maximize its soil-improving properties.
Harvesting and Managing Red Clover Residues
After the growth cycle of red clover as a cover crop comes to an end, it’s essential to properly manage its residues to maximize its benefits for soil health. Harvesting and managing red clover residues can be a crucial step in the overall success of your crop rotation plan. When it comes to harvesting red clover, timing is key to ensure that the residues retain their nutrient-rich properties while also preventing weed seed production. Once harvested, these residues can be incorporated back into the soil through tillage or other methods to improve soil structure and organic matter content.
Proper management of red clover residues can also play a role in reducing erosion, enhancing moisture retention, and promoting a healthy microbial environment in the soil. By effectively incorporating these residues back into the soil, farmers can harness the full potential of red clover’s nitrogen-fixing abilities and soil-improving properties. Strategic management of red clover residues is a sustainable practice that contributes to the long-term health and productivity of agricultural land while supporting crop growth in subsequent seasons.
Integrating Red Clover into Sustainable Farming Practices
Integrating red clover into sustainable farming practices can significantly benefit both the crops and the environment. Red clover, known for its nitrogen-fixing abilities, helps improve soil health and fertility naturally, reducing the need for synthetic fertilizers. By incorporating red clover into crop rotations, farmers can enhance soil structure, suppress weeds, and ultimately increase yields.
Furthermore, utilizing red clover as a cover crop can aid in erosion control, enhance biodiversity, and promote overall sustainability in agriculture. Its deep root system contributes to soil aeration and water retention, crucial aspects of maintaining a healthy and productive farming ecosystem. By embracing the integration of red clover into their farming practices, growers can foster long-term soil health while reducing the environmental impact of conventional farming methods.
The Economics of Using Red Clover as a Cover Crop
Red clover serves as a cost-effective solution for enhancing soil health and yield potential, making it a lucrative investment for farmers and gardeners alike. While the initial cost of incorporating red clover as a cover crop may seem higher compared to conventional methods, the long-term benefits far outweigh these expenses. Studies have shown that red clover can reduce the reliance on synthetic fertilizers, leading to significant cost savings over time. Additionally, the nitrogen-fixing properties of red clover contribute to enhanced soil fertility, resulting in higher crop yields and reduced input costs for subsequent plantings.
Moreover, the economic advantages extend beyond the direct savings on inputs. Red clover’s ability to suppress weeds and improve soil structure can lead to lower weed management expenses and reduced need for costly soil amendments. Furthermore, incorporating red clover into crop rotation plans can help break pest cycles and boost overall farm productivity. By factoring in the holistic economic benefits of using red clover as a cover crop, farmers can see a positive return on investment while promoting sustainable agricultural practices.
Watch this video to learn about red clover cover crop.
Case Studies of Successful Red Clover Cover Crop Implementation
In a study conducted by the University of Agriculture and Horticulture, red clover cover crops were found to significantly increase soil fertility and improve crop yields in a sustainable manner. The research observed a 20% increase in nitrogen levels and a 15% boost in organic matter content in fields where red clover was used as a cover crop compared to fields without this practice. Farmers reported seeing healthier plants, reduced need for synthetic fertilizers, and improved overall soil structure after incorporating red clover into their crop rotation schedules.
Another case study by the Department of Sustainable Agriculture highlighted the positive impact of red clover cover crops on weed suppression. By planting red clover between cash crops, farmers observed a reduction in weed growth by up to 70% due to the shade created by the dense foliage of the red clover plants. This natural weed management strategy not only saved time and effort in manual weeding but also minimized the use of herbicides, leading to a more eco-friendly and cost-effective farming approach.
Can red clover be used as a cover crop in all types of soils?
Red clover can thrive in a variety of soil types, but it typically performs best in well-drained soils with a pH between 6.0 and 7.0.
How long does red clover take to establish as a cover crop?
Red clover can establish quickly, with good growth seen within a few weeks of planting under ideal conditions.
Is red clover a good option for improving soil fertility?
Yes, red clover is known for its ability to fix nitrogen in the soil, which can help improve soil fertility for subsequent crops.
Can red clover be used in organic farming practices?
Yes, red clover is a popular choice for organic farmers looking to improve soil health and fertility without the use of synthetic chemicals.
What are some potential challenges of using red clover as a cover crop?
Some challenges of using red clover as a cover crop include potential competition with cash crops, managing its growth to prevent it from becoming invasive, and potential issues with disease or pest infestations.
How can farmers maximize the soil-improving benefits of red clover?
Farmers can maximize the benefits of red clover by planting it in rotation with cash crops, allowing it to grow to full maturity before terminating it, and ensuring proper management practices are in place.
Are there any specific varieties of red clover that are better suited for certain soil types?
Yes, there are different varieties of red clover available, each with its own characteristics and adaptability to different soil types. It is important to choose a variety that is well-suited to your specific soil conditions.
What is the economic impact of using red clover as a cover crop?
While there may be upfront costs associated with planting red clover as a cover crop, the long-term benefits of improved soil health, fertility, and reduced input costs can lead to cost savings and increased profitability for farmers.







