The Best Way to Know About Rockwool Production and Its Impact on the Environment
Table of Contents
Sustainable Practices: Highlighting Efforts to Minimize the Environmental Impact of Rockwool Production

Rockwool, also known as mineral wool, is a popular choice for thermal insulation due to its excellent heat and sound insulation properties. However, the production process of Rockwool Production has raised concerns regarding its environmental impact. In response to these concerns, manufacturers have implemented sustainable practices to minimize the environmental footprint of Rockwool Production.
One such practice is the use of recycled materials in the manufacturing process. Recycled glass and slag, a byproduct of the steel industry, are often used as raw materials in Rockwool Production. By utilizing these recycled materials, manufacturers can reduce the demand for virgin resources, thus conserving natural resources and reducing waste.
Additionally, energy efficiency measures have been implemented to minimize the energy consumption during rockwool production. Advanced technologies, such as high-performance furnaces and energy recovery systems, are employed to optimize energy usage and reduce greenhouse gas emissions. These practices not only reduce the environmental impact of the production process but also contribute to cost savings for the manufacturers.
• Recycled materials, such as glass and slag, are used in the manufacturing process to reduce the demand for virgin resources.
• Energy efficiency measures, including high-performance furnaces and energy recovery systems, are implemented to minimize energy consumption.
• These practices reduce the environmental impact and contribute to cost savings for manufacturers.
Rockwool production involves the transformation of natural raw materials
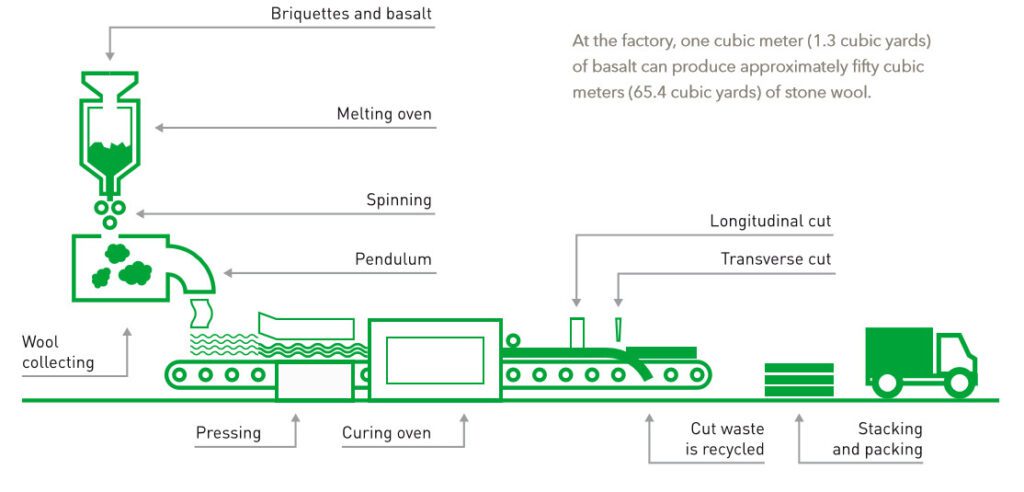
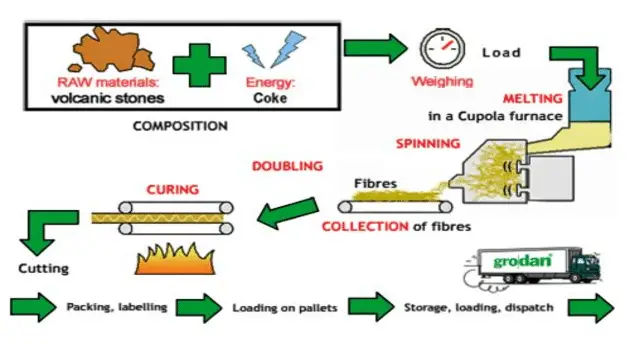
Rockwool production involves the transformation of natural raw materials, typically basalt rock or iron ore blast furnace slag, into a versatile and widely used material known as mineral wool or stone wool. The process is highly energy-intensive and requires specialized equipment. Here is an overview of the key steps involved in Rockwool production:
- Raw Material Extraction:
- The primary raw materials used in Rockwool production are basalt rock or iron ore blast furnace slag. Basalt rock is a volcanic rock rich in minerals, and iron ore blast furnace slag is a byproduct of the iron and steel industry.
- Melting and Fiberization:
- The raw materials are heated to high temperatures (above 1,600 degrees Celsius) in a furnace. This process melts the materials, and the molten substance is then spun into fibers using a spinning wheel or a similar method. The fibers are typically fine and resemble wool.
- Binder Application (if applicable):
- In some cases, a binder may be added to the fibers to enhance their cohesion and form a stable mat. This binder is often an organic substance, and its use can vary depending on the specific product requirements.
- Curing and Cooling:
- The newly formed wool-like material is cured and cooled to set its structure. This step is crucial for creating the final product’s physical properties, including its density and resilience.
- Cutting and Shaping:
- The solidified material is cut and shaped into the desired product forms. These forms can include insulation batts, boards, blankets, or customized shapes for specific applications.
- Surface Treatment (if applicable):
- Some Rockwool products may undergo surface treatments to improve their performance characteristics, such as water repellency or resistance to microbial growth.
- Packaging:
- The finished Rockwool products are packaged for distribution. Packaging may vary depending on the specific product and its intended use.
- Quality Control:
- Throughout the production process, quality control measures are implemented to ensure that the final Rockwool products meet the required specifications and standards. This includes testing for density, thickness, thermal conductivity, and other relevant properties.
It’s important to note that Rockwool production is resource-intensive, particularly in terms of energy consumption during the melting process. Some manufacturers are working to improve the sustainability of Rockwool by incorporating recycled content, optimizing energy efficiency, and implementing environmental management practices.
The environmental impact of Rockwool production should be considered within the context of the product’s life cycle, from raw material extraction to use and end-of-life disposal or recycling. Additionally, adherence to environmental standards and certifications can be an important aspect of evaluating the sustainability of Rockwool products.
Life Cycle Assessment: Understanding the Overall Environmental Performance of Rockwool
Rockwool, also known as mineral wool or stone wool, is a widely used insulation material known for its thermal and acoustic properties. As society becomes more environmentally conscious, it is vital to assess the overall environmental performance of different insulation materials, including rockwool. Life cycle assessment (LCA) is a valuable tool that enables us to understand the complete environmental impact associated with a product or process, from its raw material extraction to its eventual disposal.
LCA takes into account factors such as energy consumption, water usage, waste generation, and greenhouse gas emissions at each stage of the rockwool production process. By analyzing these key aspects, it becomes possible to identify areas for improvement and to develop strategies for reducing the environmental burden. LCA studies have shown that rockwool insulation generally has a favorable environmental profile, particularly when compared to other conventional insulation materials. However, it is important to note that the environmental impact of rockwool can vary depending on factors such as the energy source used during manufacturing and the management of waste generated during installation and removal.
This ongoing assessment of the environmental performance of rockwool helps inform decision-making processes, allowing manufacturers, policymakers, and consumers to make more informed choices. By understanding the life cycle impacts of rockwool, we can work towards further improving its sustainability and minimizing its environmental footprint. Continued research and innovation, along with collaboration among stakeholders, will be crucial in developing even greener insulation materials in the future.
• Life cycle assessment (LCA) is a valuable tool for understanding the overall environmental impact of rockwool insulation
• LCA considers factors such as energy consumption, water usage, waste generation, and greenhouse gas emissions at each stage of production
• Rockwool generally has a favorable environmental profile compared to other insulation materials
• However, the environmental impact can vary based on factors like energy source and waste management
• Ongoing assessment helps inform decision-making processes for manufacturers, policymakers, and consumers
• Understanding life cycle impacts allows for improvements in sustainability and reduction of environmental footprint
• Continued research and innovation will be crucial in developing even greener insulation materials in the future.
Rockwool, also known as mineral wool or stone wool
Is a versatile material commonly used in various applications, including insulation and horticulture. When assessing the overall environmental performance of Rockwool, several factors need to be considered:
- Resource Extraction:
- Rockwool is typically made from basalt rock or iron ore blast furnace slag. The extraction of these raw materials involves mining and energy consumption. The environmental impact of mining activities and the energy intensity of extraction processes should be considered.
- Manufacturing Process:
- The production of Rockwool involves melting the raw materials at high temperatures and then spinning the molten material into fibers. This process requires significant energy input. Assessing the energy efficiency of manufacturing facilities, the use of recycled content, and emissions during production are crucial factors.
- Energy Efficiency:
- Rockwool is often praised for its insulating properties, which contribute to energy efficiency in buildings. When used as insulation, it can help reduce energy consumption for heating and cooling, leading to lower carbon emissions over the life of a building.
- Recyclability:
- Rockwool is generally recyclable, and some manufacturers incorporate recycled content into their products. The ease of recycling and the percentage of recycled content in the final product contribute to its environmental performance.
- End-of-Life Disposal:
- Consideration should be given to how Rockwool is disposed of at the end of its life cycle. While it is recyclable, the availability of recycling facilities and proper disposal methods may vary by region.
- Environmental Impact during Use:
- In horticulture, Rockwool is commonly used as a growing medium for hydroponic systems. Its impact on plant growth, water usage, and nutrient efficiency should be considered. Additionally, any potential leaching of substances into the environment during its use needs to be assessed.
- Emissions and Air Quality:
- The manufacturing process of Rockwool can produce emissions, including particulate matter. Evaluating air quality impacts and the effectiveness of emission control measures is important.
- Transportation:
- The transportation of raw materials to manufacturing facilities and the distribution of Rockwool products to end-users contribute to its overall carbon footprint. Assessing the efficiency of transportation methods and exploring options for regional production can mitigate these impacts.
- Certifications and Standards:
- Look for certifications such as Cradle to Cradle, GreenGuard, or other third-party assessments that evaluate the environmental and health impacts of Rockwool products.
Understanding the overall environmental performance of Rockwool requires a comprehensive life cycle assessment, considering factors from raw material extraction to manufacturing, use, and disposal. Additionally, regional differences, product variations, and technological advancements in production methods play a role in determining the sustainability of Rockwool products.
Here’s a table with information about Rockwool production and its impact on the environment:
| Aspect | Description |
|---|---|
| Raw Materials | – Main components: basalt rock and chalk. – May include recycled material from industrial by-products. |
| Extraction Process | – Basalt rock is melted at high temperatures. – Resulting molten material is spun into fibers. |
| Energy Consumption | Energy-intensive process due to high temperatures needed for rock melting. |
| Environmental Impact of Raw Materials | Basalt is abundant, but mining and processing contribute to environmental disturbance. |
| Emission of Greenhouse Gases | – Production releases carbon dioxide (CO2) during the melting process. – Use of fossil fuels in the manufacturing process can contribute to emissions. |
| Water Usage | Rockwool production generally has lower water requirements compared to some other growing media. |
| Recyclability | Rockwool can be recycled and reused, reducing overall environmental impact. |
| Waste Generation | Waste is generated during the manufacturing process, but efforts are made to recycle and minimize waste. |
| Potential Environmental Concerns | – Emission of pollutants during production. – Disposal of used Rockwool may contribute to landfill waste. |
| Occupational Health and Safety | Handling Rockwool may pose health risks due to fibers; safety precautions are necessary during installation. |
| Sustainable Practices | – Some manufacturers use recycled materials in production. – Advances in technology aim to reduce environmental impact. |
| Alternative Growing Media | Peat, coconut coir, perlite, and other alternatives are considered by growers concerned about environmental impact. |
| Life Cycle Assessment (LCA) | Assessing the overall environmental impact of Rockwool, from raw material extraction to disposal, is crucial for a comprehensive understanding. |
| Regulatory Compliance | Compliance with environmental regulations and certifications ensures adherence to environmental standards. |
| Community Impact | Local communities may be affected by the environmental footprint and potential health concerns associated with Rockwool production. |
| Consumer Awareness | Educating consumers about Rockwool’s environmental impact and promoting sustainable practices in horticulture. |
Rockwool, while widely used in horticulture, does have environmental considerations in its production and use. It’s important for growers to be aware of these factors and explore sustainable practices and alternatives where possible. Ongoing research and advancements in manufacturing technology aim to minimize the environmental impact of Rockwool production.
Exploring Greener Options for Thermal Insulation: Rockwool Production
When it comes to thermal insulation, there is a wide range of alternative materials that offer greener options for environmentally conscious individuals. These alternatives not only provide effective insulation for buildings but also minimize the negative impact on the environment. One popular option is cellulose insulation, which is made from recycled materials such as newspaper and cardboard. It is treated with fire-retardant chemicals to ensure safety and effectiveness. Cellulose insulation boasts excellent thermal performance and is known for its ability to reduce energy consumption by maintaining a consistent indoor temperature. Additionally, it is a cost-effective solution that can easily be installed in both new and existing structures.
Another sustainable option for thermal insulation is sheep’s wool. Known for its exceptional insulating properties, sheep’s wool can effectively regulate temperature and moisture. It is a renewable resource that is naturally fire-resistant, eliminating the need for chemical additives. Sheep’s wool insulation is also biodegradable and has a low environmental impact throughout its life cycle. Beyond its excellent insulating properties, sheep’s wool is also known for its ability to absorb and release moisture, creating a more comfortable and healthy indoor environment. As an added bonus, it is an effective sound absorber, reducing noise pollution in buildings.
• Cellulose insulation is made from recycled materials such as newspaper and cardboard.
• It is treated with fire-retardant chemicals for safety and effectiveness.
• Cellulose insulation has excellent thermal performance and reduces energy consumption.
• It is a cost-effective solution that can be installed in new and existing structures.
• Sheep’s wool is another sustainable option for thermal insulation.
• It effectively regulates temperature and moisture.
• Sheep’s wool is a renewable resource that is naturally fire-resistant, eliminating the need for chemical additives.
• It has a low environmental impact throughout its life cycle.
Benefits of sheep’s wool insulation:
– Creates a more comfortable and healthy indoor environment by absorbing and releasing moisture
– Acts as an effective sound absorber, reducing noise pollution in buildings
By exploring these alternative insulation materials, individuals can not only improve the energy efficiency of their buildings but also contribute to a greener future. These options provide effective thermal insulation while minimizing negative impacts on the environment. Whether it’s cellulose or sheep’s wool, choosing greener alternatives ensures both comfort and sustainability.
What are some alternative insulation materials to Rockwool?
Some greener options for thermal insulation include recycled cellulose insulation, sheep’s wool insulation, and natural fiber insulation.
How do sustainable practices minimize the environmental impact of Rockwool production?
Sustainable practices in Rockwool production can include using recycled materials, reducing energy consumption, and implementing responsible waste management strategies.
What is a Life Cycle Assessment (LCA) and why is it important in understanding the environmental performance of Rockwool?
A Life Cycle Assessment is a comprehensive analysis of the environmental impact of a product throughout its entire life cycle, from raw material extraction to disposal. It is important in understanding the overall environmental performance of Rockwool as it takes into account factors such as energy usage, greenhouse gas emissions, and resource depletion.
Are there any drawbacks to using alternative insulation materials?
While alternative insulation materials may have their advantages, they can also have drawbacks. For example, some natural fiber insulation materials may be more prone to moisture absorption or require additional fireproofing treatment.
Can alternative insulation materials provide the same level of thermal insulation as Rockwool?
Yes, some alternative insulation materials can provide similar or even better thermal insulation performance compared to Rockwool. However, it is important to consider the specific needs and requirements of each project before selecting the most suitable option.
How can individuals contribute to using greener insulation materials?
Individuals can contribute to using greener insulation materials by educating themselves about sustainable options, supporting companies that prioritize environmental responsibility, and advocating for the use of greener materials in construction projects.
Are there any government incentives or programs that promote the use of greener insulation materials?
Yes, in many countries, there are government incentives and programs that encourage the use of greener insulation materials. These can include tax credits, grants, and subsidies for energy-efficient and environmentally friendly building practices.
Can alternative insulation materials be more expensive than Rockwool?
The cost of alternative insulation materials can vary depending on factors such as availability, production processes, and market demand. In some cases, alternative materials may be more expensive than Rockwool, while in others, they may be comparable or even more cost-effective.
How can I ensure that the alternative insulation material I choose is truly greener?
To ensure that the alternative insulation material you choose is truly greener, you can look for certifications or labels that indicate environmental sustainability, such as Energy Star, GreenGuard, or Cradle to Cradle. Additionally, researching the manufacturing processes and sourcing practices of the material can provide insight into its environmental impact.