Aeroponics vs Hydroponics: A Comparison of the Two Methods of Growing Plants in Air and Water
Table of Contents
Pest and Disease Management: Evaluating the Strategies Employed in Aeroponics and Hydroponics to Minimize Plant Health Risks
Pest and disease management is a critical aspect of plant cultivation, regardless of the method employed. In both aeroponics and hydroponics, minimizing plant health risks requires careful consideration and implementation of effective strategies.
In aeroponics, where plants are grown in nutrient-rich mist, the risk of pests and diseases may be reduced due to the absence of soil. Without soil, many soil-borne pests and pathogens are less likely to thrive, thus minimizing the potential impact on plant health. Additionally, aeroponic systems allow for the precise control of environmental conditions, such as temperature and humidity, which can further deter pests and diseases. However, it is still crucial to implement preventive measures, such as regular monitoring, proper sanitation, and the use of biological control agents, to ensure optimal plant health and productivity.

In hydroponic systems, where plants are grown in nutrient-rich water solutions, the risk of pests and diseases may be slightly higher compared to aeroponics. Since hydroponics involves the use of a growing medium, such as perlite or rockwool, there is still a potential for soil-borne pests and pathogens to affect plant health. However, the absence of soil can also provide some advantages. For instance, hydroponic systems can be designed to be closed and sterile, minimizing the introduction of pests and diseases. Additionally, the controlled environment in hydroponics allows for early detection and prompt response to any signs of pest infestation or disease outbreak. By implementing strict sanitation practices, regular monitoring, and the use of integrated pest management strategies, the risk of plant health problems can be effectively minimized in hydroponic systems.
Environmental Sustainability: Comparing the Ecological Footprint of Aeroponics and Hydroponics
Aeroponics and hydroponics are two innovative gardening methods that have gained significant attention for their potential to minimize the ecological footprint compared to traditional soil-based agriculture. In terms of environmental sustainability, evaluating the ecological footprint of these systems can provide valuable insights into their overall impact.
When comparing the ecological footprint of aeroponics and hydroponics, it is important to consider factors such as water usage, energy consumption, and nutrient management. Both systems excel in their ability to optimize water usage by providing plants with precise amounts of water based on their specific needs. However, hydroponics typically requires a large amount of energy to power pumps, aerators, and lighting systems, which can impact its overall ecological footprint. On the other hand, aeroponics relies on a fine mist of nutrient-rich solution to nourish plants, resulting in reduced energy requirements.
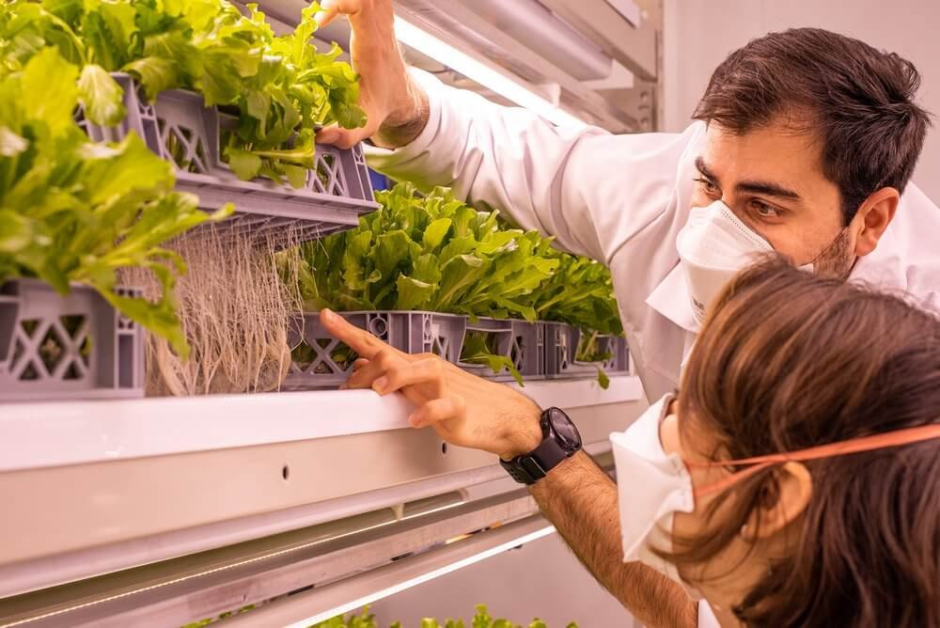

Additionally, nutrient management is a crucial aspect of ecological sustainability in both aeroponics and hydroponics. In hydroponics, a nutrient solution is continuously circulated to provide plants with essential elements. This requires careful monitoring and adjusting to ensure optimal nutrient levels and prevent waste. In aeroponics, nutrients are delivered in a mist form, allowing for precise control and conservation of resources. This method reduces the risk of nutrient runoff and pollution, further contributing to a smaller ecological footprint.
As we strive to develop sustainable agricultural practices, assessing the ecological footprint of different cultivation methods can guide us towards more environmentally conscious choices. Understanding the nuances and trade-offs between aeroponics and hydroponics will empower gardeners and farmers to make informed decisions that align with their specific environmental goals.
Adaptability and Scalability: Examining the Flexibility of Aeroponics and Hydroponics
Aeroponics and hydroponics are two innovative methods of growing plants that are gaining popularity in the field of agriculture. One key advantage of these systems is their adaptability and scalability, which allow them to be used in various environments and for different purposes.
In terms of adaptability, both aeroponics and hydroponics provide the flexibility to grow plants in locations where traditional soil-based methods may not be feasible. With aeroponics, plants are grown without the use of soil, with their roots suspended in the air and misted with nutrient-rich water. This method is particularly useful in areas with limited access to arable land or in urban environments where space is limited. On the other hand, hydroponics involves growing plants in a nutrient-rich water solution, eliminating the need for soil altogether. This flexibility allows for cultivation in various settings, including indoor environments, greenhouses, and even vertical farms.
Another aspect to consider is the scalability of these cultivation systems. Both aeroponics and hydroponics can be easily scaled up or down to meet specific needs. This scalability makes them suitable for small-scale home gardens as well as large commercial operations. Whether it’s a small hydroponic setup on a balcony or a sprawling aeroponic farm, these systems can be customized to fit the available space and desired level of production.
Overall, the adaptability and scalability of aeroponics and hydroponics make them versatile options for cultivating plants in diverse settings. Whether it’s addressing the challenges of limited space, reducing water usage, or maximizing crop yield, these systems offer innovative solutions that are both efficient and sustainable. As the demand for locally sourced, fresh produce continues to rise, exploring and understanding the flexibility of these cultivation methods can pave the way for a more resilient and productive future in agriculture.
• Aeroponics and hydroponics are flexible methods of growing plants that can be used in various environments.
• Aeroponics allows plants to grow without soil, making it suitable for areas with limited access to arable land or urban environments where space is limited.
• Hydroponics involves growing plants in a nutrient-rich water solution, eliminating the need for soil altogether and allowing cultivation in indoor environments, greenhouses, and vertical farms.
• Both aeroponics and hydroponics can be easily scaled up or down to meet specific needs, making them suitable for small-scale home gardens as well as large commercial operations.
• These systems offer innovative solutions for addressing challenges such as limited space, reducing water usage, and maximizing crop yield.
• The adaptability and scalability of aeroponics and hydroponics contribute to their efficiency and sustainability in agriculture.
What are some strategies employed in aeroponics and hydroponics to minimize plant health risks?
In aeroponics and hydroponics, strategies such as regular monitoring of plants, implementing proper sanitation practices, and using integrated pest management techniques are commonly employed to minimize plant health risks.
How do aeroponics and hydroponics compare in terms of their ecological footprint?
When considering environmental sustainability, aeroponics generally has a smaller ecological footprint compared to hydroponics. This is because aeroponics uses less water and nutrients while also reducing the need for pesticides and fertilizers.
How flexible are aeroponics and hydroponics systems?
Both aeroponics and hydroponics systems are highly adaptable and scalable. They can be easily adjusted to accommodate different plant types, sizes, and growth stages. Additionally, these systems can be expanded or scaled down as per the requirements of the user.
Can aeroponics and hydroponics be used for outdoor farming?
While aeroponics and hydroponics systems are primarily designed for indoor farming, they can be adapted for outdoor use. However, outdoor farming using these systems may require additional considerations such as protection from weather conditions and pests.
Are there any specific advantages of aeroponics over hydroponics in terms of adaptability?
Yes, aeroponics offers certain advantages over hydroponics in terms of adaptability. Since aeroponics delivers nutrients directly to the roots as a fine mist, it allows for better oxygenation and root growth. This can result in faster and more efficient plant growth compared to hydroponics.
Can aeroponics and hydroponics be used to grow a wide variety of plants?
Yes, both aeroponics and hydroponics can be used to grow a wide variety of plants, including leafy greens, herbs, vegetables, and even some fruits. The flexibility of these systems allows for customization of nutrient solutions and environmental conditions to suit the specific needs of different plants.

Pallavi Gupta is a burgeoning writer at SouthElMonteHydroponics, blending her passion for data analysis with a keen interest in biotechnology. Currently pursuing a Bachelor’s in Biotechnology at Amity University, Pallavi delves into the intricacies of life sciences while gaining hands-on experience in the exciting world of data analysis. Her unique background provides a fresh perspective on hydroponic farming, as she explores the intersection of biotechnology and sustainable agriculture. Through her writing, Pallavi aims to bridge the gap between data-driven insights and innovative farming practices, inspiring others to harness technology for a greener future.






Hello! I simply want to give an enormous thumbs up for the good information you’ve here on this post. I will likely be coming back to your weblog for more soon.