Aquaponics and Hydroponics: How They Work and How to Set Them Up
Did you know that you can grow fresh vegetables and fish together in your own home? Aquaponics and hydroponics are two innovative gardening techniques that make this possible. These systems use water instead of soil to grow plants, making them perfect for urban environments or anyone looking to maximize space and efficiency. Aquaponics combines fish farming and hydroponics in a symbiotic environment, while hydroponics focuses solely on plants.
Both methods are not only sustainable but also surprisingly easy to set up. Whether you’re a gardening novice or a seasoned green thumb, this guide will walk you through the essentials of starting your own aquaponics or hydroponics system. Let’s dive into the future of gardening!
Table of Contents
Understanding the Basics of Soilless Gardening
- Innovative Growth Method
- Grows plants without soil
- Uses a nutrient-rich water solution
- Popularity and Versatility
- Gained traction among gardening enthusiasts
- Suitable for a wide variety of plants
- High Water Efficiency
- Reduces water wastage
- Water is recirculated within the system
- More sustainable compared to soil-based gardening
- Optimal Hydration
- Provides plants with the necessary hydration
- Conserves water, our most precious resource
- Weeds and PestsControl
- Eliminates the need for pesticides and herbicides
- Controlled environment prevents weed and pest growth
- Health and Environmental Benefits
- Mitigates harmful chemical use
- Leads to cleaner, healthier produce
This not only mitigates the harmful effects of chemicals on both the environment and our health but also leads to cleaner and healthier produce.
The Benefits of Aquaponics and Hydroponics Systems
Aquaponics and hydroponics systems offer numerous benefits for gardening enthusiasts. These soilless gardening methods provide an efficient and sustainable way to grow plants, allowing for higher yields and faster growth rates compared to traditional soil-based methods.

- Water Efficiency:
- Both aquaponics and hydroponics systems recirculate water, minimizing wastage due to evaporation or drainage.
- Ideal for regions with limited water resources or prone to droughts.
- Hydroponics can use up to 90% less water compared to traditional soil-based methods.
- Precise Nutrient Control:
- These systems allow precise adjustment of nutrients levels, promoting optimal plant growth.
- Soilless cultivation eliminates soil-borne diseases and reduces reliance on pesticides.
- Environmental Impact:
- Reduced water usage and minimal soil disturbance contribute to sustainability.
- Cleaner crops with fewer chemical residues benefit both consumers and the environment.
- Aquaponics Integration:
- Aquaponics combines fish farming and plant cultivation.
- Fish waste provides nutrients for plants, creating a symbiotic relationship.
- Eliminates the need for artificial fertilizers and offers a renewable fish source.
Overall, aquaponics and hydroponics systems offer significant benefits in terms of water efficiency, nutrient control, and sustainability. Whether you’re a small-scale gardener or a commercial farmer, these methods can help you maximize your crop yield and minimize environmental impact. So why not embrace the future of gardening and explore the world of aquaponics and hydroponics?
Exploring the Key Components of Aquaponics and Hydroponics
Aquaponics and hydroponics systems are innovative solutions for cultivating plants without the use of traditional soil. These systems utilize different key components to create an optimized environment for plant growth.

Aquaponics System Components:
- Fish Tank :
- Houses aquatic animals (e.g., fish) that provide nutrients for plant growth.
- Fish waste serves as a natural fertilizer.
- Grow Bed:
- Located above the fish tank.
- Plants are cultivated here.
- Water from the fish tank is pumped up to the grow bed, providing nutrients to the plants.
- Plants filter the water, returning clean water back to the fish tank.
Hydroponics Systems Components:
- Nutrient Reservoir:
- Contains a water-nutrient mixture.
- Ensures plants receive essential elements for growth.
- Growing Medium:
- Supports plant roots.
- Examples: perlite, coconut coir, or rock wool.
- Retains moisture and provides stability.
- Water Pumps:
- Circulate nutrient-rich water.
- Deliver it to plants through pipes or tubes.
Both systems offer controlled environments for plant cultivation, reducing reliance on soil and promoting resource efficiency. 🌱🌿.The next section will delve into the specific details of how nutrients are supplied in aquaponics and hydroponics systems.
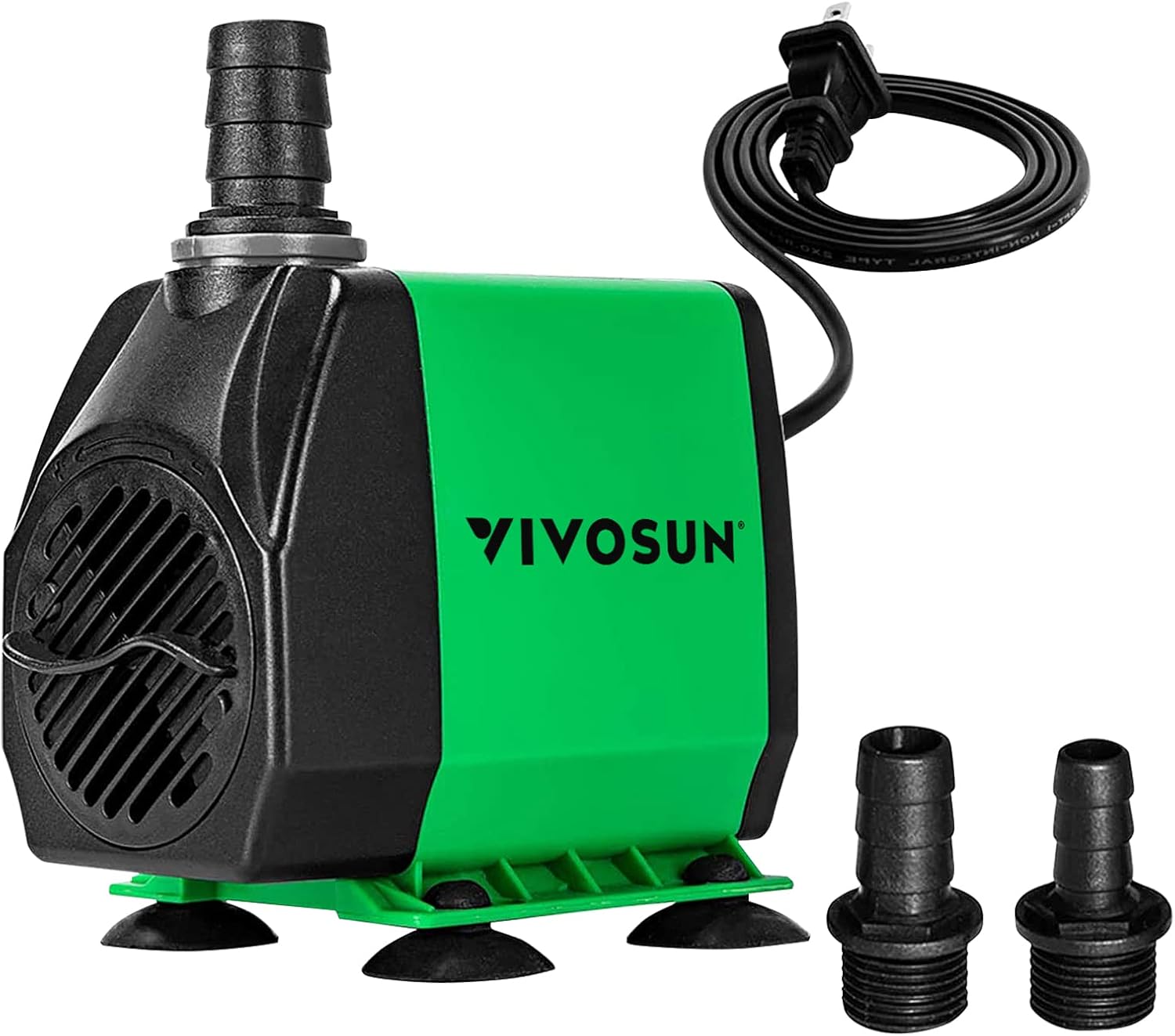
As an avid hydroponic enthusiast, I recently incorporated the VIVOSUN Submersible Water Pump into my hydroponic system, and I must say, it has exceeded my expectations. This pump delivers exceptional performance, ensuring optimal water circulation throughout my setup. Its adjustable flow rate feature allows me to tailor the water flow according to the specific requirements of my plants, promoting healthy growth and maximum nutrient uptake.
One of the standout features of this pump is its quiet operation, which creates a serene environment for my plants to thrive. Additionally, its durable construction gives me confidence in its longevity, providing reliable performance for the long term.
However, I did notice that the pump may require occasional maintenance to prevent clogging, but this is a minor inconvenience considering its overall performance.
Overall, I highly recommend the VIVOSUN Submersible Water Pump for anyone looking to enhance the efficiency and productivity of their hydroponic system. It’s a reliable and versatile solution that will undoubtedly contribute to the success of your indoor gardening endeavors.
- Powerful performance: The VIVOSUN Submersible Water Pump delivers efficient water circulation, essential for hydroponic systems.
- Versatile usage: Suitable for various applications including fountains, aquariums, and hydroponic setups.
- Adjustable flow rate: Allows for precise control over water flow, catering to different plant needs.
- Quiet operation: Operates silently, ensuring a peaceful environment for your plants.
- Durable construction: Made with high-quality materials for long-lasting reliability.
- Limited lifespan: Some users reported a shorter lifespan compared to other pumps.
- Prone to clogging: Requires regular maintenance to prevent debris buildup.
- Suction cup reliability: Suction cups may lose grip over time, necessitating occasional readjustment.
How Nutrients are Supplied in Aquaponics and Hydroponics
Aquaponics and hydroponics are unique methods of cultivating plants without traditional soil. In these systems, nutrients are supplied directly to the plants through water, allowing for efficient and sustainable growth.
| Aspect | Aquaponics | Hydroponics |
|---|---|---|
| Nutrient Source | Nutrient-rich water from fish tanks; fish waste contains essential nutrients like nitrogen, phosphorus, and potassium | Nutrient solutions mixed with water, containing a precise balance of essential elements |
| Process | Fish produce waste -> Beneficial bacteria break down waste -> Nutrients absorbed by plants -> Water recirculated back to fish tanks | Plants absorb nutrients directly from water through techniques like nutrient film technique, drip irrigation, or deep water culture |
| Ecosystem | Self-sustaining ecosystem: Fish provide nutrients for plants, plants purify water for fish | Controlled system: Precise control over nutrient content |
| Control Over Nutrients | Less precise, relies on natural processes within the ecosystem | Highly precise, tailored nutrient solutions ensure optimal growth and yield |
| Growth Rates and Yield | Maximizes growth rates and crop yields | Maximizes growth rates and crop yields |
| Pest and Disease Risk | Reduced risk due to absence of soil; plants purify water, reducing harmful substances | Reduced risk due to absence of soil; controlled environment limits exposure to pests and diseases |
| Popularity | Increasingly popular among gardening enthusiasts | Increasingly popular among gardening enthusiasts |
With a solid understanding of how nutrients are supplied in these systems, gardeners can confidently embark on their soilless gardening journey, reaping the benefits of efficient resource utilization and sustainable cultivation practices.
The Role of Fish in Aquaponics Systems
Aquaponics systems are a unique and innovative way of gardening that combines aquaculture and hydroponics. In these systems, fish play a crucial role in maintaining a balanced ecosystem and providing essential nutrients for plant growth. Unlike traditional soil-based gardening, aquaponics relies on the waste produced by fish to fertilize the plants.
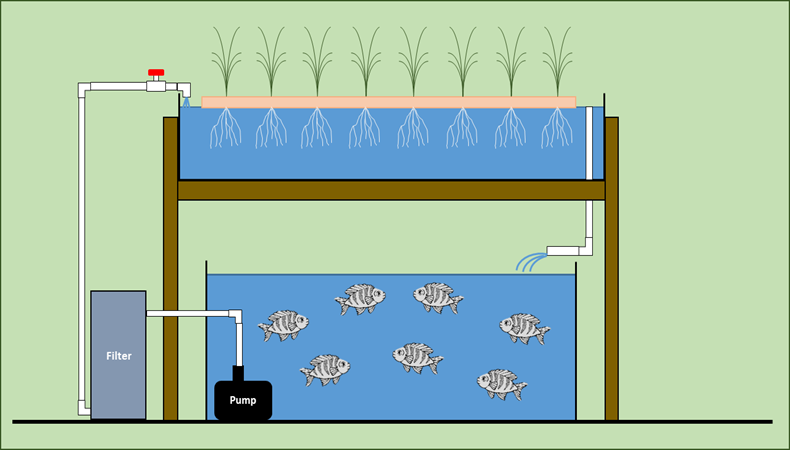
Fish produce waste (ammonia) as they eat and excrete.
Beneficial bacteria convert ammonia into nitrites and nitrates.
Nitrates serve as nutrient-rich fertilizer for the plants.
Plants take up these nutrients, purifying the water.
Symbiotic relationship: Fish feed the plants, and plants clean the fish habitat.
Unlike traditional gardening, fish in aquaponics system continuously produce waste.
This waste is converted into nutrients for plants.
Eliminates the need for artificial fertilizers.
Reduced reliance on chemical fertilizers benefits the environment.
Efficient nutrient cycling minimizes waste.
Fish add beauty and liveliness to the garden.
Creates an enjoyable and captivating gardening experience.
The Importance of Water Quality in Aquaponics and Hydroponics
Maintaining the proper water quality is a crucial aspect of aquaponics and hydroponics systems.
- Medium for Nutrient Delivery
- Water serves as the primary medium through which nutrients are delivered to plants in both aquaponics and hydroponics systems.
- Ensuring water quality is essential for maximizing crop yield and preventing potential issues.
- pH Level Monitoring
- pH measures the acidity or alkalinity of the water and significantly affects nutrient availability for plants.
- In aquaponics systems, maintaining a pH range of 6.8 to 7.2 is recommended, as it suits both the plants and the fish.
- Hydroponics systems require a slightly lower pH, typically around 5.8 to 6.2, to optimize nutrient uptake.
- Regular monitoring and adjustment of pH levels are crucial to ensure plants can access the necessary nutrients for healthy growth.
Choosing the Right Plants for Aquaponics and Hydroponics
Choosing the right plants for aquaponics and hydroponics is a crucial step in ensuring a successful and thriving gardening system. When it comes to selecting plants for these systems, there are a few key factors to consider.

- Select Suitable Varieties:
- Choose plant varieties that are specifically bred or adapted for soilless cultivation. These varieties are better suited to thrive in hydroponic or aquaponic environments.
- Look for plants that have a compact root system, as they will adapt well to the limited space provided by soilless systems.
- Consider Nutritional Requirements:
- Soilless systems rely on nutrient solutions to provide essential elements for plant growth. Consider the nutritional needs of the plants you want to grow.
- Leafy greens (e.g., lettuce, kale, spinach) are excellent choices because they have relatively low nutrient requirements. They can thrive with the nutrients available in the system.
- Fruit-bearing plants (e.g., tomatoes, peppers) may need additional nutrient supplementation to ensure optimal growth and yield.
- Monitor and Experiment:
- Regularly monitor plant health, growth, and nutrient levels. Adjust nutrient solutions as needed.
- Don’t hesitate to experiment with different plant varieties. Observe how they respond to the system and make adjustments accordingly.
Remember, successful soilless gardening involves a balance of plant selection, nutrient management, and observation. With a bit of research and careful consideration, you can choose the right plants that will flourish in your aquaponics or hydroponics system, providing you with a bountiful harvest year-round.
Review for Aquaponics: Affordable Aquaponic System
I recently used “Aquaponics: Affordable Aquaponic System” to set up my own aquaponic and hydroponic garden. The book provides a comprehensive guide with step-by-step instructions that were easy to follow. I appreciated the cost-effective solutions it offered, making it accessible for beginners like me. The practical tips and troubleshooting advice were particularly helpful when I encountered issues.
However, the book does have some limitations. It provides a basic coverage that might not be detailed enough for more advanced users, and I found it to have limited illustrations, which would have been beneficial. Additionally, the book focuses on specific system setups that may not suit everyone’s needs.
Overall, this book is a great starting point for anyone interested in aquaponics and hydroponics, especially if you are looking for affordable and practical solutions.

✅ Step-by-Step Instructions: Easy to follow for beginners.
✅ Cost-Effective Solutions: Focuses on affordable system setups.
✅ Practical Tips: Offers real-world advice and troubleshooting.
❌ Limited Illustrations: Some readers might prefer more visual aids.
❌ Specific to Certain Systems: Focuses on particular setups that may not suit everyone.
The Different Types of Aquaponics and Hydroponics Systems
Aquaponics and hydroponics systems offer great flexibility and customization options for gardeners and agricultural enthusiasts. There are several different types of systems to choose from, each with its own unique features and benefits.
Aquaponics Systems
- Media Bed System
- Plants are grown in a bed filled with a growing medium like gravel or clay pellets.
- The bed is constantly flooded with nutrient-rich water from the fish tank, providing nutrients and oxygen to the plants.
- Plants filter the water as they absorb nutrients, which is then returned to the fish tank.
- Simple to set up and maintain, ideal for beginners.
- Nutrient Film Technique (NFT) System
- Water is continuously pumped through channels, creating a thin film of nutrient-rich water over the plant roots.
- Excess water is collected and returned to the fish tank.
- Efficient use of water and space, suitable for urban environments or limited space.
Hydroponics Systems
- Deep Water Culture (DWC) System
- Plants are suspended in a nutrient-rich water solution with their roots immersed in the water.
- Air stones or diffusers add oxygen to the water, ensuring nutrient and oxygen availability for growth.
- Known for simplicity and low maintenance, popular among hobbyists and small-scale growers.
- Ebb and Flow (Flood and Drain) System
- Plants are placed in a tray or container that is periodically flooded with nutrient-rich water, then drained.
- The flooding and draining cycle oxygenates the roots and prevents water stagnation.
- Versatile system adaptable to different plant sizes and growth stages, suitable for a wide range of crops.
Overall, the different types of aquaponics and hydroponics systems offer gardeners and agricultural enthusiasts a variety of options to suit their needs and preferences. Whether you are a beginner or an experienced gardener, there is sure to be a system that fits your requirements and allows you to grow healthy and thriving plants.
The table below show these different types of Aquaponics and Hydroponics Systems:
System Type | Description | Suitability |
| Aquaponics – Media Bed System | Plants grow in a bed filled with a growing medium (e.g., gravel or clay pellets) continuously flooded with water from a fish tank. Plants absorb nutrients, and the filtered water returns to the fish tank. Simplicity makes it suitable for beginners. | Beginner-friendly, adaptable to various plants. |
| Aquaponics – Nutrient Film Technique (NFT) | Water flows through channels, creating a thin film of nutrient-rich water over plant roots. Excess water is collected and returned to the fish tank. Efficient use of water and space, ideal for urban environments and limited spaces. | Space-efficient, suitable for urban farming. |
| Hydroponics – Deep Water Culture (DWC) | Plants suspended in a nutrient-rich water solution, with roots submerged. Air stones/diffusers add oxygen. Known for simplicity and low maintenance. | Low maintenance, suitable for hobbyists and small-scale growers. |
| Hydroponics – Ebb and Flow System | Plants in a tray periodically flooded with nutrient-rich water, then drained. Helps oxygenate roots and prevent water stagnation. Versatile and adaptable to different plant sizes and growth stages. | Versatile, adaptable to various crops and growth stages. |
Designing and Setting Up Your Aquaponics or Hydroponics System
Designing and setting up your aquaponics or hydroponics system requires careful planning and consideration.

- Assess Available Space:
- Determine where you’ll set up your system (greenhouse, indoor room, or outdoor area).
- Consider sunlight availability and accessibility to water and electricity.
- Choose System Design:
- For aquaponics:
- Media-Based System:
- Plants grow in a bed filled with a growing medium (e.g., gravel, expanded clay pellets).
- Fish waste provides nutrients for plants.
- Nutrient Film Technique (NFT) System:
- Plant roots are exposed to a thin film of nutrient-rich water.
- Media-Based System:
- For hydroponic:
- Consider systems like deep water culture, ebb and flow, or drip irrigation.
- For aquaponics:
- Select Plant Species:
- Research plant nutrient requirements.
- Choose plants suited to your system:
- Leafy greens (e.g., lettuce, kale, spinach) thrive in aquaponics.
- Fruit-bearing plants (e.g., tomatoes, peppers) can do well in hydroponics.
- Acquire Equipment and Materials:
- Gather necessary items:
- Grow beds, pipes, pumps, tanks, and lighting systems.
- Consult suppliers or experienced gardeners for guidance.
- Gather necessary items:
Remember, designing and setting up your aquaponics or hydroponics system is only the first step in your gardening journey. Proper maintenance, water quality management, and plant care will be crucial to achieving optimal growth and yields in the long run. Stay tuned for the upcoming section on maintaining and troubleshooting your system, which will provide invaluable tips to help you succeed in your soilless gardening endeavor.
Maintaining and Troubleshooting Your Aquaponics or Hydroponics System
Maintaining and troubleshooting your aquaponics or hydroponics system is essential for ensuring its long-term success and optimal performance. Regular maintenance will help you identify and address any issues early on, preventing them from escalating into larger problems that could harm your plants or fish.
Regular Maintenance
- Water Quality Monitoring
- Regularly check pH levels, dissolved oxygen, temperature, and nutrient levels.
- Address significant deviations promptly to maintain a stable environment for plants and fish.
- System Component Inspection
- Inspect for leaks, clogs, and signs of wear and tear.
- Ensure pumps, filters, and irrigation systems are functioning properly.
- Clean components regularly to prevent debris, algae, or other contaminants.
Troubleshooting
- Problem Identification
- Systematically analyze potential issues like nutrient imbalances, inadequate water circulation, pest infestations, or plant/fish diseases.
- Implement effective solutions based on the root cause of the problem.
Key Practices for Success
- Proactive Maintenance
- Stay proactive in regular maintenance tasks to prevent issues.
- Address any problems as they arise to maintain optimal growth and productivity.
- Healthy Environment
- Ensure a healthy and thriving environment for both plants and fish by staying vigilant and responsive to system needs.
By consistently monitoring and maintaining your aquaponics or hydroponics system, and promptly troubleshooting any issues, you can achieve successful and sustainable growth for your plants and fish.In the following sections, we will explore additional tips and strategies for maximizing crop yield and addressing specific challenges that may arise in aquaponics and hydroponics systems.
Tips for Maximizing Crop Yield in Aquaponics and Hydroponics
Aquaponics and hydroponics offer unique and innovative methods for maximizing crop yield in gardening. By following a few key strategies, you can optimize your system and enjoy bountiful harvests.

- Water Quality Monitoring:
- Regularly test and maintain proper water parameters:
- pH Levels: Keep pH within the optimal range for plant growth (usually around 5.5 to 6.5 for hydroponics).
- Nutrient Concentrations: Monitor nutrient levels (nitrogen, phosphorus, potassium, etc.) to ensure plants receive adequate nutrition.
- Dissolved Oxygen: Maintain sufficient oxygen levels in the water for healthy root development.
- Regularly test and maintain proper water parameters:
- Plant Selection:
- Choose plant species suited to your system:
- Leafy Greens: Lettuce, herbs, and spinach thrive in aquaponics and hydroponics.
- Fruit-Bearing Plants: Tomatoes, peppers, and strawberries can also be successful.
- Choose plant species suited to your system:
- Proper Lighting:
- Supplemental lighting is crucial, especially for indoor systems or areas with limited sunlight.
- Invest in high-quality grow lights.
- Understand the light requirements of your chosen plants.
- Nutrient Management:
- In aquaponics:
- Fish waste provides nutrients for plants.
- Adjust fish feeding to maintain optimal nutrient concentrations.
- In hydroponics:
- Regularly monitor nutrient solutions.
- Adjust nutrient levels as needed for plant health.
- In aquaponics:
By following these tips and closely monitoring the key factors in your aquaponics or hydroponics system, you can maximize crop yield and enjoy a successful and productive garden.
Exploring the Future of Aquaponics and Hydroponics in Agriculture
In recent years, aquaponics and hydroponics have gained significant attention in the field of agriculture. These innovative farming methods have the potential to revolutionize how we grow crops in the future. With the increasing demand for sustainable and efficient food production, aquaponics and hydroponics offer promising solutions that address key challenges faced by traditional farming systems.
Soil-Free Growth
- Enables cultivation in urban areas with limited arable land.
- Water as the growing medium conserves resources and allows precise nutrient control.
Pest and Disease Resistance
- Eliminates risks associated with soil-borne diseases and pests.
- Attractive option for farmers and gardeners due to reduced reliance on pesticides.
Symbiotic Relationship
- Aquaponics combines aquaculture and hydroponics for a symbiotic fish-plant ecosystem.
- Fish waste serves as nutrient source for plants, while plants purify water for fish.
Sustainable Practices
- Closed-loop system offers efficient nutrient recycling and reduced water consumption.
- Integration of automation and smart monitoring technologies optimizes resource utilization.
Future Prospects
- Ongoing research and technological advancements promise improved efficiency and productivity.
- Innovation includes vertical farming for space optimization and renewable energy integration for sustainability.
The future of aquaponics and hydroponics in agriculture is bright, with continuous advancements driving efficiency, sustainability, and productivity. From urban farming solutions to smart technologies, these methods hold immense potential for revolutionizing modern agriculture.As we continue to embrace the possibilities offered by aquaponics and hydroponics, we are paving the way for a more sustainable and resilient future of agriculture.
Here are some videos to understand more about Aquaponics and Hydroponics
FAQ
What is aquaponics and hydroponics?
Aquaponics and hydroponics are soilless gardening methods that involve cultivating plants in nutrient-rich water instead of traditional soil.
What are the benefits of aquaponics and hydroponics systems?
Aquaponics and hydroponics systems offer several benefits, including higher crop yields, water conservation, reduced pesticide use, and the ability to grow plants in areas with limited access to fertile soil.
What are the key components of aquaponics and hydroponics systems?
The key components of aquaponics systems include a fish tank, grow beds, and a water pump. Hydroponics systems consist of a reservoir, a nutrient solution, and grow trays or containers.
How are nutrients supplied in aquaponics and hydroponics?
In aquaponics, nutrients are supplied through fish waste, which is broken down into usable nutrients by bacteria. In hydroponics, nutrients are directly supplied to the plants through a nutrient solution.
What is the role of fish in aquaponics systems?
Fish play a crucial role in aquaponics systems as they provide the nutrients needed for plant growth through their waste. Additionally, fish waste helps to maintain a balanced ecosystem by providing food for beneficial bacteria.
Why is water quality important in aquaponics and hydroponics?
Water quality is vital in aquaponics and hydroponics as it directly affects plant health and growth. Proper pH levels, oxygenation, and nutrient balance are essential for ensuring optimal plant growth and fish health.
How do I choose the right plants for aquaponics and hydroponics?
When selecting plants for aquaponics and hydroponics, consider factors such as nutrient requirements, pH tolerance, and growth characteristics. Leafy greens, herbs, and certain fruiting plants are commonly grown in these systems.
What are the different types of aquaponics and hydroponics systems?
There are various types of aquaponics systems, including media-based, nutrient film technique (NFT), and deep water culture (DWC). Hydroponics systems encompass techniques such as nutrient film technique (NFT), deep water culture (DWC), and aeroponics.
How do I design and set up an aquaponics or hydroponics system?
Designing and setting up an aquaponics or hydroponics system involves considering factors such as system size, location, water source, and appropriate equipment. It’s crucial to plan and assemble the necessary components correctly.
How do I maintain and troubleshoot an aquaponics or hydroponics system?
Maintaining and troubleshooting an aquaponics or hydroponics system involves monitoring water quality, adjusting nutrient levels, checking for pests or diseases, and ensuring proper system functioning. Regular maintenance and proactive troubleshooting are essential.
What are some tips for maximizing crop yield in aquaponics and hydroponics?
To maximize crop yield in aquaponics and hydroponics, it’s important to maintain optimal nutrient levels, monitor water quality closely, provide appropriate lighting and temperature conditions, and practice proper plant spacing and pruning techniques.
What does the future hold for aquaponics and hydroponics in agriculture?
The future of aquaponics and hydroponics in agriculture looks promising. These innovative methods have the potential to play a significant role in sustainable food production, especially in urban areas and regions with limited arable land. Research and technological advancements continue to improve these systems, making them more efficient and accessible.

Studied Agricultural Engineering-Plant Protection at University of California, Davis.
Head of Content writing team at Southelmontehydroponics.com









