The Pros and Cons of Aquaponics and Hydroponics: No. 1 Comprehensive Comparison
The Pros and Cons of Aquaponics and Hydroponics: The Best Comprehensive Comparison
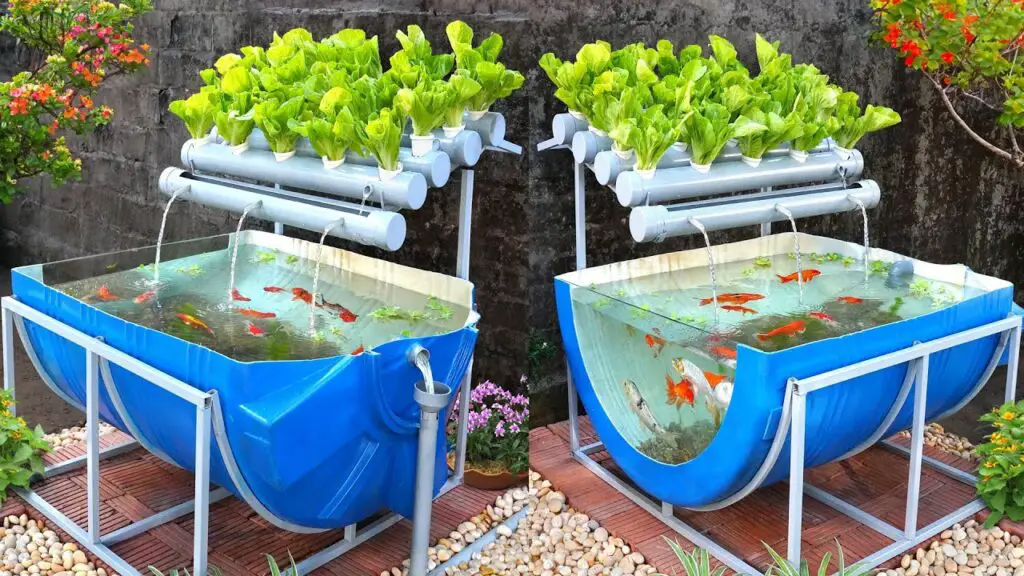

What is Aquaponics?
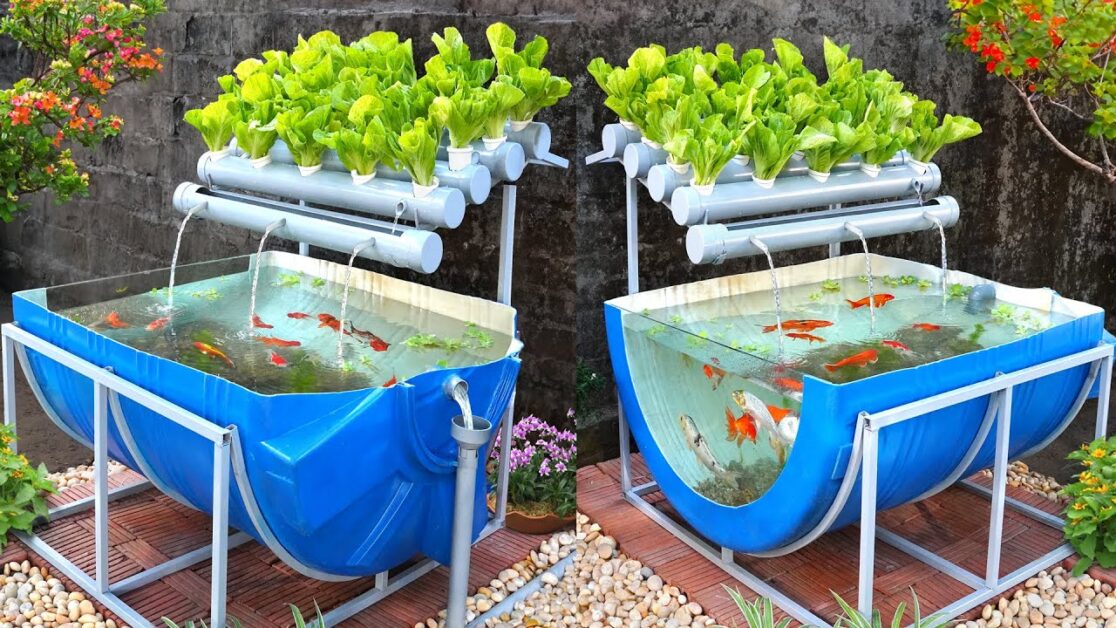
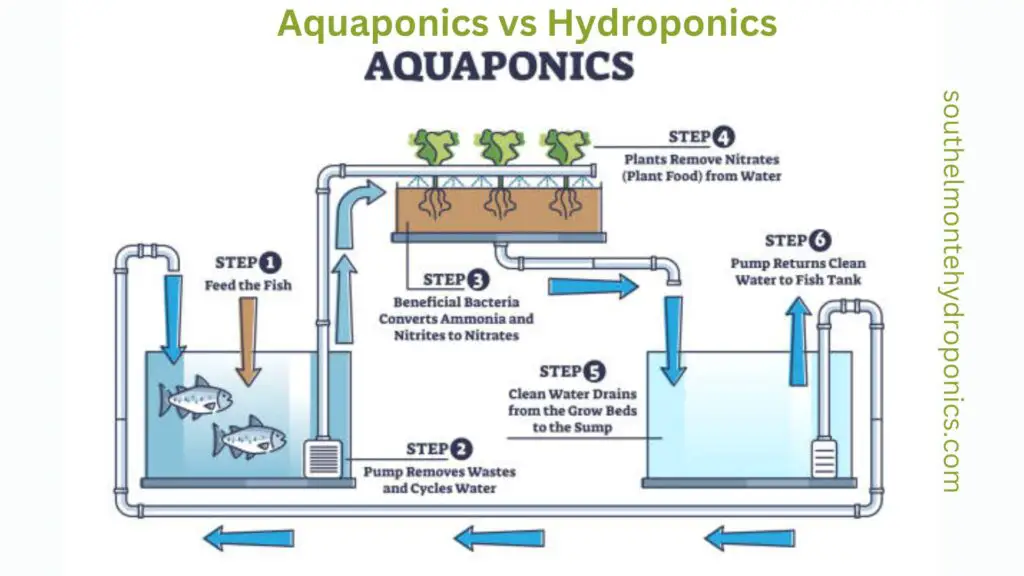
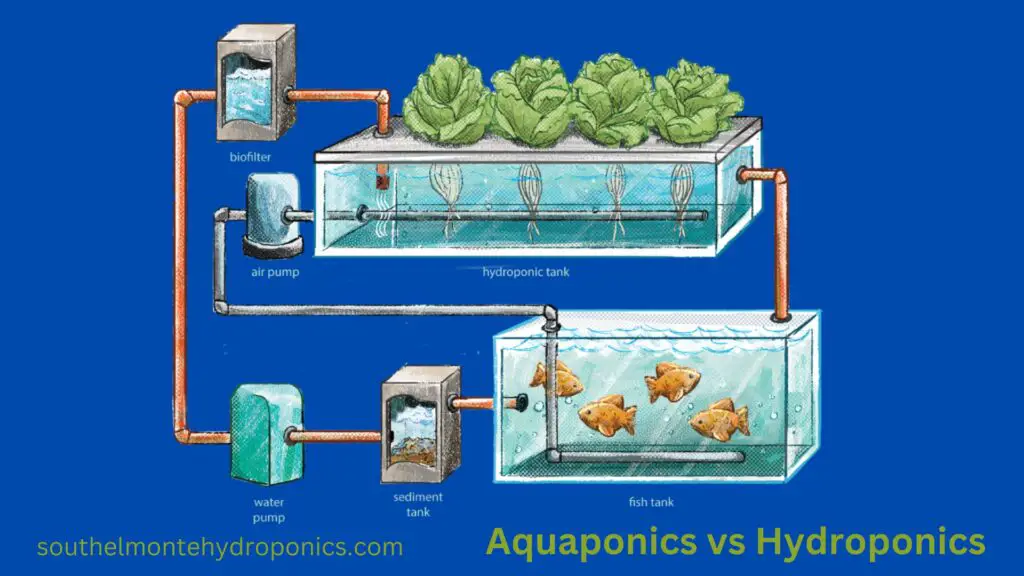
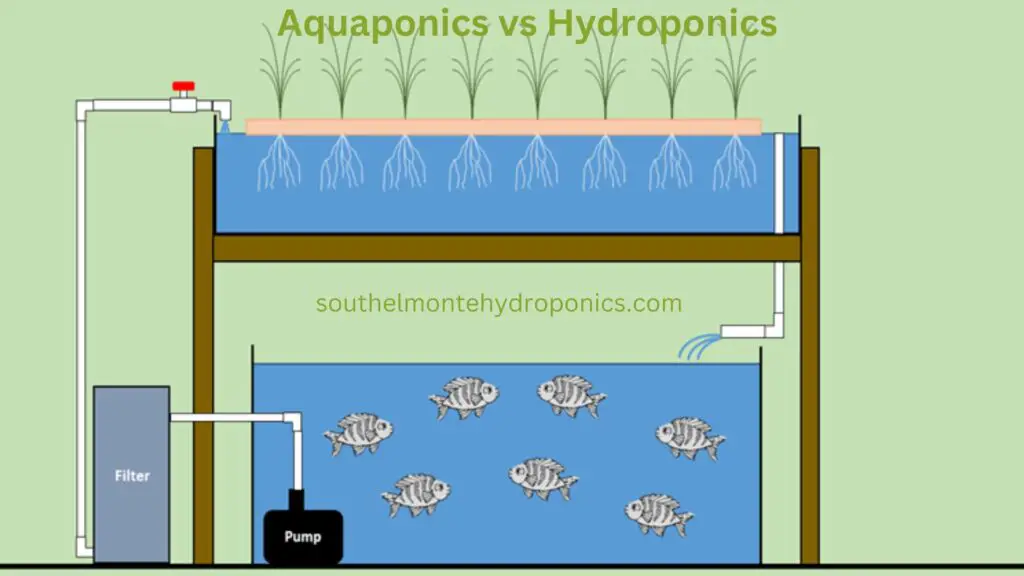
Aquaponics is a sustainable and innovative agricultural practice that combines aquaculture and hydroponics. In aquaponics systems, fish are raised in tanks, and the water from the fish tanks is used to provide essential nutrients to plants grown hydroponically. The plants, in turn, help to filter and clean the water before it is returned to the fish tanks. This symbiotic relationship between fish and plants creates a closed-loop system that maximizes resource utilization and minimizes waste.
One of the key advantages of aquaponics is its ability to produce high-quality food using significantly less water compared to traditional soil-based agriculture. This is particularly important in areas with limited water resources or regions prone to drought. By reusing water and continuously circulating it through the system, aquaponics can reduce water usage by up to 90% compared to conventional farming methods. Additionally, the enhanced nutrient uptake by plants in aquaponics systems leads to faster growth rates and higher yields, making it an efficient and sustainable method of food production.
What is Hydroponics?
Hydroponics is a modern method of growing plants that eliminates the need for soil. Instead, plants are grown in a nutrient-rich water solution, allowing them to receive all the required nutrients directly. This method is gaining popularity among gardening enthusiasts due to its numerous benefits.
One major advantage of hydroponics is its ability to maximize crop yield. With precise control over nutrient levels, pH balance, and lighting conditions, plants can grow faster and healthier compared to traditional soil-based gardening. This is particularly beneficial in areas with limited arable land or unfavorable soil conditions. Hydroponics also requires less water compared to conventional farming methods, making it more sustainable and environmentally friendly.
By harnessing technology and scientific knowledge, hydroponics offers an innovative solution to traditional farming challenges. With careful planning and attention to detail, hydroponic gardens can produce a wide variety of crops year-round, providing fresh and nutritious food options regardless of the season. As more people recognize the potential of hydroponics, it is likely to become an integral part of future agricultural practices.
Environmental Impact of Aquaponics and Hydroponics
Aquaponics and hydroponics are two innovative agricultural practices that have gained widespread attention for their potential environmental benefits. Both systems utilize water as the primary medium for plant growth, resulting in reduced land use and minimized soil erosion. Additionally, these systems offer the opportunity to grow crops in areas where traditional agriculture is challenging due to limited access to arable land or unfavorable soil conditions.
One significant environmental advantage of aquaponics and hydroponics is the efficient use of water. Compared to conventional farming methods, these systems consume significantly less water. In aquaponics, for instance, water is recirculated and reused, resulting in water savings of up to 90% compared to soil-based farming. Hydroponics, on the other hand, uses a closed-loop system where water and nutrients are continuously recycled, minimizing water wastage. Such water efficiency is vital in addressing the growing concerns of water scarcity and ensuring sustainable agricultural practices.
Furthermore, aquaponics and hydroponics reduce the need for chemical inputs, such as pesticides and fertilizers. These systems rely on carefully balanced nutrient solutions and the symbiotic relationship between fish and plants to provide the necessary nutrients for plant growth. As a result, the use of synthetic pesticides is greatly reduced or eliminated, reducing the risk of water and soil pollution. This environmentally friendly approach contributes to the maintenance of ecosystem health and promotes biodiversity.
In conclusion, aquaponics and hydroponics offer numerous environmental benefits. The efficient use of water, reduction in chemical inputs, and minimal land use make these systems an attractive option for sustainable agriculture. However, it is important to consider the overall environmental impact of these practices, including energy consumption and waste management, to ensure a comprehensive evaluation of their sustainability.
Cost Considerations of Aquaponics and Hydroponics

Cost considerations play a vital role when it comes to implementing Aquaponics and Hydroponics systems. While both systems offer numerous benefits, they also require an investment in terms of setup and maintenance.
In Aquaponics, the initial costs include the construction of the fish tanks, grow beds, and the installation of the recirculating system. Additionally, the expenses for purchasing fish, seedlings, and the necessary equipment like air pumps and water heaters need to be accounted for. Ongoing operational costs involve feed for the fish, electricity for pumps and lighting, water testing kits, and periodic maintenance. It is important to note that the overall budget will vary depending on the scale of the system and the specific requirements of the chosen fish and plant species.
Similarly, in Hydroponics, the initial costs revolve around setting up the growing infrastructure such as hydroponic trays, a nutrient reservoir, and a proper lighting system. Additionally, the expenses for purchasing nutrient solutions, growing media, and monitoring equipment should be considered. Ongoing costs typically include electricity for lighting, water pumps, and nutrient mixtures. It is notable that the overall expenditure in Hydroponics can be influenced by factors like the chosen growing technique, crop selection, and the size of the operation.
Nutrient Management in Aquaponics and Hydroponics
Nutrient management plays a crucial role in the success of aquaponics and hydroponics systems. These systems rely on carefully balanced nutrient solutions to provide the necessary elements for plant growth. In aquaponics, the fish waste provides the primary source of nutrients, while in hydroponics, nutrient solutions are manually added to the water. Regardless of the system, it is essential to monitor and adjust nutrient levels regularly to ensure optimal plant health and productivity.
One of the key considerations in nutrient management is achieving the correct nutrient balance for different crops. Different plants have varying nutrient requirements, and providing an appropriate nutrient mix is essential for their well-being and productivity. This can be achieved by testing the nutrient levels in the water or solution and adjusting the composition accordingly. Additionally, incorporating organic fertilizers or supplements can help address any deficiencies and promote healthy growth for specific plant species.
Ensuring proper nutrient management in aquaponics and hydroponics also involves avoiding nutrient imbalances that can lead to undesirable outcomes. Excessive nutrient concentrations can lead to nutrient toxicity, causing damage to the plants and reducing their overall productivity. Conversely, nutrient deficiencies can result in stunted growth, poor fruit development, and increased susceptibility to pests and diseases. Monitoring nutrient levels closely and maintaining a balanced nutrient solution or water quality is vital to avoid these issues and maximize crop yields.
In the next section, we will explore the important aspect of water usage in aquaponics and hydroponics and how these systems differ from traditional soil-based agriculture in their water requirements and conservation strategies. We will also discuss the benefits and challenges associated with water usage in these innovative cultivation methods. Stay tuned!
Water Usage in Aquaponics and Hydroponics
Water usage is a critical aspect to consider in both aquaponics and hydroponics systems. Both methods aim to optimize water usage and minimize waste, making them more sustainable alternatives to traditional soil-based gardening. In aquaponics, water usage is highly efficient due to the closed-loop system where the water is continuously recycled. The water, enriched with nutrients from fish waste, is circulated through the grow beds, providing the necessary nourishment to the plants, before returning to the fish tank. This symbiotic relationship allows for minimal water loss as the only water consumed is through plant transpiration and evaporation.
Hydroponics, on the other hand, has a slightly higher water usage compared to aquaponics as there is no fish waste to provide nutrients. However, hydroponic systems are designed to recycle and recirculate water, reducing overall consumption. The plants receive their nutrients directly from the water solution, and any excess nutrient solution is collected and reused, minimizing waste. Additionally, the controlled environment of hydroponics allows for precise irrigation, ensuring that water is delivered directly to the plants’ root systems, eliminating unnecessary water loss through evaporation or runoff. Overall, both aquaponics and hydroponics demonstrate a commitment to sustainable water usage, making them viable options for water-conscious gardeners.
Crop Selection and Growth in Aquaponics and Hydroponics
Crop selection is a crucial aspect of aquaponics and hydroponics, as the success of the system largely depends on the suitability of the chosen crops. When selecting crops for aquaponics and hydroponics, it is important to consider their growth requirements, such as light intensity, temperature, and nutrient needs. Some crops are better suited for these growing methods than others.
Leafy greens, such as lettuce, spinach, and kale, are popular choices for aquaponics and hydroponics due to their ability to thrive in nutrient-rich environments. Herbs like basil, cilantro, and mint also do well in these systems. Additionally, plants like tomatoes, cucumbers, and peppers can be successfully grown using hydroponics, as they require more space and support structures. It is important to consider the available space, growth rate, and yield potential of each crop when making selections.
In aquaponics and hydroponics, the controlled environment allows for year-round cultivation, which can result in higher crop yields compared to traditional soil-based methods. The ability to adjust environmental parameters such as pH, temperature, and nutrient levels provides an opportunity to optimize crop growth. However, it is essential to conduct thorough research and experiment with different crop varieties to determine the best fit for your specific aquaponics or hydroponics system. By carefully considering crop selection, growers can maximize productivity and enjoy a variety of fresh, healthy produce throughout the year.
Pest and Disease Management in Aquaponics and Hydroponics
Pest and disease management in aquaponics and hydroponics is a crucial aspect of maintaining healthy and thriving crops. With these soilless growing systems, it becomes even more important to be vigilant in preventing and addressing pest infestations and diseases.
One advantage of aquaponics and hydroponics is that they significantly reduce the risk of pests and diseases compared to traditional soil-based agriculture. However, it does not eliminate the possibility entirely. Common pests in these systems include aphids, whiteflies, thrips, and spider mites. These pests can quickly multiply and damage your plants if not managed properly. Similarly, diseases such as powdery mildew and root rot can also pose significant threats to crop health.
To manage pests and diseases effectively, it is essential to prioritize prevention and early detection. Regularly inspect your plants for any signs of pest damage or disease symptoms. Implementing integrated pest management (IPM) strategies is recommended for organic and sustainable growing. This approach combines cultural, biological, and chemical control methods to minimize the use of harmful pesticides. For example, introducing beneficial insects like ladybugs or lacewings can help control aphids naturally. Additionally, maintaining proper hygiene, such as keeping the growing environment clean and free of debris, can prevent the buildup of pests and pathogens. By adopting these proactive measures, aquaponics and hydroponics practitioners can ensure the health and vitality of their crops.
Scalability and Space Requirements in Aquaponics and Hydroponics
Scalability and space requirements are important considerations when planning an aquaponics or hydroponics system. Both systems offer the advantage of being scalable, allowing for expansion as desired. However, the amount of space needed can vary depending on the size and complexity of the system.
In aquaponics, the space required is determined by the number and size of the fish tanks, the size of the grow beds, and the overall layout of the system. It is important to ensure that there is enough space for the fish to grow and thrive, as well as space for the plants to receive adequate light and nutrients. Proper spacing between the components of the system is crucial to maintain a balanced and efficient ecosystem.
Similarly, in hydroponics, space requirements are influenced by the number and size of the nutrient reservoirs, the size of the grow beds or containers, and the type of crops being grown. Different types of hydroponic systems, such as nutrient film technique (NFT) or deep water culture (DWC), may require different configurations and space allocations.
When planning for scalability, it is important to consider not only the physical space available but also the logistical aspects, such as access to water and electricity, as well as any potential zoning restrictions or building permits that may be required. Additionally, it is worth considering the potential for future expansion and whether the chosen location can accommodate it.
By carefully considering scalability and space requirements, aquaponics and hydroponics enthusiasts can design their systems to maximize efficiency and productivity, while also ensuring a sustainable and manageable operation.
Energy Efficiency in Aquaponics and Hydroponics
Aquaponics and hydroponics are two innovative and sustainable methods of growing plants that offer various advantages over traditional soil-based farming. When it comes to energy efficiency, both aquaponics and hydroponics have a favorable edge compared to conventional agriculture practices. These systems utilize energy in a more targeted and efficient manner, resulting in reduced energy consumption and costs.
In aquaponics, the energy efficiency is primarily attributed to the symbiotic relationship between fish and plants. As the fish produce waste, it is converted into nutrients by beneficial bacteria, which are then used by the plants for their growth. This closed-loop system eliminates the need for synthetic fertilizers and reduces the energy required for nutrient delivery, resulting in significant energy savings. Moreover, in hydroponics, where plants are grown solely in water without any involvement of fish, the nutrient solutions can be precisely controlled and recycled, minimizing wastage and energy expenditure.
Both aquaponics and hydroponics also offer energy savings through the reduction of water usage. Compared to traditional soil-based agriculture, these soilless systems require significantly less water as it is continuously recycled within the closed-loop systems. Additionally, the controlled environment in aquaponics and hydroponics allows for targeted water delivery to plants, minimizing water loss due to evaporation and runoff. This water efficiency not only conserves a valuable resource but also contributes to overall energy savings.
Overall, aquaponics and hydroponics harness energy more efficiently than conventional farming practices. These systems optimize nutrient delivery, reduce water usage, and create a closed-loop ecosystem that minimizes waste. Embracing energy-efficient techniques like aquaponics and hydroponics not only benefits the environment but also offers a promising future for sustainable and productive agriculture.
Maintenance and Labor Requirements in Aquaponics and Hydroponics
Aquaponics and hydroponics systems require regular maintenance to ensure optimal plant growth and fish health. This maintenance involves several tasks, including monitoring water quality parameters, checking for pests and diseases, and managing nutrient levels.
Water quality is crucial in both aquaponics and hydroponics systems. Regular testing of pH, dissolved oxygen, ammonia, nitrate, and other parameters is essential to maintain a suitable environment for plants and fish. Adjustments may be needed to balance pH levels and manage nutrient levels for optimal growth. This requires regular monitoring and a basic understanding of water chemistry.
Additionally, pest and disease management is vital for maintaining healthy plants. Integrated pest management techniques, such as introducing beneficial insects or using organic pesticides when necessary, can help control pests and diseases without harming the fish or the environment. Regular inspection and identification of potential threats are essential for early intervention and prevention of widespread infestations.
Ensuring the balance of nutrients in the system is also an important maintenance task. Plants in aquaponics systems rely on the nutrients provided by the fish waste, while hydroponic systems require regular nutrient supplementation. Monitoring nutrient levels and adjusting them based on plant needs is critical to ensure healthy and productive crops.
Overall, maintaining aquaponics and hydroponics systems requires regular monitoring, testing, and intervention to maintain optimal plant growth and fish health. With proper maintenance, these systems can provide a sustainable and efficient method for growing plants while minimizing the use of water and resources.
Certainly! Below is a comparison table outlining key differences between aquaponics and hydroponics:
| Aspect | Aquaponics | Hydroponics |
|---|---|---|
| Nutrient Source | Combines aquaculture (fish farming) and hydroponics. Fish waste provides nutrients for plants. | Utilizes a nutrient solution (mineral nutrient mix) for plant growth. Nutrients are manually added and monitored. |
| Nutrient Recycling | Nutrients are recycled in a closed-loop system. Fish waste is converted by bacteria into forms usable by plants. | Nutrient solution is typically recirculated, reducing waste. Some systems may require periodic replenishment of nutrients. |
| Fish Farming | Involves raising fish alongside plant cultivation. Fish provide ammonia-rich waste, promoting nutrient cycling. | Excludes fish farming. Plants receive nutrients directly from the solution, and there is no interaction with aquatic life. |
| pH Control | Fish waste can influence pH. Regular monitoring and adjustments are necessary to maintain optimal conditions for both fish and plants. | pH levels are controlled independently based on the specific needs of the plants being cultivated. |
| Complexity | Generally more complex due to the integration of both aquaculture and hydroponics components. Requires understanding of fish care and system balance. | Simpler in design, as it focuses solely on plant cultivation and nutrient management. |
| Fish Health | Aquaponics systems require attention to both plant and fish health. Fish health impacts nutrient availability for plants. | No direct impact on fish health, as hydroponics does not involve raising aquatic life. |
| System Stability | May experience instability if there are issues with fish health, leading to fluctuations in nutrient levels. Requires balance between fish and plant needs. | Generally more stable, as nutrient levels are directly controlled. Any imbalances are typically easier to address. |
| Start-up Costs | Initial costs can be higher due to the need for fish tanks, pumps, and aeration systems. Ongoing costs include fish feed. | Generally lower start-up costs, as it doesn’t involve the complexities of fish farming. Ongoing costs may include nutrient solutions. |
| Crop Variety | Suitable for a wide range of crops, including leafy greens, herbs, and some fruiting plants. Fish selection may influence plant choices. | Adaptable to various crops, offering flexibility in plant selection based on the grower’s preferences and market demand. |
| Environmental Impact | Generally considered more sustainable, as it mimics natural ecosystems and utilizes fish waste. Requires less external input for nutrient supplementation. | Requires external nutrient inputs, and nutrient runoff may impact the environment if not managed properly. |
This table provides a comparative overview of aquaponics and hydroponics, highlighting their differences in terms of nutrient sources, complexity, environmental impact, and other key factors.
Choosing the Right System: Factors to Consider in Aquaponics and Hydroponics
Aquaponics and hydroponics offer unique and innovative ways to grow crops without soil, allowing gardening enthusiasts to cultivate fresh produce in a controlled environment. When deciding between these systems, several factors should be taken into consideration.
One crucial factor to consider is the environmental impact of the chosen system. Aquaponics, which combines aquaculture and hydroponics, has the advantage of using fish waste as a nutrient source for plants, creating a symbiotic relationship that reduces water and fertilizer use. On the other hand, hydroponics requires nutrient solutions that can have environmental consequences if mismanaged. Understanding the ecological footprint of both systems is essential in making an informed decision.
Additionally, cost considerations should not be overlooked. Hydroponic systems may require more upfront investment due to the need for specialized equipment and nutrient solutions, whereas aquaponic systems may have additional expenses associated with fish rearing. It is important to evaluate the long-term costs of both systems, including maintenance, energy usage, and the cost of inputs, to determine which is the most financially viable choice.
In conclusion
What is the main difference between aquaponics and hydroponics?
Aquaponics combines aquaculture (raising fish) and hydroponics (growing plants in water), while hydroponics solely focuses on growing plants in water without the use of fish.
How do aquaponics and hydroponics impact the environment?
Both aquaponics and hydroponics have lower environmental impacts compared to traditional agriculture. They use less water, eliminate the need for synthetic fertilizers, and reduce pesticide use.
Are aquaponics and hydroponics expensive to set up?
The initial setup costs for aquaponics and hydroponics can be higher than traditional agriculture methods. However, over time, the savings from reduced water usage and lower input costs can offset the initial investment.
How are nutrients managed in aquaponics and hydroponics systems?
In aquaponics, fish waste provides nutrients to the plants, and the plants naturally filter the water for the fish. In hydroponics, a nutrient solution is manually added to the water to provide the necessary nutrients for plant growth.
Which system uses more water, aquaponics, or hydroponics?
Hydroponics typically uses less water than aquaponics since there is no need to account for the water requirements of fish. However, both systems generally use less water than traditional soil-based agriculture.
Can all crops be grown in aquaponics and hydroponics?
Most crops can be grown successfully in aquaponics and hydroponics systems. However, certain crops with deep-rooting systems or higher nutrient demands may require additional considerations or modifications to the system.
How are pests and diseases managed in aquaponics and hydroponics?
Integrated Pest Management techniques such as biological controls, beneficial insects, and organic treatments are commonly used in aquaponics and hydroponics to manage pests and diseases without the use of synthetic chemicals.
Is scalability and space a concern in aquaponics and hydroponics?
Aquaponics and hydroponics systems can be scaled up or down depending on the available space and desired production level. Vertical farming techniques can also be implemented to maximize space utilization.
Are aquaponics and hydroponics energy-efficient?
Both aquaponics and hydroponics can be energy-efficient, particularly when utilizing energy-saving technologies such as LED lighting, efficient pumps, and renewable energy sources.
How much maintenance and labor is required for aquaponics and hydroponics systems?
Aquaponics and hydroponics systems require regular monitoring and maintenance, including checking water quality, managing nutrient levels, and ensuring proper functioning of equipment. The labor requirements vary depending on the system size and complexity.






