Diatomaceous Earth: How to Use This Natural and Safe Pest Control
Table of Contents
Diatomaceous Earth as a Non-Toxic Pest Control Alternative: Comparing it to Chemical Solutions
Diatomaceous Earth (DE) has gained popularity as a non-toxic pest control alternative, and many gardeners are considering using it as a safer option compared to chemical solutions. When comparing DE to chemical pesticides, it is important to understand the differences in their modes of action and effectiveness.
Chemical pesticides often contain synthetic toxins that are designed to kill pests quickly. While they can be effective in eliminating pests, they also pose risks to human health and the environment. Exposure to these chemicals can have detrimental effects on beneficial organisms, such as bees and other pollinators, as well as contaminate water sources and degrade soil quality.
On the other hand, DE works through a physical mechanism to control pests. It is composed of the fossilized remains of diatoms, an ancient type of algae. The microscopic sharp edges of DE particles penetrate the exoskeleton of insects and other arthropods, drying them out and causing their eventual demise. This unique mode of action makes DE a safe option as it does not involve the use of harmful chemicals.
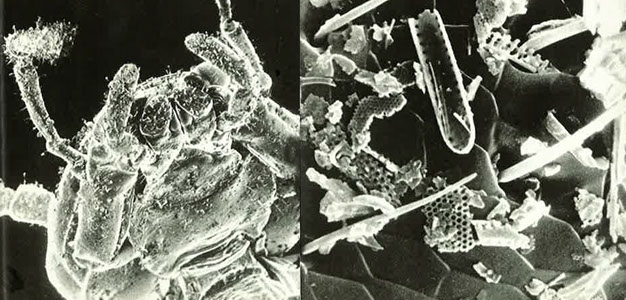
Additionally, DE has the advantage of being long-lasting. While chemical pesticides may require repeated applications to maintain their effectiveness, DE can remain in the environment for an extended period. This makes it a cost-effective solution for long-term pest control.
However, it is important to note that DE may not be as effective against certain pests compared to chemical solutions. Some insects have waxy or slippery coatings on their exoskeletons, which can reduce the efficacy of DE. In such cases, combining DE with other pest control methods or using targeted chemical pesticides may be necessary.
In conclusion, Diatomaceous Earth offers a non-toxic alternative to chemical pesticides for pest control. Its unique mode of action and long-lasting effectiveness make it an attractive option for gardeners concerned about the potential risks associated with chemical solutions. However, its efficacy may vary depending on the pest, and additional control measures may be necessary in some cases.
• Diatomaceous Earth (DE) is a non-toxic pest control alternative gaining popularity
• DE works through a physical mechanism, using fossilized remains of diatoms
• DE particles penetrate the exoskeleton of pests and dry them out, causing their demise
• Chemical pesticides contain synthetic toxins that pose risks to human health and the environment
• Exposure to chemical pesticides can harm beneficial organisms and contaminate water sources
• DE does not involve the use of harmful chemicals, making it a safe option for pest control
• DE has long-lasting effectiveness compared to chemical pesticides
• Repeated applications may be needed for chemical pesticides to maintain their effectiveness
• Combining DE with other pest control methods or targeted chemical pesticides may be necessary against certain pests
Monitoring and Maint
Monitoring and maintaining diatomaceous earth (DE) as a non-toxic pest control alternative requires attention to detail and regular upkeep. One crucial aspect of monitoring DE is ensuring that it remains dry. Moisture can affect its effectiveness, as it causes the particles to clump together, reducing their ability to puncture the exoskeletons of insects. Therefore, it is essential to inspect the treated areas regularly and take immediate action if any signs of moisture or dampness are detected. Additionally, monitoring for any insect activity or infestation is crucial to determine the effectiveness of DE as a pest control measure. By observing and documenting any changes in the pest population over time, gardeners can make informed decisions about the need for reapplication or adjustments to their pest management strategy.
Maintenance of diatomaceous earth as a pest control alternative involves periodic reapplication. Since DE is not a long-lasting solution, it is necessary to reapply it as needed, especially after heavy rainfall or excessive irrigation that may wash away the product. Similarly, if the treated area is disturbed by activities such as tilling or replanting, reapplication is recommended to ensure continuous protection. Additionally, reviewing the storage conditions of DE is crucial to maintain its efficacy. Storing the product in a cool, dry place and minimizing exposure to moisture and humidity will help preserve its integrity and ensure its effectiveness when used for pest control.
What is diatomaceous earth and how does it work as a pest control alternative?
Diatomaceous earth is a natural substance made from fossilized diatoms, a type of algae. It works by dehydrating insects and pests, ultimately leading to their demise.
Is diatomaceous earth safe to use around children and pets?
Yes, diatomaceous earth is considered non-toxic to humans and pets. However, it is important to use food-grade diatomaceous earth and follow proper application instructions to avoid any potential irritation.
How does diatomaceous earth compare to chemical pest control solutions?
Diatomaceous earth offers a non-toxic alternative to chemical pest control solutions. It is generally safer for the environment and poses minimal risks to human health compared to chemical pesticides.
Can diatomaceous earth be used for all types of pests?
Diatomaceous earth is effective against a wide range of pests, including ants, bed bugs, fleas, cockroaches, and more. However, its effectiveness may vary depending on the specific pest and the severity of the infestation.
How long does diatomaceous earth take to eliminate pests?
The time it takes to eliminate pests with diatomaceous earth can vary. In some cases, noticeable results may be seen within a few days, while in others, it may take a couple of weeks. The effectiveness also depends on proper application and treating the source of the infestation.
Can diatomaceous earth be used both indoors and outdoors?
Yes, diatomaceous earth can be used both indoors and outdoors. It can be applied to cracks, crevices, and other areas where pests may be present. However, it is important to protect it from moisture as it can lose its effectiveness when wet.
How often should diatomaceous earth be applied for pest control?
The frequency of diatomaceous earth application depends on the severity of the infestation and the pest being targeted. In some cases, reapplication may be necessary every few weeks, while in others, a single application may be sufficient.
Can diatomaceous earth be used as a preventive measure against pests?
Yes, diatomaceous earth can be used as a preventive measure against pests. By applying it in areas prone to infestations, such as entry points or storage areas, it can create a barrier that deters pests from entering.
Are there any precautions to take when using diatomaceous earth?
It is advisable to wear a mask and gloves when applying diatomaceous earth to avoid inhaling the fine particles or irritating the skin. Additionally, it is important to read and follow the instructions provided by the manufacturer for safe and effective use.
Does diatomaceous earth have an expiration date?
Diatomaceous earth does not have an expiration date as long as it is kept in a dry and sealed container. However, over time, its effectiveness may diminish, so it is best to use fresh diatomaceous earth for optimal results.

Pallavi Gupta is a burgeoning writer at SouthElMonteHydroponics, blending her passion for data analysis with a keen interest in biotechnology. Currently pursuing a Bachelor’s in Biotechnology at Amity University, Pallavi delves into the intricacies of life sciences while gaining hands-on experience in the exciting world of data analysis. Her unique background provides a fresh perspective on hydroponic farming, as she explores the intersection of biotechnology and sustainable agriculture. Through her writing, Pallavi aims to bridge the gap between data-driven insights and innovative farming practices, inspiring others to harness technology for a greener future.






