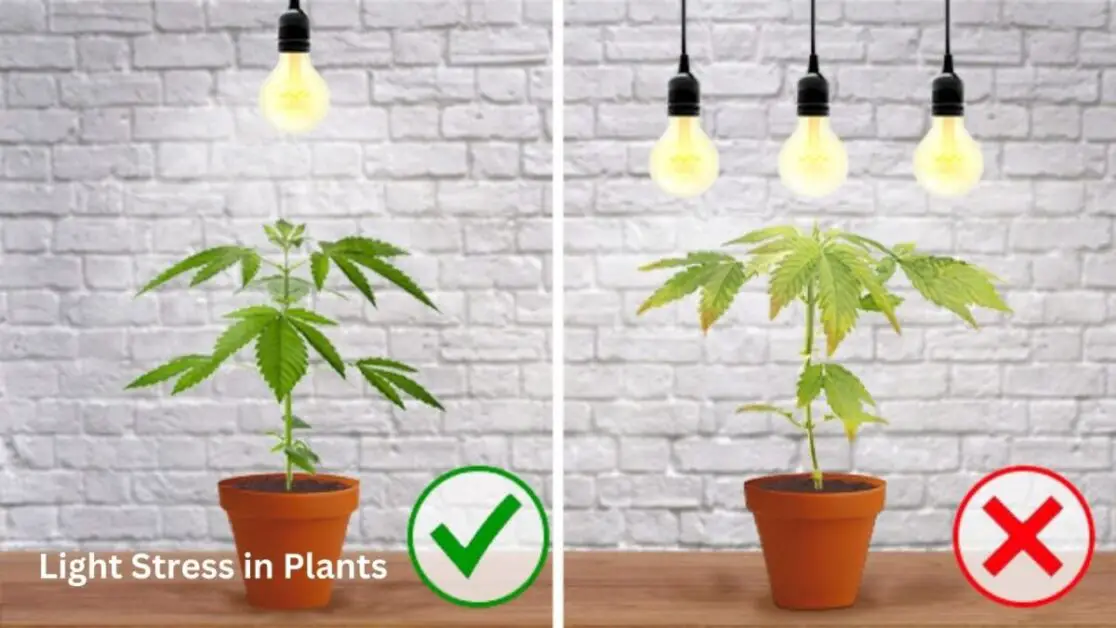
Light Stress in Plants: What It Is, 1 way to Recognize It, and How to Avoid It
Table of Contents
The Impact of Light on Light Stress in Plants Health

Light is an essential factor in the overall health and growth of plants. It plays a crucial role in their metabolic processes, photosynthesis, and overall development. The impact of light on plant health cannot be overstated, as it directly influences their ability to produce energy from sunlight and convert it into sugars for growth and development. Without sufficient light, plants may experience stunted growth, decreased chlorophyll production, and overall weakened health.
Different plants have varying requirements for light intensity, duration, and quality. Some plants thrive in direct sunlight, while others prefer shaded areas. Understanding the specific needs of different plant species is vital for providing optimal lighting conditions and ensuring their overall well-being. Furthermore, the duration of light exposure, including the length of daylight and darkness periods, also contributes significantly to plant health. By providing the right balance of light duration, plants can undergo crucial physiological processes such as respiration, flowering, and fruiting appropriately. Overall, the impact of light on plant health is a critical component that gardeners and plant enthusiasts must consider to promote optimal growth and maximize the potential of their plants.
Understanding the Effects of Light Stress on Plants
Light stress can have profound effects on the health and growth of plants. When plants are exposed to excessive light intensity or prolonged light duration, they can experience physiological changes that impact their overall well-being. One of the primary effects of light stress is the production of reactive oxygen species (ROS), which can cause oxidative damage to plant cells. This oxidative stress can lead to the degradation of important cellular components, such as proteins and lipids, and disrupt normal metabolic processes. Additionally, excessive light exposure can also result in increased production of heat, which can further contribute to the stress on plants and potentially lead to the denaturation of proteins and other vital molecules.
Furthermore, light stress can also affect the efficiency of photosynthesis in plants. While light is necessary for photosynthetic reactions, high light intensity can disrupt the balance between light absorption and the capacity for energy utilization in plants. This imbalance can result in the overproduction of energy, leading to the formation of harmful byproducts and the impairment of photosynthetic machinery. As a consequence, the overall photosynthetic efficiency of plants may decrease, affecting their growth and productivity. Understanding the effects of light stress on plants is crucial for gardeners and growers seeking to optimize the health and well-being of their plants, as it enables them to implement appropriate measures to mitigate the negative impacts and promote optimal growth conditions.
Factors Contributing to Light Stress in Plants
Light stress in plants can be caused by a variety of factors. One of the key contributors to light stress is the intensity of light that plants receive. High levels of light can lead to excessive energy absorption and production of reactive oxygen species, causing oxidative damage to plant tissues. Conversely, low light levels can lead to insufficient energy production through photosynthesis, resulting in reduced growth and development.
Another factor that contributes to light stress is the duration of light exposure. Plants require a certain amount of dark period, known as the photoperiod, for proper growth and development. Insufficient darkness can disrupt the circadian rhythm of plants, leading to physiological imbalances and stress. On the other hand, excessively long periods of darkness can also negatively impact plant health, as they rely on light for photosynthesis and energy production.
In addition to light intensity and duration, the quality of light can also play a role in causing stress in plants. Different wavelengths of light have varying effects on plant physiology. For example, an imbalance in the red to far-red light ratio can trigger changes in plant morphology and flowering time. Similarly, exposure to excessive ultraviolet (UV) light can damage plant tissues and inhibit growth.
Understanding the factors that contribute to light stress in plants is crucial for ensuring their optimal health and productivity. By carefully managing light intensity, duration, and quality, gardening enthusiasts can create an environment that promotes healthy plant growth while minimizing stress-induced damage.
Identifying Signs and Symptoms of Light Stress in Plants
Plants are highly sensitive organisms, and they can display various signs and symptoms when experiencing light stress. It is crucial for gardeners and botanists to be able to identify these indicators to take appropriate measures and alleviate any potential damage to their plants. One common sign of light stress is leaf discoloration, where the leaves may turn pale or yellowish. This occurs when the plants are receiving inadequate light or are exposed to excessive light intensity for prolonged periods. Additionally, stunted growth can be observed in plants under light stress. The limited availability of light can hamper photosynthesis, affecting the plant’s ability to produce energy and grow optimally.
Another symptom of light stress is leaf curling or wilting. When plants are exposed to high light intensity or excessive heat, they can lose water more rapidly through a process called transpiration. As a result, the leaves may curl or appear wilted in an attempt to reduce water loss and protect themselves from further stress. Furthermore, an increased susceptibility to pests and diseases can indicate light stress in plants. When plants are weakened by inadequate or excessive light, they become more vulnerable to attacks from insects and pathogens.
Being able to identify these signs and symptoms of light stress in plants is essential for gardeners and farmers alike. By promptly recognizing these indicators, appropriate measures can be taken to address the underlying cause of the stress and facilitate a healthier plant growth. In the next section of this article, we will explore the role of light intensity in plant stress and how it can impact overall plant health.
The Role of Light Intensity in Light Stress in Plants
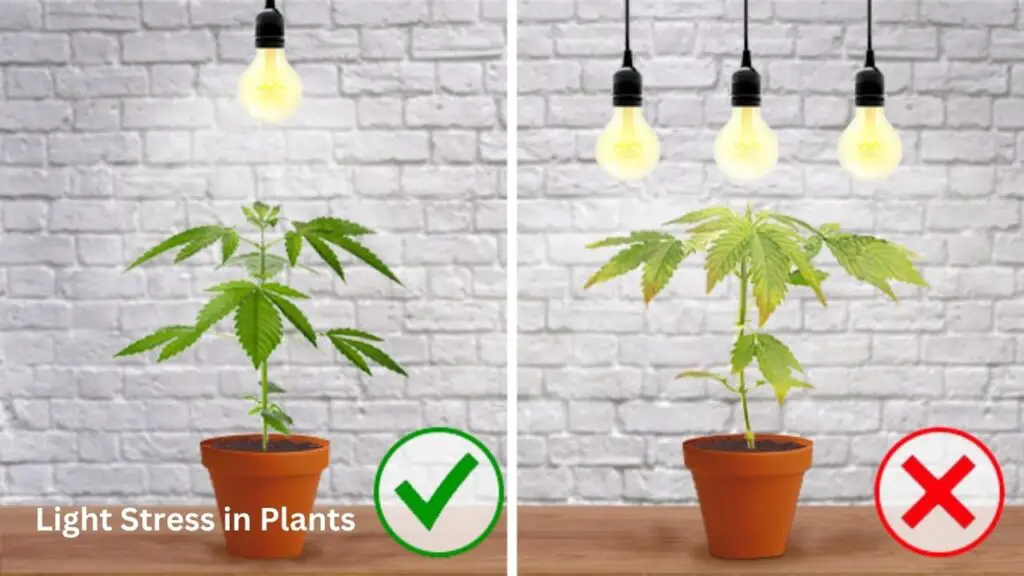
Light intensity plays a crucial role in the overall health and development of plants. The amount of light that plants receive directly affects their physiological processes, growth patterns, and productivity. Insufficient light intensity can lead to a phenomenon known as light stress, which negatively impacts plant growth and can even be fatal in extreme cases.
When plants do not receive adequate light intensity, they are unable to perform photosynthesis efficiently. Photosynthesis is the process through which plants convert light energy into chemical energy, allowing them to produce their own food. Insufficient light intensity restricts the amount of energy that can be harnessed, leading to a decrease in the production of sugars and other essential compounds necessary for growth. As a result, plant growth becomes stunted, leaves may turn pale or yellow, and the overall vigor and health of the plant declines. It is crucial for gardeners and growers to understand the light intensity requirements of different plant species and provide the appropriate lighting conditions to prevent light stress and promote healthy growth.
The Importance of Light Stress in Plants Duration for Health
The duration of light exposure plays a crucial role in maintaining the overall health and growth of plants. Plants undergo essential physiological processes, such as photosynthesis and photomorphogenesis, which heavily rely on the availability and duration of light. Understanding the importance of light duration can help gardeners and plant enthusiasts optimize their cultivation practices to ensure thriving and robust plants.
One key aspect of light duration is the photoperiod, which refers to the period of light and darkness that plants experience within a 24-hour cycle. Different plant species exhibit specific photoperiodic requirements, meaning they have adapted to thrive under certain lighting conditions. Certain plants, known as long-day plants, require a longer period of light exposure to activate critical developmental processes. On the other hand, short-day plants have evolved to flower and reproduce with shorter days and longer nights. By providing plants with the appropriate light duration based on their photoperiodic preferences, gardeners can promote healthy growth, flowering, and overall vitality.
How Light Quality Affects Light Stress in Plants Levels
Light quality plays a crucial role in determining plant stress levels. Different wavelengths of light have varying effects on plants, influencing their growth, development, and overall health. The quality of light refers to the specific wavelengths that are present, such as blue, red, green, and far-red light. Each of these wavelengths has specific effects on different plant processes.
For example, blue light is essential for regulating plant growth and morphology. It stimulates stomatal opening, chlorophyll synthesis, and phototropism. However, excessive exposure to blue light can lead to photoinhibition and oxidative stress, leading to plant stress. On the other hand, red light promotes photosynthesis and fruiting in plants. It plays a vital role in the regulation of flowering, germination, and seedling development. Green light, although less absorbed by plants, can still affect plant performance, influencing leaf expansion and chloroplast development.
Understanding the effects of light quality on plant stress levels can help gardeners and plant enthusiasts create optimal growing conditions for their plants. By providing plants with the right balance and intensity of different wavelengths, it is possible to minimize stress levels and enhance overall plant health. This can be achieved through various techniques, including using different light sources or adjusting the composition of artificial lighting systems. By harnessing the power of light quality, gardeners can help their plants thrive and flourish.
Strategies for Preventing Light Stress in Plants
Light stress can have detrimental effects on the health and growth of plants. To prevent light stress, it is important to provide the right lighting conditions for plants. One strategy is to choose the appropriate light intensity. Different plants have different light requirements, so it is crucial to understand the specific needs of the plants you are growing. Too much light can lead to photoinhibition and damage to the plant’s photosynthetic machinery, while too little light can result in poor growth and development. By providing the optimal light intensity for your plants, you can help them thrive and minimize the risk of light stress.
Another strategy for preventing light stress is to consider the duration of light exposure. Plants require a certain amount of light each day for their metabolic processes, but excessive exposure to light can be harmful. It is important to find the right balance by understanding the ideal duration of light for your plants. Some plants, like flowering plants, may require longer periods of light exposure, while others, such as certain leafy greens, may thrive with shorter durations. By closely monitoring the duration of light your plants receive, you can ensure they receive the necessary light without subjecting them to undue stress.
Implementing these strategies for preventing light stress in plants can greatly contribute to their overall health and well-being. By considering the light intensity and duration, you can create an optimal environment for your plants to thrive. Keep in mind that different plants have different light requirements, so it is crucial to do proper research and understand their individual needs. By providing the right lighting conditions, you can help your plants flourish and minimize the risk of light stress.
Choosing the Right Lighting Conditions for Indoor Plants
Indoor plants require the right lighting conditions to thrive and reach their full potential. When it comes to choosing the right lighting conditions for your indoor plants, there are a few factors to consider. First and foremost is the intensity of light. Different plants have different light requirements, so it’s important to understand the specific needs of the plants you are growing. Some plants, such as succulents, require intense, direct light, while others, like ferns, prefer lower light levels.
Another important factor to consider is the duration of light exposure. Just like humans, plants need a balance of light and darkness to grow and rest properly. Some plants, such as tropical species, thrive with longer periods of light exposure, while others, like flowering plants, require a certain amount of darkness to trigger blooming. It’s crucial to research the specific light duration requirements for each type of plant you have in your indoor garden.
Additionally, the quality of light also plays a significant role in plant health. Different colors and wavelengths of light have varying effects on plant growth and development. For instance, blue light promotes vegetative growth, while red light encourages flowering and fruiting. By understanding the specific light quality requirements of your indoor plants, you can provide them with the optimal spectrum of light to support their growth and overall health.
When it comes to choosing the right lighting conditions for your indoor plants, it’s essential to consider the intensity, duration, and quality of light. By meeting these specific lighting requirements for your plants, you are setting them up for success and ensuring their optimal growth and development. So, take the time to research and understand the lighting needs of your indoor plants, and create an environment that fosters their health and vitality.
Providing Adequate Shade for Light Stress in Plants in Outdoor Settings
Shade is a crucial factor to consider when nurturing plants in outdoor settings. While sunlight is essential for photosynthesis, excessive exposure to direct sunlight can lead to light stress and damage in plants. Providing adequate shade is imperative to protect plants from the harmful effects of intense sunlight and maintain their overall health and productivity.
When selecting an outdoor location for your plants, it is vital to consider the amount of shade they will receive throughout the day. Different plants have varying tolerance levels to sunlight, and understanding their specific light requirements is key. For instance, shade-loving plants, such as ferns and impatiens, thrive in areas with minimal direct sunlight, while sun-loving plants, like tomatoes and roses, need more exposure to thrive. By strategically placing your plants in areas with appropriate shade, you can create a balanced environment that meets their specific needs.
In addition to selecting the right location, providing shade through the use of various structures can further protect your plants. Options such as shade cloths, umbrellas, trellises, or pergolas can effectively reduce the intensity of sunlight and create a more favorable growing environment. Experimenting with different shading techniques can help you regulate sunlight exposure and minimize the risk of light stress in your outdoor plants. Remember, it is essential to strike a balance between shade and sunlight to ensure optimal plant growth and health.
Properly Timing Light Stress in Plants Exposure for Optimal Plant Growth
Properly timing light exposure is crucial for ensuring optimal plant growth. The timing of light exposure can significantly impact a plant’s development, metabolism, and overall health. Understanding the right timing and duration of light exposure can help gardeners maximize the productivity and vitality of their plants.
During the vegetative stage, plants require longer periods of light exposure to promote healthy leaf and stem growth. On the other hand, during the flowering or fruiting stage, shorter periods of light exposure are often recommended to stimulate the reproductive process. It is essential to provide the correct balance of light and darkness to mimic natural day and night cycles, as this helps regulate the plants’ growth and metabolic processes.
Research has shown that when plants are exposed to light during their inactive phase, they may experience stress and negative effects on their overall health. Similarly, depriving plants of the necessary light exposure during their active phase can result in stunted growth and reduced productivity. Therefore, it is essential to carefully manage the timing of light exposure to ensure optimal plant growth and development.
Here’s a table with information about light stress in plants:
| Aspect | Details |
|---|---|
| Definition | Light stress in plants occurs when the intensity, duration, or spectrum of light exceeds the plant’s optimal range, leading to physiological and morphological changes. |
| Symptoms | – Leaf bleaching or yellowing. – Leaf curling or twisting. – Browning or burning of leaf edges. – Stunted growth. – Reduced yield. |
| Light Intensity | High light intensity, especially in direct sunlight or under strong artificial lighting, can cause stress. |
| Duration of Light Exposure | Extended periods of light without adequate dark periods can contribute to stress, disrupting the plant’s normal metabolic processes. |
| Light Spectrum | Inappropriate light spectrum (e.g., too much blue or red light) can lead to stress. Different plants have specific light spectrum needs. |
| Prevention | – Provide the correct light intensity and duration for the specific plant species. – Ensure a balanced light spectrum. – Gradually acclimate plants to changes in light conditions. |
| Adjustable Lighting Systems | Use lighting systems with adjustable intensity and spectrum settings to tailor the light to the plant’s requirements. |
| Light Stress during Transition Phases | Be cautious during transitions between growth stages, as sudden changes in light intensity or spectrum can cause stress. |
| Light Stress vs. Light Adaptation | Plants can adapt to changes in light conditions, but sudden or extreme changes can induce stress. Gradual adjustments are generally better tolerated. |
| Mitigation | – Provide shade or reduce light intensity if necessary. – Ensure proper spacing between light sources and plants. – Monitor and adjust lighting conditions based on plant response. |
| Monitoring | Regularly monitor plant health, growth patterns, and any signs of stress. Adjust lighting conditions accordingly. |
| Impact on Photosynthesis | Excessive light can lead to photoinhibition, reducing the efficiency of photosynthesis and causing damage to the plant’s photosynthetic apparatus. |
| Impact on Yield | Prolonged or severe light stress can negatively impact yield and quality of harvested crops. |
| Light Stress and Climate | Consider the overall climate, temperature, and humidity in conjunction with lighting conditions, as they collectively influence plant health. |
| Learning Resources | Consult plant-specific lighting requirements and seek advice from reputable sources for optimal cultivation practices. |
This table provides an overview of key aspects related to light stress in plants, covering symptoms, causes, prevention, mitigation, and the impact on plant health and yield. It’s essential to understand the specific light needs of the plants you are growing and adjust lighting conditions accordingly.
Managing Light Stress in Greenhouses and Controlled Environments
Light stress can pose a significant challenge for plants in greenhouse and controlled environments. The controlled nature of these settings means that plants depend heavily on artificial lighting sources for their growth and development. However, if not managed properly, this intense light exposure can result in detrimental effects on plant health.
One key aspect of managing light stress in these environments is to carefully select and position the light sources. It is crucial to consider the light intensity and duration that plants receive to ensure optimal growth. Different plants have varying light requirements, and it is essential to tailor the lighting conditions accordingly. Additionally, the use of shading techniques can help to regulate light levels and prevent excessive exposure. Monitoring and adjusting light schedules based on the specific needs of the plants can go a long way in mitigating the risk of light stress.
Implementing Effective Light Stress Mitigation Techniques.
Implementing effective light stress mitigation techniques is crucial for maintaining the health and productivity of plants. When plants are exposed to excessive or inadequate light, they can experience stress that negatively affects their growth and overall well-being. By employing practical strategies, gardeners and growers can minimize the impact of light stress on plants and optimize their performance.
One effective technique is to provide appropriate shading for plants in outdoor settings. This can be achieved by using shade cloth or constructing structures that block direct sunlight during the hottest parts of the day. By reducing the intensity and duration of light exposure, plants can better regulate their metabolic processes and minimize the risk of stress. It is important to note that different plants have varying shade tolerance, and it is essential to choose the right level of shading for each specific species.
Additionally, managing the timing of light exposure is crucial for optimal plant growth. Certain plants thrive in specific photoperiods, which refer to the duration of light and darkness they require for proper physiological development. By carefully controlling the duration of light exposure during different growth stages, gardeners can promote healthy growth while reducing the risk of light stress. This can be achieved through the use of timers or automated lighting systems that mimic natural light cycles.
Implementing effective light stress mitigation techniques requires a proactive approach in understanding the specific light requirements and tolerances of different plant species. By providing adequate shading and managing the timing of light exposure, gardeners can create optimal growing conditions that promote the overall health and vitality of their plants. Through a combination of scientific knowledge and practical application, light stress can be minimized, leading to thriving, resilient plants that flourish in their environment.
What are some common signs and symptoms of light stress in plants?
Some common signs of light stress in plants include chlorosis (yellowing of the leaves), stunted growth, wilting, leaf burn, and early leaf drop.
How does light intensity contribute to plant stress?
Excessive light intensity can lead to photoinhibition, where the plant’s photosynthetic machinery becomes overwhelmed and can’t efficiently process the absorbed light. This can result in damage to the plant’s cells and reduced growth and productivity.
What is the importance of light duration for plant health?
Light duration, or the length of time plants are exposed to light, is crucial for their overall health. Insufficient light duration can lead to weak, spindly growth, while excessive light duration can disrupt the plant’s natural rhythms and lead to stress.
How does light quality affect plant stress levels?
The quality of light, including its color spectrum, can significantly impact plant stress levels. Different wavelengths of light can trigger specific plant responses, and inadequate or imbalanced light quality can lead to stress and poor growth.
What are some effective strategies for preventing light stress in plants?
Some strategies for preventing light stress in plants include providing adequate shading, selecting the right lighting conditions for indoor plants, and properly timing light exposure to optimize plant growth.
How can one choose the right conditions for indoor Light Stress in Plants?
When choosing lighting conditions for indoor plants, it is important to consider the specific light requirements of the plant species. Some plants thrive under bright, direct light, while others prefer indirect or lower light conditions.
What is the role of shade in mitigating in outdoor Light Stress in Plants?
Providing adequate shade for outdoor plants can help protect them from excessive sunlight and reduce the risk of light stress. It can also help regulate temperature and prevent wilting or leaf burn.
Why is proper timing of light exposure important for optimal plant growth?
Proper timing of light exposure ensures that plants receive the right amount of light during their growth stages. It allows them to undergo necessary processes like photosynthesis and rest periods, which are crucial for healthy growth and development.
How can Light Stress in Plants be managed in greenhouses and controlled environments?
In greenhouses and controlled environments, light stress can be managed by carefully adjusting the intensity, duration, and quality of light provided to the plants. This can be done through the use of shading techniques, supplemental lighting, and light filtering materials.
What are some effective Light Stress in Plants mitigation techniques for plants?
Effective light stress mitigation techniques include optimizing light levels through the use of shade cloth or light filtering materials, providing appropriate light duration and intensity, and ensuring a balanced light spectrum for optimal plant growth.







