How to Recognize and Correct Silicon Deficiency in Your Plants
Table of Contents
Signs of Silicon Deficiency in Plants
Plants are highly responsive organisms, and any nutrient deficiency can manifest in various ways. Silicon deficiency in plants is a common issue that can often go unnoticed until it affects the overall health and productivity of the plant. One of the primary signs of silicon deficiency is weakened cell walls. As silicon is responsible for strengthening cell walls, plants lacking this essential nutrient may exhibit reduced structural integrity, leading to a range of symptoms.
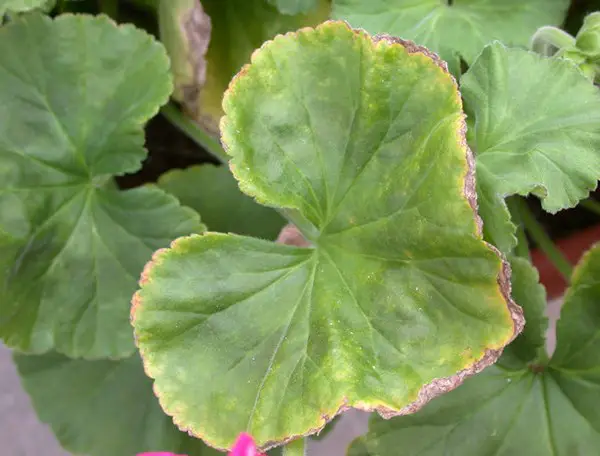

Visible symptoms of silicon deficiency can include stunted growth, decreased leaf size, and increased susceptibility to environmental stress factors such as drought or disease. In addition, plants deficient in silicon may experience higher rates of transpiration, leading to increased water loss and subsequent wilting. As silicon plays a crucial role in the uptake and transport of other essential nutrients, the deficiency can further hinder the plant’s ability to absorb and distribute nutrients effectively. As a result, the overall vigor and productivity of the plant can be significantly compromised. Recognizing these signs of silicon deficiency is vital in addressing the issue promptly and ensuring optimal plant health.
Causes of Silicon Deficiency in Plants
Silicon deficiency in plants can be caused by a range of factors that hinder adequate uptake and utilization of this essential element. One such factor is the pH level of the soil. Acidic soils, with a pH below 6.0, tend to limit the availability of silicon to plants, leading to deficiency symptoms. On the other hand, alkaline soils with a pH above 7.5 can also inhibit silicon uptake, resulting in inadequate levels in plants.
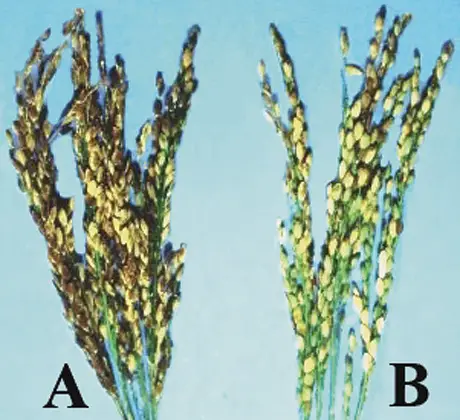

Another cause of silicon deficiency is the lack of sufficient silicon in the soil. While silicon is one of the most abundant elements in the Earth’s crust, certain soils may naturally have low levels of silicon, particularly sandy soils. In addition, intensive farming practices, such as excessive irrigation, can leach silicon out of the soil, further exacerbating deficiency issues.

Understanding the causes of silicon deficiency in plants is crucial for gardeners and farmers to effectively address and prevent this issue. By optimizing soil pH levels and ensuring an adequate supply of silicon, growers can promote healthy plant growth and mitigate the detrimental effects of silicon deficiency. Stay tuned for the next section, where we will delve into the effects of silicon deficiency on plant growth.
Effects of Silicon Deficiency on Plant Growth
Silicon plays a critical role in the growth and development of plants, and its deficiency can have detrimental effects on overall plant health. One of the most evident effects of silicon deficiency is reduced plant vigor and stunted growth. Without an adequate supply of silicon, plants struggle to build their structural integrity, resulting in weakened stems and leaves that are more susceptible to damage from various stressors. This can lead to increased vulnerability to diseases, pests, and even environmental factors such as drought and extreme temperatures.

Furthermore, the absence of silicon can hinder the transport and distribution of essential nutrients within plants. Silicon is known to enhance the uptake and translocation of certain elements, such as calcium and phosphorus, which are crucial for proper plant growth. In the absence of sufficient silicon levels, plants may experience deficiencies in these essential nutrients, further compromising their overall growth and development. Additionally, silicon deficiency can inhibit the plant’s ability to efficiently utilize water, leading to water stress and reduced drought tolerance.

In conclusion, silicon deficiency in plants can have significant repercussions on their growth and overall health. It is essential for gardeners and farmers to recognize the visual symptoms and conduct appropriate soil tests and leaf analysis to identify possible deficiencies. Understanding the effects of silicon deficiency allows for proactive measures to correct and prevent such issues, ultimately promoting robust and thriving plant growth.
Importance of Silicon in Plant Health
Silicon, often overlooked in the realm of plant nutrition, plays a crucial role in maintaining the overall health and vigor of plants. This element, abundant in the Earth’s crust, is essential for the proper functioning of numerous biological processes within plants. From promoting disease resistance to enhancing the structural integrity of plants, silicon’s significance cannot be underestimated.
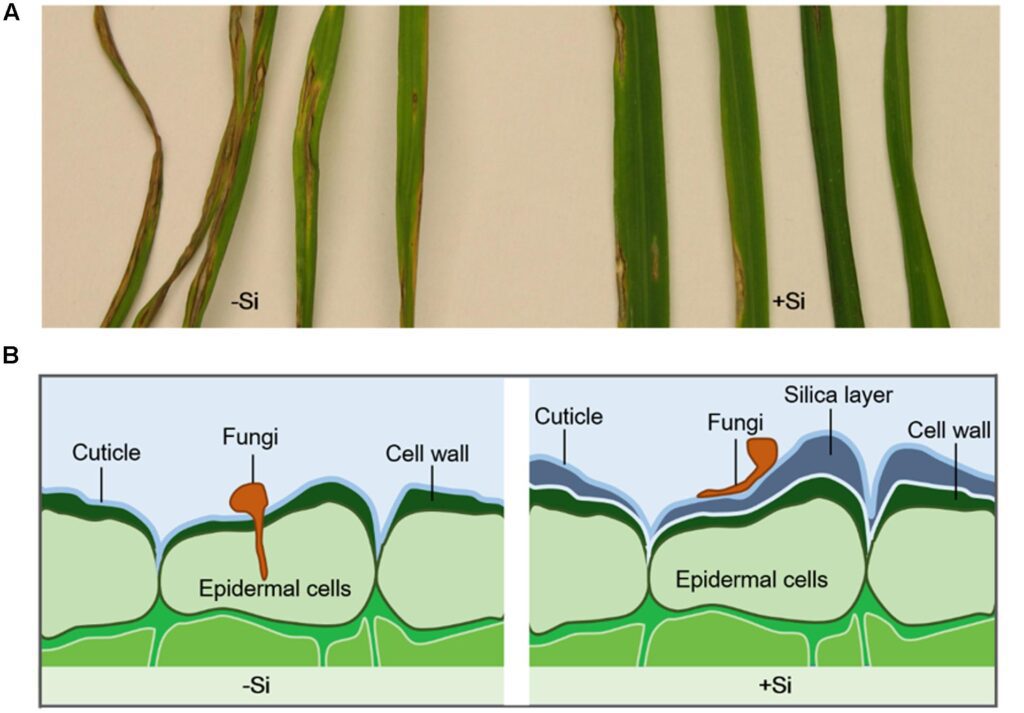
One of the primary benefits of silicon is its ability to fortify plants against various stresses. Through the deposition of silica, plants are able to develop stronger cell walls, providing a physical barrier against pathogens, pests, and environmental pressures. Furthermore, silicon aids in the activation of defense mechanisms, equipping plants with the ability to fend off diseases caused by fungi, bacteria, and viruses. Research has demonstrated that plants supplied with sufficient silicon exhibit enhanced resistance to a range of diseases, reducing the need for chemical interventions that can have adverse effects on both the environment and human health.
Additionally, silicon improves the overall structure and resilience of plants. By reinforcing cell walls, silicon enhances plant rigidity, enabling them to withstand mechanical stress, such as wind or physical contact. This is particularly important for crops that bear heavy fruits, as strong stems and branches prevent breakage and fruit loss. Moreover, silicon facilitates efficient nutrient uptake, ensuring that plants receive vital minerals required for optimal growth and development. Overall, the inclusion of silicon in plant nutrition programs is crucial for promoting sturdy and resilient plants that can thrive even in challenging conditions.
In the subsequent sections of this article, we will delve deeper into the signs, causes, and effects of silicon deficiency in plants. By understanding the importance of silicon and recognizing its role in plant health, gardeners and growers can make informed decisions to maximize the well-being and productivity of their beloved plants. Stay tuned for valuable insights and practical solutions to combat silicon deficiency and cultivate thriving greenery.
Identifying Silicon Deficiency through Visual Symptoms
Silicon deficiency in plants can often be identified through visual symptoms exhibited by the foliage. One common sign is the presence of weak and spindly stems. Plants lacking sufficient silicon may struggle to develop sturdy, erect stems, leading to a drooping or bending appearance. Additionally, leaves may exhibit yellowing or chlorosis, starting at the tips and progressing towards the base of the leaf. This discoloration is a result of impaired chlorophyll production, which is vital for photosynthesis and overall plant health.
Another visual symptom of silicon deficiency is the increased susceptibility to pests and diseases. Plants deficient in silicon have weakened cell walls, making them more vulnerable to attacks from insects and pathogens. Infested plants may show signs of mottled or discolored patches on the leaves, as well as holes or chewed edges caused by feeding insects. By closely monitoring the appearance and health of plants, gardeners can effectively identify the presence of silicon deficiency and take appropriate measures to address the issue.
Conducting Soil Tests for Silicon Deficiency
Soil testing is an essential step in determining the presence of silicon deficiency in plants. By conducting soil tests, gardeners and agronomists can gain valuable insights into the nutrient composition of their soil, including the levels of silicon present. This information is crucial for identifying the need for corrective measures and ensuring optimal plant health.
| Soil Test | Method | Ideal Range |
|---|---|---|
| pH | pH meter | 6.0 – 7.5 |
| Silicon | Plant tissue analysis | 50 – 200 ppm |
| Texture | Soil texture analysis | Balanced |
| EC | Electrical conductivity | < 0.8 dS/m |
There are various methods available for conducting soil tests to measure silicon content. One commonly used technique is the extraction method, where soil samples are collected from different areas of the garden or field and sent to a laboratory for analysis. The laboratory uses specialized equipment and methodologies to extract and quantify the silicon content in the soil. Results from the soil test can then be used to determine the level of silicon deficiency and guide the appropriate course of action to address the issue.
It is important to note that soil testing for silicon deficiency should be done periodically, especially if there are signs of nutrient imbalance or poor plant growth. Regular soil testing allows gardeners and agronomists to proactively monitor and maintain optimal silicon levels in the soil, preventing deficiencies and promoting healthy plant development. Through this approach, gardening enthusiasts can ensure that their plants receive the necessary nutrients, including silicon, for robust growth and improved overall health.
Recognizing Silicon Deficiency through Leaf Analysis
Leaf analysis is an effective method for recognizing silicon deficiency in plants. By examining the nutrient content of plant foliage, we can identify any imbalances or deficiencies in essential nutrients, including silicon. When it comes to silicon deficiency, there are specific visual symptoms that can be observed in the leaves.
One telltale sign of silicon deficiency is the appearance of yellow or pale green spots on the leaves. These spots may initially occur on the lower leaves and gradually progress to the upper leaves if the deficiency persists. As the deficiency worsens, the affected areas may become necrotic, resulting in brown or dead patches on the leaves. Additionally, leaves with silicon deficiency may exhibit reduced size and distorted shape. By carefully inspecting the foliage and noting these characteristic symptoms, we can gain valuable insights into the plant’s silicon status.
Common Plants Prone to Silicon Deficiency
Silicon deficiency can have detrimental effects on the growth and overall health of plants. While silicon is not considered an essential nutrient for most plant species, there are certain plants that are more prone to developing a deficiency.
One example is rice (Oryza sativa), which is known to be highly susceptible to silicon deficiency. Studies have shown that without an adequate supply of silicon, rice plants can suffer from reduced stem strength and increased susceptibility to pests and diseases. This can ultimately lead to decreased crop yield and quality.
Another plant that commonly experiences silicon deficiency is cucumber (Cucumis sativus). Silicon plays a crucial role in strengthening the cell walls of cucumber plants, enhancing their ability to resist environmental stressors such as drought and disease. Without sufficient silicon, cucumber plants may exhibit stunted growth, increased susceptibility to fungal infections, and overall diminished health.
Understanding which plants are more prone to silicon deficiency allows gardeners and farmers to take proactive measures to address this issue. By implementing appropriate strategies to correct silicon deficiency, such as supplementing with silicon fertilizers or incorporating silicon-rich amendments into the soil, these common plants can thrive and reach their full potential.
Factors Affecting Silicon Uptake in Plants
Soil pH plays a crucial role in the uptake of silicon by plants. Research has shown that silicon availability decreases as soil pH becomes more acidic. This is because silicon is predominantly present in its soluble form, silicic acid (Si(OH)4), in neutral to slightly alkaline soils. In acidic soils, however, silicic acid forms insoluble complexes with iron and aluminum, making it less available to plants. Therefore, it is important to maintain a slightly acidic to neutral pH in order to enhance silicon uptake and utilization by plants.
Another factor that can affect silicon uptake is the presence of other elements in the soil. High concentrations of certain elements, such as phosphorus and aluminum, have been found to inhibit silicon uptake by plants. This is due to competition for uptake sites or the formation of insoluble complexes with silicon. On the other hand, some elements, like potassium and calcium, have been shown to enhance silicon uptake. Therefore, it is necessary to consider the overall nutrient balance in the soil to ensure optimal silicon uptake and utilization by plants.
Factors Affecting Silicon Uptake in Plants:
• Soil pH: Research indicates that silicon availability decreases as soil pH becomes more acidic. Silicon is primarily present in its soluble form, silicic acid (Si(OH)4), in neutral to slightly alkaline soils. In acidic soils, however, silicic acid forms insoluble complexes with iron and aluminum, making it less accessible to plants. To enhance silicon uptake and utilization by plants, maintaining a slightly acidic to neutral pH is crucial.
• Presence of other elements: High concentrations of certain elements like phosphorus and aluminum can inhibit silicon uptake by plants. This inhibition occurs due to competition for uptake sites or the formation of insoluble complexes with silicon. Conversely, some elements such as potassium and calcium have been found to enhance silicon uptake. Thus, considering the overall nutrient balance in the soil is necessary for optimal silicon uptake and utilization by plants.
These factors play significant roles in determining the availability and accessibility of silicon for plant growth. By understanding these factors and implementing appropriate measures to maintain suitable soil conditions, farmers and gardeners can promote healthier plant growth through enhanced silicon uptake.
Methods to Correct Silicon Deficiency in Plants
One of the methods to correct silicon deficiency in plants is through soil amendments. Silicon can be added to the soil in the form of various silicon fertilizers or amendments. These products are designed to increase the silicon content in the soil, thereby addressing the deficiency in plants. It is important to carefully follow the application instructions provided by the manufacturer when using these products, as over-application can potentially have negative effects on plant growth.
Another approach to correcting silicon deficiency is through foliar application. This method involves applying a silicon solution directly to the leaves of the affected plants. Foliar sprays are commonly used in situations where quick results are desired or when the root system is compromised and unable to effectively absorb silicon from the soil. However, it is important to note that foliar application should not be considered a long-term solution, as it does not address the underlying deficiency in the soil. Regular monitoring of plant health and nutrient levels, along with appropriate soil amendments, are crucial for maintaining optimal silicon levels in plants.
Applying Silicon Fertilizers to Combat Deficiency
Silicon fertilizers can be an effective solution to combat silicon deficiency in plants. When applied correctly, silicon fertilizers can significantly improve the health and growth of plants by increasing their ability to withstand biotic and abiotic stresses. Several studies have shown that the application of silicon fertilizers to silicon-deficient plants enhances their resistance to pests, diseases, and physical damage.
One common way to apply silicon fertilizers is through foliar sprays. Foliar application allows for direct absorption of silicon by the leaves, resulting in quick uptake and utilization by the plants. Additionally, silicon can be supplied to the plants through root drenching or incorporating silicon fertilizers into the soil. However, it is essential to choose the appropriate type and concentration of silicon fertilizer based on the specific plant’s requirements and the severity of the silicon deficiency. Regular monitoring of silicon levels in the plants and soil can help determine the effectiveness of the fertilization process and ensure optimal silicon levels are maintained.
Alternative Methods to Increase Silicon Levels in Plants
One alternative method to increase silicon levels in plants is through the use of silicon-rich amendments. These amendments, such as silica sand or rock dust, can be added to the soil or growing medium to provide plants with a readily available source of silicon. Silicon-rich amendments have been found to effectively increase the silicon content in plants, leading to improved plant health and growth. Studies have shown that the addition of silica-based amendments can enhance the plant’s ability to withstand various biotic and abiotic stresses, such as pest and disease resistance, drought tolerance, and nutrient uptake efficiency. Additionally, the use of silicon-rich amendments can also improve the overall quality and yield of crops.
Another alternative method to increase silicon levels in plants is through the application of silicon foliar sprays. Foliar spraying involves directly applying a solution of silicon to the leaves of plants, allowing for efficient absorption and utilization of silicon by the plant. Silicon foliar sprays are especially beneficial for plants growing in hydroponic systems, as they provide a quick and easy way to deliver silicon to the plants. Research has shown that foliar spraying with silicon can have positive effects on plant growth and development, including increased biomass production, enhanced photosynthesis rates, and improved nutrient uptake. It is important to note that foliar sprays should be used in addition to soil amendments, as they provide supplemental silicon rather than a long-term source. Regular monitoring of silicon levels and adjusting application rates accordingly is crucial to ensure optimal silicon levels in plants.
In conclusion, alternative methods to increase silicon levels in plants include the use of silicon-rich amendments and silicon foliar sprays. These methods offer effective ways to provide plants with a readily available source of silicon, leading to improved plant health, growth, and stress tolerance. Whether it is through amending the soil or applying silicon directly to the leaves, incorporating silicon into plant care practices can be beneficial for gardening enthusiasts looking to optimize their plant’s performance.
Monitoring and Maintaining Optimal Silicon Levels in Plants
To ensure optimal silicon levels in plants, regular monitoring and maintenance are crucial. Silicon plays a vital role in promoting plant health and growth, making it essential to create a suitable environment that supports its availability. By incorporating effective monitoring strategies and implementing appropriate maintenance practices, gardeners can cultivate healthy and thriving plants.
Monitoring silicon levels can be accomplished through various methods. Conducting regular soil tests is one approach to assess the silicon content in the growing medium. These tests provide valuable insights into the availability of silicon and highlight deficiencies that may be inhibiting plant growth. Additionally, leaf analysis can be employed to determine the silicon status in plants directly. By examining the leaf tissue, gardeners can identify any deficiencies and take prompt action to rectify them.
Once the silicon levels have been assessed, maintaining optimal levels requires attention to detail. Applying silicon fertilizers is an effective method to combat deficiency and ensure plants receive an adequate supply of this essential nutrient. These fertilizers are specifically formulated to provide a readily available source of silicon, allowing plants to uptake the element and thrive. Furthermore, alternative methods, such as incorporating silicon-rich amendments into the growing medium, can be employed to boost silicon levels naturally. By incorporating these maintenance practices, gardeners can promote healthy plant growth and optimize silicon levels for their plants’ overall well-being.
For more details check the vedio below:
How can I determine if my plants are suffering from silicon deficiency?
You can identify silicon deficiency in plants through visual symptoms, such as reduced growth, weakened stems, and increased susceptibility to pests and diseases. Conducting soil tests and leaf analysis can also help confirm the deficiency.
What are the causes of silicon deficiency in plants?
Silicon deficiency in plants can occur due to factors such as low silicon availability in the soil, acidic soil conditions, excessive leaching, and imbalanced nutrient levels. Insufficient silicon uptake by plant roots can also contribute to deficiency.
What are the effects of silicon deficiency on plant growth?
Silicon deficiency can negatively impact plant growth by reducing stem strength, leading to lodging or collapse. It can also impair the plant’s ability to resist pests and diseases, resulting in decreased overall health and productivity.
Why is silicon important for plant health?
Silicon plays a crucial role in enhancing plant health by strengthening cell walls, improving resistance against pests and diseases, regulating nutrient uptake, and mitigating abiotic stress factors such as drought and heat.
How can I recognize silicon deficiency through visual symptoms?
Visual symptoms of silicon deficiency may include stunted growth, yellowing or chlorosis of leaves, increased susceptibility to pests and diseases, and weakened stems that may easily break or lodge.
How can I conduct soil tests to determine silicon deficiency?
Soil tests can be conducted by collecting soil samples from different areas of your garden or field, and sending them to a laboratory for analysis. The lab will provide you with information on the silicon content in your soil, helping to identify any deficiency.
Can leaf analysis help in recognizing silicon deficiency?
Yes, leaf analysis is an effective method to identify silicon deficiency in plants. By analyzing the silicon content in plant tissue, you can determine if the plant is lacking in this essential nutrient.
Which common plants are prone to silicon deficiency?
Common plants that are prone to silicon deficiency include rice, wheat, barley, cucumber, tomato, and many other grasses and cereals. However, silicon deficiency can occur in various other plant species as well.
What factors can affect silicon uptake in plants?
Factors such as soil pH, soil moisture levels, nutrient imbalances, and the presence of other elements can affect the uptake of silicon in plants. Additionally, certain environmental conditions and stress factors can also impact silicon uptake.
How can I correct silicon deficiency in plants?
One method to correct silicon deficiency is by applying silicon fertilizers to the soil, ensuring adequate silicon availability for plant uptake. Another approach is to use alternative methods like foliar sprays or silicon-rich amendments to increase silicon levels in plants.
How can I monitor and maintain optimal silicon levels in plants?
Regular monitoring of plant health, conducting soil tests, and leaf analysis can help you track silicon levels in your plants. Adjusting soil pH, providing balanced nutrition, and timely application of silicon fertilizers or amendments can help maintain optimal silicon levels.







