The Ultimate Guide to pH Testing and Balancing for Your Garden Soil
Understanding and maintaining the right pH level is crucial for a thriving garden. This comprehensive guide will walk you through the importance of soil pH, how to test it accurately, and effective methods to balance it for various plants.
Whether you’re a seasoned gardener or just starting, mastering soil pH can significantly enhance plant health and yield. Dive in to discover expert tips, practical advice, and step-by-step instructions to ensure your garden flourishes with the perfect pH balance. Happy gardening! 🌱
Table of Contents
Understanding the Importance of pH Levels in Garden Soil
Maintaining the ideal pH levels in garden soil is essential for the overall health and vitality of your plants. pH is a measure of how acidic or alkaline the soil is, and it directly affects the availability of nutrients to plants. Each plant has specific pH preferences, and if the soil deviates too much from their preferred range, it can hinder their growth and development.
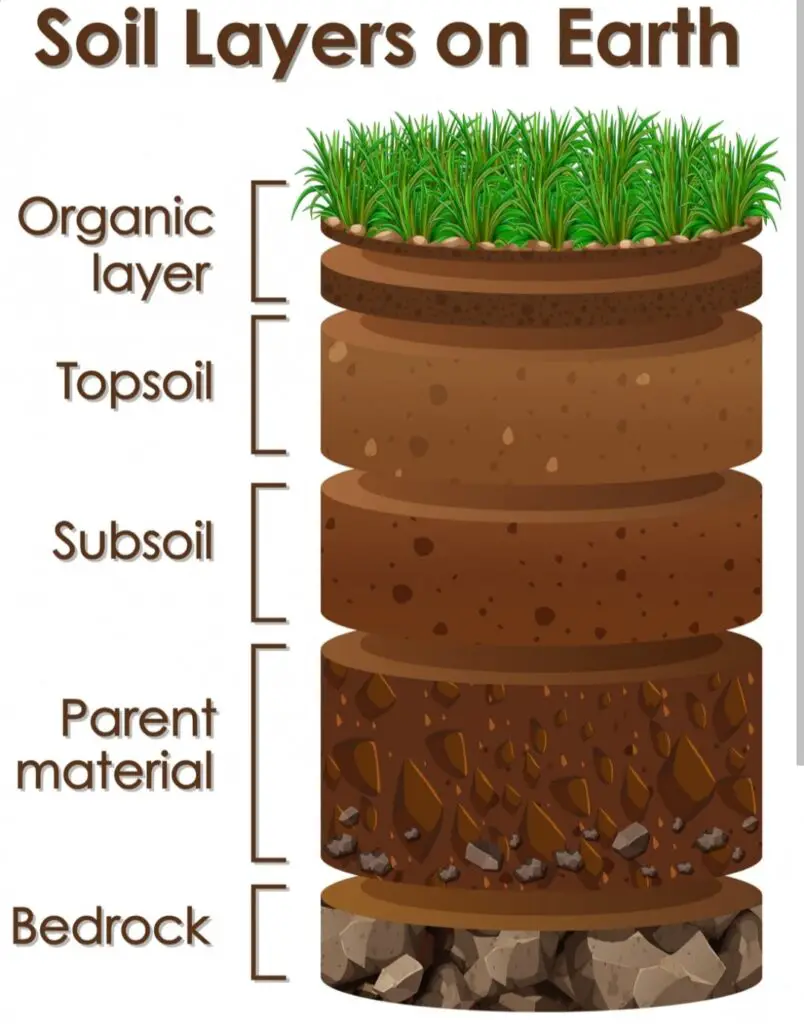
Understanding the importance of pH levels in garden soil allows you to create the optimal growing conditions for your plants. When the pH is too high or too low, it can affect the chemical reactions and microbial activity in the soil, leading to nutrient deficiencies or toxicities. By ensuring the appropriate pH levels, you provide your plants with the best environment for absorbing essential nutrients, resulting in healthier, more productive gardens.
Factors Affecting Soil pH and Their Impact on Plant Health
Factors affecting soil pH play a crucial role in determining the overall health and productivity of plants. Soil pH is a measurement of the acidity or alkalinity of the soil, and it directly influences nutrient availability for plant uptake. Various factors can influence soil pH, including the parent material of the soil, climate, vegetation, and human activities.

The parent material of the soil refers to the rocks and minerals from which the soil is formed. Different types of rocks have different compositions, which can influence the pH of the soil. For example, soils derived from limestone or chalk tend to be alkaline, while soils derived from granite or sandstone tend to be acidic. The climate in an area can also impact soil pH, with rainfall leaching minerals from the soil and potentially leading to acidification. Vegetation can also affect soil pH, as some plants release organic acids that can acidify the soil while others release alkaline compounds that can increase pH. Lastly, human activities such as agriculture and industry can significantly alter soil pH through the use of fertilizers, pesticides, and other chemicals. Understanding these factors is essential for effectively managing soil pH and promoting optimal plant growth and health.
Different pH Testing Methods for Garden Soil
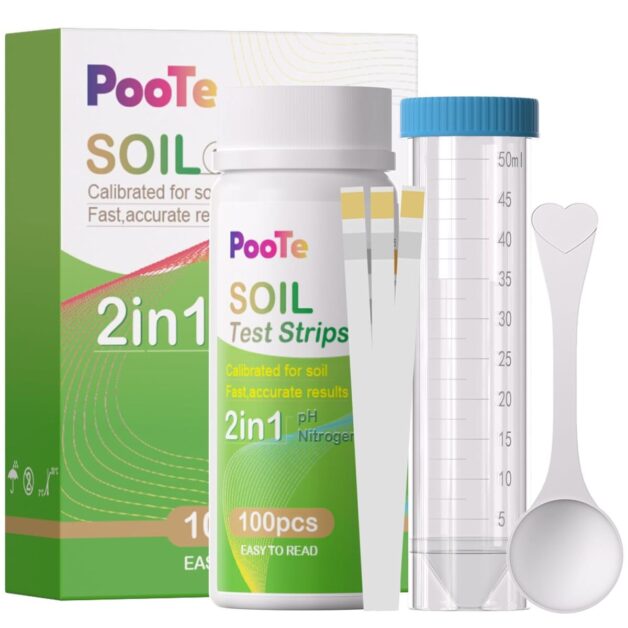
When it comes to testing the pH levels of your garden soil, there are several methods you can use to obtain accurate results. One commonly used method is the use of pH testing kits. These kits typically come with test strips that change color when exposed to different pH levels. By comparing the color of the strip to a color chart provided in the kit, you can determine the pH level of your soil.

Another pH testing method for garden soil is the use of pH meters. These devices are designed to provide more precise readings by measuring the electrical conductivity of the soil. pH meters come in different types, including handheld meters and digital meters, and they often require calibration before use to ensure accurate measurements.
While pH testing kits and meters are common methods used by gardeners, another option is to send a soil sample to a professional laboratory for analysis. This method is particularly useful when you need more detailed information about your soil’s pH levels and other essential nutrients. The laboratory will conduct a comprehensive analysis and provide you with a detailed report that can guide you in making informed decisions about soil amendments and plant choices for your garden.
In summary, there are a few different pH testing methods you can use to assess the acidity or alkalinity of your garden soil. pH testing kits, pH meters, and laboratory analysis all offer reliable ways of obtaining accurate pH measurements. Choose the method that works best for your needs and budget to ensure the optimal pH levels for your plants’ health and productivity.
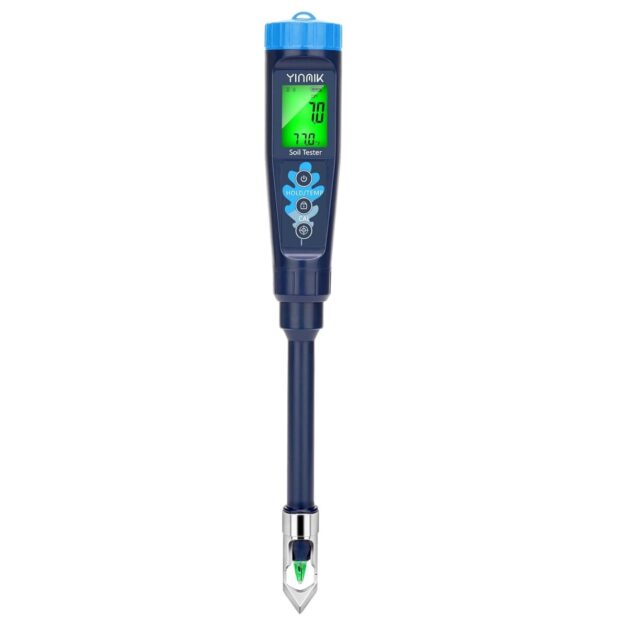
Build: Includes stainless-steel dibber for pH electrode protection.
Digital Interface: Provides quick pH readings on a digital display.
Compatibility: Suitable for various soils and water types.
Smart Features: Connects to YINMIK App for continuous monitoring and data storage.
Accuracy: Many users highlight its reliability compared to other pH testing methods, providing precise measurements crucial for plant health.
Versatility: Suitable for both amateur gardeners and professionals due to its robust build and wide application range.
App Integration: The ability to sync with a smartphone app for data storage and analysis is a significant advantage.
Price: While considered a worthwhile investment by many, the higher price point might deter budget-conscious buyers initially.
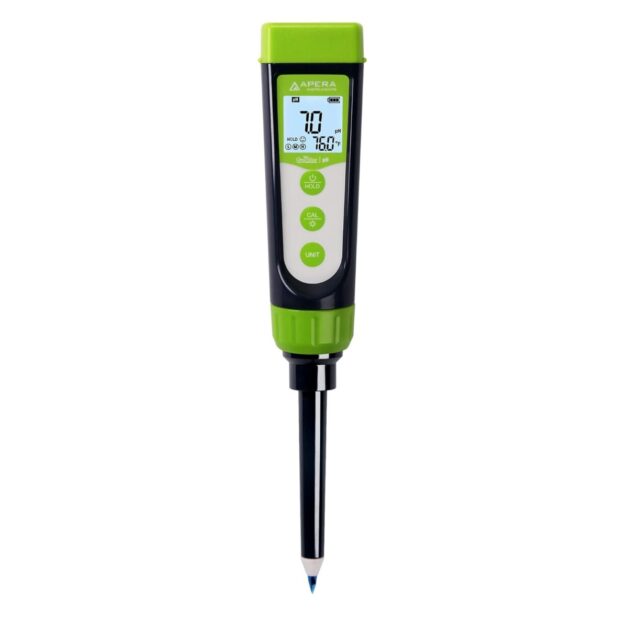
TruRead mode for averaging multiple readings, enhancing measurement reliability.
User-friendly calibration process with a 2-point calibration in under a minute.
3-color backlit HD display for clear visibility in any environment.
IP67 waterproof and dust-proof rating for durability in harsh conditions.
Built-in probe condition indicator and calibration reminder for maintenance.
Ease of Use: Simple calibration and intuitive operation make it accessible for all users.
Durability: IP67 rating ensures longevity even in challenging agricultural settings.
Replaceable Probe: The Swiss spear pH sensor is replaceable, enhancing long-term value.
Customer Support: Positive reviews highlight responsive customer service and reliable support.
Learning Curve: Some users may find the advanced features initially overwhelming.
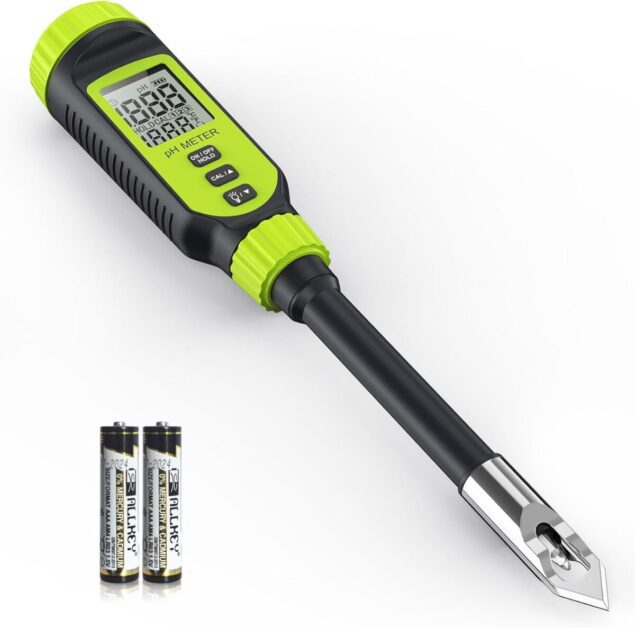
It features a sensitive electrode probe with an LCD screen and a protective zinc alloy tip. Calibration with pH 4.0, 7.0, and 10.01 buffer solutions is necessary before initial use, and regular maintenance with potassium chloride solution is recommended to keep the electrode moist.
This product includes 2 AAA batteries and comes with a manufacturer’s warranty.
Durable Build: The zinc alloy protective tip enhances durability, making it suitable for various types of soil and substances.
User-Friendly Design: It features an LCD screen with backlight, making it easy to use even in dimly lit areas.
Temperature Monitoring: Real-time temperature display aids in understanding environmental conditions affecting pH levels.
Comprehensive Package: Includes batteries, calibration solutions, and necessary accessories for immediate use
Mixed User Reviews: Some users reported inconsistencies in readings between devices or varying measurements despite calibration.
Step-by-Step Guide to Conducting a pH Test on Your Garden Soil
To ensure the health and productivity of your garden, it is essential to regularly monitor and adjust the pH levels of your soil. Conducting a pH test is a simple yet crucial step in understanding the current state of your garden soil. By following these step-by-step guidelines, you can accurately determine the pH level of your soil and make informed decisions on how to balance it for optimal plant growth.
Step 1: Gather your materials. You will need a pH testing kit, which typically includes test strips or a digital pH meter, distilled water, a clean container, and gloves to protect your hands.
Step 2: Choose a representative soil sample. Select an area in your garden that is most typical of your soil conditions. Use a trowel or spade to collect samples from various spots in this area, ensuring to take both surface soil and subsoil samples. Combine these samples in the clean container.
Step 3: Prepare the soil sample. Remove any roots, rocks, or debris from the soil sample, breaking up clumps to obtain a uniform texture. If necessary, let the sample air-dry for a few hours before testing.
Step 4: Perform the pH test. Follow the specific instructions provided with your pH testing kit. This usually involves adding distilled water to the soil sample and then inserting the test strip or pH meter. Allow the strip or meter to measure the pH level for the recommended amount of time.
Step 5: Record and interpret the results. Compare the color or numerical reading on your test strip or pH meter to the pH scale provided with your kit. Soil pH is measured on a scale of 1 to 14, with 7 being neutral. Values below 7 indicate acidic soil, while values above 7 indicate alkaline soil. Take note of the pH level, as it will guide your subsequent actions in adjusting the soil pH to meet your plants’ specific needs.
Conducting regular pH tests on your garden soil will help you maintain optimal conditions for your plants to thrive. With this invaluable information in hand, you can take appropriate measures to adjust the pH levels and create an ideal growing environment.
Interpreting pH Test Results and What They Mean for Your Plants
So you’ve conducted a pH test on your garden soil, but what do the results actually mean for your plants? Interpreting pH test results is crucial in understanding the health and vitality of your garden. The pH scale ranges from 0 to 14, with 7 being neutral. Soil with a pH below 7 is considered acidic, while soil with a pH above 7 is alkaline.
| pH Level | Interpretation | Impact on Plants |
|---|---|---|
| < 6.0 | Acidic | May lead to nutrient deficiencies; adjust for neutrality |
| 6.0-7.0 | Neutral | Ideal range for most plants’ nutrient absorption |
| > 7.0 | Alkaline | Risk of nutrient lockout; adjust to promote nutrient uptake |
Ideally, most plants prefer a slightly acidic to neutral pH range of 6 to 7.5. However, different plants have varying preferences when it comes to soil pH levels. Acid-loving plants like azaleas and blueberries thrive in more acidic soil, with a pH range of 4.5 to 6.5. On the other hand, alkaline-loving plants such as asparagus and cacti require a higher pH range of 7.5 to 8.5. It’s important to match the pH requirements of your plants with the actual pH level of your garden soil to ensure optimal growth and productivity.
When interpreting pH test results, keep in mind that extreme acidity or alkalinity can negatively impact nutrient availability in the soil, affecting plant health. Soil that is too acidic can result in deficiencies of essential nutrients like nitrogen, phosphorus, and potassium. Conversely, overly alkaline soil can lead to nutrient imbalances and hinder the absorption of important elements. An accurate understanding of your soil’s pH will allow you to make necessary adjustments to create a more favorable environment for your plants.
The Ideal pH Range for Different Types of Plants
It is important for gardeners to understand that different types of plants have specific pH requirements in order to thrive. The pH, or acidity level, of your garden soil can greatly affect the growth and health of your plants.
For instance, some plants prefer acidic soil with a pH range of 5.0 to 6.0, such as blueberries and rhododendrons. These acid-loving plants have adapted to thrive in soils with lower pH levels. On the other hand, there are plants that prefer slightly alkaline soil, with a pH range of 7.0 to 8.0, such as asparagus and beets. These plants have evolved to thrive in soils with higher pH levels.
The table lists the ideal pH range for different types of plants
| Category | Plant Name | Ideal pH Range |
|---|---|---|
| Trees | Apple | 5.0 – 6.5 |
| Trees | Ash | 6.0 – 7.5 |
| Shrubs | Azalea | 4.5 – 6.0 |
| Shrubs | Blueberry | 4.0 – 6.0 |
| Vegetables | Carrot | 5.5 – 7.0 |
| Vegetables | Tomato | 5.5 – 7.5 |
| Flowers | Begonia | 5.5 – 7.0 |
| Flowers | Rose (Hybrid Tea) | 5.5 – 7.0 |
| Shrubs | Boxwood | 6.0 – 7.5 |
| Shrubs | Hydrangea (Blue) | 4.0 – 5.0 |
| Shrubs | Hydrangea (Pink) | 6.0 – 7.0 |
| Shrubs | Holly | 4.5 – 5.5 |
| Shrubs | Lilac | 6.0 – 7.5 |
| Shrubs | Rhododendron | 4.5 – 6.0 |
| Shrubs | Forsythia | 6.5 – 7.5 |
| Shrubs | Juniper | 5.0 – 7.0 |
| Shrubs | Magnolia | 5.0 – 6.0 |
| Shrubs | Mock Orange | 6.0 – 8.0 |
| Shrubs | Wisteria | 6.5 – 8.0 |
| Vegetables | Asparagus | 6.0 – 8.0 |
| Vegetables | Beans | 6.0 – 7.5 |
| Vegetables | Beet Root | 6.0 – 7.5 |
| Vegetables | Broccoli | 6.0 – 7.0 |
| Vegetables | Brussels Sprouts | 6.0 – 7.5 |
| Vegetables | Cabbage | 6.0 – 7.5 |
| Vegetables | Cauliflower | 5.5 – 7.5 |
| Vegetables | Celery | 6.0 – 7.0 |
| Vegetables | Cucumber | 5.5 – 7.5 |
| Vegetables | Eggplant | 6.0 – 7.0 |
| Vegetables | Garlic | 5.5 – 7.5 |
| Vegetables | Kale | 6.0 – 7.5 |
| Vegetables | Lettuce | 6.0 – 7.0 |
| Vegetables | Onion | 6.0 – 7.0 |
| Vegetables | Pea | 6.0 – 7.5 |
| Vegetables | Pepper | 5.5 – 7.0 |
| Vegetables | Potato | 4.5 – 6.0 |
| Vegetables | Radish | 6.0 – 7.0 |
| Vegetables | Spinach | 6.0 – 7.5 |
| Vegetables | Turnip | 5.5 – 7.0 |
| Flowers | Alyssum | 6.0 – 7.5 |
| Flowers | Aster | 6.0 – 8.0 |
| Flowers | Black-eyed Susan | 5.5 – 7.0 |
| Flowers | Bleeding Heart | 6.0 – 7.5 |
| Flowers | Canna | 6.0 – 8.0 |
| Flowers | Carnation | 6.0 – 7.0 |
| Flowers | Chrysanthemum | 6.0 – 7.5 |
| Flowers | Clematis | 5.5 – 7.0 |
| Flowers | Cosmos | 5.0 – 8.0 |
| Flowers | Daffodil | 6.0 – 6.5 |
| Flowers | Dahlia | 6.0 – 7.5 |
| Flowers | Daisy | 6.0 – 8.0 |
| Flowers | Daylily | 6.0 – 8.0 |
| Flowers | Delphinium | 6.0 – 7.5 |
| Indoor Plants | African Violet | 6.0 – 8.0 |
| Indoor Plants | Aloe Vera | 7.0 |
| Indoor Plants | Amaryllis | 4.5 – 6.0 |
| Indoor Plants | Bamboo | 5.0 – 7.5 |
| Indoor Plants | Cactus | 4.5 – 6.0 |
| Indoor Plants | Ferns | 4.5 – 6.0 |
| Indoor Plants | Gardenia | 4.5 – 6.0 |
| Indoor Plants | Geranium | 6.0 – 8.0 |
| Indoor Plants | Orchid | 4.5 |
| Indoor Plants | Philodendron | 4.5 – 6.0 |
| Indoor Plants | Spider Plant | 6.1 – 6.5 |
It is crucial to determine the ideal pH range for the specific types of plants you are growing. This can be done by conducting a pH test on your garden soil. By knowing the ideal pH range for your plants, you can adjust the acidity or alkalinity of your soil accordingly. This will help create optimal conditions for your plants to absorb nutrients and maximize their growth potential.
Adjusting Soil pH
Organic Methods and Products
Organic methods for adjusting soil pH offer gardeners a natural and environmentally friendly solution to ensure optimal plant growth and health. One popular approach involves incorporating organic amendments into the soil to gradually adjust its pH levels. For example, adding organic materials such as compost, well-rotted manure, or peat moss can help increase acidity in alkaline soils, while using agricultural lime or wood ash can raise pH levels in acidic soils.
These are our expert recommended products for adjusting your soil pH

<a href="https://amzn.to/4ckpbq2"><strong>Down to Earth Organic Prilled Dolomite Lime, 5 lb</strong> </a> Certified Organic

<a href="https://amzn.to/3VJhX7R" target="_blank" rel="noreferrer noopener nofollow">Miracle-Gro Sphagnum Peat Moss, 8 qt.</a> Best Brand

<a href="https://amzn.to/4bvYiyk" target="_blank" rel="noreferrer noopener nofollow">Espoma Organic Land and Sea Gourmet Compost with Lobster & Crab Meal</a> Best Values
Lobster & Crab Meal Enrichment: The addition of lobster and crab meal not only enhances the nutrient content but also improves soil texture and fertility.
Versatility: It’s suitable for both in-ground gardens and container plants, making it a go-to choice for various gardening needs.
Mycorrhizae Boost: The inclusion of Myco-tone, a proprietary blend of mycorrhizae
Customer Satisfaction: The product consistently receives high ratings for ease of use, value for money, and effectiveness in promoting plant growth.
These organic amendments not only alter pH levels but also provide essential nutrients and beneficial microbial activity to the soil. They work slowly, allowing plants to adjust more gradually to the new pH conditions. Additionally, organic methods promote long-term soil fertility and sustainable gardening practices. However, it is important to note that organic methods may take longer to see significant changes in soil pH compared to their inorganic counterparts. Patience and regular monitoring through pH testing are key when using organic methods for adjusting soil pH.
Inorganic Methods and Products
Inorganic methods and products can be effective for adjusting soil pH in garden settings. One commonly used method is the application of lime to raise pH levels. Lime consists of calcium carbonate or calcium oxide, which react with acidic soil components to increase pH. It is important to note that the type and amount of lime needed will vary depending on the current pH level and soil type. Agricultural limestone is commonly used to raise pH levels, while quicklime or hydrated lime can be used for more immediate results. Ready made pH up down solutions are easy to use and calculate the precise dose like Humboldts Secret pH Up and pH Down Control Kit.
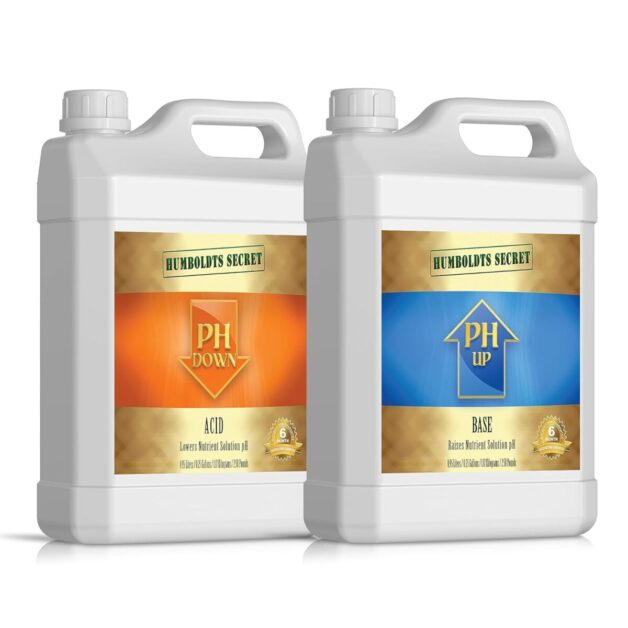

<a href="https://amzn.to/3xC56wc">Humboldts Secret pH Up and pH Down Control Kit</a> Quality product
What impressed me the most is its strength; a little amount goes a long way, making it highly cost-effective compared to other brands I’ve used.
Another inorganic method for adjusting soil pH is the application of sulfur to lower pH levels. Sulfur reacts with soil components to release sulfuric acid, which in turn reduces pH. Again, the appropriate type and amount of sulfur needed will depend on the specific soil conditions. Elemental sulfur is commonly used and can take several months to fully acidify the soil.
It is important to carefully follow the instructions provided by manufacturers when using inorganic methods and products to adjust soil pH. Applying excessive amounts can lead to imbalances and harm to plants. It is also worth noting that inorganic methods may not be suitable for all gardening situations, such as organic or sustainable gardening practices. Therefore, it is recommended to test the soil pH regularly and consult with a gardening expert or agronomist to determine the most appropriate method for adjusting soil pH in your specific garden.
Precautions and Best Practices for pH Adjustment in Garden Soil
Adjusting pH levels in garden soil is an important step for optimizing plant health and ensuring successful growth. However, it is essential to take certain precautions and follow best practices to avoid any potential negative impacts on both the soil and the plants.
One crucial precaution is to start with gradual pH adjustments. Sudden and drastic changes in soil pH can shock plants and disrupt their growth. Instead, it is recommended to make small adjustments over time, allowing plants to acclimate to the new pH levels. This can be achieved by incorporating amendments or additives slowly and monitoring the soil pH periodically.
Additionally, it is crucial to use pH-adjusting products specifically designed for garden soil. These products are formulated to provide the necessary nutrients while altering the soil’s pH levels. Using homemade mixtures or untested products can lead to imbalances in the soil and hinder plant growth. Therefore, it is advisable to rely on reputable brands and products recommended by gardening experts.
Another best practice is to follow the instructions provided by the pH adjustment product manufacturer. Each product may have specific guidelines regarding the application rate, frequency, and timing. Adhering to these instructions ensures accurate and consistent adjustments, enhancing the effectiveness of the product and minimizing the risk of overdosing.
Furthermore, testing the soil pH regularly is essential even after adjusting the levels. As soil characteristics and plant needs may change over time, maintaining optimal pH levels requires ongoing monitoring. By conducting regular pH tests, gardeners can identify any pH fluctuations and address them promptly, allowing for continuous plant health and growth. Soil pH and nutrients can be tested at convenience of home using this simple soil testing kit
By considering these precautions and best practices, you can effectively adjust the pH levels in your garden soil while minimizing the risk of adverse effects on your plants and the environment. Remember, a well-maintained pH balance contributes to healthy and vibrant plant growth, setting the stage for a thriving garden.
The Role of pH in Nutrient Availability for Plants
The pH level of garden soil plays a critical role in the availability of nutrients for plants. Nutrients in the soil exist in different forms, and their availability to plants is directly influenced by the soil’s pH. In slightly acidic to neutral soil, most essential nutrients are readily available for plants to uptake. However, extremes in soil pH can limit nutrient uptake and negatively impact plant health.
Influence of pH on Nutrient Availability for Plants:
- Optimal Nutrient Uptake: pH plays a crucial role in determining the availability of nutrients in the soil for plant uptake.
- Nutrient Solubility: The pH level influences the solubility of minerals and nutrients in the soil. Some nutrients are more accessible to plants at specific pH ranges.
- Acidic Conditions: In acidic soils (pH < 7), nutrients like iron, manganese, and aluminum are more available, but excessive acidity can lead to toxicity issues for certain plants.
- Alkaline Conditions: In alkaline soils (pH > 7), nutrients such as phosphorus, calcium, and magnesium are more accessible, but micronutrient availability may decrease.
- Neutral pH (Around 6-7): Generally, a slightly acidic to neutral pH is optimal for most plants, as it provides a balanced availability of essential nutrients.
- pH and Root Uptake: pH levels influence the chemical forms of nutrients, affecting their absorption by plant roots. Suboptimal pH can hinder nutrient uptake, leading to deficiencies or toxicities.
- Soil Testing: Regular pH testing is essential to assess soil conditions and adjust them if needed, ensuring plants receive the right balance of nutrients for healthy growth.
When soil pH deviates from the optimal range, nutrient availability can be greatly affected. For example, in acidic soil, commonly referred to as having a low pH, essential nutrients such as phosphorus, calcium, and magnesium become less available to plants. On the other hand, in alkaline soil with a high pH, essential elements like iron, manganese, and zinc can become less accessible to plant roots. These fluctuations in nutrient availability can lead to nutrient deficiencies, stunted growth, and overall poor plant health.
Understanding the intricate relationship between soil pH and nutrient availability is crucial for gardeners and plant enthusiasts. By regularly testing and monitoring the pH of garden soil, it becomes possible to identify any imbalances in nutrient availability and take appropriate actions to rectify them. Whether it involves adjusting the pH through organic or inorganic methods or selecting plants that thrive in specific pH ranges, maintaining optimal soil pH levels ensures that plants have the best chance of absorbing the essential nutrients they need for healthy growth and development.
pH Testing and Balancing for Container Gardens
Container gardening is a popular choice for many gardening enthusiasts, as it allows for flexibility and convenience. However, ensuring the right pH levels in the soil is crucial for the success of your container garden. pH testing and balancing in container gardens is essential to provide optimal growing conditions for your plants.
To begin the process, it is important to conduct a pH test on your container soil. This can be done using a soil pH test kit, which is readily available at garden centers or online like this one
By following the step-by-step instructions provided with the kit, you can obtain accurate pH readings of your soil. The pH level will determine the acidity or alkalinity of your soil and will give you an idea of whether it is suitable for your plants. Once you have obtained the pH reading, it is time to assess whether any adjustments need to be made to bring the pH within the ideal range for your plants.
Maintaining the optimal pH level in container gardens can be achieved through the use of organic or inorganic methods and products. Organic options include the use of compost, peat moss, or well-rotted manure, which can help lower pH levels in alkaline soils or raise pH levels in acidic soils. Inorganic methods involve the use of pH-adjusting substances such as sulfur to lower pH or lime to raise pH. It is important to follow the recommended application rates and guidelines provided by manufacturers when using these products. Regular pH monitoring and adjustment will ensure the long-term success of your container garden and promote healthy plant growth.
pH Testing and Balancing for Raised Bed Gardens
Raised bed gardens can provide many benefits for gardeners, including improved drainage and soil structure. However, just like any other garden, it is essential to maintain the correct pH levels to ensure optimal plant health and growth. pH testing and balancing for raised bed gardens is a crucial step in achieving successful and bountiful harvests.
When it comes to testing the pH levels in raised bed gardens, there are various methods available. One of the most common and accurate methods is using a pH testing kit or meter. These tools allow gardeners to measure the acidity or alkalinity of the soil accurately. It is recommended to test the pH levels in different areas of the raised bed garden, as the pH can vary within a single garden. By testing multiple spots, gardeners can identify any inconsistencies and take appropriate measures to achieve a balanced pH throughout the bed.
Maintaining Optimal Soil pH Levels for Long-Term Garden Success
Maintaining optimal soil pH levels is crucial for long-term garden success. The pH level of your soil directly affects the availability of nutrients to your plants, and different plants thrive in different pH ranges. By understanding the ideal pH range for the plants you are growing and taking steps to adjust the soil pH accordingly, you can create an environment that promotes healthy plant growth and maximizes nutrient uptake.
One important aspect of maintaining optimal soil pH levels is regular testing. pH testing allows you to monitor the acidity or alkalinity of your soil and make informed decisions about pH adjustment. There are various testing methods available, including using pH test kits or meters, which provide quick and accurate results. Conducting pH tests at regular intervals throughout the year will help you identify any changes in soil pH and take appropriate action to maintain the desired pH range for your plants.
• Regular testing is crucial for maintaining optimal soil pH levels
• pH testing allows you to monitor acidity or alkalinity of the soil
• Different testing methods are available, such as pH test kits or meters
• Conducting regular tests helps identify changes in soil pH and take appropriate action
For more details check the video below:
FAQS
Why is it important to maintain optimal soil pH levels in a garden?
Maintaining optimal soil pH levels is crucial because it directly affects the availability of nutrients to plants. Different plants have different pH preferences, and if the soil pH is not within the ideal range, plants may struggle to absorb essential nutrients, leading to poor growth and productivity.
What are the factors that can affect soil pH and how do they impact plant health?
Factors such as the parent material of the soil, rainfall, organic matter decomposition, and the types of fertilizers used can affect soil pH. If the pH becomes too acidic or alkaline, it can hinder the availability of certain nutrients, resulting in nutrient deficiencies or toxicities in plants.
What are the different methods to test the pH of garden soil?
There are several methods to test soil pH, including using a pH test kit, pH meters, or sending soil samples to a laboratory for analysis. Each method has its own pros and cons, so it’s important to choose the one that suits your needs and budget.
How do I conduct a pH test on my garden soil?
Conducting a pH test on your garden soil typically involves collecting a soil sample, preparing it for testing, and then following the instructions provided by the chosen testing method. The article provides a step-by-step guide on how to conduct a pH test on your garden soil.
How do I interpret the pH test results and what do they mean for my plants?
pH test results are typically given on a scale of 0-14, where pH 7 is considered neutral, below 7 is acidic, and above 7 is alkaline. The article provides information on how to interpret pH test results and explains the optimal pH range for different types of plants.
Are there organic methods to adjust soil pH?
Yes, there are organic methods to adjust soil pH. The article discusses some organic methods and products that can be used to raise or lower soil pH, such as adding organic matter or using certain amendments like sulfur or lime.
What are inorganic methods to adjust soil pH?
Inorganic methods to adjust soil pH involve the use of chemical products. The article provides information on inorganic methods and products, such as the application of sulfur or aluminum sulfate for acidifying soil or using lime to raise pH.
Are there any precautions or best practices to consider when adjusting soil pH?
Yes, there are precautions and best practices to consider when adjusting soil pH. The article covers some important guidelines, such as wearing protective gear, following product instructions, avoiding over-application, and retesting soil pH after adjustments.
How does pH affect nutrient availability for plants?
pH plays a crucial role in nutrient availability for plants. The article explains how soil pH influences the solubility and mobility of various nutrients, affecting their accessibility to plant roots. Imbalanced pH levels can lead to nutrient deficiencies or toxicities.
Is pH testing and balancing important for container gardens and raised bed gardens as well?
Yes, pH testing and balancing are equally important for container gardens and raised bed gardens. The article provides specific sections dedicated to explaining pH testing and balancing methods for these types of gardens.
How can I maintain optimal soil pH levels in the long term for garden success?
The article concludes by providing some key tips for maintaining optimal soil pH levels in the long term, such as regular pH testing, using organic matter, practicing crop rotation, and monitoring the health of plants for any signs of nutrient deficiencies or imbalances.












