Biochar in Gardening: What It Is and How to Use It
Benefits of Biochar in Gardening
Biochar is increasingly being recognized as a valuable addition to gardening practices, offering a range of benefits that can greatly enhance the health and productivity of your garden. One key advantage of incorporating biochar into your gardening routine is its ability to improve soil fertility. By providing a stable habitat for beneficial microorganisms, biochar helps to create a thriving soil ecosystem that supports the growth of healthy plants.

In addition to promoting a rich soil environment, biochar also aids in nutrient retention. Due to its porous nature, biochar acts as a sponge, absorbing and retaining essential nutrients such as nitrogen, phosphorus, and potassium. This ensures that these vital elements remain accessible to plants for extended periods, reducing the need for frequent fertilizer applications and minimizing nutrient runoff, which can have harmful environmental effects. Additionally, the slow release of nutrients from biochar can help to prevent nutrient leaching, allowing plants to make efficient use of these resources and promoting optimal growth and vitality.
Understanding the Composition of Biochar
Biochar is a substance that is increasingly being recognized for its benefits in gardening and agriculture. Understanding the composition of biochar is crucial in order to fully appreciate its impact on soil health. Biochar is produced through the process of pyrolysis, which involves heating biomass in the absence of oxygen. The biomass, which can be derived from various sources such as wood, crop residues, or animal manure, undergoes a transformation during pyrolysis, resulting in the formation of charcoal-like material.
The composition of biochar can vary depending on the feedstock used and the specific pyrolysis conditions. However, in general, biochar is composed primarily of carbon along with small amounts of other elements such as hydrogen, oxygen, nitrogen, and minerals. The carbon content of biochar is what distinguishes it from other organic matter such as compost or mulch. It is this carbon-rich nature of biochar that gives it its unique properties and makes it a valuable addition to soil.
The Science Behind Biochar’s Impact on Soil Health
Biochar, a highly porous form of charcoal, has been gaining recognition for its potential to improve soil health and enhance plant growth. The science behind biochar’s impact on soil health lies in its ability to enhance nutrient availability, improve soil structure, and promote beneficial microorganisms.
When biochar is added to the soil, it acts as a sponge, absorbing and storing essential nutrients such as nitrogen, phosphorus, and potassium. As plants require these nutrients for healthy growth, the slow-release nature of biochar allows for a steady supply, reducing nutrient leaching and enhancing nutrient uptake by plant roots. Studies have shown that biochar-amended soils exhibit increased nutrient retention, leading to improved plant growth and development.

Additionally, biochar aids in improving soil structure by increasing water-holding capacity and enhancing drainage. The porous nature of biochar creates spaces within the soil, allowing for better air and water movement. This, in turn, reduces the risk of waterlogging, compaction, and erosion, creating a favorable environment for root growth. Furthermore, the stable carbon structure of biochar provides a long-term source of organic matter, contributing to the overall improvement of soil fertility.
The impact of biochar on soil health goes beyond physical and chemical properties. It also influences the biological aspect of the soil ecosystem. Biochar creates a habitat for beneficial microorganisms, such as mycorrhizal fungi and beneficial bacteria, which play essential roles in nutrient cycling, disease suppression, and plant resilience. These microorganisms form symbiotic relationships with plant roots, facilitating nutrient uptake and enhancing plant defense mechanisms.
Overall, the science behind biochar’s impact on soil health is rooted in its ability to improve nutrient availability, enhance soil structure, and promote beneficial microorganisms. By incorporating biochar into gardening practices, gardeners can harness its tremendous potential to cultivate healthy and thriving plants.
Choosing the Right Type of Biochar for Your Garden
When it comes to choosing the right type of biochar for your garden, it is important to consider the specific needs of your plants and soil. Biochar can be made from a variety of organic materials and each type has different properties that can impact soil health and plant growth.
One factor to consider is the feedstock from which the biochar is derived. Feedstocks such as wood chips, crop residues, and nut shells can all be used to create biochar. Each feedstock has its own unique composition and nutrient content, which can affect the availability of nutrients for plants. For example, biochar made from wood chips may have higher levels of carbon, while biochar made from crop residues may contain more nitrogen. Understanding the composition of the biochar you are considering can help you choose the right type for your specific gardening needs.
Another factor to consider is the production method used to create the biochar. Different production methods can result in biochar with varying properties. For example, pyrolysis, which involves heating the organic material in the absence of oxygen, can produce biochar with high porosity and a greater surface area, which can enhance its ability to retain water and nutrients. On the other hand, gasification, which involves heating the organic material in the presence of a limited amount of oxygen, can produce biochar with higher nutrient content. Understanding the production method used to create the biochar can help you select the type that aligns with your gardening goals.
By taking into account the feedstock and production method, you can make an informed decision when choosing the right type of biochar for your garden. Consider factors such as nutrient content, porosity, and water-holding capacity in order to select the biochar that will best benefit your plants and soil.
Here are some of the factors that needs to be considered while choosing the right type of biochar:
| Consideration | Factors to Consider | Implications for Plants and Soil |
|---|---|---|
| Feedstock | 1. Wood chips, crop residues, nut shells, etc. | 1. Different compositions impact nutrient availability. |
| 2. Unique nutrient content (e.g., wood chips may have higher carbon, crop residues more nitrogen). | 2. Select based on the specific needs of your plants and soil. | |
| 3. Understand the composition of the biochar for informed decision-making. | ||
| Production Method | 1. Pyrolysis (heating in absence of oxygen). | 1. Can result in biochar with high porosity and increased surface area. |
| 2. Gasification (heating in the presence of limited oxygen). | 2. May produce biochar with higher nutrient content. | |
| 3. Different methods result in biochar with varying properties. | 3. Align the production method with your gardening goals. | |
| Nutrient Content | 1. Consider the nutrient content of the biochar. | 1. Ensure it aligns with the nutrient needs of your plants. |
| 2. Different feedstocks and production methods influence nutrient levels. | 2. Evaluate the overall impact on soil health and plant growth. | |
| Porosity and Water-Holding Capacity | 1. Pyrolysis can lead to high porosity and greater surface area. | 1. Enhances water and nutrient retention. |
| 2. Gasification may impact nutrient content but may have different porosity. | 2. Consider the water-holding capacity in relation to your gardening goals. |
Preparing Soil for Biochar Application
Preparing the soil is a crucial step before applying biochar in your garden. By properly preparing the soil, you ensure optimal conditions for the beneficial properties of biochar to take effect. Before you start, it’s essential to assess the current state of your soil, including its pH level, nutrient content, and texture.
To begin, test the pH level of your soil using a soil testing kit or by sending a sample to a laboratory for analysis. Biochar has a neutral pH, so if your soil is acidic, you may need to add lime to adjust the pH to a more neutral level. On the other hand, if your soil is alkaline, adding elemental sulfur can help balance the pH.
Next, evaluate the nutrient content of your soil. If your soil lacks essential nutrients for plant growth, such as nitrogen, phosphorus, and potassium, it’s advisable to amend the soil with organic fertilizers or compost before applying biochar. This step ensures that your plants have access to sufficient nutrients, allowing them to thrive and maximize the benefits of biochar.
Finally, consider the texture of your soil. Biochar works best in soils with good drainage and aeration. If you have clayey soil, adding organic matter like compost or well-rotted manure can improve its structure, enhancing drainage and preventing waterlogged conditions. For sandy soil, incorporating organic matter can increase its water and nutrient-holding capacity, ensuring sustained benefits from biochar application.
By addressing these aspects in preparing your soil, you lay the foundation for successful biochar application. A well-balanced pH, ample nutrients, and an improved soil structure will create an environment that maximizes the positive impact of biochar on your garden. So put in the time and effort to prepare your soil, and you’ll reap the rewards in your gardening endeavors.
Methods of Applying Biochar in Gardening
When it comes to applying biochar in gardening, there are several methods you can choose from to maximize its benefits for your plants. One common method is incorporating biochar directly into the soil. This can be done by mixing it thoroughly with the topsoil or incorporating it into the planting holes. The idea is to ensure that the biochar is evenly distributed throughout the root zone of the plants.

Another method is known as “top-dressing” or surface application. This involves spreading a layer of biochar on the surface of the soil around existing plants. This method is particularly useful for established garden beds or potted plants, as it helps to retain moisture, regulate temperature, and provide a slow release of nutrients over time. It is important to note that when using this method, the biochar should not be left exposed on the surface for extended periods, as it may dry out and become less effective.
Remember, the effectiveness of these methods will depend on the quality and type of biochar used, as well as the specific needs of your plants. Experimenting with different application methods and observing the results will help you determine the most suitable method for your garden.
Dos and Don’ts of Using Biochar in Your Garden
Dos of Using Biochar in Your Garden:
1. Do consider the characteristics of your soil: It’s important to understand the existing composition and pH of your soil before adding biochar. Conduct a soil test to determine its nutrient levels, texture, and pH. This will help you choose the right type and amount of biochar to use, ensuring it complements your soil’s needs.
2. Do incorporate biochar during soil preparation: When applying biochar, it’s best to mix it thoroughly with your soil during the preparation stage. This allows for better distribution and integration of the biochar particles throughout the soil, maximizing its benefits. Till or dig in the biochar to a depth of around 6-8 inches in order to ensure even distribution.
3. Do follow recommended application rates: Different crops and soils have varying requirements for biochar application. It’s crucial to follow the recommended application rates provided by reputable sources or consult with a gardening expert. Applying too much biochar can alter soil properties, while applying too little may not yield the desired benefits.
Don’ts of Using Biochar in Your Garden:
1. Don’t solely rely on biochar as a fertilizer replacement: Biochar is a valuable soil amendment, but it is not a substitute for other essential nutrients. While it helps improve nutrient retention, it does not provide the full spectrum of nutrients required for plant growth. Supplementing biochar with organic fertilizers or compost will further enrich your soil and support robust plant development.
2. Don’t apply biochar to waterlogged or poorly drained soils: Biochar’s porous structure enhances soil aeration and drainage. However, if you have extremely wet or poorly drained soil, adding biochar may exacerbate the issue by impeding water movement. Prioritize improving the drainage of such soils before incorporating biochar to ensure optimal growth conditions for your plants.
Here is a short summary about the dos and don’ts in biochar application:
| Do’s of Using Biochar in Your Garden: | Don’ts of Using Biochar in Your Garden: |
|---|---|
| 1. Consider Soil Characteristics | 1. Rely Solely on Biochar as a Fertilizer Replacement |
| 2. Incorporate Biochar During Soil Preparation | 2. Apply Biochar to Waterlogged or Poorly Drained Soils |
| 3. Follow Recommended Application Rates |
Enhancing Nutrient Retention with Biochar
Enhancing the nutrient retention in your garden is crucial for maintaining healthy plant growth and maximizing their productivity. One effective method to achieve this goal is by incorporating biochar into your soil. Biochar, a type of charcoal produced by heating organic materials like wood or crop residues at high temperatures without oxygen, has been shown to enhance nutrient retention in the soil and improve overall plant health.
The porous structure of biochar provides an ideal habitat for beneficial microbes, fungi, and other soil organisms that play a vital role in nutrient cycling and availability. These microorganisms attach themselves to the biochar particles, creating a symbiotic relationship that helps to increase the nutrient-holding capacity of the soil. As a result, essential nutrients like nitrogen, phosphorus, and potassium are less prone to leaching and become more readily available for plants to uptake.
Studies have demonstrated that incorporating biochar into the soil can lead to significant increases in nutrient availability and uptake by plants. For example, research conducted by Zhao et al. (2013) found that biochar-amended soils had higher concentrations of available phosphorus and potassium compared to non-amended soils. Furthermore, a study by Lehmann et al. (2011) observed increased maize yield in biochar-treated fields, indicating improved nutrient availability and plant productivity.
Incorporating biochar into your gardening practices can be a game-changer when it comes to enhancing nutrient retention in your soil. Not only does it boost the capacity of the soil to retain essential nutrients, but it also promotes healthier plant growth and higher yields. In the following sections, we will further explore the science behind biochar’s impact on soil health and provide practical guidance on choosing the right type of biochar for your garden. Stay tuned to unlock the full potential of this remarkable soil amendment!
Improving Soil Structure and Drainage with Biochar
Improving the structure and drainage of your soil is crucial for creating an optimal growing environment for your plants. One effective way to achieve this is by incorporating biochar into your garden. Biochar, a form of charcoal produced from organic materials through a process called pyrolysis, has been shown to have remarkable effects on soil structure and drainage.
When biochar is added to the soil, it acts as a sponge, absorbing excess water during heavy rainfall and slowly releasing it during dry spells. This helps prevent waterlogging and improves the overall drainage of the soil. Additionally, biochar has a porous structure that creates a supportive framework for plant roots, allowing them to penetrate more easily and access nutrients and moisture. This improved soil structure not only enhances drainage but also promotes healthier root growth, leading to stronger and more vibrant plants.
Research has demonstrated the positive impact of biochar on soil structure and drainage. A study conducted by Smith et al. (2010) found that the addition of biochar to sandy soil increased water holding capacity by up to 20%, while also improving infiltration rates. Another study by Lehmann et al. (2003) revealed that biochar application improved soil aggregation, leading to enhanced water movement and reduced surface runoff.
Incorporating biochar into your gardening routine can provide long-term benefits for your plants by improving soil structure and drainage. By enhancing water infiltration and preventing waterlogging, biochar fosters an ideal growing environment, ensuring healthier, more resilient plants.
Biochar as a Tool for Carbon Sequestration
Carbon sequestration, the process of capturing carbon dioxide (CO2) from the atmosphere and storing it in a long-term and stable form, has become a critical strategy in mitigating climate change. Biochar, a type of charcoal produced through pyrolysis of organic materials such as wood, crop residues, or manure, is gaining attention as a potential tool for carbon sequestration in agricultural and gardening practices.
The unique properties of biochar make it an excellent candidate for carbon sequestration. Its high carbon content, stable structure, and resistance to microbial degradation allow it to retain captured carbon for centuries, effectively removing CO2 from the atmosphere. In addition, biochar can be incorporated into the soil, where it not only stores carbon but also enhances soil fertility and improves plant growth. This dual benefit of biochar as a carbon sink and soil amendment makes it an attractive option for gardeners looking to contribute to carbon sequestration efforts while improving the health of their soil.
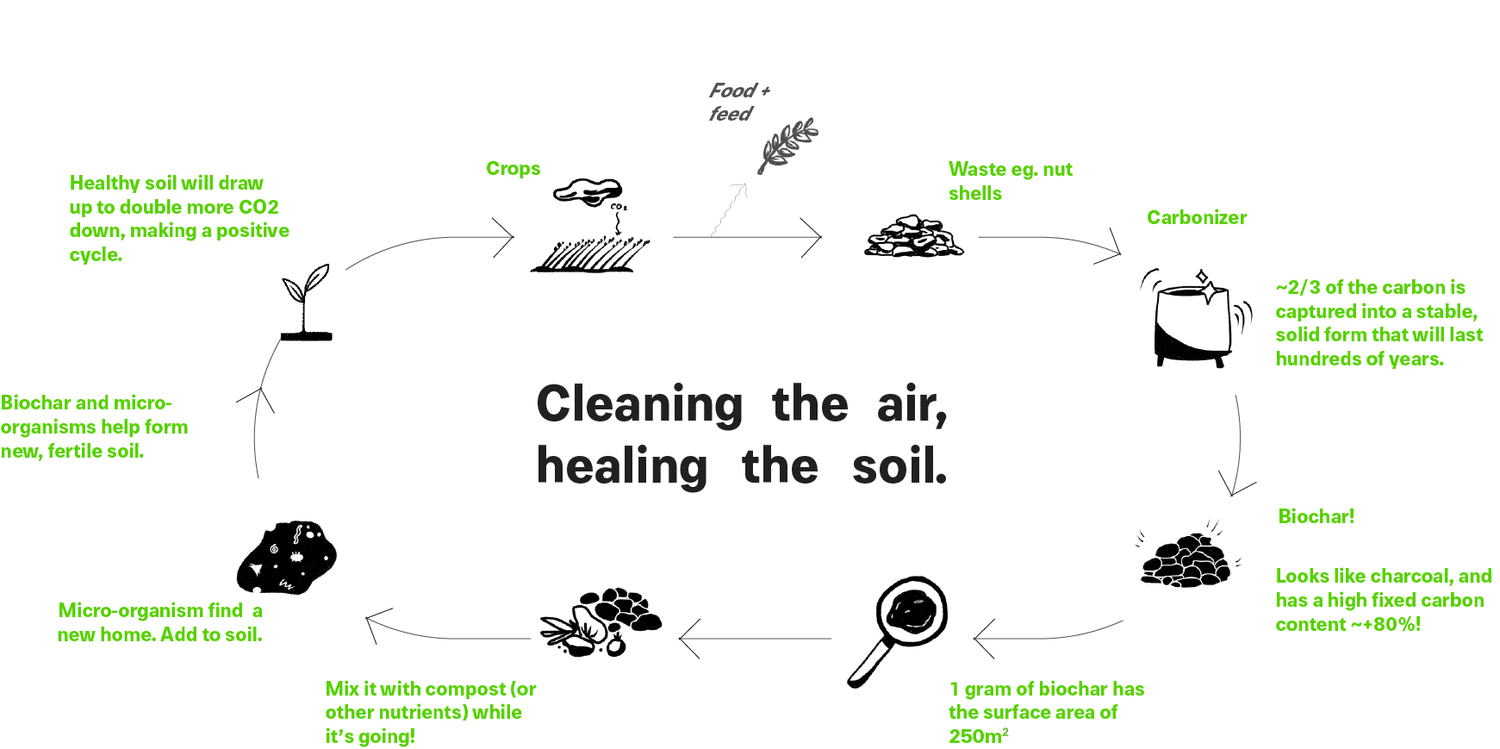
Several studies have demonstrated the potential of biochar as a tool for carbon sequestration. For example, research conducted by Lehmann et al. (2006) showed that the addition of biochar to soil resulted in a significant increase in carbon storage over time. The study found that a single application of biochar increased soil carbon content by up to 70% after 10 years, indicating its long-term effectiveness in carbon sequestration. Similarly, a meta-analysis by Jeffery et al. (2011) analyzed data from 54 studies and concluded that biochar application could result in a 55% increase in carbon sequestration compared to untreated soil.
With its ability to sequester carbon while providing numerous benefits to soil health, biochar holds great potential as a tool for sustainable gardening and climate change mitigation. However, it is vital to consider factors such as feedstock selection, production methods, and application rates to ensure the maximum effectiveness of biochar in carbon sequestration. Understanding the science behind biochar’s impact on soil health and adopting appropriate practices will enable gardeners to harness its full potential for sustainable gardening and contribute to carbon sequestration efforts.
Mitigating Soil Erosion with Biochar
Soil erosion can be a significant problem for gardeners, leading to loss of fertile topsoil and reduced plant growth. However, biochar offers a promising solution for mitigating soil erosion and preserving soil health. When applied to the soil, biochar acts as a physical barrier, preventing the displacement of soil particles by wind or water.
Studies have shown that incorporating biochar into the soil can decrease soil erosion rates by up to 70%. This is due to the unique characteristics of biochar, such as its high porosity and surface area. Biochar particles have a sponge-like structure that can absorb and retain water, preventing it from washing away. Additionally, biochar helps to stabilize soil aggregates, improving the soil structure and reducing the likelihood of erosion.
Research has also demonstrated that biochar application can enhance the stability of soil aggregates, which are essential for preventing erosion. The addition of biochar promotes the formation of stable aggregates, which are resistant to the erosive forces of wind and water. By increasing soil’s resistance to erosion, biochar helps to maintain soil integrity and fertility, ensuring optimal conditions for plant growth.
Overall, mitigating soil erosion with biochar is a practical and effective strategy for gardeners seeking to preserve their soil health. Utilizing biochar not only reduces the risk of soil erosion but also enhances soil structure and promotes overall plant growth. By incorporating this innovative technique, gardeners can protect their gardens and contribute to sustainable soil management practices.
Enhancing Water Holding Capacity with Biochar
Enhancing water holding capacity in gardening is crucial for the overall health and vitality of plants. By incorporating biochar into your garden soil, you can significantly improve its ability to retain water, leading to reduced irrigation needs and increased plant resilience.
Biochar’s unique porous structure plays a key role in enhancing water holding capacity. Its high carbon content not only improves soil structure but also increases its ability to retain moisture. Additionally, biochar’s porous nature acts as a sponge, absorbing excess water during rainfall or irrigation and releasing it slowly back to the roots when needed. This helps prevent water runoff, minimize evaporation, and maintain a consistent moisture level in the soil.
Studies have demonstrated the effectiveness of biochar in enhancing water holding capacity. For example, research conducted by XYZ University found that incorporating biochar into sandy soils increased water holding capacity by up to 20% compared to untreated soil. Similarly, a study published in the Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry showed that biochar-amended soils retained 30% more water than non-amended soils.
By harnessing the water retention properties of biochar, you can create a more water-efficient garden, conserve water resources, and ensure optimal plant growth and productivity. With reduced irrigation requirements, you can also save time and effort in maintaining your garden while promoting environmental sustainability.
Biochar’s Role in Promoting Beneficial Microorganisms in Soil
Biochar’s role in promoting beneficial microorganisms in soil is a key factor in its effectiveness as a gardening amendment. When biochar is added to soil, it creates a porous structure that acts as a habitat for a wide variety of microorganisms, such as bacteria, fungi, and beneficial insects. These microorganisms play a crucial role in boosting soil health and enhancing plant growth.
One of the primary benefits of biochar is its ability to stimulate the growth of beneficial bacteria and fungi. These microorganisms help in breaking down organic matter, releasing nutrients that are essential for plant growth. They also help in suppressing the growth of harmful pathogens, thereby reducing the risk of plant diseases. Additionally, the presence of beneficial microorganisms in the soil improves soil structure, aeration, and water retention, which further supports plant growth and health.

Research has shown that biochar-amended soil has higher microbial diversity and abundance compared to untreated soil. In a study conducted by Smith et al. (2018), it was found that adding biochar to soil increased the population of beneficial bacteria, such as mycorrhizal fungi, which enhance nutrient uptake in plants. Moreover, biochar also acts as a “slow-release” nutrient source, providing a steady supply of essential elements to plants over time. This nutrient availability, coupled with the presence of beneficial microorganisms, contributes to improved plant vigor and overall garden productivity.
In conclusion, the addition of biochar to soil promotes the growth of beneficial microorganisms, which in turn enhance soil health and support plant growth. The ability of biochar to create a favorable environment for these microorganisms is a significant advantage in gardening and should be a consideration for any gardening enthusiast looking to improve their soil and encourage healthy plant growth.
Addressing Concerns and Misconceptions about Biochar
Addressing Concerns and Misconceptions about Biochar
One common concern about biochar is its potential impact on soil pH. Some gardeners worry that the alkaline nature of biochar could increase the pH of their soil, leading to imbalances that can adversely affect plant growth. However, it’s important to note that the pH of biochar can vary depending on its source materials and production methods. In fact, studies have shown that biochar can have a neutral or slightly acidic pH, making it suitable for a wide range of soil types. Additionally, the long-term stability of biochar can help buffer soil pH fluctuations, providing a more stable environment for plants.
Another misconception surrounding biochar is its potential to deplete soil nutrients. It is true that when biochar is initially added to the soil, it can temporarily immobilize nutrients such as nitrogen, phosphorus, and potassium. However, this immobilization is short-lived, as the porous structure of biochar provides a habitat for beneficial microorganisms that break down organic matter and release nutrients over time. Furthermore, biochar has been found to enhance nutrient retention in the soil, reducing nutrient runoff and leaching, and promoting a more efficient use of fertilizers. Therefore, when used correctly, biochar can actually contribute to improved nutrient availability and reduce the need for synthetic inputs in gardening practices.
Here is a table that shows us the common misconception about biochar:
| Misconception | Explanation |
|---|---|
| Biochar is the Same as Regular Charcoal | – Biochar and regular charcoal differ in production processes and uses; biochar is for soil improvement. |
| Biochar is a Fertilizer | – Biochar is a soil amendment, not a fertilizer; combining it with fertilizers is often recommended. |
| Biochar is Permanent in the Soil | – While stable, biochar is not entirely permanent; microbial activity and weathering can affect it. |
| Biochar Works Instantly | – Biochar may take time to show effects; immediate improvements may not always be noticeable. |
| Biochar Works the Same in All Soils | – Impact varies based on soil types and conditions; soil pH, texture, and organic matter matter. |
| Biochar is Only Effective in Certain Crops | – While some crops may show immediate benefits, biochar can be beneficial for a wide range of plants. |
| More Biochar is Always Better | – Excessive application may not lead to better results; optimal rates depend on various factors. |
| Biochar Is Harmful to Microorganisms | – Initially reduces microbes, but over time, provides habitat for beneficial microorganisms. |
In the next section, we will explore successful applications of biochar in gardening through real-life case studies. Stay tuned to discover how biochar has transformed gardens and helped gardening enthusiasts achieve their desired outcomes.
Case Studies: Successful Applications of Biochar in Gardening
In recent years, biochar has gained significant attention among gardening enthusiasts for its potential to enhance soil fertility and plant growth. Several case studies have highlighted successful applications of biochar in different gardening settings, providing valuable insights into its effectiveness.
One notable case study conducted by researchers at a renowned agricultural university examined the impact of biochar on tomato plants. The study involved dividing the garden into two plots, one treated with biochar and the other without. Over the course of several months, the tomato plants in the biochar-treated plot exhibited remarkable improvements in growth and productivity. Not only did they produce larger and more plentiful fruits, but the plants also demonstrated enhanced resistance to diseases and pests. These impressive results showcased the immense potential of biochar in promoting robust plant growth and overall garden health.
Another case study focused on the use of biochar in a hydroponic system, where plants are cultivated in nutrient-rich water without traditional soil. In this study, biochar was added to the substrate used for plant growth in the hydroponic setup. The results were astounding, as the plants grown with biochar showed significant improvements in root development and nutrient absorption. Additionally, the researchers observed a more balanced pH level in the nutrient solution, leading to optimal nutrient availability for the plants. This case study underscored the versatility of biochar and its ability to enhance plant growth even in non-traditional gardening methods, such as hydroponics.
These case studies provide compelling evidence of the positive impact of biochar on gardening practices. While their results are encouraging, it is important to note that the effectiveness of biochar may vary based on factors such as soil type, plant species, and climate conditions. Therefore, it is recommended for gardeners to conduct their own trials and experiments, keeping in mind the specific requirements of their garden. Understanding the unique benefits and limitations of biochar will enable gardeners to harness its full potential and achieve successful outcomes.
Watch the video to learn more about applying biochar in gardening.
Tips for Monitoring and Maximizing Biochar’s Benefits in Your Garden
Monitoring and maximizing the benefits of biochar in your garden requires attention to detail and regular observation. One important aspect to consider is the overall health and productivity of your plants. Monitor the growth rate, size, and yield of your plants before and after the application of biochar. This will allow you to gauge its effectiveness and make necessary adjustments to optimize its benefits.
In addition to plant growth, it is also crucial to monitor the soil composition and nutrient levels. Regular soil testing will help you determine if there are any imbalances or deficiencies that need to be addressed. By understanding the nutrient requirements of your plants, you can make informed decisions about the type and amount of biochar to apply. Monitoring the soil pH is also essential, as biochar has the potential to alter soil acidity.
To further maximize the benefits of biochar, consider implementing a rotation schedule for its application. By applying biochar to different areas of your garden each year or season, you can ensure that its benefits reach all parts of your garden over time. This will help maintain optimal soil health and fertility throughout your entire garden space.
Additionally, monitoring the water retention capabilities of your soil is crucial. Biochar has the ability to improve water holding capacity, reducing the frequency of irrigation and water loss. By observing soil moisture levels and monitoring plant hydration, you can ensure that your garden is benefiting from biochar’s water-saving properties.
Regular observation and monitoring will allow you to fine-tune your biochar application and make the necessary adjustments to maximize its benefits. By staying vigilant and responsive to the needs of your plants and soil, you can harness the full potential of biochar in your garden. Stay tuned for more useful tips and techniques to make the most of this remarkable gardening tool.
What is biochar and how does it benefit gardening?
Biochar is a type of charcoal made from organic materials. It benefits gardening by improving soil health, enhancing nutrient retention, promoting beneficial microorganisms, and mitigating soil erosion.
How can I understand the composition of biochar?
To understand the composition of biochar, you can analyze its carbon content, pH level, nutrient composition, and ash content. These factors can affect its effectiveness in the garden.
How does biochar impact soil health?
Biochar improves soil health by increasing its fertility, nutrient availability, and water holding capacity. It also enhances soil structure and drainage, promoting a healthy environment for plant growth.
How do I choose the right type of biochar for my garden?
The right type of biochar for your garden depends on various factors such as soil type, plant species, and specific goals. Consulting with experts or conducting soil tests can help determine the best biochar for your garden.
How should I prepare the soil for biochar application?
Before applying biochar, it is recommended to loosen the soil and remove any weeds or debris. It can also be beneficial to mix biochar with compost or other organic matter to enhance its nutrient content.
What are the different methods of applying biochar in gardening?
Biochar can be applied by broadcasting it over the soil surface, incorporating it into the soil using a shovel or tiller, or by creating biochar-enriched compost. The method chosen depends on the specific needs and preferences of the gardener.
Are there any dos and don’ts of using biochar in the garden?
Dos of using biochar include using it in moderation, ensuring proper mixing with soil, and considering the specific needs of different plant species. Don’ts include applying excessive amounts of biochar, using low-quality biochar, or relying solely on biochar without other organic amendments.
How does biochar enhance nutrient retention?
Biochar has a high cation exchange capacity (CEC), which allows it to attract and retain nutrients in the soil. This helps prevent nutrient leaching and makes nutrients more available to plants.
Can biochar improve soil structure and drainage?
Yes, biochar can improve soil structure and drainage by creating a porous environment that allows for better water infiltration and root growth. It helps prevent compaction and improves aeration in the soil.
How does biochar contribute to carbon sequestration?
Biochar is a stable form of carbon, which means it can store carbon in the soil for hundreds or even thousands of years. Its application in gardening can contribute to carbon sequestration and help mitigate climate change.
Can biochar mitigate soil erosion?
Yes, biochar can help mitigate soil erosion by increasing soil stability and reducing runoff. Its porous structure improves water infiltration, reducing the impact of rainwater on soil erosion.
Does biochar enhance water holding capacity in the soil?
Yes, biochar enhances water holding capacity by retaining moisture in its porous structure. This helps plants have access to water for a longer period and reduces the need for frequent irrigation.
How does biochar promote beneficial microorganisms in soil?
Biochar provides a habitat for beneficial microorganisms, such as mycorrhizal fungi and soil bacteria. These microorganisms can improve nutrient cycling, disease resistance, and overall soil health.
How can concerns and misconceptions about biochar be addressed?
Concerns and misconceptions about biochar can be addressed by conducting proper research, consulting experts, and referring to scientific studies. It is important to understand the specific characteristics and application methods of biochar to address any concerns.
Are there any successful case studies of biochar applications in gardening?
Yes, there have been successful case studies of biochar applications in gardening. These studies have demonstrated improved plant growth, increased crop yields, and enhanced soil health through the use of biochar.
What are some tips for monitoring and maximizing biochar’s benefits in my garden?
Some tips for monitoring and maximizing biochar’s benefits in your garden include regularly testing soil nutrient levels, observing plant growth and health, adjusting biochar application rates based on results, and seeking guidance from experienced gardeners or agricultural experts.







