How to Avoid Nitrogen Toxicity in Your Garden Plants
Did you know that too much of a good thing can actually harm your garden? Nitrogen, an essential nutrient for plant growth, can turn toxic if overused, leading to yellowing leaves and stunted growth. In this guide, we’ll explore practical tips to prevent nitrogen toxicity and keep your garden thriving. With years of gardening expertise, we understand the delicate balance needed for healthy plants.
Whether you’re a seasoned gardener or just starting out, understanding how to manage nitrogen levels is crucial. Read on to learn how to avoid this common pitfall and ensure your garden flourishes with vibrant, lush greenery. Let’s dive into the science of soil management and plant care!
Table of Contents
Common Causes of Nitrogen Toxicity in Garden Plants
Nitrogen is an essential element for the growth and development of plants. However, too much of a good thing can be harmful, and nitrogen toxicity is a common issue that many gardeners face. Understanding the common causes of nitrogen toxicity can help prevent this problem and ensure the health of your garden plants.
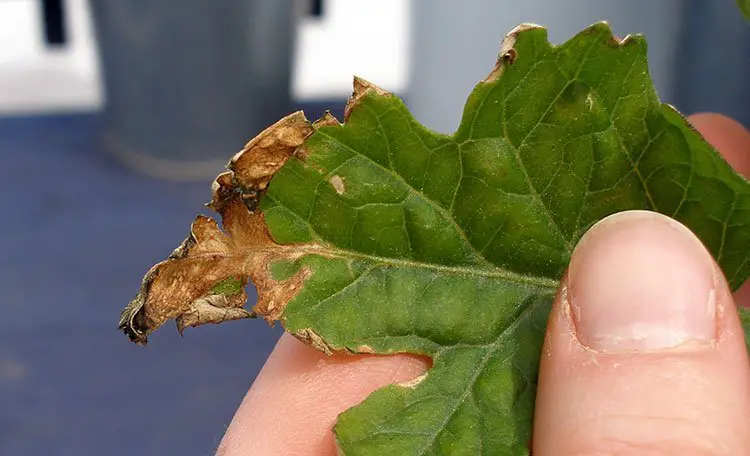

- Excessive Fertilization:
- Nitrogen toxicity often occurs when gardeners apply an excessive amount of nitrogen-rich fertilizer to their plants.
- The excess nitrogen accumulates in the soil, overwhelming the plants’ ability to intake and process it effectively.
- This can lead to toxicity symptoms such as leaf discoloration, stunted growth, and reduced overall health.
- Types of Nitrogen Fertilizers:
- Certain types of fertilizers, particularly those high in ammonium or nitrate forms of nitrogen, are more likely to cause toxicity.
- Ammonium-based fertilizers release nitrogen slowly, while nitrate-based ones provide a rapid nitrogen supply.
- Overuse of either type can disrupt the balance and harm plant health.
- Application Guidelines:
- To avoid nitrogen toxicity, follow recommended dosage and application instructions for fertilizers.
- Consider factors like soil type, plant species, and growth stage when determining fertilizer amounts.
- Regular soil testing can help monitor nutrient levels and prevent overloading plants with nitrogen.
Remember, balanced fertilization is essential for healthy plant growth. 🌱🌿🌼
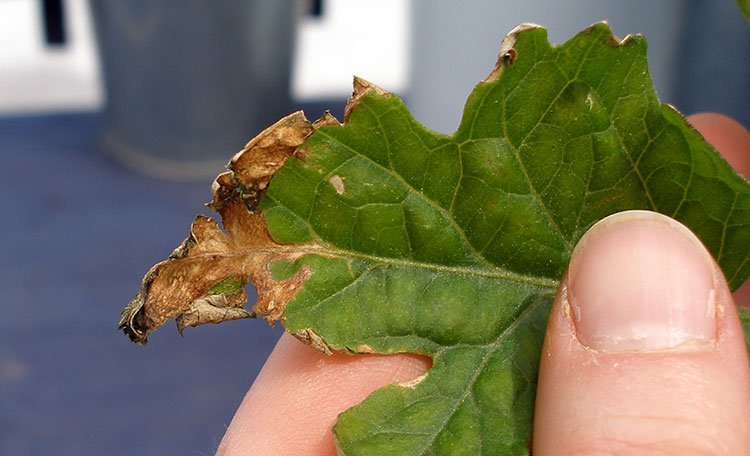
Signs and Symptoms of Nitrogen Toxicity in Garden Plants
Nitrogen is an essential element for plant growth and development, but excessive levels can lead to toxicity in garden plants. Recognizing the signs and symptoms of nitrogen toxicity is crucial for maintaining a healthy gardening environment.
- Lush Vegetative Growth
- Abundance of dark green foliage
- Rapid shoot development
- Leaves lack vitality, becoming more susceptible to diseases and pests
- Stunted or Distorted Growth
- Imbalance of other nutrients such as calcium, potassium, and magnesium
- Negative impact on root development and overall plant structure
- Results in stunted or abnormal growth patterns
- Negative Influence on Flowering and Fruiting
- Delayed or inhibited flowering
- Poor or no fruit set
- Production of weak or inferior-quality fruits due to nutrient imbalances
Being vigilant about signs and symptoms of nitrogen toxicity is crucial for maintaining a healthy and thriving garden. By identifying these indications early on, gardeners can take appropriate measures to address the issue and restore a balanced and optimal growing environment for their plants.
Understanding the Role of Nitrogen in Plant Growth
Nitrogen is an essential nutrient for the growth and development of plants. It plays a fundamental role in various biochemical processes, making it a key element in plant physiology.

- Chlorophyll Production
- Supports chlorophyll production, crucial for photosynthesis
- Enables conversion of sunlight into chemical energy
- Synthesizes sugars and other organic compounds necessary for growth
- Amino Acid Formation
- Vital component of amino acids, the building blocks of proteins
- Proteins are essential for cell division, enzyme production, and overall plant structure
- Root Development
- Involved in root development
- Enhances the plant’s ability to absorb water and nutrients from the soil
Importance of Maintaining Proper Nitrogen Levels
- Significance in Plant Growth
- Maintaining proper nitrogen levels is paramount for healthy plant growth
- Risks of Excessive Nitrogen
- Excessive nitrogen can lead to toxicity, hindering plant health
- Understanding nitrogen’s role helps in identifying and preventing nitrogen toxicity
Implementing strategies to balance nitrogen levels is essential for preventing toxicity and ensuring optimal plant health.By ensuring a balanced nitrogen supply, gardeners can optimize their plants’ overall health and productivity.
Importance of Proper Nitrogen Levels in Garden Plants
Maintaining proper nitrogen levels in garden plants is crucial for their overall health and growth.
- Role of Nitrogen:
- Nitrogen is essential for various plant processes, including leaf and stem development, protein synthesis, and photosynthesis.
- It is a critical component of chlorophyll, which enables plants to capture sunlight and convert it into energy.
- Balancing Nitrogen Levels:
- Achieving the right balance of nitrogen is crucial.
- Deficiency: Insufficient nitrogen leads to stunted growth, yellowing leaves, and reduced yields.
- Excess: Too much nitrogen can result in nitrogen toxicity, negatively affecting plant health.
- Gardener’s Responsibility:
- Gardeners must understand nitrogen’s importance and implement strategies to maintain optimal levels.
- Proper fertilization practices, soil testing, and monitoring plant health are essential.
Remember, balanced nitrogen levels contribute to healthy and productive plants!
| Importance of Proper Nitrogen Levels in Garden Plants | Key Points |
|---|---|
| 1. Essential for Growth and Development | – Structural Component: Nitrogen is a key component of amino acids, proteins, and chlorophyll, essential for plant growth. |
| – Cell Division: Nitrogen supports cell division and elongation, contributing to overall plant development. | |
| 2. Promotes Lush Foliage and Green Color | – Chlorophyll Synthesis: Nitrogen is a central element in chlorophyll, the pigment responsible for green coloration. |
| – Photosynthesis: Facilitates photosynthesis, crucial for energy production and carbohydrate synthesis. | |
| 3. Enhances Yield and Crop Productivity | – Increased Biomass: Adequate nitrogen levels result in larger and more vigorous plants, leading to higher yields. |
| – Fruit and Seed Formation: Nitrogen supports the development of fruits, seeds, and reproductive structures. | |
| 4. Improves Resistance to Stress and Diseases | – Stress Tolerance: Plants with optimal nitrogen levels are better equipped to handle environmental stressors. |
| – Disease Resistance: Nitrogen helps strengthen cell walls, enhancing resistance to certain diseases and pests. | |
| 5. Regulates Enzyme Activity | – Enzymatic Functions: Nitrogen is a component of various enzymes that regulate biochemical processes in plants. |
| – Metabolism: Essential for nitrogen metabolism, influencing the utilization and conversion of other nutrients. | |
| 6. Supports Nitrogen-Fixing Symbiotic Relationships | – Symbiotic Associations: Certain plants form symbiotic relationships with nitrogen-fixing bacteria, enhancing nitrogen availability. |
| – Legumes and Rhizobia: Leguminous plants, like peas and beans, can fix atmospheric nitrogen through rhizobia bacteria. | |
| 7. Environmental Impact | – Water Quality: Excessive nitrogen runoff from fertilizers can contribute to water pollution, impacting aquatic ecosystems. |
| – Air Quality: Ammonia emissions from agricultural practices can influence air quality and contribute to atmospheric pollution. |
By ensuring that plants receive the appropriate amount of nitrogen, gardeners can optimize their crop yield, enhance plant health, and promote lush foliage. This can be achieved through various practices such as using balanced fertilizers, implementing timely and precise fertilizer applications, and regularly monitoring nitrogen levels in the soil. Ultimately, prioritizing proper nitrogen levels in garden plants contributes to the overall success and vitality of the garden.
Factors That Contribute to Nitrogen Toxicity in Garden Plants
Nitrogen toxicity in garden plants can occur due to various factors, all of which are essential to understand in order to prevent and mitigate this problem.
Overabundance of nitrogen leads to toxicity
Imbalance in soil due to improper calculation of plant needs
Plants absorb excessive nitrogen, causing detrimental effects on health and development
Overwatering or inappropriate irrigation design can leach nitrogen from soil
Accumulation of excess nitrogen in plant tissues
Symptoms include stunted growth, yellowing leaves, and root damage
Understanding these factors that contribute to nitrogen toxicity is crucial for gardeners to effectively manage their plants’ health. By being aware of the potential risks associated with excessive nitrogen use and irrigation practices, gardeners can take preventive measures to maintain a balanced nutrient supply and promote the overall well-being of their garden plants.
Choosing the Right Fertilizer to Prevent Nitrogen Toxicity
Choosing the right fertilizer for your garden is crucial in preventing nitrogen toxicity in your plants. When it comes to selecting a fertilizer, it is important to pay attention to the formulation and the ratio of nutrients it provides. For preventing nitrogen toxicity, it is recommended to choose a fertilizer with a lower nitrogen content and a higher proportion of other essential nutrients.

- Balanced Fertilizers: Opt for a balanced fertilizer with equal or lower nitrogen content compared to phosphorus and potassium. This helps maintain a proper nutrient balance in the soil. Nitrogen toxicity can occur when there’s an excess of nitrogen relative to other nutrients.
- Slow-Release Fertilizers: Consider using slow-release fertilizers. These provide a steady supply of nutrients over an extended period, reducing the risk of nitrogen accumulation. Slow-release formulations prevent sudden nutrient spikes that can harm plants.
- Organic Fertilizers: Use organic fertilizers like compost or well-rotted manure. These naturally release nutrients into the soil. Organic fertilizers typically have lower nitrogen concentrations than synthetic ones, minimizing the risk of nitrogen overload.
- Application Rates: Always follow the recommended application rates provided on the fertilizer packaging. Over-application can lead to nutrient imbalances and toxicity in your garden plants.
By choosing the right fertilizer and being mindful of nitrogen content, you can effectively prevent nitrogen toxicity in your garden and promote healthy plant growth.
The Andersons Balanced 10-10-10 Fertilizer with Micronutrients proved effective in preventing nitrogen toxicity in my garden. Its balanced formula ensured a controlled release of nitrogen, preventing excessive buildup in the soil. With the inclusion of essential micronutrients, my plants received comprehensive nutrition without the risk of nutrient imbalances. The slow-release feature also provided a steady supply of nutrients, minimizing the chances of over-fertilization and subsequent nitrogen toxicity. Overall, this fertilizer offered a reliable solution for maintaining healthy plant growth while mitigating the risks associated with nitrogen overload.
- Balanced Nutrients: Provides a comprehensive mix of 10% nitrogen, 10% phosphorus, and 10% potassium, ideal for overall plant health.
- Micronutrients Included: Contains essential micronutrients that support various plant functions and improve overall growth.
- Versatile Use: Suitable for a wide range of plants, including flowers, vegetables, and lawns, making it a versatile addition to any garden.
- Slow-Release Formula: The slow-release formulation ensures a steady supply of nutrients over time, reducing the need for frequent applications.
- Granular Form: Easy to apply and evenly distribute across your garden or lawn.
- May Need Supplemental Feeding: Depending on the specific needs of your plants, additional supplements might be required for optimal growth.
- Cost: Higher price point compared to some other fertilizers, which may be a consideration for budget-conscious gardeners.
- Potential for Over-fertilization: Without careful application, there is a risk of over-fertilizing, which can harm plants.
- Not Organic: This product is not organic, which may be a drawback for those seeking organic gardening solutions.
- Storage Requirements: Needs proper storage to prevent moisture absorption and clumping of the granular product.
Appropriate Timing and Frequency for Fertilizer Application
Appropriate timing and frequency for fertilizer application are crucial factors in maintaining healthy and well-balanced nitrogen levels in garden plants. Knowing when and how often to apply fertilizer can optimize nutrient uptake, promote growth, and minimize the risk of nitrogen toxicity.
- Timing of Fertilizer Application
- Apply during active growth periods, such as spring or early summer
- Ensures nutrients are available for plant uptake and utilization
- Specific timing depends on plant type and growth stage
- Annual flowers and vegetables: more frequent applications during peak growing season
- Perennials: early spring application to support new growth
- Frequency of Fertilizer Application
- Balance is crucial: avoid over-fertilization and under-fertilization
- Divide total recommended fertilizer amount into multiple applications
- Gradual nutrient absorption prevents imbalances and toxicity
| Appropriate Timing and Frequency for Fertilizer Application | Key Practices |
|---|---|
| 1. Early Spring | – Before Growth Resumes: Apply a balanced fertilizer early in spring before active growth begins. |
| – Promotes Vigorous Growth: Provides nutrients needed for initial growth and development. | |
| 2. Late Spring to Early Summer | – During Active Growth: Apply a slow-release fertilizer during the growing season for sustained nutrient supply. |
| – Before Flowering: Supports flower and fruit development in flowering plants. | |
| 3. Early Fall | – Prepares for Winter: Apply a balanced fertilizer in early fall to help plants prepare for the dormant period. |
| – Storage of Nutrients: Assists plants in storing nutrients for winter resilience. | |
| 4. Specific Growth Stages | – Vegetative Growth: Apply nitrogen-rich fertilizers during vegetative growth stages for leafy plants. |
| – Blooming Phase: Use phosphorus-rich fertilizers during the blooming phase for flowering plants. | |
| 5. Soil Testing | – Regular Testing: Conduct soil tests to determine nutrient levels and tailor fertilizer application accordingly. |
| – Customized Nutrient Plans: Adjust fertilizer types and amounts based on specific soil deficiencies. | |
| 6. Avoid Overfertilization | – Follow Recommendations: Adhere to recommended dosage on fertilizer labels to prevent overfertilization. |
| – Environmental Impact: Minimize the risk of nutrient runoff, pollution, and harm to non-target organisms. | |
| 7. Container Plants | – Regular Feeding: Container plants often need more frequent fertilization; use a balanced liquid fertilizer every 2-4 weeks. |
| – Leaching Concerns: Be mindful of nutrient leaching in container-grown plants and adjust application rates. | |
| 8. Specialized Fertilizers for Certain Plants | – Seasonal Requirements: Some plants, like roses or citrus, may benefit from specialized fertilizers tailored to their needs. |
| – Specific Nutrient Ratios: Adjust fertilizers to meet the unique nutrient requirements of specific plant varieties. |
However, it is important to note that the specific timing and frequency of fertilizer application may vary depending on various factors, including soil type, plant species, climate conditions, and the type of fertilizer used. Conducting a soil test can provide valuable insights into nutrient levels and help determine the appropriate fertilizer application schedule for your specific garden. By being mindful of timing and frequency, gardeners can effectively provide their plants with the necessary nutrients while minimizing the risk of nitrogen toxicity.
Implementing Soil Testing to Monitor Nitrogen Levels
Soil testing is an essential practice for gardeners who want to effectively monitor the levels of nitrogen in their soil. By implementing soil testing, you can gather valuable information about your soil’s nutrient content, including nitrogen levels, and make informed decisions regarding fertilizer application. Testing your soil can help you identify if your garden plants are at risk of nitrogen toxicity, allowing you to take preventive measures before any damage occurs.
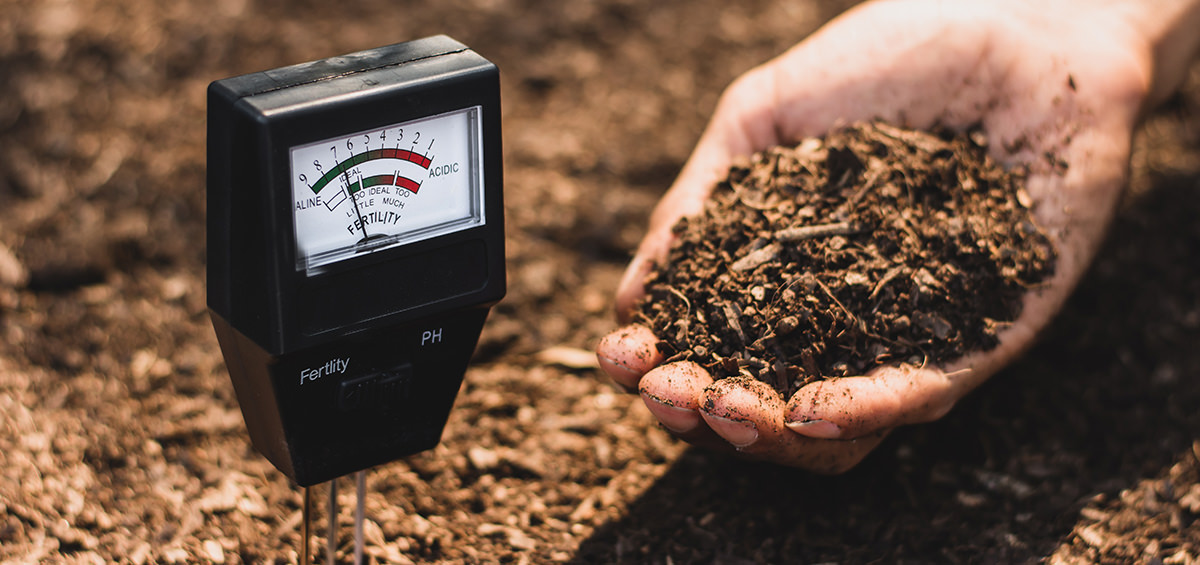

- Collect Representative Samples: Obtain soil samples from various locations in your garden. Dig down at least six to eight inches and collect soil using a trowel or soil auger. Combine the samples in a clean container, mix thoroughly, and remove any debris.
- Send Samples to a Soil Testing Laboratory: Choose a reputable soil testing laboratory and send your prepared sample for analysis. The lab will determine the nitrogen content and provide specific levels.
- Valuable Information: The results will offer insights into your soil’s nitrogen levels. You’ll receive recommendations for adjustments if needed.
- Monitor Nitrogen Levels: Regular soil testing helps assess whether your garden plants are getting the right amount of nitrogen.
- Avoid Over-Application: Soil testing prevents excessive nitrogen use, which can lead to toxicity.
Implementing regular soil testing will enable you to maintain the optimal nitrogen levels in your garden and promote healthy plant growth.
Effective Strategies for Reducing Nitrogen Toxicity in Garden Plants
Nitrogen toxicity in garden plants can have detrimental effects on their growth and overall health. However, there are several effective strategies that can help reduce this issue and maintain a balanced nitrogen level in the garden.

- Proper Fertilizer Application Practices
- Avoid excessive use of nitrogen-based fertilizers
- Use organic fertilizers or slow-release nitrogen sources for balanced nutrient release
- Ensures a steady supply of nitrogen without overwhelming plants
- Companion Planting Techniques
- Plant nitrogen-fixing plants (e.g., legumes) alongside other crops
- Nitrogen-fixing plants enhance soil nitrogen levels through symbiosis with nitrogen-fixing bacteria
- Minimizes chances of nitrogen toxicity
- Intercropping for Efficient Nitrogen Utilization
- Plant different crops with varying nitrogen requirements and uptake abilities
- Promotes efficient use of available nutrients
- Reduces risk of nitrogen buildup and toxicity
By adopting these effective strategies, gardeners can successfully reduce nitrogen toxicity in their garden plants. It is important to carefully monitor nitrogen levels, choose the right fertilizers, and implement sustainable practices to ensure the health and vitality of the garden. Taking a proactive approach in managing nitrogen levels will not only enhance plant growth but also contribute to a more sustainable and environmentally friendly gardening experience.
Optimal Watering Practices to Prevent Nitrogen Buildup
To prevent nitrogen buildup in garden plants, implementing optimal watering practices is crucial. Proper watering techniques not only ensure the overall health and vigor of plants but also help maintain a balanced nitrogen level in the soil.

Prevents excessive runoff that carries away essential nitrogen nutrients
Ensures plants receive necessary elements for growth
Prevents nitrogen concentration in the root zone, which can lead to toxicity
Maintains overall plant health
Monitor soil moisture regularly
Water when the top inch of soil becomes slightly dry
Avoid shallow, frequent watering that promotes shallow root growth
Water deeply and less frequently to encourage deep root systems
Ensures effective access to water and nutrients
Conserves moisture and reduces evaporation
Prevents excessive nitrogen leaching
Helps maintain balanced nitrogen levels in the soil
By incorporating these optimal watering practices into their routine, gardeners can successfully prevent nitrogen buildup and promote healthy plant growth.
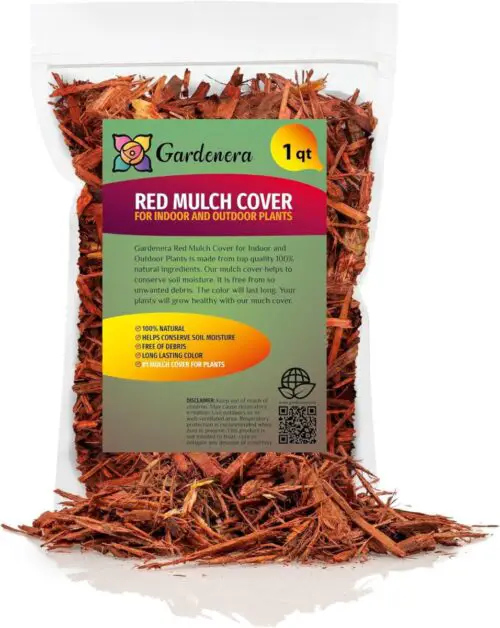
Gardenera’s Premium Mulch Cover proved highly effective in preventing nitrogen toxicity in my garden. Its nutrient-rich composition acted as a natural barrier, regulating soil nitrogen levels and promoting balanced plant growth. Additionally, its easy application and durability make it a top choice for any gardener looking to maintain optimal soil health.
✔ Effective Weed Suppression: Acts as an effective barrier against weeds, reducing the need for frequent weeding.
✔ Moisture Retention: Helps retain moisture in the soil, reducing water evaporation and conserving water.
✔ Temperature Regulation: Regulates soil temperature, protecting plants from extreme heat or cold.
✔ Natural Appearance: Blends seamlessly with garden aesthetics, enhancing the overall visual appeal.
❌ Availability: Limited availability in certain regions may make it challenging to procure.
❌ Application Difficulty: Depending on the packaging and application method, spreading the mulch evenly may require additional effort.
❌ Decomposition Rate: Depending on environmental conditions, the mulch may decompose at varying rates, necessitating periodic replenishment.
❌ Potential for Pest Attraction: Organic mulches like Gardenera Premium Mulch Cover may attract pests such as insects or rodents if not properly managed.
Utilizing Organic Matter to Balance Nitrogen Levels in Garden Soil
Utilizing organic matter is an effective strategy to balance nitrogen levels in garden soil. Organic matter, such as compost or well-rotted manure, is rich in essential nutrients, including nitrogen, phosphorus, and potassium. When incorporated into the soil, organic matter slowly releases nitrogen, providing a steady supply to plants over time.

- Improves Soil Structure
- Enhances porosity for better water infiltration and air circulation
- Facilitates root development and nutrient uptake
- Promotes Microbial Activity
- Decomposition of organic matter supports beneficial microorganisms
- Microorganisms convert nitrogen into plant-usable forms, enhancing nutrient availability
- Incorporation into Soil
- Mix organic matter into the soil before planting or during preparation stages
- Ensure thorough mixing with topsoil for uniform distribution
- Optimal Ratio
- Aim for a 25-30% ratio of organic matter to maintain balanced nitrogen levels
- Regular Applications
- Apply organic matter annually or biennially to enhance soil fertility
- Supports long-term sustainability and healthy plant growth
By harnessing the power of organic matter, gardeners can optimize nitrogen levels in their soil, fostering healthy and productive plant growth.
Importance of Crop Rotation in Reducing Nitrogen Toxicity
Crop rotation is a fundamental practice in farming and gardening that offers numerous benefits, including the reduction of nitrogen toxicity in garden plants.

- Crop Rotation: Systematically rotate crops to prevent nitrogen buildup in the soil. Growing the same crops in the same location year after year depletes specific nutrients, including nitrogen.
- Disrupting the Nitrogen Cycle: Crop rotation disrupts the nitrogen cycle. Different plant species have varying nitrogen requirements and capacities to fix atmospheric nitrogen.
- Alternating Nitrogen-Hungry and Nitrogen-Fixing Plants: Alternate nitrogen-hungry plants (e.g., leafy greens, brassicas) with nitrogen-fixing legumes (e.g., beans, peas). Nitrogen-fixing plants convert atmospheric nitrogen into a usable form, benefiting subsequent crops.
- Root Structures and Soil Microbes: Different plant families have varying root structures and exudates, influencing the soil microbial community and nutrient cycling.
By diversifying your crop selection and practicing crop rotation, you can reduce nitrogen toxicity and maintain a balanced nutrient environment for healthier, more productive plants.
Companion Planting Techniques to Promote Nitrogen Balance
Companion planting is a valuable technique that can be employed to promote nitrogen balance in garden plants. By strategically pairing certain plant species together, gardeners can harness the power of symbiotic relationships that enhance nitrogen availability in the soil. One such example is the classic partnership of legumes and non-legumes.
- Legume-Nitrogen Fixation
- Legumes (e.g., beans, peas, clover) fix atmospheric nitrogen
- Form symbiotic relationship with rhizobia bacteria in roots
- Convert nitrogen into a usable form for plants
- Benefits of Legume-Non-Legume Pairings
- Plant legumes alongside non-legumes (e.g., tomatoes, cucumbers)
- Legumes transfer fixed nitrogen to neighboring plants
- Improves nitrogen uptake and growth of non-legumes
- Reduces risk of nitrogen overload and toxicity
- Diverse Root Systems
- Prevent nitrogen leaching and promote efficient nutrient uptake
- Deep-rooted plants (e.g., comfrey, dandelion) access deep soil nitrogen reserves
- Shallow-rooted plants (e.g., lettuce, radishes) utilize surface nitrogen
- Selecting Appropriate Plant Combinations
- Choose plants based on compatibility and requirements (sunlight, water, nutrients)
- Optimize nitrogen availability while minimizing risk of toxicity
- Regular Soil Monitoring
- Conduct soil tests to monitor nitrogen levels
- Fine-tune companion planting strategies based on test results
- Ensure optimal nitrogen balance for healthy, productive gardens
Implementing these companion planting techniques helps optimize nitrogen availability and maintains garden health.
Identifying and Addressing Other Nutrient Imbalances in Garden Plants
Nutrient imbalances can significantly affect the health and productivity of garden plants, leading to stunted growth, reduced yields, and increased susceptibility to diseases and pests. While nitrogen toxicity is a common concern, it is crucial to also identify and address other nutrient imbalances that can impact plant growth. Two essential nutrients that often require attention are phosphorus (P) and potassium (K).
- Phosphorus (P):
- Role: Crucial for energy transfer, root development, and overall plant growth.
- Deficiency: Stunted plants, poor root systems, delayed flowering, and fruiting.
- Excess: Can lead to calcium and zinc deficiencies due to competition for uptake.
- Potassium (K):
- Role: Vital for water and nutrient movement, cell division, and disease resistance.
- Deficiency: Weak stems, poor fruit quality, increased pest susceptibility.
- Excess: Reduces uptake of other essential nutrients (e.g., magnesium, calcium).
- Soil Testing:
- Conduct regular soil testing to assess nutrient levels and pH.
- Valuable information for informed actions.
- Detect deficiencies or excesses.
- Targeted Fertilization:
- Use suitable fertilizers with balanced nutrient ratios.
- Address specific deficiencies or excesses.
- Additional Practices:
- Incorporate organic matter into the soil.
- Adjust pH as needed.
- Implement proper irrigation techniques.
By closely monitoring and managing phosphorus and potassium levels, gardeners can promote optimal plant health and maximize their garden’s productivity. It is crucial, however, to remember that each plant species has different nutrient requirements, so it is essential to consult specific guidelines and recommendations for the plants being grown.
For more information watch the video:
FAQ
What are some common signs of nitrogen toxicity in garden plants?
Symptoms of nitrogen toxicity in garden plants can include dark green leaves, weak stems, delayed fruit ripening, and reduced flowering.
How does nitrogen contribute to plant growth?
Nitrogen is an essential nutrient for plants as it plays a crucial role in promoting leaf and stem growth, chlorophyll production, and overall plant vigor.
What factors contribute to nitrogen toxicity in garden plants?
Excessive or imbalanced fertilizer application, high levels of organic matter decomposition, poor drainage, and overwatering can all contribute to nitrogen toxicity in garden plants.
How can I choose the right fertilizer to prevent nitrogen toxicity?
To prevent nitrogen toxicity, it is important to choose a fertilizer with a balanced nutrient ratio, specifically one that has a lower nitrogen content and adequate levels of other essential nutrients.
Can soil testing help monitor nitrogen levels in the garden?
Yes, soil testing is an effective way to monitor nitrogen levels and ensure they remain within the appropriate range for optimal plant growth.
What are some effective strategies for reducing nitrogen toxicity in garden plants?
Strategies for reducing nitrogen toxicity include adjusting fertilizer application rates, improving soil drainage, incorporating organic matter into the soil, and practicing crop rotation.
How can optimal watering practices prevent nitrogen buildup?
Proper watering practices, such as watering deeply and infrequently, can prevent excessive nitrogen buildup by leaching it down through the soil profile.
How can companion planting promote nitrogen balance in the garden?
Companion planting, where nitrogen-fixing plants are grown alongside nitrogen-demanding plants, can help maintain nitrogen balance by naturally replenishing the soil with this essential nutrient.
Are there other nutrient imbalances that can affect garden plants?
Yes, apart from nitrogen toxicity, garden plants can be affected by imbalances of other essential nutrients such as phosphorus, potassium, calcium, magnesium, and micronutrients like iron, zinc, and manganese.
How can I identify and address other nutrient imbalances in garden plants?
Regular soil testing, observing plant symptoms, and consulting with a horticultural expert can help identify nutrient imbalances. Addressing them involves adjusting fertilizer application, amending the soil, and providing targeted nutrient supplementation if necessary.

Studied Agricultural Engineering-Plant Protection at University of California, Davis.
Head of Content writing team at Southelmontehydroponics.com