How to Calibrate a pH Pen: A Guide to Using This Device to Measure and Adjust the pH Level of Your Water or Soil
Table of Contents
Understanding pH Buffer Solutions: Explaining the role of pH buffer solutions in calibration and the importance of using them correctly for accurate readings.
pH buffer solutions play a crucial role in the calibration of pH meters and the accuracy of pH measurements. These solutions are designed to maintain a stable pH level, making them ideal for calibrating pH meters before conducting any measurements. By using pH buffer solutions, gardeners and professionals can ensure that their pH meter is accurately calibrated, leading to precise and reliable results.
One of the essential aspects of using pH buffer solutions correctly is selecting the appropriate buffer solution for calibration. pH buffer solutions are available in various pH values, typically ranging from pH 4 to pH 10. It is essential to choose buffer solutions that are close to the pH range of the samples you will be measuring. This ensures that the pH meter is calibrated specifically for the pH range of interest, leading to more accurate measurements. Using the wrong buffer solution can result in incorrect readings, undermining the validity and usefulness of the pH measurements taken. Therefore, it is vital to carefully read and follow the manufacturer’s instructions and consult reliable resources when selecting the appropriate buffer solution.
Performing a pH Measurement: Step-by-step instructions on how to conduct a pH measurement using your calibrated pH pen, ensuring precise results.
To ensure accurate results, it is crucial to conduct pH measurements using a calibrated pH pen. Here are step-by-step instructions on how to perform a pH measurement:
1. Prepare your pH pen: Start by ensuring that your pH pen is properly calibrated. Follow the manufacturer’s instructions to calibrate the pen using pH buffer solutions. This process involves immersing the pen in a solution with a known pH value, typically 7.0 or 10.0, and adjusting the pen accordingly.
2. Gather your sample: Collect a small sample of the substance you wish to measure, whether it’s water, soil, or any other solution. Make sure that the sample is representative and free from any visible impurities.
3. Rinse and dry the pH pen: Before immersing the pH pen into the sample, rinse it with distilled water to remove any residue from previous measurements. Gently pat it dry with a clean tissue or cloth.
4. Immerse the pen: Insert the pH pen into the sample solution, ensuring that the sensing electrode is fully immersed. It is important to give the pen sufficient time to stabilize and accurately measure the pH value, usually a few seconds.
5. Read the pH value: Once the reading is stabilized, record the pH value displayed on the pH pen’s screen. Take note of any decimal places provided, as they are crucial in determining the precise acidity or alkalinity of the solution.
Remember that pH measurements can be affected by temperature, so it’s advisable to perform the measurement at the recommended temperature for accurate results. By following these steps and using a calibrated pH pen, you can obtain precise pH measurements and ensure the accuracy of your analysis.
• Prepare your pH pen: Ensure that your pH pen is properly calibrated using pH buffer solutions.
• Gather your sample: Collect a representative and impurity-free sample of the substance you wish to measure.
• Rinse and dry the pH pen: Before immersing it into the sample, rinse the pH pen with distilled water and gently pat it dry.
• Immerse the pen: Insert the pH pen into the sample solution, ensuring full immersion of the sensing electrode. Allow sufficient time for stabilization.
• Read the pH value: Once stabilized, record the displayed pH value on the screen, noting any decimal places for accuracy.
• Consider temperature effects: Remember that temperature can impact pH measurements; perform them at recommended temperatures for precise results.

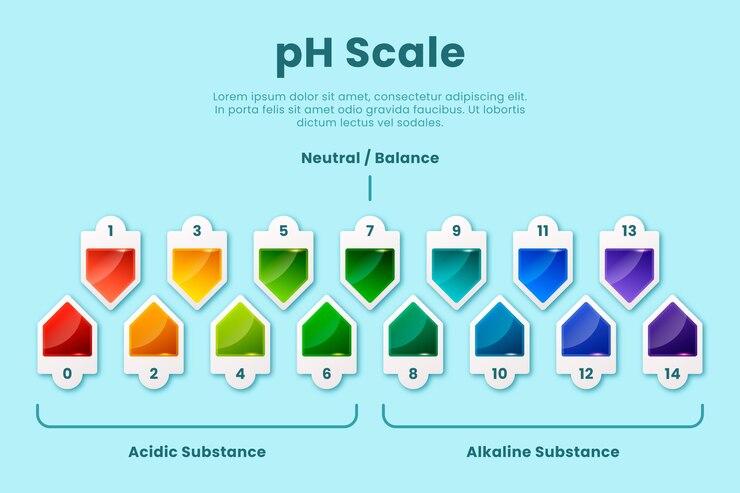
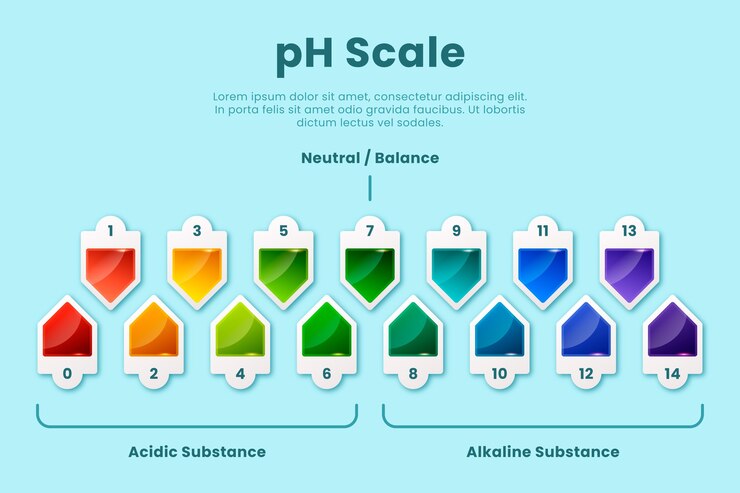
Interpreting pH Readings: A comprehensive guide on understanding pH readings and their significance in determining the acidity or alkalinity of your water or soil.
pH readings play a crucial role in determining the acidity or alkalinity of water or soil. Understanding these readings is key to maintaining optimal conditions for plant growth and optimizing crop production.
A pH reading is a numerical value that indicates the intensity of acidity or alkalinity on a scale of 0 to 14. A pH value of 7 is considered neutral, while values below 7 indicate acidity and values above 7 indicate alkalinity.
When it comes to gardening, the ideal pH range varies depending on the plants being grown. Most plants thrive in slightly acidic to neutral soil, with a pH range of 6 to 7.5. However, some plants have specific pH requirements. For example, blueberries prefer acidic soil with a pH range of 4.5 to 5.5, while certain varieties of roses prefer slightly alkaline soil with a pH range of 7 to 8.
Interpreting pH readings accurately can help gardeners diagnose and address any issues that may be affecting plant health. Monitoring pH levels regularly allows for proactive adjustments to ensure an optimal growing environment. Whether you’re testing the pH of your garden soil or the water used in hydroponic systems, understanding and interpreting these readings is essential for successful gardening.
| Aspect | Description |
|---|---|
| pH Definition | pH is a measure of the acidity or alkalinity of a solution, ranging from 0 to 14, with 7 considered neutral. |
| Acidic Solutions | pH values below 7 indicate acidity. The lower the pH, the more acidic the solution. |
| Alkaline (Basic) Solutions | pH values above 7 indicate alkalinity. The higher the pH, the more basic the solution. |
| Neutral Solutions | pH of 7 is considered neutral, indicating a balance between acidity and alkalinity. |
| Importance in Water | pH impacts water quality and its suitability for various purposes such as drinking, agriculture, and industry. |
| Effects on Soil | pH influences soil fertility, nutrient availability, and the health of plants. |
| Ideal pH Range for Water | Drinking water: 6.5 – 8.5; Aquatic habitats: 6.5 – 9.0 |
| Ideal pH Range for Soil | Most plants prefer soil pH between 6.0 and 7.5. |
| Testing Methods | pH meters, pH strips, and chemical indicators are commonly used to measure pH. |
| Adjusting pH | pH can be adjusted using pH-adjusting chemicals or natural amendments like lime (for acidic soil) or sulfur (for alkaline soil). |
| Monitoring and Maintenance | Regular pH testing and adjustments are necessary to maintain optimal conditions for water and soil. |
Adjusting pH Levels: Exploring various methods and techniques to adjust
Adjusting pH levels is an important aspect of maintaining optimal growing conditions for plants. The pH of the growing medium directly affects nutrient availability and plant growth. When the pH levels are too high or too low, it can result in nutrient deficiencies or toxicities, leading to stunted growth and poor yields. Fortunately, there are various methods and techniques available to adjust pH levels and create a balanced environment for your plants.
One common method used to lower pH levels is by applying substances such as sulfur, peat moss, or organic acids. These additives can help lower the alkalinity of the growing medium, making it more suitable for acid-loving plants. On the other hand, if the pH is too low and needs to be raised, the addition of materials such as limestone, dolomite, or wood ashes can help elevate the pH levels. It is important to carefully monitor the pH levels after applying these adjustments and make further amendments if necessary. Additionally, it’s worth noting that adjusting pH levels may require time for the changes to take effect, so patience is key when striving for optimal pH conditions.
What are some common methods for adjusting pH levels?
Some common methods for adjusting pH levels include adding acidic or alkaline substances such as vinegar or baking soda, using pH adjustment chemicals like sulfuric acid or sodium hydroxide, or using natural materials like limestone or peat moss.
Is it important to adjust pH levels in water or soil?
Yes, adjusting pH levels in water or soil is important as it directly affects the availability of nutrients to plants and the overall health of aquatic ecosystems. Improper pH levels can lead to nutrient deficiencies or toxicities, affecting plant growth and the survival of aquatic organisms.
How do I determine the ideal pH level for my water or soil?
The ideal pH level for water or soil depends on the specific plants or organisms you are trying to support. Different plants have different pH preferences, so it is important to research the optimal pH range for your specific needs.
Can I adjust pH levels naturally without using chemicals?
Yes, you can adjust pH levels naturally without using chemicals. For example, you can use organic matter like compost or manure to increase soil pH or add citrus juice to lower pH levels in water. However, it is important to note that natural methods may take longer to achieve desired results compared to using chemical adjustments.
Are there any risks involved in adjusting pH levels?
Yes, there can be risks involved in adjusting pH levels. It is important to follow proper safety precautions when handling pH adjustment chemicals and to carefully monitor pH levels to avoid overcorrection. Additionally, sudden and drastic changes in pH can also stress plants or organisms, so gradual adjustments are generally recommended.
How often should I test and adjust pH levels?
The frequency of testing and adjusting pH levels depends on various factors, such as the stability of the system and the specific needs of the plants or organisms. It is generally recommended to regularly monitor pH levels and adjust as necessary, especially if you notice signs of nutrient deficiencies or imbalances.

Ankit Garg is a seasoned writer at South El Monte Hydroponics, blending his passion for agriculture with a penchant for storytelling. With a degree in Agricultural Sciences from a prestigious institution, Ankit’s expertise lies in hydroponics, sustainable farming, and innovative cultivation techniques. His keen interest in exploring the intersection of technology and agriculture has led him to delve deep into the realm of hydroponic farming, where he thrives in uncovering the latest advancements and sharing insights through his engaging prose. Ankit’s dedication to promoting eco-friendly and efficient farming practices through his writing has earned him recognition within the agricultural community and beyond.