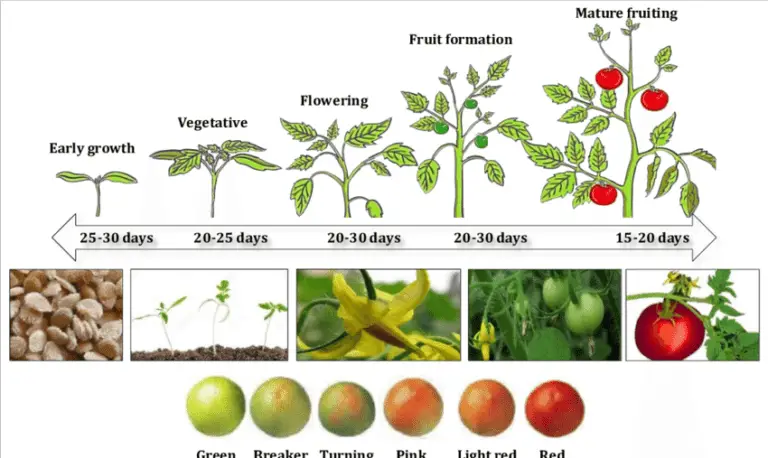
Hydroponic Potatoes vs. Soil-Grown Potatoes: Which One Tastes Better?
🥔 Looking to spice up your spuds game? Ever wondered if hydroponic potatoes pack a punch against their soil-grown counterparts? Well, get ready to dig into this savory debate! While both methods have their loyal followers, the taste showdown between hydroponic and soil-grown potatoes is one for the ages. But fret not, dear tater enthusiasts, as we peel back the layers to uncover the truth.
In this blog, we’ll delve into the juicy details, exploring flavor profiles, nutrient levels, and the ultimate winner in the battle of the buds. So, grab your fork and let’s settle the score once and for all! 🌱🥔 #HydroponicVsSoil #TaterTasteTest #DigIn
Table of Contents
Understanding the Growing Methods: Hydroponics Vs Soil-based Cultivation
Hydroponics and soil-based cultivation are two popular methods of growing plants, each with its own unique characteristics and benefits.
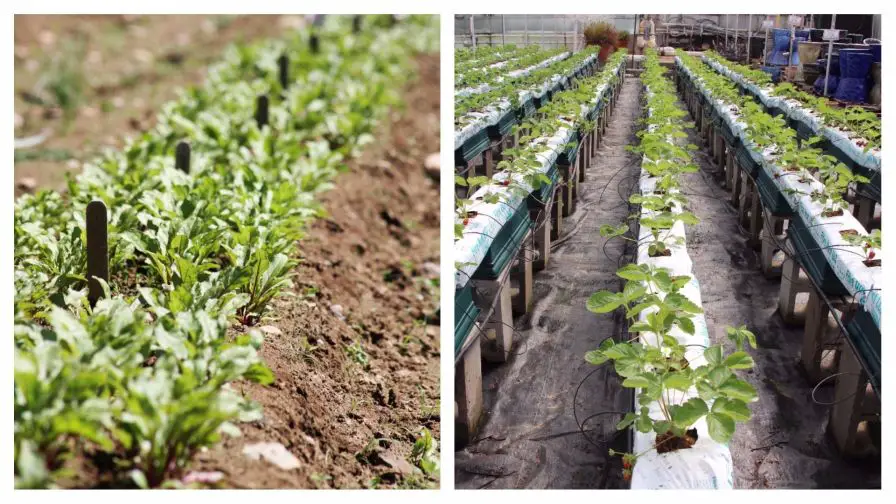

- Hydroponics is a soilless farming method utilizing water-based nutrient solutions instead of soil.
- Allows precise control over nutrient levels, pH balance, and water availability, leading to faster growth and higher yields.
- Eliminates the need for pesticides and reduces water usage compared to soil-based cultivation.
- Particularly suitable for urban farming or areas with limited space due to its space-efficient nature.
- Soil-based cultivation involves planting crops directly in the ground, utilizing soil as a natural medium for nutrient and water acquisition.
- Promotes microbial activity and organic matter decomposition, contributing to better soil structure and long-term sustainability.
- More accessible and cost-effective for small-scale farmers or those with available land resources.
- Understanding these methods helps gardening enthusiasts make informed decisions based on their specific needs and preferences.
Whether it’s maximizing space utilization and efficiency with hydroponics or enjoying the natural benefits of soil-based cultivation, both methods offer opportunities for successful and rewarding plant growth.
Analyzing the Impact of Growing Medium on Potato Taste
Potato taste is influenced by various factors, and one important aspect to consider is the growing medium. The growing medium refers to the substance in which the potatoes are grown, whether it be soil or a hydroponic solution. Understanding the impact of the growing medium on potato taste can help growers make informed decisions and achieve optimal results.
| Aspect | Soil-based Cultivation | Hydroponics |
|---|---|---|
| Growing Environment | Natural environment with soil as the medium | Soilless environment with water-based solution |
| Nutrient Source | Relies on nutrients present in the soil | Nutrients provided through water solution |
| Control over Nutrients | Limited control over nutrient levels and availability | Precise control over nutrient levels |
| Soil Influence on Taste | Soil composition influences flavor profile | Absence of soil variability can result in distinct taste |
| Disease and Pest Management | Susceptible to soil-borne diseases and pests | Reduced risk of soil-borne diseases and pests |
| Yields and Growth | Potentially lower yields and slower growth | Higher yields and faster growth |
| Shelf Life | Shorter shelf life due to soil-borne pathogens | Longer shelf life due to reduced disease risk |
| Dry Matter, Starch, Sugar Content | Higher dry matter, starch, and sugar content | Lower dry matter, starch, and sugar content |
| Flavor and Aroma | More complex flavor and aroma | Less intense flavor and aroma |
| Consumer Preference | Preference may vary based on individual taste and expectations | Some may prefer for freshness and uniformity |
Further research and studies can help shed light on specific nutrient profiles and their contribution to overall flavor, enabling growers to harness the potential of both growing mediums for superior potato taste.
Examining the Nutrient Levels in Hydroponic Potatoes Hydroponic Potatoes vs. Soil-Grown Potatoes
When it comes to comparing the nutrient levels in hydroponic potatoes and soil-grown potatoes, there are several factors to consider. While both growing methods have their advantages and disadvantages, understanding the nutrient composition can help gardeners make informed choices for their potato cultivation.
- Nutrient Availability:
- Hydroponic: Nutrients are supplied directly to plant roots through a nutrient-rich solution. This precise delivery allows optimal uptake and utilization by the plants.
- Soil: Nutrient availability in soil varies based on factors like soil type, organic matter content, and nutrient interactions.
- Control and Consistency:
- Hydroponics:
- Provides precise control over nutrient levels.
- Consistent nutrient supply.
- Soil:
- Natural and diverse nutrient supply.
- Less consistent due to soil variability.
- Hydroponics:
- Nutritional Profiles:
- Researchers analyze mineral content, vitamins, and other essential nutrients in hydroponic and soil-grown potatoes.
- Comparing profiles helps identify significant differences between the two cultivation methods.
- Informed Decisions:
- Gardeners can maximize nutritional value by understanding nutrient levels.
- Choose the growing method (hydroponics or soil) that aligns with their preferences and goals.
Remember, both methods have their advantages, and the choice depends on individual preferences, available resources, and desired outcomes. The upcoming sections will explore specific nutrient components and their implications for the flavor and quality of potatoes grown through different methods.
| Aspect | Hydroponic Potatoes | Soil-Grown Potatoes |
| Nutrient Delivery | Precise, controlled delivery via nutrient-rich solution | Relies on natural soil composition with variable nutrient availability |
| Key Nutrients (e.g., Potassium, Phosphorus) | Potentially higher concentrations due to controlled uptake | Variable levels influenced by soil composition and environmental factors |
| Nutrient Consistency | Consistent nutrient levels | Potential fluctuations based on soil variations |
| Scientific Studies | Studies analyze mineral content, vitamins, and nutrients | Contribution of data for understanding nutrient nuances |
| Flavor and Quality | Nuanced impact on taste and quality | Interplay of minerals and vitamins may influence flavor |
| Decision-Making for Gardeners | Informed choices based on precise nutrient control | Consideration of natural diversity in nutrient supply |
Evaluating the Role of Watering Techniques in Potato Flavor
Watering techniques play a crucial role in the development of potato flavor. Proper watering is essential for maintaining the right moisture levels in the soil, which directly affects the taste of the potatoes. Overwatering can lead to excessive leaching of nutrients and dilution of flavors, while underwatering can cause the potatoes to become dry and lack flavor.

1. Deep Watering Technique:
- Description: Deep watering involves providing a long, slow soak to the plants, allowing water to penetrate deep into the soil.
- Benefits: Promotes deep root growth, increasing nutrient uptake and flavor development in potatoes.
- Mechanism: Ensures water reaches lower levels of the root system, facilitating access to essential nutrients and minerals.
- Result: Produces richer and more flavorful potatoes due to enhanced nutrient absorption.
2. Drip Irrigation Systems:
- Description: Drip irrigation delivers water directly to the base of the plants, minimizing water waste.
- Benefits: Reduces the risk of overwatering and minimizes moisture on foliage, decreasing the likelihood of diseases and rot.
- Mechanism: Provides controlled watering, ensuring plants receive the optimal amount of water for growth and taste.
- Result: Promotes healthier and more flavorful potatoes by maintaining optimal moisture levels.
Review for HIRALIY Drip Irrigation System
As an avid gardener, I decided to try out the HIRALIY Drip Irrigation System for my backyard garden, and I must say, I’m impressed. Setting it up was a breeze, thanks to the straightforward instructions provided. Once installed, the system efficiently distributed water to my plants, ensuring they received the right amount of moisture without any wastage.
One of the things I love most about this system is its customizability. I could easily adjust the drip nozzles to cater to the specific watering needs of different plants in my garden. Plus, the automated functionality saved me a significant amount of time and effort, as I no longer had to manually water each plant.
However, I did encounter a minor issue with nozzle clogging initially, but a quick clean solved the problem, and it hasn’t been an issue since. Additionally, I found that the system’s performance was somewhat dependent on water pressure, requiring occasional adjustments to ensure optimal functionality.
Overall, I’m highly satisfied with the HIRALIY Drip Irrigation System. It’s made gardening more convenient and efficient for me, and I would definitely recommend it to other gardening enthusiasts looking to simplify their watering routine.
- Efficient Water Distribution: Ensures precise watering, promoting healthy plant growth.
- Easy Installation: Simple setup process makes it suitable for beginners and experienced gardeners alike.
- Customizable: Adjustable drip nozzles allow for tailored watering based on plant needs.
- Time-saving: Automated system reduces the need for manual watering, saving time and effort.
- Versatile: Suitable for use in gardens, greenhouses, and outdoor spaces.
- Potential Clogging: Some users may experience issues with nozzle clogging, requiring occasional maintenance.
- Water Pressure Dependency: Performance may vary based on water pressure levels, requiring adjustments.
- Limited Coverage: May not be suitable for larger garden areas without additional components.
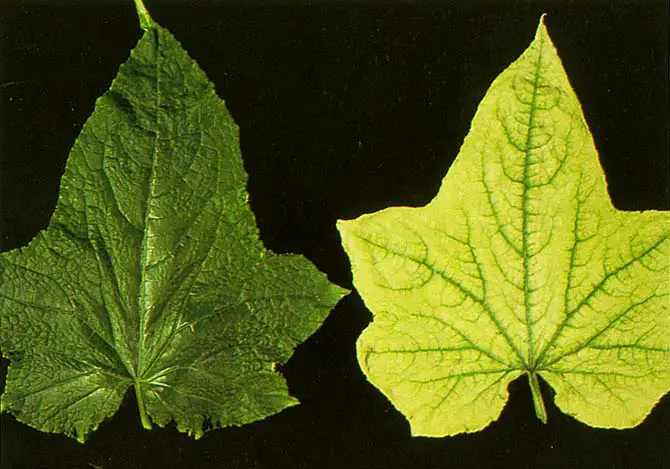
Considering the Influence of Light Exposure on Potato Taste
Light exposure plays a crucial role in shaping the taste of potatoes. The amount and quality of light that potato plants receive during their growth can have a profound impact on the flavor profile of the tubers they produce. This is primarily due to the role of light in the process of photosynthesis, where plants convert sunlight into energy to support their growth and development.

Potatoes grown in direct sunlight tend to have higher sugar content, resulting in a sweeter taste.
Conversely, potatoes grown in shaded areas or under artificial lighting have a milder taste due to lower sugar levels.
The quality of light spectrum (wavelengths emitted) also affects potato flavor.
Different light types (natural sunlight, fluorescent bulbs, LED lights) influence the synthesis of compounds in potato plants.
Blue light stimulates the production of flavor-enhancing compounds, while red light promotes starch accumulation.
Light affects the production of chlorophyll, carotenoids, and anthocyanins—pigments that influence color and flavor.
Varying light levels impact the overall taste profile of potatoes.
Hydroponic and aeroponic systems can use artificial lights to control the light spectrum and intensity.
Traditional soil-based cultivation relies on natural sunlight.
In summary, understanding and manipulating light exposure allow growers to fine-tune potato flavor to suit different culinary preferences.Further research and experimentation in this area can provide valuable insights for potato enthusiasts and agronomists alike.
Exploring the Effects of Pest Control Methods on Potato Flavor
Pest control methods play a crucial role in the overall quality and flavor of potatoes. When it comes to potato cultivation, pests can significantly impact the taste and texture of the tubers. It is essential for gardeners and farmers to understand the effects of pest control methods on potato flavor in order to make informed decisions.
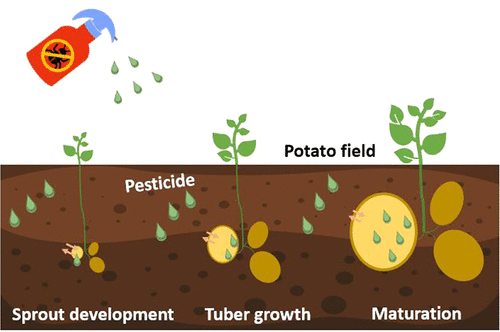
Chemical Pesticides:
- Effectiveness: Effectively controls pests and reduces crop losses.
- Adverse Effects on Flavor: Residues of chemical pesticides on potatoes can contribute to off-flavors and alter the natural taste.
- Nutritional Composition: Certain pesticide formulations may affect the nutritional composition of potatoes, influencing their overall flavor profile.
Organic Pest Control Methods:
- Approach: Utilizes biological controls such as beneficial insects, crop rotation, and companion planting.
- Goal: Manages pests without synthetic chemicals, aiming to enhance the natural flavors of the tubers.
- Flavor Quality: Organically grown potatoes often exhibit a more pronounced and well-balanced taste, offering a superior flavor experience for consumers.
Conclusion: The choice of pest control methods in potato cultivation significantly impacts the flavor of the tubers. While chemical pesticides effectively control pests, they may compromise the taste and nutritional value of potatoes. In contrast, organic pest control methods maintain the natural flavors of the tubers, providing a more desirable eating experience.As gardeners and farmers strive for sustainable and flavorful crop production, understanding the effects of different pest control methods is crucial.
Investigating the Impact of Temperature on Potato Taste
Temperature plays a crucial role in determining the taste of potatoes. As a gardener or gardening enthusiast, understanding the impact of temperature on potato taste can help you achieve optimal flavor in your harvest. Different stages of potato growth are affected by temperature variations, influencing the taste and texture of the final product.
Early Stages:
- Warmer Temperatures: Contribute to faster growth and promote starch accumulation in tubers.
- Result: Produces a starchier and denser potato, ideal for certain culinary preparations.
Later Stages:
- Cooler Temperatures: Lead to sweeter and creamier potatoes as sugars within tubers develop.
- Result: Yields potatoes with a sweeter and creamier taste profile.
Temperature Management:
- Consistency: Maintaining a consistent and appropriate temperature range throughout the growing process is crucial.
- Optimization: By optimizing temperature conditions from seed planting to harvest, gardening enthusiasts can manipulate the taste and texture of potatoes to suit their preferences and culinary needs.
Discussing the Importance of Soil Composition in Potato Flavor Development
Soil composition plays a crucial role in the development of potato flavor. The specific combination of nutrients, minerals, and organic matter present in the soil can greatly impact the taste and quality of the potatoes that are grown.
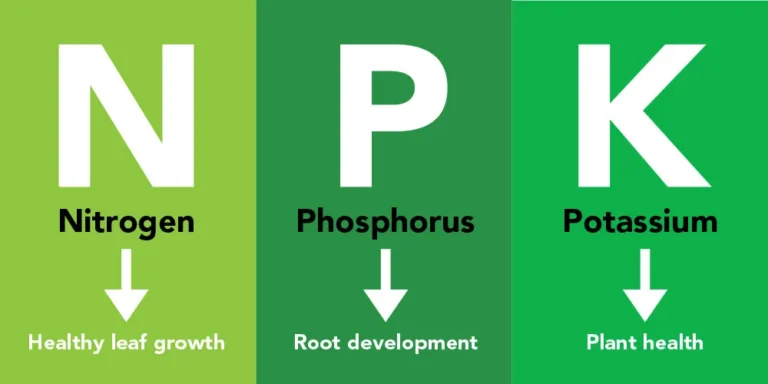
- Essential Nutrients:
- Potatoes require a balanced supply of essential nutrients (nitrogen, phosphorus, potassium) for proper growth.
- These nutrients are crucial for forming starches and sugars, which contribute to potato flavor.
- Soil with an optimal nutrient balance supports robust and delicious-tasting potatoes.
- Trace Elements and Micronutrients:
- Soil composition influences the availability of trace elements (e.g., calcium, magnesium, zinc).
- These elements impact metabolic processes within potato plants.
- Concentrations of minerals in the soil directly affect potato flavor and texture.
- For instance, calcium-rich soil promotes better texture and flavor, while deficiencies lead to blandness.
- Importance of Nutrient-Rich Soil:
- Ensuring a well-balanced and nutrient-rich soil is essential for cultivating potatoes with exceptional flavor.
In summary, nutrient content and mineral composition play a vital role in shaping the taste of potatoes. 🥔🌱👩🌾
The following table explains the importance of soil composition in potato flavor development:
| Soil Component | Importance in Potato Flavor Development | Effects on Potato Flavor |
| Nutrients (Nitrogen, Phosphorus, Potassium) | Essential for starch and sugar formation | Optimal levels promote robust and delicious potato flavor; deficiency may result in dull flavors |
| Trace Elements (Calcium, Magnesium, Zinc) | Influences metabolic processes | Adequate levels contribute to taste and texture; deficiency may lead to taste abnormalities or blandness |
| Organic Matter | Enhances soil structure and nutrient retention | Improves overall soil fertility, indirectly impacting potato flavor |
| pH Levels | Affects nutrient availability | Optimal pH range (slightly acidic to neutral) supports nutrient uptake for better flavor development |
| Soil Texture | Influences water drainage and root development | Proper drainage and root growth contribute to consistent potato flavor |
Upon using Jobe’s Organics Compost Starter for my potato cultivation, I must say it exceeded my expectations. The organic composition of this starter ensures that my potatoes grow in a healthy and sustainable environment, whether in soil or hydroponic setups. It’s easy to apply and has significantly boosted the nutrient content of the soil, leading to robust plant growth and high yields.
Despite its initial odor, which dissipates quickly, the benefits far outweigh any minor inconvenience. Overall, it’s a must-have for anyone looking to cultivate healthy and thriving potato plants, whether in traditional soil beds or hydroponic systems.
✅ Enhanced Nutrient Uptake: The compost starter enriches the soil with essential nutrients, promoting robust plant growth and development.
✅ Versatility: Suitable for use in both hydroponic and soil-based gardening, providing flexibility for different growing methods.
✅ Easy Application: The product is easy to apply, making it convenient for both beginner and experienced gardeners.
✅ Improved Soil Health: Regular use of the compost starter improves soil structure and fertility, creating an optimal growing environment for potatoes.
❌ Bag Size: The available bag sizes may not be sufficient for larger garden plots, requiring multiple purchases for extensive gardening projects.
Comparing the Texture of Hydroponic Potatoes vs Soil-Grown Potatoes
Hydroponic potatoes and soil-grown potatoes differ not only in their growing methods but also in their texture. When comparing the two, it is important to consider the unique characteristics each method brings to the table.

Hydroponically Grown Potatoes:
- Texture: Exhibits a smoother and more uniform texture.
- Reason: Controlled environment in hydroponics ensures optimal nutrient uptake and water distribution, minimizing variations.
- Soil Absence: Absence of soil reduces the risk of compaction, resulting in potatoes less prone to clumping and with a consistent texture.
Soil-Grown Potatoes:
- Texture: May display slight variations due to natural conditions.
- Factors: Soil composition, moisture levels, and environmental factors influence texture, leading to a potentially diverse range.
- Advantage: Appreciated for earthy and slightly uneven texture, offering a unique sensory experience.
Understanding the differences in texture between hydroponic and soil-grown potatoes is crucial for individuals seeking to achieve a specific culinary outcome or preference. By examining the growing methods and recognizing the impact they have on texture, gardeners and enthusiasts can make informed decisions when selecting potatoes for their desired recipes or meal preparations.
Addressing the Role of Environmental Factors on Potato Taste
Environmental factors play a critical role in shaping the taste of potatoes. From temperature and light exposure to soil composition and watering techniques, these factors can significantly impact the flavor and overall quality of the potatoes grown. Understanding the interplay between environmental conditions and potato taste is essential for gardeners and growers who are striving to produce the best-tasting spuds.
- Temperature:
- Potatoes thrive in cool-season temperatures (60–70°F or 15–20°C during the day).
- Excessively high temperatures can make potatoes taste bitter or starchy.
- Colder temperatures hinder starch-to-sugar conversion, resulting in a lack of sweetness and dull flavor.
- Optimal temperature balance is crucial for achieving well-rounded potato flavor.
- Light Exposure:
- Potatoes require moderate light to produce chlorophyll and develop their taste.
- Insufficient light leads to poor coloration and lack of sweetness.
- Excessive light causes chlorophyll formation in undesirable areas, resulting in a bitter, green taste.
- Balancing light exposure (shade or controlled lighting) enhances potato flavor.
In summary, managing temperature and light effectively contributes to the desired taste profiles in potatoes.
Delving into the Differences in Nutritional Value between Hydroponic and Soil-Grown Potatoes
When comparing the nutritional value of hydroponic and soil-grown potatoes, it’s important to consider various factors that may influence their composition. While both methods can yield nutritious crops, there are some notable differences to be aware of.
Mineral Content:
- Hydroponic Potatoes: Controlled environment allows for precise nutrient delivery, potentially resulting in higher levels of minerals like potassium and phosphorus.
- Soil-Grown Potatoes: Mineral content varies depending on soil composition, leading to a wider range of mineral levels.
Vitamin Content:
- Hydroponic Potatoes: Controlled growing conditions may contribute to higher levels of certain vitamins, such as vitamin C.
- Soil-Grown Potatoes: Vitamin content can also vary based on soil composition and environmental factors.
Nutritional Value Overview:
- Moderate Differences: Variances in nutritional value between hydroponic and soil-grown potatoes are not drastic.
- Essential Nutrients: Both types still provide essential nutrients, albeit with potential differences in levels.
- Other Influences: Personal preferences, cultivation techniques, and other factors can also impact taste, texture, and overall quality.
To draw a comprehensive conclusion on which type of potato tastes better, it is necessary to consider a broader range of factors beyond just the nutritional content.
Summarizing the Findings: Which Type of Potato Tastes Better?
Potatoes are a dietary staple and a versatile ingredient that can be prepared in countless ways. In order to determine which type of potato tastes better, we conducted a comprehensive analysis comparing hydroponically grown potatoes to those cultivated in soil-based systems. Our findings reveal that taste is influenced by multiple factors, including growing medium, nutrient levels, watering techniques, light exposure, pest control methods, temperature, soil composition, and environmental factors.
- Growing Medium:
- Hydroponically grown potatoes:
- Tend to have a slightly milder and cleaner flavor.
- Benefit from a controlled environment where nutrient levels can be precisely adjusted.
- Soil-grown potatoes:
- Exhibit a stronger and earthier taste.
- Absorb nutrients from the natural composition of the soil.
- Hydroponically grown potatoes:
- Nutrient Levels:
- Hydroponic potatoes receive precisely controlled nutrients, resulting in a consistent taste.
- Soil-grown potatoes rely on the nutrient availability in the soil, which can vary.
- Growing Conditions:
- Differences in growing conditions contribute to the subtle taste variations.
In summary, hydroponic potatoes offer a cleaner taste due to controlled nutrients, while soil-grown potatoes have a more robust flavor influenced by natural soil composition. 🥔🌱🌿
Learn more about the difference between Hydroponics and Soil-Grown:
FAQ
What is hydroponics and how does it relate to potato cultivation?
Hydroponics is a method of growing plants without using soil. It involves growing plants in nutrient-rich water solutions instead. In relation to potato cultivation, hydroponics can provide a controlled environment for optimal growth and potentially influence the taste of the potatoes.
How do nutrient levels differ between hydroponic potatoes and soil-grown potatoes?
Nutrient levels can vary between hydroponic potatoes and soil-grown potatoes. Hydroponically grown potatoes have their nutrient levels carefully controlled through the water solution they are grown in. Soil-grown potatoes, on the other hand, rely on the nutrients present in the soil, which can vary depending on the composition and quality of the soil.
Does the watering technique affect the flavor of potatoes?
Yes, the watering technique can have an impact on the flavor of potatoes. The amount and frequency of watering can affect the overall moisture content of the potatoes, which can influence their taste and texture.
How does light exposure affect the taste of potatoes?
Light exposure can influence the taste of potatoes. Potatoes that are exposed to excessive light can develop a bitter taste due to the production of solanine, a natural toxic compound. Therefore, proper light management is important to ensure the desired flavor of potatoes.
What are the different pest control methods used in potato cultivation?
There are various pest control methods used in potato cultivation, including chemical pesticides, biological control agents, and cultural practices. Chemical pesticides are often used to control pests, but their use can potentially affect the flavor of potatoes. Biological control agents, such as predatory insects, are an environmentally friendly alternative. Cultural practices, like crop rotation, can also help manage pests.
Does temperature affect the taste of potatoes?
Yes, temperature can affect the taste of potatoes. Extreme temperatures, such as excessive heat or cold, can impact the growth and development of potatoes, potentially affecting their flavor. Optimal temperature conditions are necessary for the potatoes to develop their desired taste.
How does soil composition contribute to potato flavor development?
Soil composition plays a significant role in potato flavor development. The nutrients present in the soil, as well as its pH levels and overall structure, can influence the taste of the potatoes. Different soil compositions can result in variations in flavor profiles.
How does the texture of hydroponic potatoes compare to soil-grown potatoes?
The texture of hydroponic potatoes and soil-grown potatoes can differ. Hydroponic potatoes are often known for their consistent texture and tend to have a smoother and more uniform appearance. Soil-grown potatoes, on the other hand, may exhibit more variation in texture due to the influence of soil composition and growing conditions.
What environmental factors influence the taste of potatoes?
Several environmental factors can influence the taste of potatoes, including temperature, light exposure, humidity, and air quality. These factors can affect the growth and development of potatoes, ultimately impacting their flavor.
Are there any differences in nutritional value between hydroponic and soil-grown potatoes?
Yes, there can be differences in nutritional value between hydroponic and soil-grown potatoes. The nutrient levels in hydroponic potatoes are carefully controlled, which may result in higher or more consistent nutrient content compared to soil-grown potatoes. However, it is important to consider the specific nutrient composition of the growing medium and soil to determine the exact variations in nutritional value.

Studied Agricultural Engineering-Plant Protection at University of California, Davis.
Head of Content writing team at Southelmontehydroponics.com