Strawberry Growth Timeline: From Planting to Picking
Table of Contents
Planting the Strawberry Growth

Once you have acquired your Strawberry Growth seeds, it is time to prepare them for planting. Begin by selecting a well-draining potting mix to ensure optimal growth conditions for your seeds. Moisten the mix slightly before planting to provide the necessary moisture for germination. Place the seeds on the soil surface, gently pressing them down for good seed-to-soil contact. Avoid burying the seeds too deeply as they require light to germinate.
After planting the strawberry seeds, cover the container with a clear plastic lid or wrap to create a greenhouse effect. This will help maintain the moisture level and temperature needed for successful germination. Place the container in a warm location with indirect sunlight. Regularly check the moisture level of the soil to ensure it remains consistently damp but not waterlogged. With proper care and attention, you will soon witness the exciting sight of your strawberry seeds sprouting and beginning their journey towards becoming fruitful plants.
Germination and Sprouting
Upon reaching the germination stage, the strawberry seeds begin their journey towards sprouting and growth. This critical phase involves the absorption of water, triggering metabolic processes within the seed, eventually leading to the emergence of the radicle. The sprouting process is a delicate balance of moisture, warmth, and oxygen, essential for the seed to break dormancy and initiate growth. As the seedling emerges from the soil, it embarks on a quest for light, essential for photosynthesis and the production of energy needed for further development.
The sprouting strawberry seedling exhibits its vigor as it stretches upwards, displaying its tiny yet determined leaves. This early growth phase is crucial for establishing the foundation of the plant’s structure and function. The emerging leaves are pivotal in capturing sunlight, essential for the production of sugars through photosynthesis, fueling the plant’s growth and development. As the seedling continues to unfurl its leaves, it marks the beginning of a remarkable journey towards blooming and eventually bearing the sweet fruits of labor.
Establishing Roots
When strawberry seeds sprout, the first order of business is establishing strong roots. Roots play a crucial role in nutrient absorption and water uptake, providing the foundation for a healthy and productive plant. As the seedling grows, you’ll notice fine root hairs extending into the surrounding soil, anchoring the plant in place and allowing it to access essential resources for growth.
It’s important to ensure that the soil is well-draining and moist but not waterlogged during this critical stage of root development. Excess water can lead to root rot, while insufficient moisture can hinder root growth. By maintaining optimal soil conditions and providing proper care, you can help the strawberry plant establish a robust root system that will support its growth and fruit production in the future.
Growth of Leaves and Stems
As strawberry plants continue to grow, their leaves and stems play a crucial role in photosynthesis, the process by which plants convert light energy into chemical energy. The leaves of the strawberry plant are responsible for absorbing sunlight and carbon dioxide, using these elements in conjunction with water to produce sugars that serve as the plant’s energy source for growth and development.
Alongside the leaves, the stems of the strawberry plant provide structural support and transport essential nutrients and water throughout the plant. The stems act as conduits, allowing for the movement of water from the roots to the leaves and sugars produced during photosynthesis from the leaves to other parts of the plant. Additionally, the stems of the strawberry plant play a vital role in anchoring the plant in the soil and positioning the leaves to receive optimal sunlight for the photosynthesis process.
Flower Bud Formation
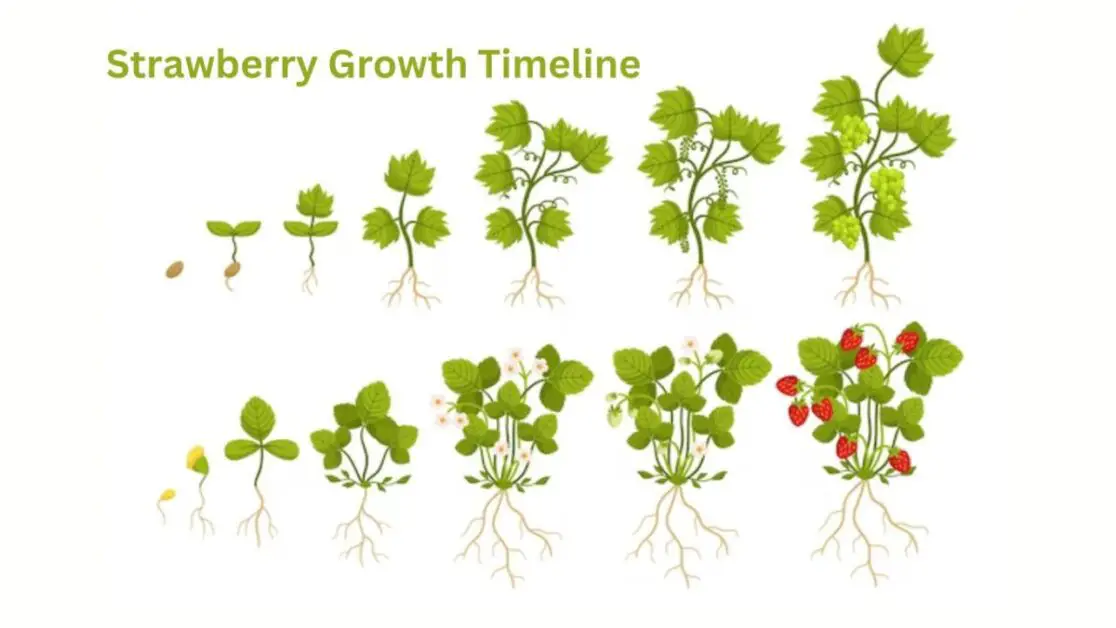
Once the strawberry plants have reached a certain stage of growth, they begin the process of forming flower buds. This is a crucial stage in the development of the plant as it marks the transition from vegetative growth to reproductive growth. The formation of flower buds is triggered by various environmental factors such as temperature, light, and nutrient availability. As the buds begin to develop, they undergo a series of complex physiological changes that ultimately lead to the production of flowers.
The formation of flower buds is a highly orchestrated process that involves the activation of specific genetic pathways within the plant. These pathways regulate the expression of genes that are responsible for the development of the floral structures. As the buds continue to mature, they gradually swell and take on a distinct shape, signaling the impending arrival of the flowering stage. The formation of flower buds is a critical milestone in the life cycle of the strawberry plant, setting the stage for the next phase of growth and development.
Pollination Process
During the pollination process, the transfer of pollen from the male reproductive organ (anther) to the female reproductive organ (stigma) of the flower occurs. This crucial step is essential for the fertilization and production of fruit in the strawberry plants. The pollination can be facilitated by wind, insects like bees, or even through human intervention by hand-pollination in controlled environments.
Once the pollen lands on the stigma, it travels down the style to reach the ovary where fertilization takes place, leading to the formation of seeds within the strawberry fruit. The successful pollination process is vital for ensuring a bountiful harvest of ripe and juicy strawberries. It is fascinating to observe nature’s intricate mechanisms at work in the pollination of strawberry plants, ultimately resulting in the delicious fruits that we enjoy.
Fruit Development
During the fruit development stage of the strawberry plant, the tiny green berries start to grow in size and take on their familiar red hue as they mature. This process is crucial for the formation of juicy and flavorful strawberries that are enjoyed by many. The berries swell and increase in sweetness as they absorb nutrients from the plant, reaching their optimal taste and texture for harvest.
As the strawberries continue to develop, it is essential to monitor their progress closely to ensure they ripen evenly and are not affected by pests or diseases. Adequate watering and sunlight are crucial factors during this stage to support healthy fruit growth. Proper care during fruit development can result in a bountiful harvest of delicious strawberries that can be enjoyed fresh or used in various culinary creations.
Ripening of the Strawberries
As the strawberries reach their peak ripeness, their color deepens, transitioning from a vibrant green to a luscious red hue that signals the perfect moment for harvest. This color transformation is a result of the natural ripening process, during which the sugars concentrate and the berries develop their characteristic sweet flavor. It is essential to monitor the ripening progress closely to ensure that the fruits are picked at the ideal stage for optimal taste and juiciness.
In addition to the color change, the strawberries will also emit a tantalizing aroma that fills the air with their fruity fragrance. This scent is a clear indicator of the rich and delectable flavors that await within the ripe berries. When gently pressed, a ripe strawberry will yield slightly, indicating its readiness for picking. By paying attention to these visual and olfactory cues, you can savor the joy of harvesting perfectly ripe strawberries straight from your garden, ready to be enjoyed fresh or incorporated into a variety of culinary delights.
Harvesting the Strawberries
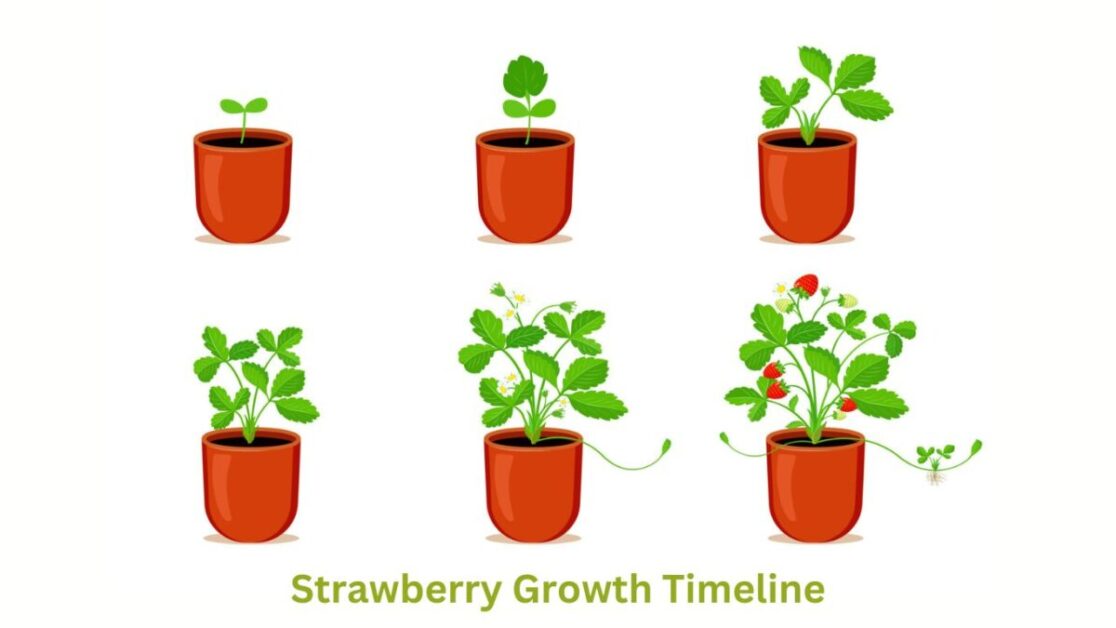

When the strawberries are ready for harvesting, it is important to pick them at the right time to ensure optimal flavor and sweetness. Ripe strawberries should be bright red all over and have a plump appearance. Gently twist the strawberries off the plant, being careful not to pull too hard and damage the delicate fruits. Harvesting in the morning when the fruits are cool can help prolong their freshness and flavor.
Regularly check your strawberry patch for ripe fruits, as they can quickly become overripe and attract pests if left unpicked. It is recommended to harvest strawberries every few days during peak season to ensure you gather them at their prime. Once harvested, store the strawberries in a cool place or refrigerate them to maintain their freshness. Enjoy the sweet and juicy rewards of your labor either fresh or use them in various culinary creations like jams, pies, and smoothies.
Caring for the Strawberry Plants
After planting your strawberry plants, caring for them is essential to ensure healthy growth and bountiful harvests. Regular watering is crucial, keeping the soil moist but not waterlogged. Mulching around the plants helps retain moisture, suppress weeds, and maintain even soil temperature.
Regularly feeding your strawberry plants with a balanced fertilizer will provide them with essential nutrients for robust growth and fruit development. It’s recommended to use a fertilizer specifically formulated for strawberries and to follow the manufacturer’s instructions for application. Additionally, monitoring for pests and diseases is important in maintaining the health of your plants. Early detection and appropriate treatment can prevent significant damage and loss of yield.
Pruning and Thinning
When it comes to maintaining the health and productivity of your strawberry plants, pruning and thinning play crucial roles. Pruning involves the selective removal of certain plant parts, such as old leaves, runners, or damaged stems. This practice helps improve air circulation, reduce disease incidence, and stimulate new growth. By removing dead or diseased foliage, you can prevent the spread of pathogens and ensure that the plant’s resources are channeled towards healthy tissue development.
Thinning, on the other hand, involves the strategic removal of excess shoots, flowers, or fruits to optimize plant growth and fruit production. By thinning out overcrowded areas, you allow the remaining berries to develop to their full potential, resulting in larger and sweeter fruits. Proper thinning also helps prevent the plant from becoming overly stressed and promotes the even ripening of the remaining berries. When done correctly, pruning and thinning can enhance the overall health and yield of your strawberry plants, ultimately leading to a more bountiful harvest.
Protecting from Pests and Diseases
To safeguard your strawberry plants from pests and diseases, it is essential to employ preventive measures and early intervention strategies. One common pest that affects strawberries is the two-spotted spider mite, known for causing damage by sucking sap from the leaves. Regularly inspect the undersides of the leaves for any signs of these tiny pests or webbing, and consider introducing natural predators like ladybugs to help control their population.
Another threat to strawberry plants is gray mold, a fungal disease that thrives in moist conditions and can quickly spread in crowded plantings. To mitigate this risk, ensure proper spacing between plants for adequate airflow, and avoid overhead watering to reduce humidity levels. Applying a preventative fungicide treatment early in the season, following product instructions carefully, can also help protect your crop from succumbing to gray mold. Remember, early detection and proactive management are key in preserving the health and productivity of your strawberry plants.
Preparing the Soil for the Next Season
When preparing the soil for the next season, it is crucial to focus on replenishing the nutrients that were depleted by the previous crop. Nutrient-rich soil is essential for healthy plant growth and abundant yields. Conduct a soil test to determine which nutrients are lacking and amend the soil accordingly.
In addition to nutrient replenishment, it is important to improve the soil structure for optimal plant growth. Incorporating organic matter such as compost or well-rotted manure can enhance soil structure, promote good drainage, and increase the soil’s ability to retain moisture. This will create a favorable environment for roots to develop and plants to thrive throughout the growing season.
Continuing Care and Maintenance

To ensure the health and vitality of your strawberry plants, it is essential to continue providing proper care and maintenance throughout their growing season. Regular watering is crucial, especially during hot and dry periods, to keep the soil consistently moist but not waterlogged. Mulching around the plants can help retain moisture and suppress weeds, promoting optimal growth. Additionally, feeding the plants with a balanced fertilizer at recommended intervals will supply essential nutrients for robust development.
Regularly monitoring your strawberry plants for signs of pests and diseases is paramount in maintaining their well-being. Inspecting the leaves, stems, and fruits for any abnormalities such as discoloration, spots, or wilting can help you identify problems early on. Implementing natural remedies or approved pesticides when necessary can help mitigate issues before they escalate. Furthermore, promoting good air circulation around the plants by spacing them adequately and removing any overcrowded or diseased plant material can aid in preventing common fungal diseases.
here’s a simple table outlining the typical timeline for the growth of strawberries from planting to picking:
| Stage | Timeframe |
|---|---|
| Planting | Late winter to early spring |
| Germination | 1 to 3 weeks |
| Seedling Growth | 4 to 6 weeks |
| Transplanting | Late spring to early summer |
| Flowering | Late spring to early summer |
| Fruit Development | Early summer to late summer |
| Ripening | Late spring to early fall |
| Picking | Late spring to early fall |
Keep in mind that these timeframes can vary depending on factors such as climate, variety of strawberry, and growing conditions.
Enjoying the Fruits of Your Labor
Once your strawberry plants have grown and matured, it’s time to reap the rewards of your hard work and patience. The vibrant red fruits gleaming against the green foliage signify a successful journey from seed to harvest. The sweet and juicy strawberries are not only a delight to the taste buds but also a visual treat in your garden.
Savor the experience of plucking ripe strawberries straight from the plant, feeling the sun-warmed fruit in your hand before taking a bite. Whether you enjoy them fresh, in a salad, as a topping on desserts, or blended into smoothies, the possibilities are endless. Sharing your bountiful harvest with friends and family can also bring joy and satisfaction as you witness the fruits of your labor being enjoyed and appreciated by others.
How long does it take for a strawberry plant to start producing fruit?
It typically takes around 4-6 weeks for a strawberry plant to start producing fruit after the flowers have been pollinated.
Do strawberry plants need a lot of sunlight to thrive?
Yes, strawberry plants thrive in full sunlight and require at least 6-8 hours of sunlight per day for optimal growth and fruit production.
Can I grow strawberries in containers or do they need to be planted in the ground?
Yes, you can definitely grow strawberries in containers as long as they have enough space, proper drainage, and receive adequate sunlight.
How often should I water my strawberry plants?
Strawberry plants need consistent moisture, so it’s important to water them regularly, especially during dry periods. Aim to keep the soil evenly moist but not waterlogged.
When is the best time to harvest strawberries?
The best time to harvest strawberries is when they are fully ripe, which is usually indicated by a deep red color and sweet fragrance. Be gentle when picking them to avoid damaging the delicate fruit.