Mulch Around Trees: Benefits and Considerations
Table of Contents
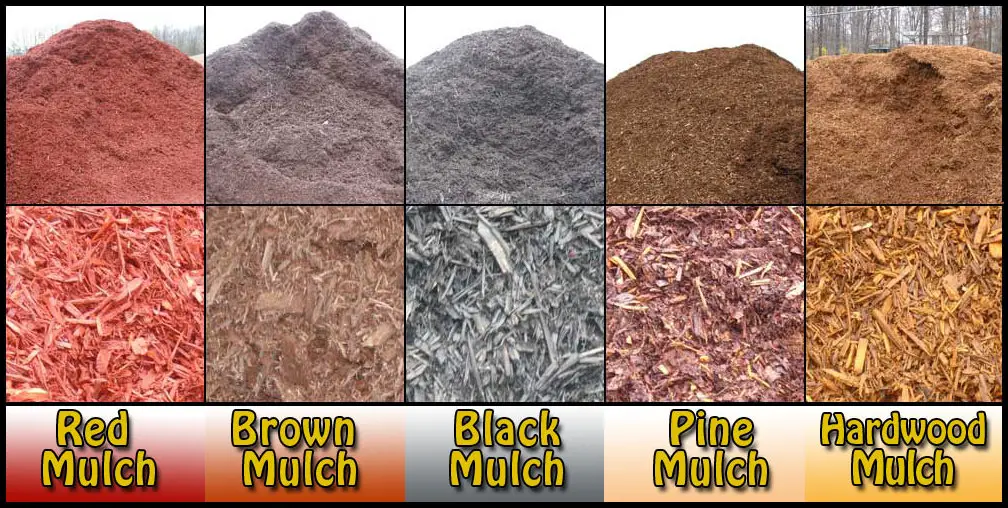
Types of Mulch for Trees
Choosing the right type of mulch for trees is crucial for their overall health and growth. There are several options available in the market, each with its own unique characteristics and benefits. One popular type is organic mulch, which includes materials like wood chips, bark, and leaves. Organic mulch not only adds nutrients to the soil as it decomposes but also helps improve soil structure and retains moisture effectively.
Inorganic mulch, on the other hand, is made up of materials like rocks, gravel, or rubber chips. While inorganic mulch does not provide nutrients to the soil, it offers excellent weed control and can be long-lasting. Additionally, inorganic mulch doesn’t break down over time, making it a low-maintenance option for tree mulching. It is important to note that inorganic mulch may not be as effective in retaining moisture as organic mulch, so it should be used cautiously in areas prone to drought or with trees that require ample moisture.
Ultimately, the choice of mulch will depend on various factors such as the tree species, climate, soil conditions, and personal preferences. It is always recommended to consult with local gardening experts or arborists to determine the most suitable mulch option for your specific tree and gardening needs.

Importance of Mulching Around Trees
Mulching is an essential practice for maintaining the health and vitality of trees in any landscape. By creating a protective barrier around the base of the tree, mulch offers a multitude of benefits that can greatly impact the overall well-being of the tree.
One of the primary reasons for mulching around trees is its ability to conserve moisture. By acting as a natural insulator, mulch helps to reduce soil evaporation, thus preventing water loss. This is particularly advantageous in hot and dry climates or during periods of drought. The moisture-retaining properties of mulch also provide a stable environment for the tree’s roots, ensuring they stay hydrated and have access to the water necessary for their growth and development. Additionally, the presence of mulch can help regulate soil temperature, keeping it cooler in the summer and warmer in the winter, further aiding in the tree’s ability to withstand extreme weather conditions.
Furthermore, mulch acts as a natural weed barrier, preventing the growth and competition of undesirable plant species around the tree. By inhibiting weed growth, mulch reduces the need for manual or chemical weed control methods, which can be harmful to the tree and surrounding environment. This not only saves time and effort but also allows the tree to utilize nutrients and water more efficiently, exclusively benefiting its growth and health. Additionally, as organic mulch breaks down over time, it contributes valuable nutrients back into the soil, further enhancing its fertility and ensuring the tree’s nutritional needs are met.
In conclusion, mulching around trees provides numerous advantages that promote their overall health and vitality. From conserving moisture and regulating soil temperature to acting as a weed barrier and enhancing soil fertility, mulch plays a significant role in protecting and nourishing trees. By incorporating proper mulching techniques, gardeners can greatly enhance the success and longevity of their trees while minimizing the use of harmful chemicals and reducing water consumption. So, don’t underestimate the importance of mulching around trees – it’s a simple yet effective practice that can yield remarkable results.
How Mulch Helps Retain Moisture
Mulch plays a vital role in retaining moisture around trees, especially during hot and dry periods. By acting as a protective layer, mulch helps to reduce evaporation from the soil surface, preserving precious water that trees need for optimal growth and health.
When properly applied, mulch forms a barrier between the soil and the air, preventing moisture from escaping through evaporation. This is particularly important in regions with high temperatures and low humidity, where water loss from the soil can be significant. In fact, research has shown that mulching can reduce soil moisture loss by up to 75%, helping to maintain a stable and favorable environment for tree roots.
In addition to preventing water loss, mulch also aids in water absorption. Its porous nature allows rainwater or irrigation to penetrate the soil more effectively, enabling tree roots to access the water they need. This is particularly advantageous in areas with compacted or poorly draining soils, as mulch helps to improve water infiltration and percolation rates.
By retaining moisture and facilitating water absorption, mulch helps to create an optimal growing environment for trees. Alongside providing essential nutrients and ensuring proper irrigation, mulching plays a fundamental role in promoting the overall health and vitality of trees in both residential and commercial landscapes. So, when it comes to water conservation and tree care, mulching is an indispensable practice to consider.
Mulch as a Weed Barrier
Mulching around trees is an essential practice for maintaining a healthy and thriving landscape. In addition to its numerous benefits, mulch also serves as an effective weed barrier. By creating a physical barrier between the soil and the surrounding environment, mulch helps to prevent weed growth and competition for essential nutrients and water.
Weed growth can be detrimental to the health of trees, as they compete for resources that are crucial for tree growth and development. Weeds can also hinder the establishment of young trees by stifling their nutrient uptake and impeding their access to sunlight. Moreover, the presence of weeds can create a breeding ground for pests and diseases, further compromising the overall vitality of the tree.
By using mulch as a weed barrier, gardeners can significantly reduce the risk of weed infestation while promoting the well-being of their trees. Mulch acts as a protective layer that suppresses weed germination and growth by blocking sunlight, impeding their ability to thrive. Furthermore, organic mulches such as wood chips, bark, or straw also break down over time, providing an additional benefit of enriching the soil with nutrients as they decompose. It’s important to note that using a proper mulching technique and applying an adequate layer of mulch are essential for achieving optimal weed control and overall tree health.
Enhancing Soil Fertility with Mulch
Enhancing soil fertility is crucial for maintaining healthy and thriving trees in your garden. Mulching plays a vital role in this regard, as it can significantly contribute to the overall fertility of the soil. By providing a protective layer over the soil surface, mulch helps to retain moisture, regulate temperature, and prevent erosion. Moreover, as the mulch breaks down over time, it enhances the nutrient content of the soil, thereby promoting the growth and development of trees.
The gradual decomposition of organic mulch materials releases essential nutrients into the soil. These nutrients, such as nitrogen, phosphorus, and potassium, are vital for the optimal growth of trees. Additionally, organic mulches, such as wood chips or compost, can also improve the soil structure by enhancing its water-holding capacity and promoting the growth of beneficial microorganisms. As the mulch breaks down, it also acts as a slow-release fertilizer, steadily providing nutrients to the tree’s root system. This process not only ensures a steady supply of nutrients but also reduces the need for excessive fertilization, leading to a more sustainable and eco-friendly gardening approach.

Improving Soil Structure with Mulch
Improving the soil structure is essential for healthy tree growth and overall garden productivity. One effective method to enhance soil structure is by incorporating mulch into the garden bed. Mulch serves as a protective layer that helps to regulate soil temperature and maintain moisture levels. Additionally, it plays a significant role in promoting the activity of beneficial organisms such as earthworms and microorganisms, which contribute to soil fertility.
By applying a layer of organic mulch, such as wood chips, compost, or straw, around the base of trees, you create a favorable environment for microbes and earthworms to thrive. These organisms break down organic matter within the mulch, gradually improving the soil structure. As they decompose the mulch, they create air pockets and increase the soil’s water-holding capacity. This improved soil structure allows for better aeration and nutrient absorption by the tree roots, ultimately leading to healthier and more robust tree growth. Moreover, the decomposition of mulch adds organic matter to the soil, further enriching its fertility and supporting a diverse and flourishing ecosystem.
In conclusion, using mulch as a soil amendment is a practical and sustainable practice for improving soil structure. The decomposition of organic mulch materials enhances soil aeration, moisture retention, and nutrient availability, creating an optimal environment for tree growth. By incorporating mulching into your gardening routine, you can experience the beneficial effects of improved soil structure on the overall health and vitality of your trees and garden.
Mulching to Protect Tree Roots
Protecting tree roots is essential for their overall health and longevity. Mulching is an effective technique that can provide a protective barrier for tree roots, safeguarding them from a variety of external factors and promoting their optimal growth. By creating a layer of mulch around the base of the tree, gardeners can reap numerous benefits while ensuring the roots remain healthy and undisturbed.
One of the primary advantages of mulching to protect tree roots is the regulation of soil temperature. Mulch acts as an insulating layer, shielding the roots from extreme heat or cold. This insulation helps to stabilize the soil temperature, creating a favorable environment for root development and minimizing stress on the tree. Additionally, the mulch layer helps retain moisture in the soil, reducing water evaporation and maintaining a consistent level of hydration for the roots. This moisture retention is especially crucial during dry spells or in regions experiencing drought conditions, as it enhances the tree’s ability to access water and nutrients. By conserving moisture, mulch also prevents soil compaction, which can impede root growth and nutrient absorption. Overall, mulching around tree roots provides a natural protection system that ensures optimal conditions for healthy root development and the overall well-being of the tree.
Preventing Soil Erosion with Mulch
Soil erosion is a natural process that can cause significant damage to the landscape and affect the health of trees. However, by implementing mulching techniques, we can effectively prevent soil erosion and maintain the stability of the soil around trees.
One of the main benefits of using mulch to prevent soil erosion is its ability to act as a protective barrier. Mulch creates a physical barrier between the soil and the forces of nature, such as raindrops and strong winds. By slowing down water flow and reducing the impact of raindrops on the soil surface, mulch decreases the likelihood of soil particles being washed away. Additionally, the layer of organic mulch helps to retain moisture in the soil, reducing the risk of erosion caused by dry conditions.
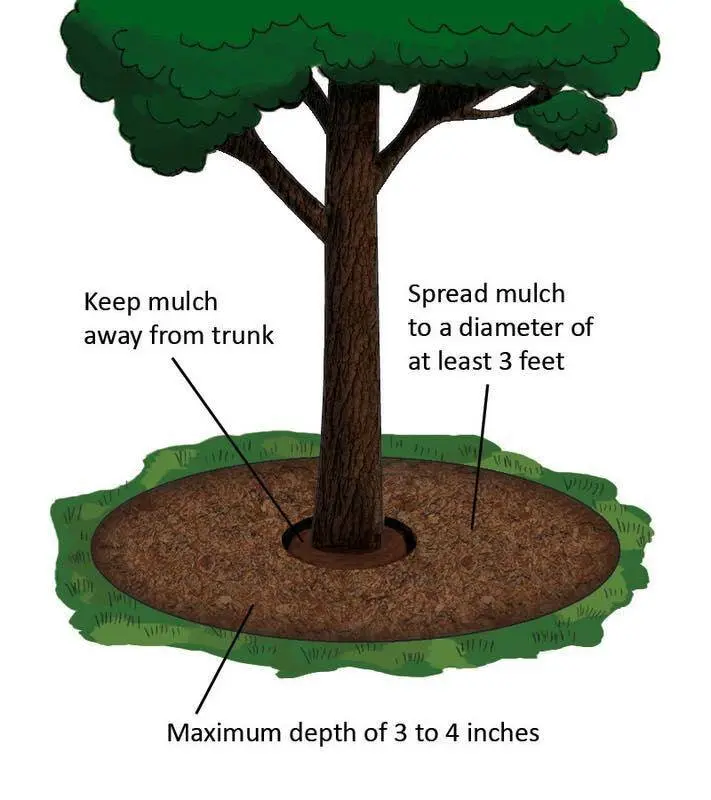
Choosing the Right Depth for Mulching
When it comes to mulching around trees, choosing the right depth is crucial to maximize the benefits and promote healthy growth. The depth of mulch plays a significant role in providing insulation, retaining moisture, and suppressing weed growth. However, it’s important to strike the right balance and avoid over-mulching, which can have adverse effects on the tree’s health.
A general rule of thumb for choosing the right depth of mulch is to aim for a layer that is 2-4 inches deep. This thickness provides an adequate barrier against weed growth, helps to retain moisture in the soil, and insulates the tree’s roots from extreme temperature fluctuations. However, keep in mind that this recommendation may vary depending on the type of mulch used and the specific needs of the tree species.
Too much mulch can create a barrier that prevents water from reaching the tree’s roots and restricts the exchange of gases. This can lead to the development of root rot or other moisture-related issues. On the other hand, insufficient mulch may not provide enough insulation or weed suppression. Striving for the recommended depth ensures that the tree receives the right balance of moisture, temperature regulation, and protection for optimal growth and health.
Proper Mulching Techniques
Mulching is a critical aspect of tree care, and when done correctly, it can provide numerous benefits to the health and growth of your trees. Proper mulching techniques not only protect tree roots but also ensure moisture retention, weed control, and improved soil fertility. One key aspect of mulching is choosing the right type of mulch. Organic mulches, such as wood chips, straw, or shredded leaves, are commonly preferred as they decompose over time, enriching the soil with nutrients.
The depth of mulch is another essential consideration. Applying a mulch layer that is around 2-4 inches thick is generally recommended. This depth is enough to provide adequate insulation and protection to the tree’s shallow roots while allowing proper airflow and water penetration. However, it is crucial to avoid piling mulch directly against the tree trunk, as this can lead to moisture retention and invite disease and pests. Maintaining a small space around the base of the tree, known as the “mulch-free zone,” is vital for preventing root rot and ensuring the tree’s overall health and vigor. By following these proper mulching techniques, you can create an optimal environment for your trees, promoting their longevity and vitality.

Common Mistakes to Avoid When Mulching Trees
One common mistake that many people make when mulching trees is piling the mulch too high around the base of the tree. While it may seem like a good idea to create a thick layer of mulch to provide extra protection and insulation, this can actually have negative effects on the tree’s health. Excessive mulch can retain too much moisture, leading to root rot and other fungal diseases. Additionally, mulch piled too high can create a barrier that prevents oxygen from reaching the roots, stifling their growth.
Another mistake to avoid is mulching too close to the trunk of the tree. It is important to leave a gap between the mulch and the tree’s base, known as the “mulch volcano.” When mulch is placed directly against the trunk, it creates a moist environment that can encourage the growth of bacteria and fungi, increasing the risk of disease. Furthermore, close contact between the mulch and the trunk can also lead to decay and rot, compromising the structural integrity of the tree. To avoid these issues, always leave a few inches of space between the mulch and the tree’s trunk, allowing for proper airflow and preventing excess moisture accumulation.
Mulch and Temperature Regulation
Mulch, when properly applied around trees, can play a crucial role in regulating temperature and creating a favorable environment for their growth. The layer of mulch acts as an insulating barrier, helping to maintain a more constant soil temperature throughout the year. This is particularly important in regions with fluctuating climate conditions, as extreme temperature variations can have detrimental effects on tree roots.
The insulating properties of mulch help to mitigate temperature extremes, keeping the soil cooler in hot summer months and preventing it from freezing in cold winter periods. By acting as a buffer, mulch can protect tree roots from damage caused by temperature fluctuations, reducing the risk of heat stress or freeze injury. Additionally, the layer of mulch helps to conserve moisture and prevent evaporation, aiding in the maintenance of a stable soil temperature.
In conclusion, mulch serves as a valuable tool in regulating temperature around trees. Its insulating properties help to create a more constant soil temperature, protecting tree roots from the detrimental effects of extreme weather conditions. By utilizing mulch effectively, gardening enthusiasts can provide their trees with a suitable environment for optimal growth and minimize the risk of temperature-related stress or injury.
Mulching for Disease Prevention
Disease prevention is a critical aspect of maintaining the health and vitality of your trees. Mulching can play a key role in this regard, as it can help create a protective barrier against various pathogens. By applying a layer of mulch around the base of your trees, you can reduce the risk of diseases caused by fungal spores and other harmful microorganisms.
One of the primary ways mulch contributes to disease prevention is by acting as a natural defense mechanism. Organic mulches, such as wood chips or bark, release certain compounds as they break down. These compounds possess antifungal properties that can inhibit the growth and spread of disease-causing organisms. Additionally, the physical barrier created by the mulch can prevent splashing of soil-borne pathogens onto the trunk and lower branches of the tree, reducing the likelihood of infection. By implementing mulching practices, you can effectively protect your trees from common diseases and promote their overall well-being.
Certainly! Let’s explore the benefits of mulching for disease prevention. Mulch not only conserves moisture and suppresses weeds but also plays a crucial role in safeguarding plants from diseases. Here’s a table highlighting how different types of mulch contribute to disease prevention:
| Type of Mulch | Disease-Preventing Property | Best Used For |
|---|---|---|
| Straw | Minimizes Soil Splashing: Straw mulch creates a protective layer, reducing soil splashing onto leaves. This helps prevent the spread of soil-borne diseases. | Vegetable gardens, berry patches |
| Compost | Boosts Soil Health: Compost-rich mulch enhances soil structure, promotes beneficial microorganisms, and strengthens plant immunity against diseases. | Flowerbeds, around trees |
| Grass Clippings | Nitrogen-Rich Defense: Grass clippings provide nitrogen, which supports plant growth and helps fend off diseases. | Vegetable beds, herb gardens |
| Wood Chips | Slow Decomposition: Wood chip mulch decomposes gradually, releasing nutrients and creating a disease-resistant environment. | Around shrubs, fruit trees |
Mulch and Pest Control
Pests can pose a significant threat to the health and vitality of trees, and mulching is a valuable tool in pest control for these plants. Mulch acts as a physical barrier that helps to deter insects and other pests from crawling up the trunk of the tree and infesting its branches and leaves.
Some types of mulch, such as cedar or cypress, have natural insect-repellent properties that can further aid in pest control. These mulches release aromatic compounds that insects find unpleasant, keeping them away from the tree. Additionally, mulch helps to create a drier environment around the base of the tree, which can discourage pests that thrive in moist conditions.
By providing a layer of mulch around the tree, gardeners can help protect their trees from pests without resorting to harmful chemicals. However, it is important to note that mulching alone may not be sufficient to completely eliminate all pest problems. Integrated pest management techniques, which combine cultural, mechanical, and biological methods, should be employed alongside mulching to ensure effective pest control and promote the overall health of the tree.
Certainly! Let’s delve into the world of mulch and its role in pest control. Mulching is not just about aesthetics; it serves as a natural defense mechanism against various pests. Here’s a table highlighting the benefits of using mulch for pest control:
| Type of Mulch | Pest-Deterring Property | Best Used For |
|---|---|---|
| Wood chips | Suppresses weed growth | Flowerbeds |
| Straw | Retains soil moisture | Vegetable gardens |
| Cocoa hulls | Emits deterring scent | Ornamental gardens |
When to Mulch Around Trees
Mulching around trees is a vital task that helps maintain their health and promote optimal growth. However, knowing when to apply mulch is just as important as the type of mulch used. Ideally, the best time to mulch around trees is in the spring or fall when the soil is moist and temperatures are moderate.
Applying mulch too early in the spring can prevent the soil from warming up, inhibiting root development. On the other hand, mulching too late can lead to the loss of moisture during the hot summer months, leaving the trees susceptible to drought stress. By timing the mulching process correctly, you can provide a protective layer that assists in moisture retention, weed suppression, and temperature regulation throughout the entire growing season.
In conclusion, understanding when to mulch around trees is a crucial element in tree care. By considering the appropriate timing based on the season and weather conditions, you can provide your trees with the necessary support and create an environment conducive to healthy growth. With proper timing, your trees can thrive and bring beauty and benefits to your outdoor space.
Potential Risks and Considerations of Mulching
Mulching around trees can provide numerous benefits, but it is important to consider the potential risks and take certain precautions before mulching. One of the main risks associated with improper mulching is the formation of a “mulch volcano.” This occurs when too much mulch is piled up around the base of the tree, creating a cone-like shape that holds excess moisture against the trunk. This excessive moisture can lead to the development of fungal diseases, decay, and even the death of the tree. Proper mulching requires maintaining a mulch-free zone around the base of the tree to prevent these issues.
Another consideration when mulching around trees is the potential for suffocating the root system. Excessive mulch applied too thickly can restrict oxygen and water flow to the roots, hindering their ability to efficiently uptake nutrients and causing the tree to become stressed. Additionally, some organic mulches, such as fresh wood chips or sawdust, can temporarily reduce soil nitrogen levels as they decompose, potentially leading to nutrient deficiencies for the tree. It is essential to monitor the mulch depth and choose the appropriate type of mulch to ensure the tree’s health and prevent any negative effects on its growth and development.
for more information watch the below video.
What are the potential risks of mulching around trees?
While mulching offers many benefits, there are a few potential risks to consider. Over-mulching, where mulch is piled too high around the trunk, can lead to excessive moisture retention and rotting of the tree’s bark. It can also attract pests and promote fungal growth. Additionally, using certain types of mulch, such as fresh wood chips, can deplete soil nitrogen levels and affect the tree’s nutrient uptake.
Can mulch attract pests to trees?
Yes, if mulch is not properly managed, it can attract pests such as termites, ants, and rodents. These pests may cause damage to the tree’s roots or even infest nearby structures. It’s important to regularly inspect and maintain the mulch to prevent pest problems.
Does mulching trees prevent weed growth completely?
While mulch can act as a weed barrier, it may not completely prevent weed growth. Some persistent weeds may still find their way through the mulch layer. Regular maintenance, such as hand-pulling or spot herbicide treatments, may be necessary to control weed growth effectively.
Can mulching around trees cause soil compaction?
Improper mulching techniques, such as piling mulch too high against the trunk, can lead to soil compaction. This can restrict oxygen and water flow to the tree’s roots, hindering its growth and overall health. It is crucial to ensure proper mulch depth and placement to avoid soil compaction.
Is there a specific time of year that is best for mulching trees?
It is generally recommended to mulch trees in the spring or fall when the soil is moist and the tree is not in its active growing phase. Avoid mulching during extreme temperature conditions or when the ground is frozen.
How often should mulch be replenished around trees?
Mulch should be replenished annually to maintain its effectiveness. However, it is essential to remove any old mulch or excessive buildup before adding new layers to prevent issues like excessive moisture retention or fungal growth.
Can mulching around trees cause root suffocation?
If mulch is piled too high against the tree trunk, it can lead to root suffocation. This occurs when the mulch layer restricts oxygen from reaching the roots, which can result in root decay and tree decline. It is crucial to keep the mulch several inches away from the trunk to prevent root suffocation.
Can mulch help regulate soil temperature around trees?
Yes, mulch acts as an insulator and can help regulate soil temperature. It keeps the soil cooler in the summer and warmer in the winter, providing a more stable environment for the tree’s roots.
Are there any specific mulch types that are more prone to fungal growth?
Certain organic mulch types, such as wood chips or bark mulch, can be more prone to fungal growth if not properly maintained. To prevent fungal issues, it is recommended to regularly turn or fluff the mulch and avoid excessive moisture retention.
Can mulching trees attract diseases?
Poor mulching practices, such as piling mulch against the tree trunk, can create a favorable environment for disease development. It is important to maintain proper mulch depth and keep it away from the tree’s base to reduce the risk of disease.

Nicole Burke is a dynamic writer at SouthElMonteHydroponics, fueled by her passion for horticulture and environmental sustainability. Armed with a degree in Environmental Science from a renowned institution, Nicole’s expertise lies in hydroponic gardening, organic farming, and biodiversity conservation. Her insatiable curiosity and love for nature drive her to explore innovative techniques in hydroponics, seeking to revolutionize the way we grow crops in urban environments. Nicole’s writing reflects her deep commitment to promoting eco-conscious practices and fostering a deeper connection between humans and the natural world. Through her engaging storytelling, she inspires others to embrace sustainable living and harness the power of hydroponics for a greener future.






