The Evolution of Hydroponics: A Historical Perspective
Table of Contents
1. The Origins of Hydroponics: Tracing Back to Ancient Civilizations
Hydroponics, the practice of growing plants without soil, has a history that dates back to ancient civilizations. Although the concept may seem modern and innovative, its origins can be traced back thousands of years. Ancient civilizations such as the Aztecs, Babylonians, and ancient Egyptians all practiced some form of hydroponics, albeit unknowingly.
The Aztecs, for example, created “chinampas,” which were floating gardens used to cultivate crops in the swampy areas of Mexico. These chinampas were essentially artificial islands made from layers of mud and vegetation, and crops were grown on top of them. This method allowed the Aztecs to maximize their agricultural output and provide food for their growing population.
Similarly, the ancient Egyptians utilized hydroponic techniques in their agricultural practices. The fertile soil along the Nile River was limited, so the Egyptians developed a system of irrigation canals to bring water to their crops. These canals served as a form of hydroponics, delivering water and nutrients directly to the plants’ roots, bypassing the need for soil.
The ancient Babylonians also had their own hydroponic marvel known as the Hanging Gardens of Babylon. This wonder of the ancient world was believed to be a series of tiered gardens built on rooftops, with plants growing in containers filled with nutrient-rich water. The Babylonians ingeniously used clay pots to hold the plants, which allowed for the recycling of water and nutrients, creating a sustainable and efficient system.
These early examples of hydroponics highlight the ingenuity and resourcefulness of ancient civilizations. While they may not have had a complete understanding of the science behind hydroponics, they intuitively grasped the concept of growing plants without soil. Their experiments and innovations laid the foundation for the development of modern hydroponics, paving the way for further advancements in the centuries to come.
2. Early Innovations: Hydroponics in Mesopotamia and Ancient Egypt
Hydroponics, the practice of growing plants without soil, has a long and fascinating history that dates back to ancient civilizations. Among these civilizations, Mesopotamia and Ancient Egypt stand out as early pioneers in the field of hydroponics.
In Mesopotamia, one of the earliest known civilizations, hydroponics was employed to overcome the region’s arid climate and limited agricultural land. The Hanging Gardens of Babylon, one of the Seven Wonders of the Ancient World, are believed to have utilized hydroponic techniques. These gardens, built by King Nebuchadnezzar II in the 6th century BCE, showcased the engineering marvel of water channels and reservoirs that allowed plants to thrive in a desert landscape.
Similarly, Ancient Egypt, with its fertile land along the Nile River, developed hydroponic systems to maximize crop production. The Egyptians used a technique called “ebb and flow,” where plants were periodically flooded and then drained, ensuring a consistent water supply while avoiding waterlogging. Their advanced knowledge of hydroponics was evident in their use of rafts made from papyrus, which supported the plants and provided necessary nutrients.
These early innovations in hydroponics laid the foundation for future advancements in agricultural practices, demonstrating the ingenious ways in which civilizations adapted to the challenges of their environments. While these techniques may seem rudimentary compared to modern hydroponics systems, they represent the earliest recorded instances of harnessing the power of water to cultivate plants, setting the stage for the hydroponic revolution yet to come.
3. The Hanging Gardens of Babylon: A Remarkable Hydroponic Wonder
The Hanging Gardens of Babylon are renowned as one of the Seven Wonders of the Ancient World. This incredible feat of engineering and horticulture has fascinated historians and archaeologists for centuries. What makes this wonder even more remarkable is its innovative use of hydroponics.
Built in the 6th century BCE, the Hanging Gardens were a testament to the advanced knowledge and skills possessed by the Babylonians. Situated in the city of Babylon (present-day Iraq), these gardens were an elevated oasis, consisting of terraces filled with lush vegetation. What sets them apart is the fact that they were essentially suspended in the air, with no natural soil to support the plants.
But how was this achieved? The secret lies in the ingenious hydroponic systems employed by the Babylonians. By utilizing water and mineral-rich solutions, the gardeners were able to nourish the plants directly through their roots, eliminating the need for traditional soil-based cultivation. This method allowed them to cultivate a diverse range of plants and trees, creating a breathtaking and self-sustainable landscape. The Hanging Gardens of Babylon exemplify the early innovation and mastery of hydroponics in ancient civilizations, setting the stage for future developments in this field.
4. Renaissance Revival: Hydroponics in the 15th to 17th Centuries
During the Renaissance period from the 15th to the 17th centuries, there was a renewed interest in scientific inquiry and exploration. This intellectual curiosity not only led to groundbreaking discoveries in various fields but also sparked a revival of interest in hydroponics.
One notable figure during this time was the Italian physician and botanist, Andrea Cesalpino, who recognized the potential of growing plants without soil. Cesalpino conducted numerous experiments and documented his findings in his influential work, “De Plantis.” His research laid the foundation for future advancements in hydroponic systems.
Additionally, Leonardo da Vinci, renowned for his diverse talents, also explored the concept of soil-less cultivation. In his notebooks, da Vinci sketched and described various hydroponic methods, showcasing his innovative thinking and curiosity about nature.
The Renaissance period witnessed a resurgence of interest in hydroponics, as scholars and scientists began to unravel the mysteries of plant growth without soil. These early pioneers set the stage for further advancements in the centuries to come, paving the way for modern hydroponic practices that would revolutionize agriculture and horticulture.
5. The Scientific Revolution: Advancements in Hydroponics during the 18th Century
The 18th century marked a significant period of advancement in hydroponics, as scientists and researchers began to explore the possibilities of soil-less agriculture. One pioneering figure during this time was Swedish botanist and physician Carl Linnaeus, who conducted experiments that laid the foundation for modern hydroponics. Linnaeus developed a technique known as “water culture,” in which he cultivated plants in water fortified with essential nutrients.
Linnaeus’s experiments with water culture not only demonstrated the feasibility of plant growth without soil, but also highlighted the importance of nutrient supplementation. He observed that plants could thrive and produce healthy yields when provided with a balanced nutrient solution, thus challenging the notion that soil was an essential component for plant growth. This breakthrough paved the way for further research and experimentation in hydroponics throughout the 18th century.
Another notable contribution to hydroponics during this time was made by Scottish physician and chemist Joseph Priestley. Known for his discoveries in the field of chemistry, Priestley conducted experiments that focused on the role of gases in plant growth. He demonstrated the significance of carbon dioxide in photosynthesis, which had profound implications for hydroponics. By introducing carbon dioxide into the water culture system, Priestley was able to enhance plant growth and productivity. His findings further solidified the scientific understanding of hydroponics and its potential in revolutionizing agriculture.
As the scientific revolution unfolded, researchers in various countries began to explore different methods and techniques in hydroponics. The 18th century served as a crucial stepping stone in the development of modern hydroponics, setting the stage for further advancements and innovations in the centuries to come. The potential of soil-less agriculture was becoming increasingly recognized, laying the groundwork for the commercialization and widespread adoption of hydroponics in the future.
6. The Rise of Commercial Hydroponics: 19th Century Developments
During the 19th century, hydroponics experienced a significant rise in interest and application, marking the beginning of commercial hydroponics. One of the pioneering developments during this time was the adaptation of hydroponics for commercial greenhouse cultivation. Farmers and horticulturists saw the potential of hydroponics as a way to maximize crop production and overcome various challenges posed by traditional soil-based agriculture.
One notable figure in the rise of commercial hydroponics was Julius von Sachs, a German plant physiologist. He conducted extensive research on plant nutrition and developed the concept of nutrient solutions for growing plants without soil. Sachs’ work laid the foundation for the commercial application of hydroponics, as it provided a better understanding of the important role of essential nutrients for plant growth and development.
With the growing interest in hydroponics, commercial systems started to emerge during the 19th century. For instance, the Nutriculture System, developed by William Frederick Gericke in the 1930s, demonstrated the viability of commercial hydroponics on a large scale. Gericke’s system utilized nutrient solutions to grow crops without soil, achieving remarkable yields and catching the attention of agricultural communities worldwide.
The rise of commercial hydroponics during the 19th century marked a significant turning point in agricultural practices. It opened up new possibilities for year-round crop production, improved resource utilization, and greater control over plant growth conditions. These developments laid the groundwork for the further exploration and innovation that would shape the future of hydroponics in the decades to come.
7. The 20th Century Breakthroughs: Hydroponics Enters the Mainstream
Hydroponics, a method of growing plants without soil, made significant breakthroughs in the 20th century, entering the mainstream of agricultural practices. As scientific knowledge and technology advanced, researchers and horticulturists began to explore the potential of hydroponics for sustainable food production. This led to a series of discoveries and innovations that revolutionized the way we cultivate plants.
One of the key breakthroughs in the 20th century was the development of nutrient solutions specifically designed for hydroponic systems. Researchers fine-tuned the composition and ratios of essential elements, ensuring that plants received the necessary nutrients for healthy growth. This precise control over nutrient delivery allowed for optimal plant development and higher yields, cementing hydroponics as a viable alternative to traditional soil-based farming.
Moreover, advancements in irrigation systems played a crucial role in bringing hydroponics to the forefront of agriculture. The introduction of automated and efficient watering systems, such as drip irrigation and fogging, minimized water waste and ensured that plants received adequate hydration. By precisely delivering water to the plants’ roots, hydroponic growers could conserve water resources, reducing their environmental impact.
Stay tuned for further exploration of hydroponics in the 20th century, as we delve into the various techniques and systems that propelled this innovative method into the mainstream of modern agriculture.
Here’s a table summarizing the key breakthroughs related to hydroponics in the 20th century:
| Breakthrough | Description |
|---|---|
| Ancient Origins | The Hanging Gardens of Babylon, if real, were an early example of successful hydroponics. Built around the 6th century BCE, these gardens relied solely on the Euphrates River for irrigation, as soil was scarce in the arid desert. Similarly, the Aztecs reportedly used floating gardens in nearby lakes during the 10th century, and the Chinese practiced hydroponics for rice fields devoid of soil in the 13th century. |
| Jan van Helmont (16th Century) | Belgian scientist Jan van Helmont conducted early science-based research on hydroponics. He observed that water delivered nutrients to plants, laying the groundwork for future developments. |
| John Woodward (1699) | John Woodward created the world’s first hydroponic nutrient solution. He concluded that plant growth benefited more from nutrients in water than from soil. |
| Dr. William F. Gericke (1920s) | Dr. Gericke, a researcher at the University of California, extended laboratory experiments to practical, commercial crops grown outdoors. He coined the term “hydroponics,” derived from the Greek words “hydro” (water) and “ponos” (labor). His work forms the basis for modern hydroponic practices. |
| US Military Innovations | In the 20th century, the US Military made hydroponic advances out of necessity. For instance, on Wake Island—an atoll in the Pacific Ocean—where traditional farming was impossible due to rocky terrain, the US Air Force set up small hydroponic growing beds. These beds produced a weekly yield of 90 pounds of fresh produce. |
| Contemporary Advances | Hydroponics has continued to evolve. Today, we understand that healthy plants require water, sunlight, carbon dioxide, and nutrients. Smart hydroponic systems have further improved efficiency and yields. |
Hydroponics, as a soilless cultivation method, has come a long way, from ancient wonders to cutting-edge technology!
8. Hydroponics and NASA: The Connection with Space Exploration
Hydroponics, the practice of growing plants without soil, has found an unlikely connection with space exploration through NASA’s innovative research and experiments. As scientists began planning for prolonged space missions, such as future missions to Mars, the challenge of providing astronauts with fresh food became a crucial aspect to address. With limited space, resources, and the absence of gravity, traditional soil-based agriculture was deemed impractical. This is where hydroponics stepped in, offering a promising solution for sustainable food production in space.
NASA recognized the potential of hydroponics in space and began conducting experiments in the late 1980s to explore its feasibility. These experiments aimed to evaluate the growth and yield of various vegetable crops, such as lettuce, radishes, and mustard greens, in a hydroponic system under simulated microgravity conditions. The results were encouraging, with plants thriving and producing nutritious crops without the need for soil. The success of these initial experiments sparked further research and development, leading to the creation of advanced hydroponic systems specifically designed for space missions.
Through their partnership with hydroponics experts and the integration of cutting-edge technologies, NASA developed the Vegetable Production System, also known as “Veggie.” This system utilizes LED lights to provide plants with the necessary light spectrum for photosynthesis, while nutrient-rich water is circulated to provide the plants with essential minerals. Veggie has been successfully used on the International Space Station (ISS), enabling astronauts to grow and consume fresh produce, improving their diet and overall well-being during their missions.
Moreover, hydroponics not only offers the benefit of sustainable food production in space, but it also serves as a valuable tool for psychological and aesthetic purposes. The sight of lush green plants growing in a sterile and harsh environment can have a positive impact on astronauts’ mental health, providing a sense of connection to nature and Earth.
As NASA continues to explore deep space missions and the potential colonization of other planets, hydroponics remains an integral aspect of their plans. Through ongoing research, collaborations, and advancements in hydroponic technology, NASA aims to create more efficient and robust systems that can sustainably support long-duration missions, ensuring that astronauts have access to fresh and nutritious food, no matter how far they are from Earth.
9. Hydroponics in World War II: The Need for Sustainable Food Production
During World War II, the need for sustainable food production became critical as nations faced the challenge of feeding their populations amidst the chaos and destruction of war. Traditional agricultural methods were often unable to keep up with the demands, leading to food shortages and hunger. As a result, hydroponics emerged as a promising solution that could provide a reliable and efficient method of growing crops in a controlled environment.
Hydroponics offered several advantages during this time of crisis. One of the key benefits was the ability to grow crops without the need for fertile soil, which was often in short supply in war-torn areas. By using nutrient-rich solutions to deliver essential elements directly to the plants’ roots, hydroponics allowed for the cultivation of crops in various locations, regardless of the soil quality or availability.
Furthermore, hydroponics allowed for precise control over the growing conditions, including temperature, humidity, and light levels, which could be crucial during wartime. By optimizing these factors, hydroponic systems could accelerate plant growth and ensure higher crop yields, thus contributing to addressing the urgent need for food production.
As the world faced the challenges of World War II, hydroponics emerged as a technology that offered hope and practical solutions for sustainable food production. From its ability to bypass limitations imposed by wartime circumstances to its capacity for maximizing crop yields, hydroponics proved its worth in meeting the pressing demands of the era. The advancements made during this period set the stage for the widespread adoption of hydroponic farming in the decades to come, as societies began to recognize its potential in addressing not only wartime needs but also the global challenges of food security and sustainability.
10. Hydroponics in Modern Agriculture: Increasing Efficiency and Sustainability
As modern agriculture faces the challenges of population growth and limited resources, hydroponics has emerged as an efficient and sustainable solution. By eliminating the need for soil and utilizing nutrient-rich water solutions, hydroponics allows for the cultivation of crops in controlled environments, maximizing productivity and minimizing waste.
One of the key advantages of hydroponics in modern agriculture is its ability to conserve water. Traditional farming methods require large amounts of water, which is often lost through evaporation or runoff. In contrast, hydroponics systems can reuse and recycle water, reducing overall consumption by up to 90%. This not only conserves a precious resource but also reduces the strain on water supplies, particularly in arid regions where water scarcity is a pressing concern.
Moreover, hydroponics offers increased efficiency in crop production. By providing plants with the precise nutrients they need in optimal conditions, growers can achieve higher yields and faster growth rates compared to traditional farming methods. This efficiency is further enhanced by the ability to control factors such as temperature, humidity, and lighting, creating an ideal environment for plant growth. As a result, hydroponics systems have been shown to produce up to 30% more crops compared to conventional agriculture, offering a promising solution to global food security challenges.
11. The Role of Technological Advancements in Hydroponics
Technological advancements have played a pivotal role in the evolution and success of hydroponics. As researchers and scientists continue to push the boundaries of innovation, these advancements have enabled hydroponic systems to become more efficient, sustainable, and productive.
One notable technological advancement in hydroponics is the development of advanced environmental control systems. These systems allow growers to precisely regulate factors such as temperature, humidity, light intensity, and nutrient levels, creating optimal conditions for plant growth. By fine-tuning these variables, growers can maximize crop yields and quality while minimizing resource consumption.
Furthermore, the integration of automation and artificial intelligence has revolutionized the way hydroponic systems are managed. Automated nutrient dosing systems, for example, ensure that plants receive the precise amount of nutrients they need at any given time. This not only eliminates the guesswork for growers but also minimizes the risk of over or under-fertilization.
Additionally, sensor technologies and data analytics have enabled growers to monitor and optimize their hydroponic systems in real-time. Sensors can provide valuable information about pH levels, nutrient concentrations, and other crucial parameters, allowing growers to make data-driven decisions and make adjustments as needed. By harnessing the power of data, hydroponic growers are able to continuously improve their practices and achieve higher levels of productivity.
In conclusion, technological advancements have greatly enhanced the efficiency and effectiveness of hydroponics. From advanced environmental control systems to automation and data analytics, these technological innovations have allowed growers to optimize their hydroponic systems and produce higher yields with greater precision. As technology continues to evolve, it is likely that hydroponics will continue to thrive as a sustainable and viable method of agriculture.
Here’s a table highlighting the pivotal role of technological advancements in hydroponics:
| Advancement | Impact on Hydroponics |
|---|---|
| Data-Driven Automation | The technology supporting hydroponic growers is evolving rapidly. Solutions are becoming more data-reliant, providing insights that enhance crop production. By focusing on data acquisition and automation, growers can reduce reliance on labor for repetitive tasks. This frees up labor for more specialized activities, such as documentation and trend analysis. The result is reliable production and improved efficiency. |
| Automated Picking Machines | Automation and machine learning are making significant strides in hydroponic growing. Innovations in picking, monitoring, and pesticide applications are transforming crop management. Permanent sensor placements, drones, and enhanced image capturing enable efficient data collection, leading to better decision-making. |
| Greater Control and Efficiency | Modern hydroponic techniques leverage advanced technologies, granting gardeners unprecedented control over growing environments. These innovations enhance efficiency and allow precise adjustments to factors like light, nutrients, and temperature. |
| IoT and Robotics | Automation, robotics, and the Internet of Things (IoT) play a crucial role in hydroponics. They enable real-time monitoring of variables in plant growth, root zones, and environmental conditions, contributing to optimal crop management. |
As technology continues to advance, hydroponics stands at the forefront of sustainable and efficient agriculture!
12. Hydroponics and Environmental Conservation: Reducing Water Consumption
Hydroponics, as a method of soilless cultivation, offers significant advantages when it comes to environmentally sustainable practices. One of the key benefits is the reduction of water consumption, a critical consideration in an era of increasing water scarcity and climate change impacts. Traditional soil-based agriculture requires the regular irrigation of crops, leading to significant water loss due to evaporation, inefficient absorption, and runoff. In contrast, hydroponics utilizes a closed-loop system that maximizes water efficiency by recirculating nutrient-rich water directly to the plant roots. This closed-loop system not only conserves water but also minimizes the risk of nutrient runoff that can pollute nearby water bodies.

The statistics are promising. Studies have shown that hydroponic systems can reduce water consumption by up to 90% compared to traditional soil-based agriculture. Take lettuce production, for example. While conventional lettuce farming consumes approximately 25 gallons of water per head, hydroponics can produce the same amount of lettuce using less than one gallon of water. This dramatic reduction is mainly due to the precise control and delivery of water in hydroponics, ensuring that plants receive only what they need, when they need it. Additionally, the closed-loop recirculation system allows for the continuous reuse of water, minimizing waste and enhancing the overall sustainability of the cultivation process.
13. Urban Gardening and Hydroponics: Transforming Cities into Green Spaces
Urban gardening and hydroponics have emerged as innovative solutions to transform cities into green spaces. With the rise of urbanization and limited land availability, these practices offer a sustainable approach to cultivate plants and vegetables without the need for traditional soil-based methods. By utilizing hydroponics, cities can overcome the constraints of space and environmental limitations, while promoting a greener and healthier environment.
One of the main advantages of urban gardening and hydroponics is their ability to maximize space utilization. In densely populated areas, finding suitable land for traditional gardening can be challenging. However, hydroponics allows for vertical and indoor farming, enabling individuals to cultivate plants in a limited area. By utilizing techniques such as vertical stacking or tiered systems, growers can create multi-layered gardens that maximize the use of available space. This not only increases the efficiency of land usage but also provides opportunities for urban dwellers to actively engage in gardening and enjoy the benefits of fresh produce.
Moreover, urban gardening and hydroponics offer unique advantages in terms of environmental sustainability. These methods typically require less water compared to traditional soil-based cultivation. By carefully controlling the water and nutrient supply, hydroponics minimizes water wastage and reduces the negative environmental impact associated with excessive irrigation and runoff. Additionally, these systems allow for the efficient recycling and reuse of water, further contributing to water conservation efforts in urban areas. The reduced reliance on pesticides and herbicides in hydroponics also promotes a healthier and greener urban environment, making it an attractive option for those seeking more sustainable and eco-friendly gardening practices.
14. Hydroponics in Developing Countries: Addressing Food Security Challenges
Hydroponics has emerged as a potential solution to the food security challenges faced by developing countries. With limited arable land and unpredictable weather conditions, traditional farming methods often struggle to meet the ever-growing demand for food. However, hydroponics offers a promising alternative by allowing crops to be cultivated in controlled environments using nutrient-rich water instead of soil.
One of the key advantages of hydroponics in developing countries is its ability to maximize crop production with minimal resources. By eliminating the reliance on fertile soil and reducing water consumption, hydroponics allows for the cultivation of crops in areas where traditional farming may not be feasible. This is particularly crucial in regions prone to drought or desertification, where arable land is scarce. Moreover, the controlled environment of hydroponic systems minimizes the risk of pests and diseases, leading to higher crop yields and reduced crop losses.
In addition to its potential for increased food production, hydroponics also offers economic benefits for developing countries. The ability to grow high-value crops, such as fresh fruits and vegetables, throughout the year could open up new opportunities for farmers to access lucrative markets. By embracing hydroponics, developing countries have the potential to improve their agricultural productivity, enhance food security, and generate income for rural communities, ultimately contributing to their overall economic development.
With its ability to address food security challenges, maximize resource efficiency, and promote economic growth, hydroponics holds great promise for developing countries. However, it is important to ensure that the necessary infrastructure, resources, and knowledge are in place to effectively implement and sustain hydroponic systems. Collaboration between governments, agricultural institutions, and international organizations will be crucial in providing the necessary support, training, and investment to enable the widespread adoption of hydroponics in developing countries.
15. Hydroponics and Vertical Farming: Overcoming Space Limitations
Hydroponics has paved the way for a groundbreaking solution to the space limitations faced by traditional agriculture. With vertical farming, gardening enthusiasts and commercial growers alike can now maximize their production in the smallest of spaces. By stacking layers of grow beds, hydroponic systems can utilize vertical space efficiently, allowing for multiple crops to be grown in the same area that would have once only yielded a single harvest.
Vertical farming offers several advantages beyond space utilization. In addition to increasing crop yield per square foot, this method also allows for better control over environmental conditions. By precisely regulating temperature, humidity, and lighting, growers can create optimal conditions for plant growth. This level of control minimizes the risk of pests and disease and enables year-round cultivation, bypassing the limitations imposed by seasonal changes. Additionally, vertical farming reduces the need for pesticides and herbicides, resulting in cleaner and healthier produce.
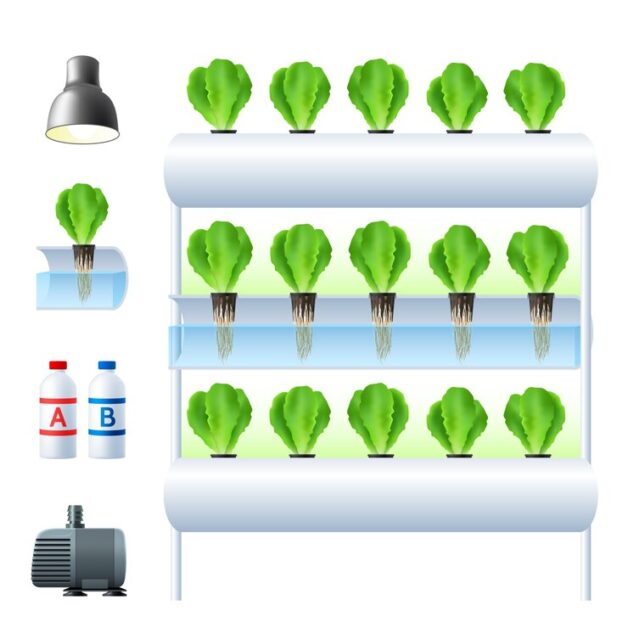
Despite these advantages, vertical farming does come with its own set of challenges. The high initial cost of setting up a vertical farm can deter some growers, as specialized equipment and technology are required. Additionally, optimizing the vertical farming system to ensure proper air circulation, adequate lighting, and efficient nutrient distribution can be a complex task. However, advancements in technology and ongoing research in the field are continually improving and making vertical farming more accessible and economical.
In conclusion, vertical farming through hydroponics is proving to be a formidable solution to the limitations imposed by space constraints. By utilizing vertical space efficiently and providing optimal environmental conditions for crop growth, growers can achieve higher yields and year-round cultivation. Although there are challenges to overcome, the continued advancements in technology and research are making vertical farming increasingly viable and beneficial for both urban gardening enthusiasts and commercial growers.
16
Hydroponics and vertical farming have emerged as innovative solutions to overcome the space limitations faced by modern agriculture. With the increasing global population and the surge in urbanization, traditional farming methods struggle to meet the growing demand for food. However, vertical farming presents an opportunity to maximize crop production in limited spaces, making it especially attractive in densely populated cities.
By utilizing vertical space, such as walls or multi-layered systems, hydroponic systems in vertical farms can significantly increase the crop yield per square foot compared to conventional methods. This efficient use of space allows for the cultivation of a wide variety of crops, ranging from leafy greens and herbs to fruits and vegetables. Vertical farming also minimizes the need for pesticides, as controlled environments and strict hygiene measures contribute to reduced pest and disease problems.
Moreover, vertical hydroponic systems offer the potential for year-round farming, independent of weather conditions. By providing precise control over temperature, humidity, lighting, and nutrient delivery, this method supports consistent growth and optimum plant health. As a result, farmers can harvest crops throughout the year, helping to stabilize food production and maintain a reliable food supply.
Overall, the integration of hydroponics into vertical farming has the potential to transform urban landscapes into highly productive green spaces. By embracing these innovative methods, cities can address food insecurity, promote sustainability, and create a greener future. Nonetheless, further research and development are required to optimize these systems for different crops and overcome potential challenges, ensuring the widespread adoption and success of this promising agricultural revolution.
Please do watch video!
What are the key benefits of using hydroponics in modern agriculture?
Hydroponics in modern agriculture offers increased efficiency and sustainability compared to traditional farming methods. It allows for precise control of nutrients, water, and environmental conditions, resulting in higher yields, faster growth rates, and reduced water consumption.
How does hydroponics contribute to environmental conservation?
Hydroponics helps reduce water consumption by recycling and reusing nutrient solutions, resulting in up to 90% less water usage compared to conventional farming. Additionally, it minimizes the need for chemical pesticides and herbicides, promoting a more environmentally friendly approach to farming.
Can hydroponics be implemented in urban areas?
Yes, hydroponics is well-suited for urban areas. Its space-efficient nature allows for vertical farming, where crops are grown in stacked layers, maximizing land use. Urban gardening utilizing hydroponics can transform cities into green spaces, improving air quality and providing fresh, locally grown produce.
How does hydroponics address food security challenges in developing countries?
Hydroponics can help address food security challenges in developing countries by enabling year-round crop production, regardless of climatic conditions. It offers the opportunity to grow crops in controlled environments, ensuring a stable food supply and reducing dependence on imports.
How does hydroponics overcome space limitations in vertical farming?
Vertical farming, a technique often used in hydroponics, allows for the cultivation of plants in vertically stacked layers, maximizing space utilization. By utilizing this method, hydroponics enables the production of a large quantity of crops in a relatively small area, making it ideal for urban environments with limited available land.

Nicole Burke is a dynamic writer at SouthElMonteHydroponics, fueled by her passion for horticulture and environmental sustainability. Armed with a degree in Environmental Science from a renowned institution, Nicole’s expertise lies in hydroponic gardening, organic farming, and biodiversity conservation. Her insatiable curiosity and love for nature drive her to explore innovative techniques in hydroponics, seeking to revolutionize the way we grow crops in urban environments. Nicole’s writing reflects her deep commitment to promoting eco-conscious practices and fostering a deeper connection between humans and the natural world. Through her engaging storytelling, she inspires others to embrace sustainable living and harness the power of hydroponics for a greener future.






