Cutworms in Your Garden: Eradicating Noctuidae Caterpillars
Items:
Noctuidae caterpillars can be a bothersome pest in your garden, causing damage to a variety of plant species. These caterpillars are part of the large and diverse moth family known as Noctuidae, which includes more than 1,000 species. They are primarily active at night and hide during the day, making it challenging to spot them directly. However, there are certain signs that can help you identify their presence in your garden.
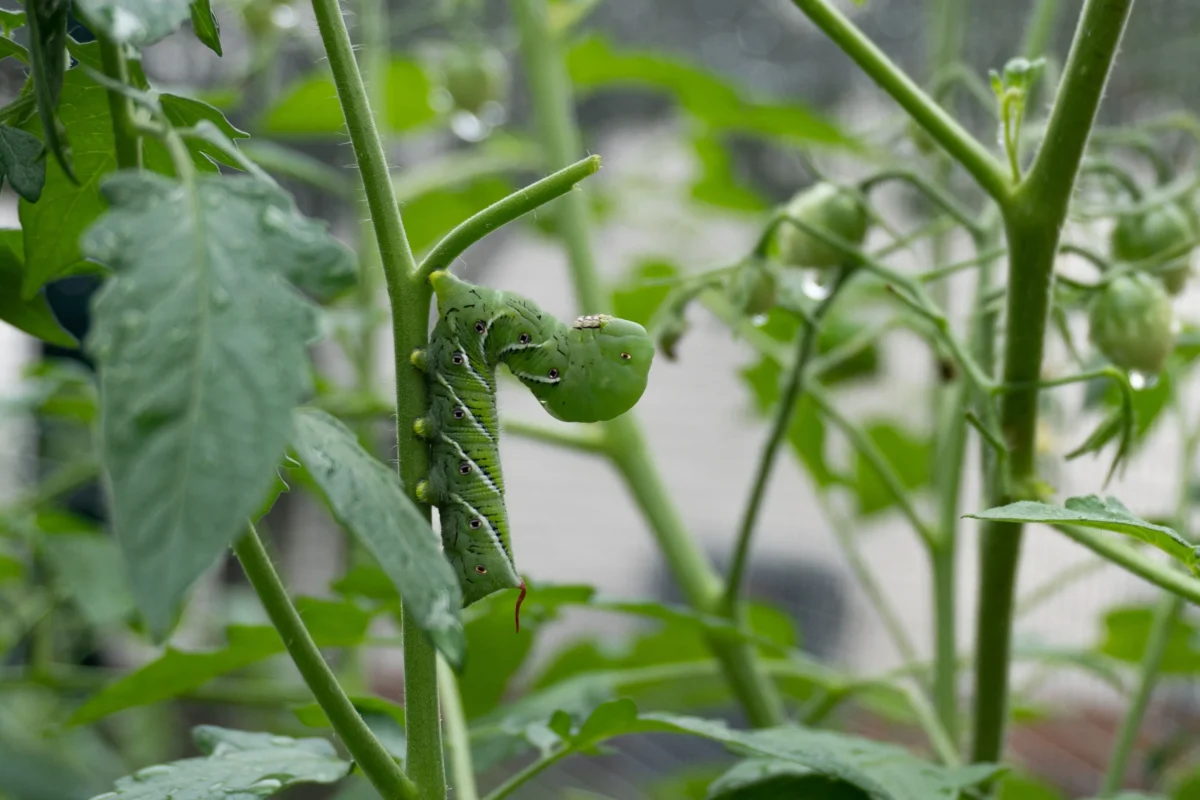

One of the most obvious signs of Noctuidae caterpillars is the presence of chewed or damaged foliage. These pests are voracious eaters and can quickly consume leaves, stems, and even fruits of your plants. If you notice irregular holes or ragged edges on your plant leaves, it’s likely that Noctuidae caterpillars are responsible. Additionally, you may find their droppings, known as frass, near the damaged foliage. Keep an eye out for these signs so you can take appropriate measures to control their population and protect your garden from further damage.
Understanding the Threat: Identifying Noctuidae Caterpillars in Your Garden
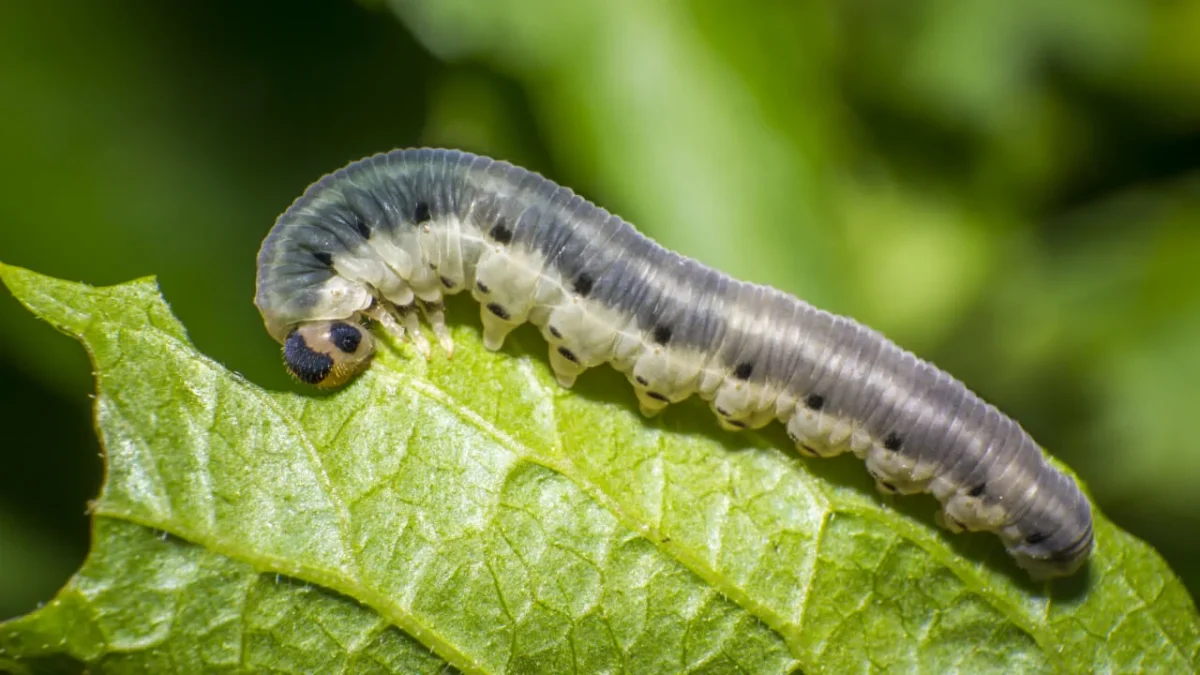
Noctuidae caterpillars are a common threat to gardens, causing significant damage to plants if left unchecked. Identifying these caterpillars is an essential first step in protecting your garden. Noctuidae caterpillars, also known as owlet moths, belong to a large family of insects that includes many pest species. These caterpillars can vary in appearance, but they typically have robust bodies with smooth or hairy skins. They are usually gray, brown, or green, making them blend in well with plant foliage. To determine if you have Noctuidae caterpillars in your garden, closely inspect your plants for signs of chewing damage and the presence of these caterpillars on the leaves, stems, or fruits. Keep in mind that not all caterpillars you encounter in your garden will be Noctuidae, so it’s crucial to accurately identify them to implement appropriate control measures.
The Lifecycle of Noctuidae Caterpillars: From Egg to Adult
Noctuidae caterpillars, also known as cutworms, undergo a fascinating lifecycle from the time they hatch as tiny eggs to their eventual transformation into adult moths. This lifecycle is marked by distinct stages, each with its own unique characteristics and behaviors.
It all begins with the female moth depositing her eggs on the undersides of leaves or in the soil near host plants. These eggs are incredibly small and can be difficult to detect with the naked eye. Once the eggs hatch, the newly emerged caterpillars must start feeding immediately to fuel their growth.
During the larval stage, the cutworms voraciously consume plant material, often causing significant damage to the leaves, stems, and even the roots of susceptible plants. They have a cylindrical body shape and are typically brown, green, or gray in color, blending in with their surroundings. As they feed and grow, the larvae go through several instars, shedding their skin multiple times to accommodate their increasing size. This molting process allows the cutworms to continue their growth until they reach their full size.
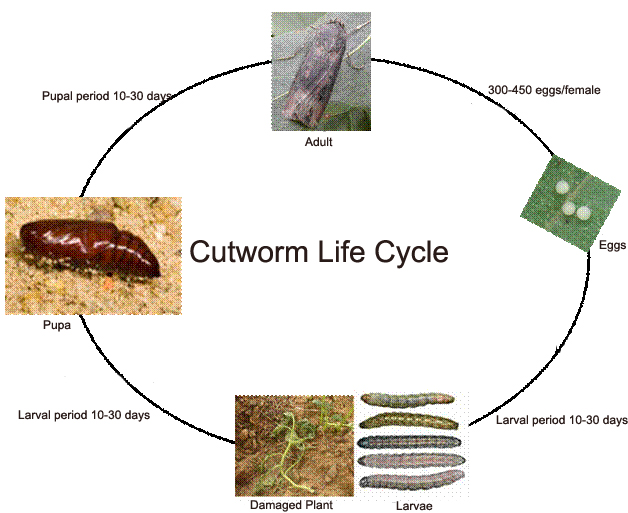
As the larvae near maturity, they will tunnel into the soil to pupate and transform into adult moths. The pupal stage is a period of rest and transformation, during which the caterpillar’s body undergoes remarkable changes to prepare for its final form. Finally, the adult moth emerges from the pupa, ready to mate and initiate the cycle anew.
Understanding the lifecycle of Noctuidae caterpillars is vital for effective pest management strategies. By identifying the various stages of their development and knowing when and where they are most vulnerable, gardeners can implement targeted control measures to minimize the impact of these voracious herbivores on their plants.
Recognizing the Signs: Common Symptoms of Cutworm Infestation
Cutworm infestations can cause significant damage to your garden, so it is crucial to recognize the common symptoms early on. One telltale sign of a cutworm infestation is the presence of cut or wilted seedlings. These destructive caterpillars feed on the stems of young plants, severing them at or just below the soil surface. As a result, the affected seedlings will appear damaged, droopy, or even completely severed from their roots. It is important to note that cutworms are most active during the night, so you may not witness their feeding habits directly.
In addition to damaged seedlings, another sign of a cutworm infestation is the presence of small burrows or holes in the soil near affected plants. Cutworms are nocturnal pests that prefer to hide in the soil during the day. They create shallow burrows as they search for their next meal, leaving behind distinct evidence of their activity. These burrows may vary in size and shape, but they are usually found within close proximity to damaged plants. Keeping a close eye on the soil surface can help you detect these subtle signs and take action before the infestation worsens.
The table below gives us more details about the infestation of cutworm:
| Cutworm Infestation Signs | Description |
|---|---|
| Cut or Damaged Seedlings | – Severed young seedlings, causing wilting. |
| Irregular Holes in Leaves | – Notches or holes in leaves of established plants. |
| Seedlings Leaning or Toppled | – Seedlings leaning or toppled due to cutworms cutting stems at the base. |
| Nocturnal Feeding Habits | – Nocturnal feeding, causing damage overnight; hiding in soil during the day. |
| Presence of Droppings | – Small, dark droppings (frass) near damaged plants indicate cutworm activity. |
| Wilting Despite Adequate Water | – Wilting, even with adequate water, due to cutworm damage to stems. |
| Cutworms in Soil or Surroundings | – Observe soil surface for cutworms or feeding trails, especially during the evening. |
| Uneaten Plant Parts Nearby | – Partially eaten plant parts left near damaged areas. |
| Plant Damage in Rows or Clusters | – Localized damage in rows or clusters; cutworms feed on plants in specific areas. |
| Young Plants Particularly Vulnerable | – Preference for young, tender plants, making seedlings vulnerable to infestation. |
Garden Preparation: Creating a Healthy Environment to Prevent Cutworms
Creating a healthy environment in your garden is crucial for preventing cutworm infestations. By implementing some key practices, you can significantly reduce the risk of these destructive pests damaging your plants.
Firstly, maintaining proper sanitation is essential. Cutworms tend to hide in debris and dense vegetation, so regularly removing fallen leaves, weeds, and other organic matter will eliminate potential hiding spots. Additionally, keeping your garden clean and free from weeds will provide fewer opportunities for cutworms to lay their eggs.
Secondly, proper watering practices are essential for preventing cutworms. These pests thrive in moist environments, so it’s important to water your plants at the base rather than overhead. This method not only reduces the moisture level on the surface but also encourages plants to develop deep root systems, making them less susceptible to cutworm damage.
Additionally, creating a physical barrier around your plants can be an effective preventive measure. Placing collars made of material like cardboard or aluminum foil around the base of each plant will act as a deterrent, preventing cutworms from reaching them. Make sure these barriers extend at least an inch into the soil to block any potential burrowing.
Natural Predators: Encouraging Beneficial Insects for Cutworm Control
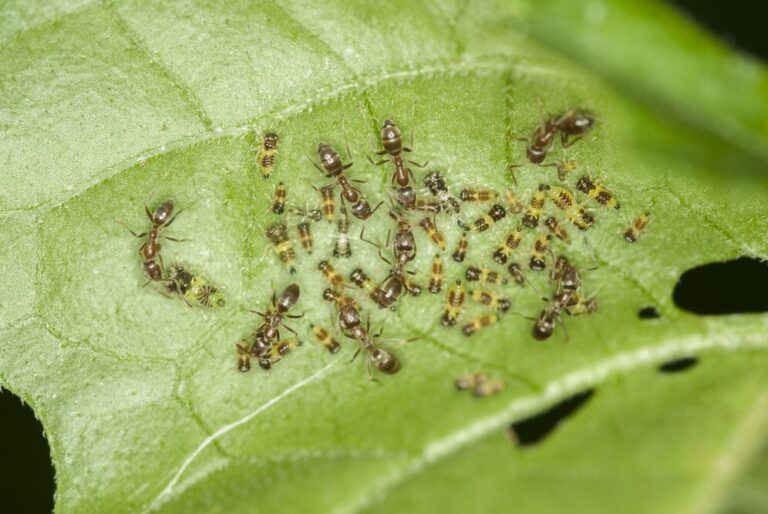
Natural predators play a crucial role in controlling cutworm populations in the garden. By attracting and encouraging beneficial insects, gardeners can create a balanced ecosystem that keeps cutworms in check naturally. These beneficial insects feed on cutworm eggs, larvae, and even adult moths, helping to reduce their numbers and prevent infestations.
One example of a beneficial insect that preys on cutworms is the ground beetle. These nocturnal hunters feed on cutworm larvae, patrolling the soil surface in search of their prey. Another natural predator is the parasitic wasp, which lays its eggs inside cutworm caterpillars. When the wasp larvae hatch, they consume the caterpillar from within, effectively killing it. Ladybugs and lacewings are also valuable allies in the fight against cutworms, as they feed on the eggs and early stages of the larvae.
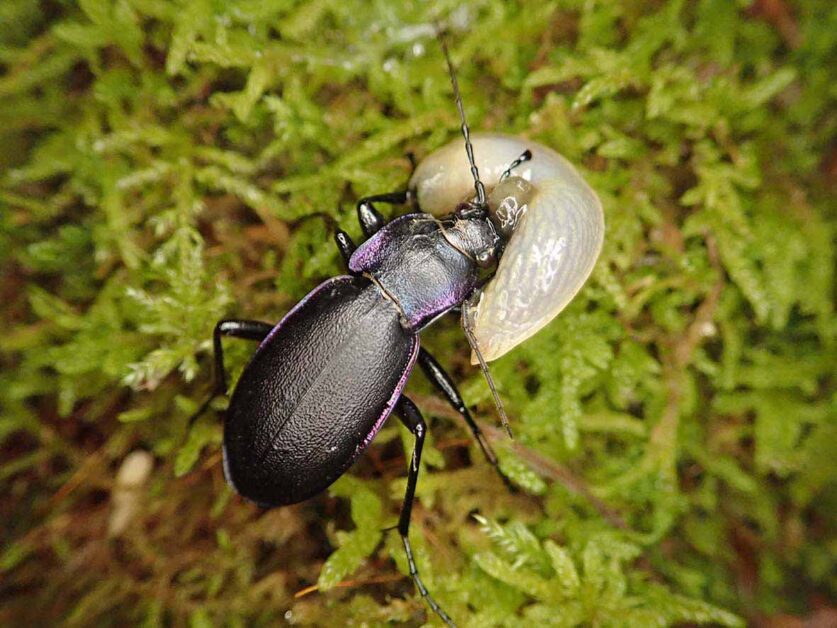

To attract these beneficial insects to the garden, it’s important to provide them with suitable habitats and food sources. Planting a diverse range of flowering plants, particularly those with small, nectar-rich flowers, can attract beneficial insects and encourage them to stay in the garden. It’s also helpful to avoid using broad-spectrum pesticides, as these can harm beneficial insects along with pests. By creating an environment that supports natural predators, gardeners can harness the power of nature to keep cutworm populations under control.
Mechanical Measures: Physical Barriers and Traps to Protect Your Plants
Physical barriers and traps can be effective tools in protecting your plants from cutworm damage. One popular method is the use of cardboard collars around the base of your plants. These collars act as a physical barrier, preventing the cutworms from reaching the stems and leaves of your plants. To create the collars, simply cut small strips of cardboard and wrap them around the base of each plant, burying them slightly in the soil. This method has been found to be particularly effective for crops such as tomatoes, peppers, and cabbage.
Another physical barrier technique is the use of copper tape. Cutworms are known to dislike the sensation of copper and will avoid crawling over it. By wrapping copper tape around the base of your plants, you can deter these pests from reaching your crops. It’s important to ensure that the tape forms a complete circle around the plant to prevent any gaps that cutworms could potentially exploit. Copper tape can be especially useful for protecting container plants or raised beds, where the perimeter can be easily lined with the tape.
Organic Solutions: Using Safe and Effective Methods to Combat Cutworms
Organic solutions offer safe and effective methods to combat cutworms, ensuring the health and vitality of your garden. These methods are not only environmentally friendly but also beneficial for the overall balance of your garden ecosystem. By utilizing organic approaches, you can effectively manage cutworm populations without the use of harmful pesticides.
One effective organic solution is the use of biological controls. Beneficial insects such as parasitic wasps and ground beetles can be introduced into the garden to prey on cutworms and reduce their numbers. These natural predators feed on the cutworm eggs, larvae, and pupae, helping to maintain a healthy balance in your garden. Additionally, attracting birds to your garden by providing birdbaths or birdhouses can also aid in controlling cutworm populations, as birds are known to feed on these pests. By incorporating these natural enemies into your garden, you can effectively minimize cutworm damage without resorting to chemical interventions.
Chemical Control: Understanding the Use of Pesticides for Cutworm Eradication
Chemical Control: Understanding the Use of Pesticides for Cutworm Eradication
When it comes to combating cutworm infestations, chemical control is often considered as a last resort. While it can be effective in eliminating these destructive pests, it’s crucial to understand the proper use of pesticides for cutworm eradication.
Pesticides formulated specifically for cutworms can provide targeted control, but it’s important to note that these chemicals can also harm beneficial insects and disrupt the natural balance of your garden ecosystem. Therefore, it’s vital to exercise caution and follow the instructions provided by the pesticide manufacturer.
Before applying any pesticides, it’s essential to identify the species of cutworms present in your garden. Different cutworm species may respond differently to various pesticides, so using the right product is crucial for successful eradication. Consult with local agricultural extension services or reputable gardening professionals to identify the specific pests in your area and determine the most effective pesticide to use. Remember, always choose products labeled for use on cutworms and follow the recommended rates and application timings for optimal results.
Timing is Key: When and How to Apply Control Measures
Timing is crucial when it comes to applying control measures for cutworms. By understanding the life cycle of these pests, you can effectively target them at their most vulnerable stages. Early detection and monitoring are key, as it allows you to intervene before the infestation becomes severe.
When it comes to timing, there are a few important factors to consider. First, it’s essential to implement control measures in the early spring before cutworm populations explode. This is particularly critical for plants that are most susceptible to cutworm damage, such as young seedlings. By taking action early, you can prevent significant losses in your garden.
Additionally, applying control measures in the evening or during cloudy weather is recommended. Cutworms are nocturnal creatures, so they are most active at night. By targeting them during their peak activity times, you increase the chances of eliminating a larger portion of the population. However, it’s important to check the specific instructions on the chosen control method to ensure it is suitable for the time of application and the plants being protected.
In the next section, we will explore the various control measures available for combating cutworms, ranging from organic solutions to chemical control. Each method has its own advantages and considerations, and understanding the right timing and application techniques will maximize their effectiveness in eradicating these garden pests. As we delve further into the topic, you’ll gain valuable insights into how to safeguard your plants from cutworm damage throughout the growing season. So let’s continue our exploration of the different strategies for managing these voracious caterpillars.
Companion Planting: Utilizing Plant Relationships to Deter Cutworms
Companion planting is a valuable technique in managing cutworm infestations in your garden. By strategically placing certain plant species together, you can harness the power of natural relationships to deter these pests. One effective companion plant for deterring cutworms is the marigold (Tagetes spp.).
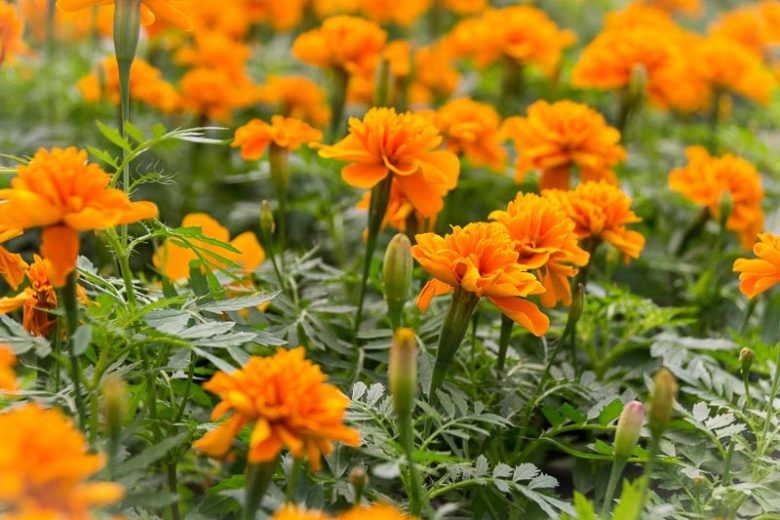

Marigolds emit a strong scent that repels many insects, including cutworms. Planting marigolds around susceptible crops acts as a natural deterrent, reducing the risk of cutworm damage. Additionally, marigolds attract beneficial insects such as parasitic wasps and ground beetles, which feed on cutworms and their larvae. This symbiotic relationship helps control cutworm populations without the need for harmful pesticides.
Another effective companion plant for deterring cutworms is thyme (Thymus spp.). Thyme releases a chemical compound called thymol, which repels several pests, including cutworms. By interplanting thyme with your vulnerable crops, you create an unfavorable environment for cutworms, effectively reducing their presence. Thyme also offers the added benefit of attracting pollinators such as bees and butterflies, promoting overall garden health.
The table below shows the plants that can help eradicating the cutworms:
| Companion Planting for Cutworm Deterrence | Description |
|---|---|
| Marigolds (Tagetes) | – Emit a strong scent that repels cutworms and various pests, acting as a natural deterrent. |
| Thyme (Thymus) | – Thyme releases aromatic oils that can help deter cutworms, providing a protective effect. |
| Nasturtiums (Tropaeolum) | – Serve as a trap crop, attracting cutworms away from main crops and helping protect valuable plants. |
Crop Rotation: Breaking the Cycle of Cutworm Infestation
Crop rotation is a time-tested agricultural technique that can effectively break the cycle of cutworm infestations in your garden. By strategically planning the succession of crops in different areas of your garden’s rotation, you can disrupt the life cycle of cutworms and reduce their populations.
Cutworms tend to target specific crops, such as tomatoes, peppers, and corn, so rotating these susceptible plants with less susceptible ones can greatly reduce the risk of infestation. For example, you can follow a tomato crop with a rotation of beans or lettuce. By varying the types of plants grown in each area from one season to the next, you make it more difficult for cutworms to find their preferred hosts, ultimately decreasing their overall impact on your garden.
Additionally, crop rotation enhances the overall health of your garden by reducing the build-up of pests and diseases in the soil. Different plant families have different nutrient requirements and are susceptible to different pests and diseases. By rotating crops, you can prevent the depletion of specific nutrients, maintain soil fertility, and break the cycle of pests and diseases that may have developed during the previous season. This helps create a balanced ecosystem in your garden, promoting plant health and reducing the need for chemical interventions.
Soil Management: Improving the Health of Your Garden to Discourage Cutworms
Healthy soil is the foundation of a thriving garden, and it plays a critical role in discouraging cutworm infestations. By focusing on soil management techniques, you can create an environment that is less appealing to these destructive pests. One key aspect of soil management is maintaining proper fertility levels. Cutworms are more attracted to plants that are growing in nutrient-deficient soil, as these plants are weaker and more vulnerable to attack. By regularly testing your soil and amending it with organic matter and appropriate fertilizers, you can ensure that your plants are receiving the nutrients they need to grow strong and healthy.
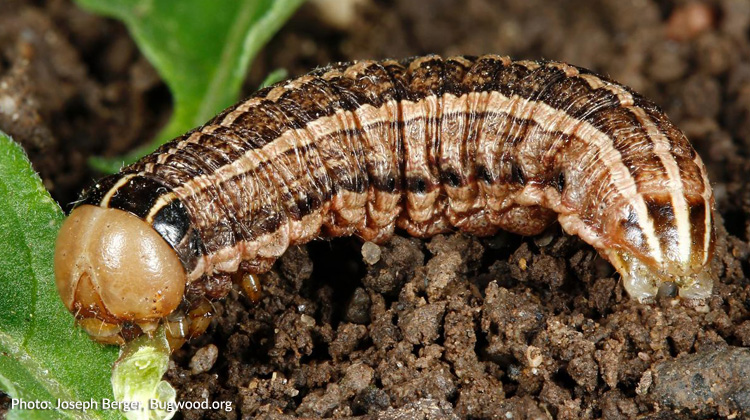

In addition to fertility, soil structure is also crucial for deterring cutworms. Compacted soil provides a perfect hiding place for these pests, allowing them to burrow and feed on plant roots without much resistance. To improve soil structure, consider incorporating organic amendments such as compost or well-rotted manure. These materials enhance soil porosity, allowing for better drainage and root development. It’s also beneficial to practice proper tillage techniques, avoiding overworking the soil and creating compaction. By maintaining healthy soil structure, you can create an inhospitable environment for cutworms and promote the overall health of your garden.
Cultural Practices: Tips for Clean Gardening Techniques to Minimize Cutworms
When it comes to gardening, practicing clean techniques is essential for minimizing the presence of cutworms in your garden. These pests can cause significant damage to your plants by cutting through the stems at or just below the soil line. However, by following a few simple cultural practices, you can greatly reduce their impact on your garden.
One important tip for clean gardening is to remove any garden debris or decaying plant material regularly. Cutworms are known to lay their eggs in these areas, and by removing them, you eliminate potential breeding grounds. Additionally, keeping your garden clean helps prevent the accumulation of moisture, which can attract cutworms and other pests.
Another key practice is to practice proper crop rotation. Cutworms tend to target specific plants, and by rotating your crops each season, you disrupt their life cycle and make it harder for them to establish a population in your garden. This technique also helps maintain soil health, as different crops have different nutrient needs and can help prevent the buildup of pests and diseases.
By implementing these clean gardening techniques, you can minimize the presence of cutworms in your garden and maintain a healthy and thriving crop. Remember, prevention is key when it comes to dealing with these pests, and a little extra effort now can save you from potential headaches later.
Here is a table that summarizes the tips for clean garden:
| Clean Gardening Techniques to Minimize Cutworms | Description |
|---|---|
| Remove Garden Debris Regularly | – Regularly clear garden debris and decaying plant material to eliminate potential cutworm breeding grounds. |
| – Reduces the likelihood of cutworms laying eggs in these areas and helps prevent their population buildup. | |
| Prevent Moisture Accumulation | – Maintain a clean garden to prevent the accumulation of moisture, as excess moisture can attract cutworms and pests. |
| – Dry conditions discourage cutworm activity, minimizing the risk of plant damage. | |
| Practice Proper Crop Rotation | – Rotate crops each season to disrupt the cutworm life cycle and make it challenging for them to establish in the garden. |
| – Promotes soil health by preventing the buildup of pests and diseases specific to certain plants. | |
| – Varies nutrient needs, reducing the risk of nutrient imbalances in the soil. |
Early Detection and Monitoring: Regular Inspections for Cutworm Activity
Regular inspections for cutworm activity are an essential component of early detection and monitoring in your garden. By conducting these inspections on a consistent basis, you can identify signs of cutworm infestation early on and take necessary measures to protect your plants.
During your inspections, keep an eye out for several key indicators of cutworm presence. Look for plants that have been partially or completely severed at the base, as cutworms typically feed on the stem just above ground level. Additionally, check for seedlings that have been entirely consumed or have wilted suddenly without any apparent cause. If you notice tiny, dark droppings or curled-up caterpillars in the soil, these can also be signs of cutworm activity. Be thorough in your inspections, examining both the surface and the soil to ensure you don’t miss any potential infestation.
Watch the video for preventing cutworms.
Integrated Pest Management: Incorporating Various Approaches for Sustainable
Effective pest management is crucial in maintaining a sustainable and thriving garden. By incorporating various approaches into an integrated pest management (IPM) strategy, gardeners can minimize the use of harmful chemicals and promote the overall health of their plants.
One approach in IPM is the use of biological controls, which involve introducing natural predators or parasites to control pest populations. These beneficial insects can target specific pests, such as aphids or caterpillars, without harming other beneficial organisms or the environment. Ladybugs, lacewings, and trichogramma wasps are among the commonly used beneficial insects in garden pest management. When implemented correctly, biological controls can greatly reduce the reliance on synthetic pesticides while maintaining a balanced ecosystem in the garden.
Another important aspect of IPM is cultural controls, which focus on creating unfavorable conditions for pests and promoting plant health to prevent infestations. Practices such as crop rotation, companion planting, and proper soil management play a significant role in reducing pest pressure. By rotating crops and avoiding planting susceptible species in consecutive growing seasons, gardeners disrupt the life cycle of pests, making it more difficult for them to establish and multiply. Additionally, planting certain companion plants, such as marigolds or basil, can repel pests or attract beneficial insects. Improving soil health through organic matter additions, proper watering, and balanced nutrition can also enhance plant vigor, making them less susceptible to pests and diseases.
By combining these and other approaches, gardeners can develop a comprehensive IPM strategy that not only protects their plants from pests but also promotes a sustainable and environmentally friendly gardening practice.
What are some natural predators that can help control cutworms in my garden?
Natural predators of cutworms include birds, ground beetles, parasitic wasps, and predatory nematodes.
How can I create a healthy environment in my garden to prevent cutworms?
To create a healthy environment, practice good sanitation by removing weeds and debris, maintain proper soil drainage, and avoid over-fertilization.
What are some safe and effective organic methods to combat cutworms?
Organic methods to combat cutworms include using natural repellents like garlic or neem oil, introducing beneficial insects, such as ladybugs or lacewings, and using biological control agents like Bacillus thuringiensis (Bt).
When and how should I apply control measures for cutworms?
Control measures should be applied in the early evening or early morning when cutworms are most active. Follow the instructions on the product label for proper application.
How can companion planting help in deterring cutworms?
Companion planting involves growing certain plants together that have a beneficial relationship, such as planting marigolds or onions around susceptible plants to deter cutworms with their strong smell.
How can crop rotation help break the cycle of cutworm infestation?
Crop rotation involves planting different crops in different areas each year, which disrupts the life cycle of cutworms and reduces their population.
How can I improve the health of my garden soil to discourage cutworms?
Improve soil health by adding organic matter, practicing proper watering and drainage, and avoiding overuse of chemical fertilizers, as healthy soil can deter cutworms.
What are some tips for clean gardening techniques to minimize cutworms?
Clean gardening techniques include removing garden debris, practicing crop rotation, avoiding over-watering, and regularly inspecting plants for signs of cutworm activity.
How can early detection and monitoring help in controlling cutworms?
Regular inspections of your garden can help you identify signs of cutworm activity early on, allowing you to take appropriate control measures before the infestation becomes severe.
What is Integrated Pest Management (IPM) and how can it be used for sustainable pest control?
Integrated Pest Management is a holistic approach that combines multiple pest control strategies, including biological, cultural, and mechanical methods, to manage pests sustainably while minimizing the use of chemical pesticides.







