How to Increase Your Yield and Quality with Low Stress Training (LST) Techniques
Table of Contents
Understanding the Benefits of Low-Stress Training (LST)
Low-stress training (LST) is a horticultural technique that has gained popularity among gardening enthusiasts and professionals alike. By gently bending and tying down the branches of a plant, LST encourages horizontal growth and allows for better light penetration, resulting in increased overall yields and improved quality of the harvest.
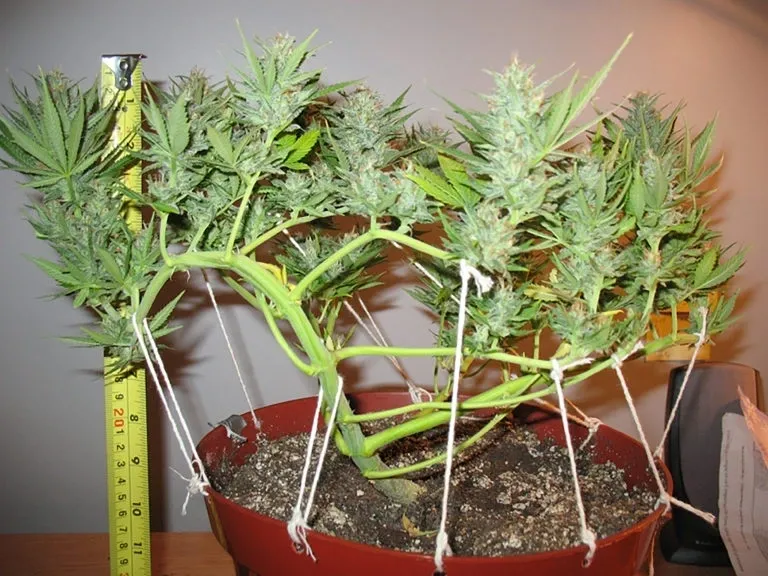

One of the key benefits of LST is the ability to optimize the use of available space. By manipulating the plant’s growth to spread horizontally instead of vertically, growers can maximize their yield potential even in limited areas. Additionally, LST helps create a uniform canopy, ensuring that all parts of the plant receive adequate light and nutrients for optimal growth. This technique also enhances airflow and reduces the risk of mold or mildew formation, which can be detrimental to the health and productivity of the plant. Overall, by implementing LST techniques, gardeners can make the most out of their growing space and achieve healthier, more productive plants.
Identifying the Right Strains for Low-Stress Training
When it comes to low-stress training (LST), choosing the right strains is crucial for success. Certain cannabis strains are more adaptable and responsive to LST techniques, making them ideal candidates for this method of plant manipulation. Additionally, selecting strains with desirable characteristics such as high yields, short internodal spacing, and sturdy branching structure can further enhance the effectiveness of LST.

One key factor to consider when identifying the right strains for LST is their genetic makeup. Indica-dominant and hybrid strains are generally more suitable for LST compared to sativa-dominant varieties. Indica-dominant strains tend to have a bushier growth pattern, with shorter internodal spacing and dense foliage. This makes them easier to manipulate through LST techniques, promoting lateral branch development and maximizing potential yield. Hybrid strains, on the other hand, offer a balance between the characteristics of indica and sativa, making them versatile options for LST growers.
Another important aspect to consider is the strain’s growth habits and characteristics. Opting for strains that naturally exhibit low-stretch and compact growth will make the LST process more manageable. These strains are usually more responsive to training techniques and tend to produce more uniform and balanced plants. Additionally, strains with strong branching structures and flexible stems are desirable as they can handle the stress imposed by LST without sacrificing overall plant health.

By carefully selecting strains that are genetically predisposed to thrive under low-stress training, growers can set themselves up for success right from the start. With the appropriate strains, the foundation for a successful LST operation can be laid, allowing for optimal branch development and increased overall yield.
Choosing the Ideal Growing Medium for LST Techniques
When it comes to low-stress training (LST) techniques for cannabis cultivation, choosing the ideal growing medium is crucial. The growing medium serves as the foundation for the plant’s root system and plays a significant role in nutrient absorption and water retention, ultimately impacting the overall health and development of the plants.
One popular growing medium for LST techniques is coco coir. Coco coir is made from the outer husk of coconut shells and is an excellent alternative to traditional soil. It has good drainage properties, allowing excess water to drain away easily, preventing overwatering issues. Additionally, coco coir has a neutral pH, which means it doesn’t significantly alter the nutrient availability of the plants. Its ability to retain moisture and provide ample aeration to the root system makes it an ideal choice for LST growers.
Another suitable growing medium for LST techniques is a soilless mix. Unlike traditional soil, a soilless mix is composed of various organic materials like peat moss, perlite, and vermiculite. One of the significant advantages of soilless mixes is that they provide excellent drainage while still retaining moisture for the roots. This promotes rapid and healthy root growth, allowing the plants to take full advantage of the LST training techniques. Soilless mixes can also be customized with nutrient-rich additives, further enhancing the plants’ growth and development.
Creating a Suitable Environment for Low-Stress Training
To successfully implement low-stress training (LST) techniques, it is crucial to create a suitable environment that promotes healthy plant growth. Providing an optimal environment will not only ensure the plant’s overall but also maximize the effectiveness of the LST techniques employed.
First and foremost, maintaining the ideal temperature and humidity levels is essential. Most cannabis strains thrive in temperatures around 70-85°F (21-29°C) during the day and slightly lower temperatures of around 65-75°F (18-24°C) during the night. Additionally, maintaining a relative humidity (RH) level of 40-60% during the vegetative stage can help prevent issues like mold or mildew growth. Utilizing a hygrometer and thermometer to monitor and adjust these factors will allow for a controlled environment conducive to LST success.

Furthermore, proper airflow and ventilation play a critical role in creating a suitable LST environment. Adequate air circulation helps prevent the development of stagnant air and reduces the risk of pests, fungal diseases, and other adverse effects. Investing in fans or an exhaust system to ensure a constant flow of fresh air is highly recommended. Additionally, using carbon filters can help eliminate unwanted odors and maintain a discreet growing space.
Creating a suitable environment for low-stress training involves careful attention to factors such as temperature, humidity, airflow, and ventilation. By establishing an ideal setup, gardeners can provide their plants with the optimal conditions necessary for successful LST techniques. In doing so, they can maximize their yields and promote healthy plant growth throughout the cultivation process.
Providing Adequate Lighting for Maximum Yield and Quality
When it comes to low-stress training (LST), providing adequate lighting is essential for achieving maximum yield and quality in your plants. Light is the primary energy source for photosynthesis, the process by which plants convert light into vital nutrients. By ensuring that your plants receive the right amount and quality of light, you can promote healthy growth, increase plant productivity, and optimize the overall quality of your harvest.
To provide adequate lighting for LST, it is crucial to understand the different factors that contribute to optimal light conditions. The intensity, duration, and spectrum of light all play significant roles in plant development. Light intensity refers to the amount of light energy reaching the plants, and it is crucial to strike a balance that is neither too weak nor too intense. The duration of light exposure should mimic natural photoperiods, with an appropriate balance between light and darkness. Lastly, the spectrum of light, including different wavelengths such as red and blue, can influence various aspects of plant growth, such as vegetative growth or flower development. By carefully managing these factors, you can ensure that your LST plants receive the right amount and quality of light necessary for maximum yield and quality.
In conclusion, providing adequate lighting for LST is a critical factor in achieving optimal plant growth and maximizing your harvest. By understanding and managing factors such as light intensity, duration, and spectrum, you can create an ideal lighting environment for your plants. Stay tuned for the next section, where we will explore how to handle and manipulate plant growth during LST to further enhance branch development and overall plant structure.
Properly Handling and Manipulating Plant Growth During LST
During Low Stress Training (LST), proper handling and manipulation of plant growth are crucial to achieve desired results. LST aims to encourage horizontal growth and create an even canopy, maximizing light penetration and promoting uniform bud development. To accomplish this, it is important to understand how to handle and manipulate plant growth effectively.
| Step | Description |
|---|---|
| 1 | Identify main stem and secondary branches |
| 2 | Gently bend stems using soft ties or training wire |
| 3 | Secure bent stems to promote horizontal growth |
| 4 | Monitor and adjust as the plant grows |
| 5 | Provide adequate support for heavy buds |
One key technique in handling plant growth is bending and securing the branches. This can be done using training stakes, trellises, or soft plant ties. Gently bend the branches downwards to encourage lateral growth and secure them in place. It is essential to be cautious and avoid any excessive bending that may damage the plants. By gently guiding the growth, you can create a more open and even canopy, ensuring that each bud site receives adequate light.
Additionally, pruning plays an important role in managing plant growth during LST. Removing unnecessary foliage and side branches helps redirect the plant’s energy towards the main stem and upper bud sites. Regular pruning ensures that the plants focus their energy on vertical growth and the development of high-quality buds. Remember to use sterilized tools when pruning to minimize the risk of infection or damage to the plants. By skillfully handling and manipulating plant growth, you can optimize the LST technique and achieve impressive yields and quality in your cannabis cultivation.
Implementing Training Techniques for Optimal Branch Development
Implementing training techniques for optimal branch development is a crucial step in optimizing plant growth and maximizing yield. By strategically manipulating the growth of branches, growers can encourage a more efficient distribution of nutrients and light, leading to healthier and more productive plants.
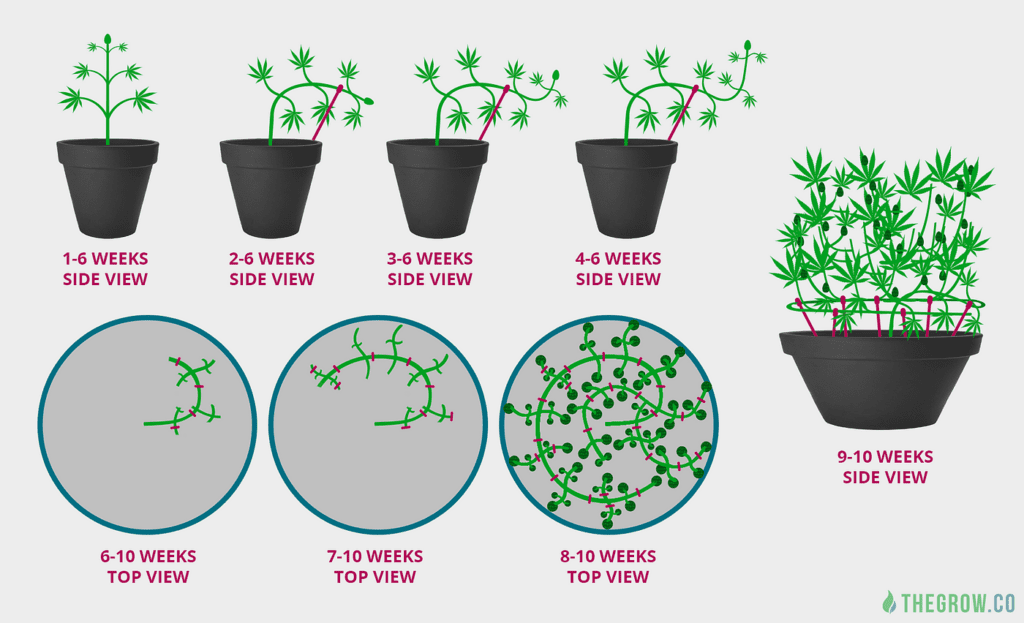
One effective method for branch development is known as low-stress training (LST). LST involves gently bending and securing the branches of the plant to create a more even canopy, allowing each branch to receive equal access to light and nutrients. This technique not only stimulates lateral growth but also ensures that no branch is overshadowed by others, promoting uniform development throughout the plant. By implementing LST early in the vegetative stage, growers can shape the plant’s growth pattern and encourage the production of multiple colas, resulting in higher yields and improved bud quality. Additionally, LST helps to strengthen the branches, reducing the risk of breakage under the weight of heavy buds later in the flowering stage.
To implement LST techniques effectively, it is important to start with young and flexible plants. Gently bending the branches using soft ties or plant training tools allows for gradual manipulation without causing damage or stress. As the plant continues to grow, regularly adjusting and securing the branches helps to maintain an even canopy and encourages strong, healthy branch development. By carefully monitoring the plant’s response and making necessary adjustments, growers can shape the plant to optimize light penetration and increase overall productivity. Training techniques such as topping, filming, and super cropping can also be utilized in conjunction with LST to further enhance branch development. However, it is important to remember that each strain may have different responses to these techniques, so it is essential to adapt the training methods accordingly.
• Low-stress training (LST) is an effective method for branch development
• LST involves bending and securing branches to create an even canopy
• This technique promotes uniform development and stimulates lateral growth
• Early implementation of LST shapes plant growth patterns and encourages multiple colas, resulting in higher yields and improved bud quality
• LST strengthens branches, reducing the risk of breakage during flowering stage
To implement LST effectively:
– Start with young and flexible plants
– Gently bend branches using soft ties or plant training tools
– Gradually manipulate without causing damage or stress
– Regularly adjust and secure branches to maintain an even canopy
– Monitor the plant’s response and make necessary adjustments
Other training techniques that can enhance branch development:
– Topping: Removing the top portion of the main stem to encourage more lateral growth
– Fimming: Pinching off a portion of new growth tips to promote branching
– Super cropping: Strategically damaging stems to redirect energy toward lower branches
Remember:
– Each strain may respond differently to these techniques, so adapt accordingly.
Maintaining Proper Nutrient Levels for LST Success
Maintaining proper nutrient levels is crucial for the success of low-stress training (LST) techniques. By providing your plants with the essential nutrients they need, you can optimize their growth, health, and overall yield. Nutrient deficiencies or imbalances can significantly impact the effectiveness of LST, so it’s important to understand the key nutrients and their roles in plant development.
One of the fundamental nutrients for LST success is nitrogen. Nitrogen plays a vital role in promoting leaf and stem growth, which is essential for creating a robust framework for training and shaping your plants. It helps plants produce chlorophyll, the pigment responsible for photosynthesis and facilitates the synthesis of proteins that are necessary for various physiological processes. To ensure adequate nitrogen levels, it’s advisable to select fertilizers with a higher nitrogen content during the vegetative stage when plants require more leaf development. However, it’s important to strike a balance, as excessive nitrogen can lead to overly vigorous growth, making plants more challenging to manage during training.
Managing Watering and Irrigation for LST Growth
Managing watering and irrigation is a crucial aspect of low-stress training (LST) for optimal growth and development of plants. Watering and irrigation practices can significantly impact the success of LST techniques, ensuring healthy and robust plants.
When it comes to watering LST-grown plants, it’s essential to strike a balance. Overwatering can lead to root rot and nutrient deficiencies, while underwatering can cause stress and hinder growth. The key is to provide just the right amount of water to maintain a moist but not waterlogged growing medium.
One effective method for managing watering in LST is the “wet-dry cycle.” This technique involves thoroughly saturating the growing medium and allowing it to dry out before watering again. By promoting a cycle of alternating wet and dry periods, you encourage the development of a robust root system. Additionally, it helps prevent the buildup of excess moisture, reducing the risk of fungal diseases and allowing oxygen to reach the roots.

When irrigating LST-grown plants, it’s crucial to consider the specific needs of each stage of growth. Seedlings and young plants, for example, require more frequent and gentle watering to ensure their delicate roots have access to the moisture they need. As plants mature, watering should be adjusted accordingly, allowing the growing medium to dry out slightly between watering sessions.
Furthermore, the method of irrigation also plays a role in managing water effectively. Techniques like drip irrigation or bottom-watering can be particularly beneficial for LST plants. These methods deliver water directly to the root zone, minimizing water waste and reducing the risk of foliage dampness, which can attract pests and diseases.
By carefully monitoring and managing watering and irrigation practices in LST, gardeners can ensure healthy, thriving plants that yield impressive results.
Preventing and Managing Pests and Diseases in LST Plants
Pests and diseases can pose a significant threat to the health and productivity of plants undergoing low-stress training (LST). Therefore, growers must take preventive measures and actively manage these issues to ensure the success of their LST plants.
One effective way to prevent pests and diseases in LST plants is through regular monitoring and inspection. By regularly checking your plants for any signs of infestation or disease, you can detect potential problems early on and take immediate action. Look out for common signs such as discolored leaves, wilting, unusual spots or patterns, and the presence of pests. Additionally, maintaining a clean and hygienic growing environment is essential. Regularly clean and disinfect your tools, equipment, and growing area to prevent the spread of pathogens. Use appropriate protective gear, such as gloves and masks, to reduce the risk of introducing pests and diseases to your plants.

Implementing proper sanitation and hygiene practices is another vital aspect of preventing and managing pests and diseases in LST plants. Remove any dead or decaying plant material from the growing area promptly, as it can attract pests and serve as a breeding ground for diseases. Dispose of the waste material properly to prevent its reentry into the cultivation system. Regularly clean and sterilize your growing containers and hydroponic systems to eradicate any pathogens that may be present. Additionally, consider implementing a strict quarantine protocol for any new plants or materials entering your growing area. This can help prevent the introduction of pests or diseases that may be hiding in these new additions. By adopting these preventive measures and maintaining a clean and sanitary environment, you can significantly reduce the risk of pests and diseases in your LST plants.
Monitoring and Adjusting LST Techniques for Desired Results
Monitoring and adjusting low-stress training (LST) techniques is crucial for achieving the desired results in plant development and yield. By closely monitoring the progress of the training process, gardeners can identify any potential issues or deviations from the ideal training plan and make necessary adjustments to optimize the outcomes.
Regular monitoring involves closely observing the plants’ response to the training techniques and recording any changes in their growth patterns or overall health. This can be done through visual inspection, measuring the distance between nodes, or using various tools to assess plant health indicators such as leaf color and turgidity. By keeping a detailed record of these observations, gardeners can track the progress of their LST efforts and make informed decisions on adjusting the techniques accordingly.

Adjusting LST techniques requires a nuanced understanding of the plant’s specific requirements and growth patterns. It may involve altering the angle or tension of the training wires, manipulating the direction of growth, or redistributing the canopy for better light penetration. Additionally, adjusting nutrient levels and providing appropriate support, such as trellises or stakes, can also contribute to achieving the desired results. The key is to carefully analyze the plants’ response and make targeted adjustments to ensure continued healthy growth and optimal yield. By closely monitoring and adjusting LST techniques throughout the plant’s life cycle, gardeners can harness the full potential of this training method and achieve the best possible results.
Harvesting and Curing Techniques for LST-Grown Plants
Harvesting and curing are crucial steps in the overall success of LST-grown plants. When it comes to harvesting, timing is key. You want to ensure that you harvest your plants at the optimal point of maturity to achieve the desired potency, flavor, and aroma. Keep in mind that each strain may have different flowering times, so it’s important to closely monitor the trichomes using a magnifying tool or microscope. Look for milky or cloudy trichomes with a hint of amber for an indication of peak cannabinoid production. At this stage, the plant’s energy has been focused on resin production, providing a potent end product.

Once your plants have been harvested, proper curing techniques are essential to preserving the quality, flavor, and potency of your LST-grown plants. Curing involves drying the harvested buds slowly and steadily to eliminate excess moisture while retaining desirable terpenes and cannabinoids. Start by trimming the excess leaves carefully to improve airflow around the buds. Hang the trimmed buds upside down in a cool, dark, and well-ventilated area with optimal humidity levels of around 50-60%. Monitor the drying process regularly and adjust the humidity levels accordingly. After a few days, when the buds feel crispy on the outside but still slightly moist on the inside, transfer them to airtight glass jars. This allows for further drying and curing through the process of oxidation. Open the jars for a short period daily in the first few weeks to release any excess humidity and prevent mold formation. After several weeks of proper curing, your LST-grown plants will be ready to deliver their full potential in terms of flavor, aroma, and effects.
Troubleshooting Common Issues in Low-Stress Training
Common issues may arise during the process of low-stress training (LST) that can hinder its success. One common issue is the incorrect use of training techniques, such as bending or tying branches too aggressively, which can lead to plant stress and damage. It’s important to remember that LST should be a gentle and gradual process, allowing the plant to adjust and respond positively to the training. Another issue that may occur is over or under-watering the plants. Both situations can have detrimental effects on the plant’s growth and overall health. It’s crucial to find a balance and monitor the plant’s moisture levels regularly, adjusting watering habits accordingly.
Another common issue in LST is the improper maintenance of nutrient levels. The health and growth of the plant depend on a well-balanced nutrient intake. If the plant lacks essential nutrients, it can lead to stunted growth, deficiencies, and lower yields. On the other hand, excessive nutrients can cause nutrient burn or toxicity, which can be equally damaging. It is crucial to follow a nutrient feeding schedule specific to LST plants and monitor the plant’s response, adjusting the nutrient levels as necessary.
Additionally, pests and diseases can pose significant challenges during the LST process. Insects, fungi, and bacteria can target the weakened or exposed areas of the plants that result from the training. Regular monitoring and preventive measures such as using beneficial insects, organic pest control methods, and maintaining sanitary conditions are vital to prevent and manage these issues.
By addressing and properly troubleshooting these common issues during low-stress training, gardeners can maximize the success of the technique and achieve the desired results.
For more details check the video:
What are the benefits of Low Stress Training (LST)?
LST helps to increase yield and quality by promoting even light distribution, improving airflow, and allowing for better nutrient absorption.
How can I identify the right strains for Low Stress Training?
Look for strains that have flexible branches and respond well to training techniques. Indica-dominant strains are often more suitable for LST.
What is the ideal growing medium for LST techniques?
A well-draining and airy growing medium, such as coco coir or a mixture of perlite and vermiculite, is recommended for LST.
How can I create a suitable environment for Low Stress Training?
Maintain proper temperature, humidity, and ventilation levels in the growing area to ensure optimal conditions for LST.
What kind of lighting is necessary for maximum yield and quality in LST?
High-quality grow lights, such as LED or HID lights, should be used to provide adequate and adjustable lighting for LST plants.
How should I handle and manipulate plant growth during LST?
Gently bend and secure branches using soft ties or plant training clips to achieve the desired shape and direction of growth.
What training techniques should I implement for optimal branch development?
Techniques like bending, tying, or using trellis nets can be used to train branches and encourage lateral growth.
How can I maintain proper nutrient levels for LST success?
Regularly monitor and adjust nutrient solutions to ensure plants receive the necessary macro and micronutrients for healthy growth.
What is the best approach for watering and irrigation in LST growth?
Water plants thoroughly but avoid overwatering. Implement a watering schedule that allows the growing medium to dry out between waterings.
How can I prevent and manage pests and diseases in LST plants?
Regularly inspect plants for signs of pests or diseases and promptly address any issues with appropriate pest control methods or treatments.
How should I monitor and adjust LST techniques for desired results?
Regularly observe plant growth and adjust training techniques as needed to achieve the desired shape, size, and yield.
What are the recommended harvesting and curing techniques for LST-grown plants?
Harvest plants at the appropriate time, trim buds carefully, and follow proper curing methods to preserve flavor, potency, and quality.
What are some common issues in Low Stress Training and how can they be troubleshooted?
Common issues in LST include branch breakage, nutrient deficiencies, and pest infestations. To troubleshoot, reinforce weak branches, adjust nutrient levels, and address pests promptly with suitable treatments.

Kanike Sreekanth, a prolific writer at SouthElMonteHydroponics, brings a unique blend of creativity and scientific rigor to the table. With a degree in Horticulture from a prestigious institution, Kanike’s expertise spans hydroponic farming, plant biology, and agricultural sustainability. Their passion for exploring innovative cultivation methods and promoting environmental stewardship drives them to uncover new insights in the realm of hydroponics. Kanike’s writing serves as a conduit for sharing their knowledge and inspiring others to embrace alternative farming practices for a more sustainable future.







