Eliminating Leafhopper Pests Effectively
Table of Contents
Understanding the Life Cycle of Leafhopper Pests

The life cycle of leafhopper pests is crucial to understand in order to effectively manage and control their populations. Leafhoppers go through a simple form of metamorphosis, which consists of three main stages: the egg, nymph, and adult.

The female leafhopper typically lays her eggs on the undersides of leaves, often in large groups. These eggs are tiny, oval-shaped, and can be translucent or pale in color. Once the eggs hatch, the nymphs emerge and start feeding on plant sap. They resemble smaller versions of the adult leafhoppers but lack wings and are incapable of flight. Nymphs undergo several molts, shedding their exoskeletons as they grow. Finally, they reach the adult stage, where they develop wings and become fully mobile. Leafhopper adults are typically small, with vibrant colors and intricate patterns on their wings.
Understanding the life cycle of leafhopper pests is essential for implementing effective management strategies. By disrupting their reproductive processes or targeting the vulnerable nymph stage, gardeners and farmers can significantly reduce leafhopper populations and prevent extensive damage to plants.
Identifying Leafhopper Pest Species in Your Garden
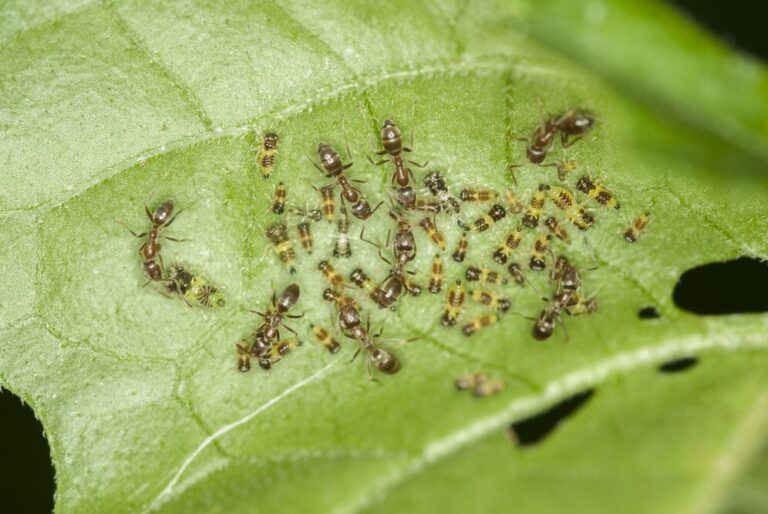
Leafhopper pests can cause significant damage to garden plants, so it is important to be able to identify the species that might be causing trouble in your garden. One common type of leafhopper that you might encounter is the potato leafhopper (Empoasca fabae). These pests are small, green insects that feed on the sap of plants, particularly those in the bean family. They can be identified by their wedge-shaped bodies and their ability to jump or fly short distances.
Another leafhopper pest that you might come across is the rose leafhopper (Edwardsiana rosae). These insects are slightly larger than potato leafhoppers and are typically yellow or green in color. They are known for their ability to produce a frothy substance called spittle, which can sometimes be found on the stems or leaves of infested plants. These pests can cause stunted growth and leaf damage, so it is important to keep an eye out for them in your garden.
The Damage Caused by Leafhopper Pests to Plants
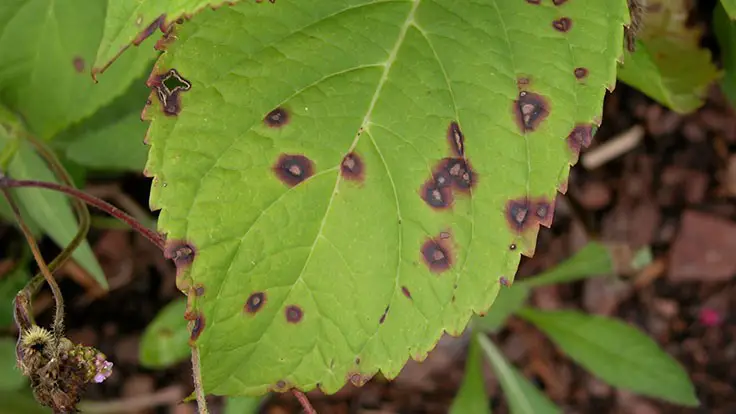
Leafhopper pests can cause significant damage to plants in your garden. These tiny insects feed on the sap of plants, piercing the tissues with their sharp mouthparts. As they feed, they inject toxic saliva into the plants, which can lead to various issues. One of the most common problems caused by leafhoppers is the stunting of plant growth. The toxic saliva disrupts the flow of nutrients within the plant, hindering its development and resulting in stunted, underdeveloped foliage.

In addition to stunting, leafhopper pests can also transmit diseases to plants. Some species of leafhoppers carry viruses that can infect a wide range of plants, including vegetables, ornamentals, and fruits. These viruses can lead to severe symptoms, such as yellowing, curling, and distortion of leaves, as well as necrosis and reduced yield. It is crucial to be vigilant and monitor your plants regularly to prevent the spread of these diseases and minimize long-term damage.
Natural Predators and Biological Control Methods for Leafhopper Pests
Natural predators and biological control methods are effective means of managing leafhopper pests in gardens and farms. These methods involve the use of organisms that prey on or parasitize leafhoppers, helping to keep their populations in check. One common natural predator is the ladybird beetle, also known as the ladybug. Ladybirds feed on leafhopper eggs, nymphs, and adults, making them valuable allies in leafhopper control. Other natural predators include lacewings, spiders, and predatory mites.
In addition to natural predators, biological control methods can also involve the use of beneficial insects and pathogens. For example, the parasitic wasp can be introduced in areas with heavy leafhopper infestations. These wasps lay their eggs inside leafhopper nymphs, which eventually die as the wasp larvae develop. Similarly, fungal pathogens such as Beauveria bassiana can be used to infect and kill leafhoppers. These biological control methods are often used in integrated pest management (IPM) strategies to reduce the reliance on synthetic pesticides and minimize the environmental impact of pest control practices.
Cultural Practices to Prevent Leafhopper Infestations

One effective cultural practice to prevent leafhopper infestations is to regularly remove weeds from your garden. Leafhoppers are attracted to a variety of plants, including common garden weeds. By keeping your garden weed-free, you can reduce the potential hiding and feeding spots for these pests. Additionally, practicing good sanitation by removing any leaf debris or fallen fruits can also help prevent leafhopper infestations. These pest insects often lay their eggs in plant debris, so by removing this potential breeding ground, you can decrease their population in your garden.
Another cultural practice that can be implemented is proper plant spacing. Leafhoppers prefer densely packed plants, as it provides cover and a continuous food source. By giving your plants enough space to grow and allowing for proper air circulation, you can discourage leafhoppers from settling in your garden. This practice not only helps prevent infestations but also promotes overall plant health by reducing the risk of moisture-related diseases. So, make sure to follow recommended spacing guidelines when planting your garden, allowing your plants to thrive while deterring leafhopper pests.
Using Physical Barriers to Protect Plants from Leafhopper Pests
Using physical barriers is an effective method to protect your plants from leafhopper pests. These barriers create a physical obstacle that prevents the pests from reaching your plants and causing damage. There are various types of physical barriers that you can use, such as mesh netting, row covers, and floating row covers.
Mesh netting is a popular choice as it allows air, sunlight, and water to reach your plants while keeping the leafhopper pests out. Simply cover your plants with the netting, ensuring that it is secured tightly to prevent any gaps. Row covers, on the other hand, are made of lightweight fabric and provide protection against not only leafhoppers but also other pests like aphids and caterpillars. Floating row covers are similar to row covers but are designed to float above your plants, providing a more breathable environment. Whichever type of physical barrier you choose, it is important to regularly inspect and maintain them to ensure their effectiveness in keeping leafhopper pests at bay.
Proper Planting Techniques to Minimize Leafhopper Pests
Planting techniques play a crucial role in minimizing the presence of leafhopper pests in your garden. By implementing proper planting practices, you can create an environment that is less conducive to their survival and reproduction. One effective technique is to practice crop rotation. This involves changing the location of your plants each year to disrupt the leafhoppers’ preferred habitats. By doing so, you reduce the likelihood of a continuous infestation, as the pests will struggle to locate their preferred plants.
Another important planting technique is to maintain adequate spacing between your plants. Leafhoppers are highly mobile insects and can easily move from one plant to another if they are closely situated. By providing ample spacing, you create physical barriers that make it more difficult for leafhoppers to move around your garden. Additionally, proper spacing increases air circulation between plants, which helps to dry out foliage and reduce the humidity levels that leafhoppers thrive in. Implementing these planting techniques can significantly reduce the attractiveness of your garden to leafhopper pests, ultimately minimizing the risk of infestations and the damage they cause.
Selecting Resistant Plant Varieties for Leafhopper Control
Selecting resistant plant varieties for leafhopper control is an essential aspect of integrated pest management. By choosing plants that possess natural resistance to leafhopper pests, growers can significantly reduce the need for chemical interventions and minimize the potential damage caused by infestations. However, it is crucial to note that not all plant varieties exhibit the same level of resistance, and understanding the factors that contribute to resistance is key in making informed decisions.
One frequently asked question regarding resistant plant varieties is whether all species have naturally occurring resistance. The answer is no. Plant resistance to leafhopper pests can vary greatly, both within and between different plant species. While some plants have developed their own defense mechanisms against these pests, others may be more susceptible to infestations. Therefore, it is crucial for growers to research and identify specific plant varieties that have demonstrated resistance to leafhopper pests. This information can typically be obtained from reputable seed suppliers, agricultural extension services, or research publications.
| Plant Species | Variety | Resistance Traits |
|---|---|---|
| Tomato (Solanum lycopersicum) | ‘Defiant’ | Resistant to Tomato Spotted Wilt Virus (TSWV), a virus often transmitted by leafhoppers. |
| Potato (Solanum tuberosum) | ‘King Harry’ | Exhibits resistance to leafhopper-transmitted diseases. |
| Beans (Phaseolus vulgaris) | ‘Etna’ | Resistant to common leafhopper pests. |
| Grapes (Vitis vinifera) | ‘Thompson Seedless’ | Shows resistance to Pierce’s Disease, a bacterial infection transmitted by leafhoppers. |
| Peppers (Capsicum annuum) | ‘Cayenne’ | Displays resistance to leafhopper-transmitted diseases. |
| Zinnias (Zinnia elegans) | ‘Profusion’ series | Resistant varieties that deter leafhopper feeding. |
| Alfalfa (Medicago sativa) | ‘Resistant Common’ | Resistant to various leafhopper species. |
| Lettuce (Lactuca sativa) | ‘Jericho’ | Leafhopper-resistant variety suitable for lettuce crops. |
| Celery (Apium graveolens) | ‘Conquistador’ | Exhibits resistance to certain leafhopper species. |
| Cotton (Gossypium hirsutum) | ‘DP 1611 B2RF’ | Bred for resistance to cotton leafhopper. |
Note: Choosing plant varieties with inherent resistance to leafhoppers is a proactive strategy in integrated pest management, promoting healthier crops with natural defense mechanisms.
Effective Monitoring and Detection Methods for Leafhopper Pests
Leafhopper pests can cause significant damage to plants in gardens and landscapes, making it crucial to have effective monitoring and detection methods in place. One commonly used approach is visual inspection, where the leaves and stems of plants are carefully examined for the presence of leafhoppers. Look for the characteristic triangular shape, vibrant colors, and hopping movement of these pests. Additionally, the use of a hand lens can be helpful in detecting smaller nymphs and eggs that may be difficult to see with the naked eye. Regular monitoring should be conducted throughout the growing season to catch infestations early and prevent widespread damage.
In addition to visual inspection, sticky traps can also be used as an effective monitoring and detection method for leafhopper pests. These traps, often yellow in color, are coated with a sticky substance that attracts and captures the pests when they come into contact with it. Place the traps near plants that are susceptible to leafhopper infestation, such as crops or ornamental plants. By regularly checking the traps, you can determine the population density of leafhoppers in your garden and take appropriate action if necessary. Keep in mind that sticky traps should be replaced regularly to maintain their effectiveness.
Organic Insecticides and Their Application for Leafhopper Control
Organic insecticides provide an alternative method for controlling leafhopper pests in the garden. These products are derived from natural sources and do not contain synthetic chemicals that can harm the environment or pose risks to human health. One popular organic insecticide for leafhopper control is neem oil, which is extracted from the seeds of the neem tree. Neem oil works by disrupting the feeding and reproductive behaviors of leafhoppers, ultimately reducing their population. To apply neem oil, mix the recommended amount with water and spray it directly onto the plants, making sure to coat both sides of the leaves. It’s important to follow the manufacturer’s instructions to ensure proper application and effectiveness. Other organic insecticides that can be effective against leafhoppers include insecticidal soaps, pyrethrin-based products, and botanical extracts. Before using any organic insecticide, it’s essential to thoroughly read the label and understand the target pests and application rates.
One common question about organic insecticides is whether they are safe for beneficial insects in the garden. While organic insecticides are generally considered safer than synthetic ones, it’s still important to take precautions to protect beneficial insects such as bees, ladybugs, and parasitic wasps. To minimize harm to these beneficial insects, it’s recommended to use organic insecticides during times when they are least active, such as early morning or late evening when bees are less likely to be foraging. Additionally, avoid spraying blooms or flowering plants where bees are present. It’s also important to remember that organic insecticides are not selective in their impact and may harm beneficial insects if used in excessive amounts. Therefore, always follow the recommended application rates and consider spot-treating affected areas rather than blanket spraying the entire garden.
Integrated Pest Management Strategies for Leafhopper Pests
Leafhopper pests can wreak havoc on your garden, causing damage to a wide variety of plants. To effectively manage these pests, integrated pest management (IPM) strategies offer a comprehensive approach. One essential strategy is to promote a healthy garden ecosystem that encourages natural predators of leafhoppers. These predators, such as ladybugs, lacewings, and spiders, can help control leafhopper populations naturally. By providing suitable habitats and food sources for these beneficial insects, you can create a balance in your garden that keeps leafhopper numbers in check.
In addition to attracting natural predators, another important aspect of IPM is the use of physical barriers to protect plants from leafhopper pests. Installing row covers or netting can help create a physical barrier that keeps the pests away from your precious plants. It is crucial to ensure that the barriers are correctly secured and have no gaps where leafhoppers can enter. Regular monitoring and inspection are also vital to identify any signs of leafhopper activity and make prompt adjustments to the barriers as needed. By integrating these physical barriers into your pest management plan, you can effectively prevent leafhopper infestations and safeguard your garden from their damaging effects.
Timing and Frequency of Leafhopper Control Measures
Leafhoppers are notorious for their ability to damage plants, so it’s crucial to know when and how often to implement control measures. Timing is key when it comes to combating leafhopper infestations. It’s important to monitor your plants regularly for the presence of leafhoppers and to begin control methods as soon as the pests are detected. Early intervention can prevent leafhoppers from reproducing and causing extensive damage to your plants.
The frequency of leafhopper control measures will vary depending on the severity of the infestation and the specific control methods you choose. In some cases, a single application of an organic insecticide may be enough to control the pests. However, if the infestation persists or if you’re using biological control methods, such as introducing natural predators, you may need to implement control measures multiple times throughout the growing season. Regular monitoring of your plants will help you determine when additional control measures are necessary to keep leafhoppers under control.
The Role of Temperature and Humidity in Leafhopper Infestations
Temperature and humidity play a crucial role in the infestation patterns of leafhopper pests. These tiny insects are highly sensitive to changes in their environment, particularly when it comes to temperature extremes and moisture levels. Leafhoppers are most active and reproduce rapidly in warm weather conditions, with temperatures between 70°F to 90°F (21°C to 32°C) being optimal for their growth and development. However, excessive heat can also be detrimental to leafhopper populations, causing them to seek shelter in cooler areas or go into a sort of hibernation state, slowing down their reproductive cycles.
Humidity levels also have a significant impact on leafhopper infestations. These pests thrive in areas with moderate humidity, as high humidity can lead to fungal growth and diseases that can reduce their populations. Conversely, low humidity levels can result in desiccation and mortality of leafhoppers, especially if they are exposed to direct sunlight for extended periods. Therefore, understanding the relationship between temperature, humidity, and leafhopper infestations can help gardeners and farmers implement appropriate preventive and control measures to protect their plants.
Potential Risks and Precautions When Using Chemical Control for Leafhopper Pests
The use of chemical control methods for leafhopper pests can be effective in reducing populations and minimizing damage to plants. However, it is important to be aware of potential risks and take necessary precautions when using these chemicals. One potential risk is the possibility of harming beneficial insects, such as bees and ladybugs, which play a crucial role in pollination and natural pest control. Therefore, it is essential to carefully select and apply insecticides that specifically target leafhoppers while minimizing harm to beneficial insects.
Another precaution to consider is the potential for chemical residues on plants. Some insecticides may leave behind residues that can be harmful to humans and pets if ingested. It is crucial to read and follow the instructions provided by the manufacturer regarding the application rates and intervals. Additionally, it is advisable to avoid applying chemicals on plants near edible crops and to wash fruits and vegetables thoroughly before consumption. Ensuring proper timing and frequency of chemical control measures can help minimize risks and maximize their effectiveness.
Common Mistakes to Avoid in Leafhopper Pest Management
Incorrect identification of leafhopper pest species is a common mistake that many gardeners make in leafhopper pest management. This can lead to ineffective control measures being implemented, as different species of leafhoppers may have varying behaviors and susceptibilities to certain control methods. It is crucial to accurately identify the specific leafhopper species present in your garden before deciding on the most appropriate control strategy. Consult with local extension services or entomology experts to obtain assistance in correctly identifying leafhopper pests.
Another common mistake in leafhopper pest management is neglecting to monitor and detect infestations in a timely manner. Leafhoppers are small and can go unnoticed, especially in the early stages of an infestation. Regular inspection of plants for the presence of leafhoppers or their characteristic feeding damage is essential. Failure to monitor and detect leafhopper populations early can result in rapid population growth and significant damage to plants. Implement an effective monitoring program, such as using sticky traps or visual inspections, to regularly assess the presence and severity of leafhopper infestations in your garden.
Evaluating the Effectiveness of Leafhopper Control Methods
Evaluating the effectiveness of leafhopper control methods is crucial in order to determine the most suitable approach for managing pest infestations. It involves assessing the impact of various techniques and strategies on reducing leafhopper populations and minimizing damage to plants. One frequently asked question is, “How do I know if a particular control method is working?”
To evaluate the effectiveness of leafhopper control methods, monitoring plays a pivotal role. Regularly inspect your plants to observe the presence of leafhoppers and assess the extent of damage caused. By comparing the population levels and degree of injury before and after applying a control method, you can gauge its efficacy. Keep in mind that it may take some time for certain control measures to show noticeable results, so patience and consistent monitoring are key. Additionally, seeking advice from local agricultural extension services or consulting with experienced farmers and gardeners can provide valuable insights on the effectiveness of specific leafhopper control methods in your area.
What are leafhopper pests?
Leafhopper pests are small insects that feed on the sap of plants, causing damage to leaves and stunting growth.
How can I identify leafhopper pest species in my garden?
Leafhoppers can vary in appearance, but they typically have a slender body and long hind legs. It is best to consult a field guide or contact a local entomologist for accurate identification.
What kind of damage do leafhopper pests cause to plants?
Leafhopper pests can cause yellowing or browning of leaves, curling or cupping of leaves, and stunted growth in plants. They may also transmit plant diseases.
Are there natural predators that can control leafhopper pests?
Yes, there are natural predators such as ladybugs, lacewings, and parasitic wasps that can help control leafhopper populations.
What are some cultural practices that can prevent leafhopper infestations?
Cultural practices include removing weeds, maintaining proper plant spacing, and practicing good sanitation in the garden to reduce leafhopper populations.
How can I use physical barriers to protect my plants from leafhopper pests?
Physical barriers like row covers or netting can be used to prevent leafhoppers from accessing plants and laying eggs.
Are there certain plant varieties that are resistant to leafhopper pests?
Yes, some plant varieties have natural resistance to leafhoppers. It is recommended to select and plant these resistant varieties in your garden.
What are some effective monitoring and detection methods for leafhopper pests?
Monitoring leafhopper pests can be done by regularly inspecting plants for signs of damage, using sticky traps, or performing visual counts of leafhoppers.
Can organic insecticides be used to control leafhopper pests?
Yes, there are organic insecticides available that can be used for leafhopper control. However, it is important to follow the instructions and precautions provided by the manufacturer.
What is integrated pest management for leafhopper pests?
Integrated pest management (IPM) involves using a combination of control methods, such as cultural practices, biological control, and targeted pesticide use, to manage leafhopper pests in a sustainable and environmentally-friendly manner.
How often should leafhopper control measures be implemented?
The timing and frequency of leafhopper control measures will depend on the severity of the infestation and the specific control methods being used. It is important to monitor the situation and take action as needed.
Does temperature and humidity affect leafhopper infestations?
Yes, leafhopper populations can be influenced by temperature and humidity. Warm and dry conditions are often favorable for their reproduction and development.
What are the potential risks and precautions when using chemical control for leafhopper pests?
When using chemical control, it is important to follow the instructions on the pesticide label and take necessary precautions to protect yourself, other organisms, and the environment from potential risks.
What are some common mistakes to avoid in leafhopper pest management?
Common mistakes to avoid include using excessive pesticides, not properly identifying leafhopper species, and not implementing a well-rounded integrated pest management approach.
How can I evaluate the effectiveness of leafhopper control methods?
You can evaluate the effectiveness of control methods by monitoring the population of leafhoppers, assessing plant health and damage, and comparing results before and after implementing control measures.






