Grow Light vs Sunlight: How They Compare and Which One to Use for Hydroponics
The Importance of Light in Hydroponic Systems
Light is one of the most critical factors in hydroponic systems, playing a crucial role in the growth and development of plants. With the absence of soil, hydroponics relies heavily on the provision of artificial light to replicate the conditions that plants typically experience in natural sunlight. Understanding the importance of light in hydroponics is key to optimizing plant growth and ensuring successful harvests.
In a hydroponic system, light serves as the energy source for photosynthesis, the process by which plants convert light into chemical energy and synthesize organic compounds. Without adequate light, plants may struggle to produce the energy they need for healthy growth, resulting in stunted development, weakened immune systems, and reduced yields. Furthermore, light plays a significant role in regulating various physiological processes, including germination, flowering, fruiting, and overall plant morphology. By providing the right type, intensity, and duration of light, hydroponic gardeners can manipulate these processes to their advantage and maximize plant health and productivity.

• Light is the energy source for photosynthesis in hydroponic systems.
• Without adequate light, plants may experience stunted growth and reduced yields.
• Light regulates various physiological processes in plants, including germination, flowering, fruiting, and overall morphology.
• By providing the right type, intensity, and duration of light, hydroponic gardeners can manipulate these processes to optimize plant health and productivity.
Understanding the Differences Between Grow Lights and Sunlight
Grow lights and sunlight are two sources of light that play a crucial role in the success of hydroponic systems. While they both provide the necessary light energy for plant growth, there are significant differences between the two.
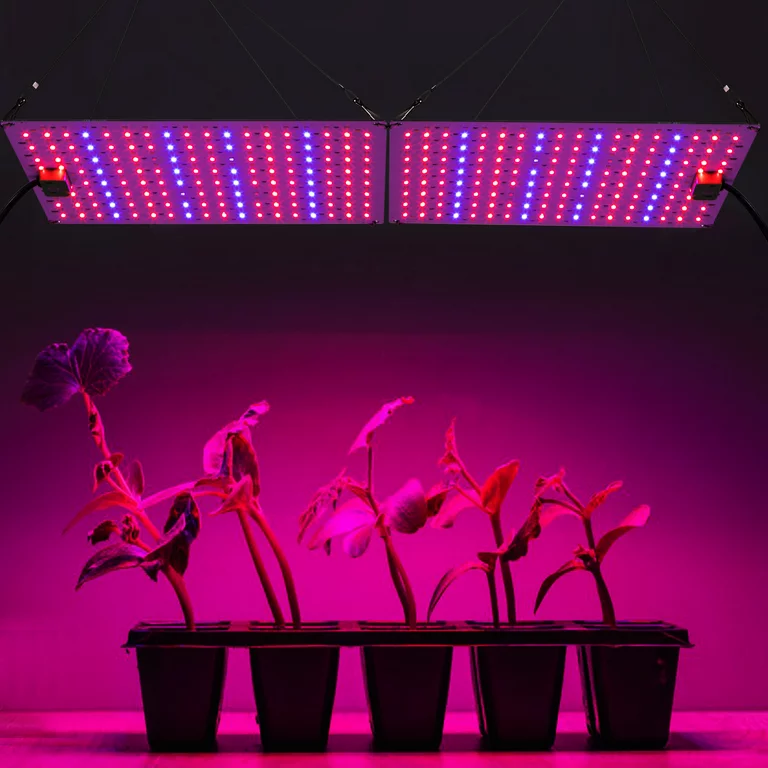
Firstly, one of the key differences lies in the spectrum of light they emit. Sunlight contains the full spectrum of light, including ultraviolet (UV) and infrared (IR) rays, which can be beneficial for plant growth. On the other hand, grow lights are designed to emit specific wavelengths of light, typically targeting the red and blue spectrum, which are crucial for photosynthesis. This targeted spectrum can optimize plant growth and yield in controlled indoor environments.
Another important distinction is the intensity of light. Sunlight is naturally intense, especially during peak daylight hours, providing high levels of energy for plants. Grow lights, on the other hand, can be adjusted to provide various intensity levels depending on the specific needs of different plant species or growth stages. This flexibility allows growers to tailor the light intensity to maximize plant productivity and efficiency.
Understanding these differences is fundamental for hydroponic growers to make informed decisions when it comes to choosing the right light source for their plants. Whether it’s harnessing the full spectrum of sunlight or utilizing the precise spectrum and intensity of grow lights, finding the perfect balance of light is essential for optimal plant growth and overall success in hydroponics.
• Sunlight contains the full spectrum of light, including UV and IR rays
• Grow lights emit specific wavelengths of light, targeting the red and blue spectrum for photosynthesis
• Sunlight is naturally intense, providing high levels of energy for plants
• Grow lights can be adjusted to provide various intensity levels based on plant needs
• Understanding these differences allows hydroponic growers to choose the right light source for their plants
• Finding the perfect balance of light is essential for optimal plant growth in hydroponics.
The table below shows us the difference between grow light and sunlight:
| Aspect | Grow Light | Sunlight |
|---|---|---|
| Light Spectrum | Can be customized for specific needs. | Offers a broad spectrum of light. |
| Intensity | Adjustable for different stages. | Intensity varies with time and location. |
| Duration and Control | Control over duration and intensity. | Day-night cycle, seasonal variations. |
| Consistency | Provides consistent light as needed. | Subject to weather and atmospheric conditions. |
| Energy Efficiency | Can be energy-efficient with LEDs. | Naturally abundant but not controllable. |
| UV Radiation | Some emit UV, tailored for plants. | Contains natural UV rays. |
| Heat Production | LED lights produce less heat. | Sun’s heat varies based on conditions. |
| Cost and Installation | Initial investment but controllable. | Free but dependent on location. |
| Indoor Cultivation | Essential for indoor plant growth. | Limited in indoor settings. |
| Plant Growth Stages | Adjustable for various growth stages. | Natural changes during the day. |
The Spectrum of Light
Light is a fundamental element in the successful growth of plants in hydroponic systems. One crucial aspect of light to consider is its spectrum. The spectrum of light refers to the range of wavelengths or colors that make up the light we see. Each color within the spectrum has a different effect on plant growth and development.
Plants primarily utilize two main parts of the spectrum for photosynthesis: blue light (400-500nm) and red light (600-700nm). Blue light is essential for promoting vegetative growth, as it stimulates the production of chlorophyll and helps regulate plant height and leaf expansion. On the other hand, red light is crucial for flowering and fruiting, as it triggers the transition from the vegetative to the generative phase.
To ensure optimal plant growth in hydroponic systems, it is important to provide a balance of both blue and red light. This can be achieved by using specific types of grow lights that emit the appropriate wavelengths. Different light sources, such as LEDs, fluorescent lights, and high-intensity discharge (HID) lights, offer varying spectra, which allows growers to tailor the light environment to suit the specific needs of their plants. By understanding the spectrum of light and its effects on plant growth, hydroponic enthusiasts can make informed decisions when selecting the most suitable grow lights for their systems.
• Blue light (400-500nm) stimulates chlorophyll production and promotes vegetative growth
• Red light (600-700nm) triggers flowering and fruiting, transitioning plants from vegetative to generative phase
• Balancing both blue and red light is crucial for optimal plant growth in hydroponic systems
• Grow lights such as LEDs, fluorescent lights, and HID lights offer varying spectra to meet specific plant needs
• Understanding the spectrum of light helps hydroponic enthusiasts select suitable grow lights for their systems.
| Plant Growth Stage | Spectrum Segment | Wavelength Range (nanometers) | Color Representation | Biological Significance |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Germination | Ultraviolet (UV) | 10 – 400 | Violet | Stimulates seed germination; helps develop stronger seedlings. |
| Seedling Growth | Visible Light | 400 – 700 | Violet to Red | Supports photosynthesis, chlorophyll production, and overall seedling development. |
| Vegetative Growth | Visible Light | 400 – 700 | Blue to Red | Blue light promotes vegetative growth, while red light encourages branching and foliage development. |
| Flowering | Visible Light | 400 – 700 | Red | Red light plays a crucial role in flowering and fruiting processes, influencing bloom formation and yield. |
| Fruiting | Visible Light | 600 – 700 | Red | Enhances fruit development and ripening; red light is essential for fruit-bearing plants. |
| Overall Growth | Infrared (IR) | 700 – 1,000 | Red to Infrared | Infrared light contributes to overall plant growth, elongation, and increased biomass. |
This above table shows us the different wavelengths of lights for different stages of plants’ life.
The Intensity of Light
The intensity of light plays a crucial role in the success of hydroponic systems. It directly affects plant growth, development, and overall productivity. Light intensity refers to the amount of light energy reaching the plants per unit area. The right level of light intensity ensures the optimal photosynthesis process, where plants convert light into chemical energy to synthesize sugars and other essential nutrients.
Different plant species have different light intensity requirements. For instance, leafy greens and herbs thrive well under moderate to high-light conditions, while fruiting plants like tomatoes and peppers require higher light intensities. It is important to consider the light intensity requirements of the plants you are growing and adjust your lighting system accordingly. Insufficient light intensity can lead to weak, spindly plants with elongated stem growth, while excessive light intensity can cause leaf scorching and stunted growth.
To ensure the ideal light intensity, it is essential to carefully select appropriate grow lights and position them at the optimal distance from the plants. LED grow lights are a popular choice as they offer adjustable light intensity settings and allow precise control over brightness levels. Additionally, using reflective surfaces within the growing area can help enhance light distribution and prevent light wastage. Monitoring light intensity levels regularly and making necessary adjustments will provide the plants with the right amount of light energy they need to thrive in a hydroponic system.
• The intensity of light directly affects plant growth, development, and overall productivity in hydroponic systems.
• Light intensity refers to the amount of light energy reaching the plants per unit area.
• Optimal photosynthesis process depends on the right level of light intensity.
• Different plant species have different light intensity requirements.
• Leafy greens and herbs thrive well under moderate to high-light conditions.
• Fruiting plants like tomatoes and peppers require higher light intensities.
• Insufficient light intensity can lead to weak, spindly plants with elongated stem growth.
• Excessive light intensity can cause leaf scorching and stunted growth.
• Carefully selecting appropriate grow lights is essential for ensuring ideal light intensity.
• LED grow lights are a popular choice as they offer adjustable settings for controlling brightness levels.
• Positioning grow lights at the optimal distance from plants is crucial for maintaining proper light distribution.
• Using reflective surfaces within the growing area can enhance light distribution and prevent wastage.
• Regular monitoring of light intensity levels is important for making necessary adjustments in a hydroponic system.
The Duration of Light
The duration of light plays a crucial role in the growth and development of plants in hydroponic systems. Just as plants in nature rely on the daily cycle of sunrise and sunset, hydroponic plants require an appropriate amount of light exposure to thrive.
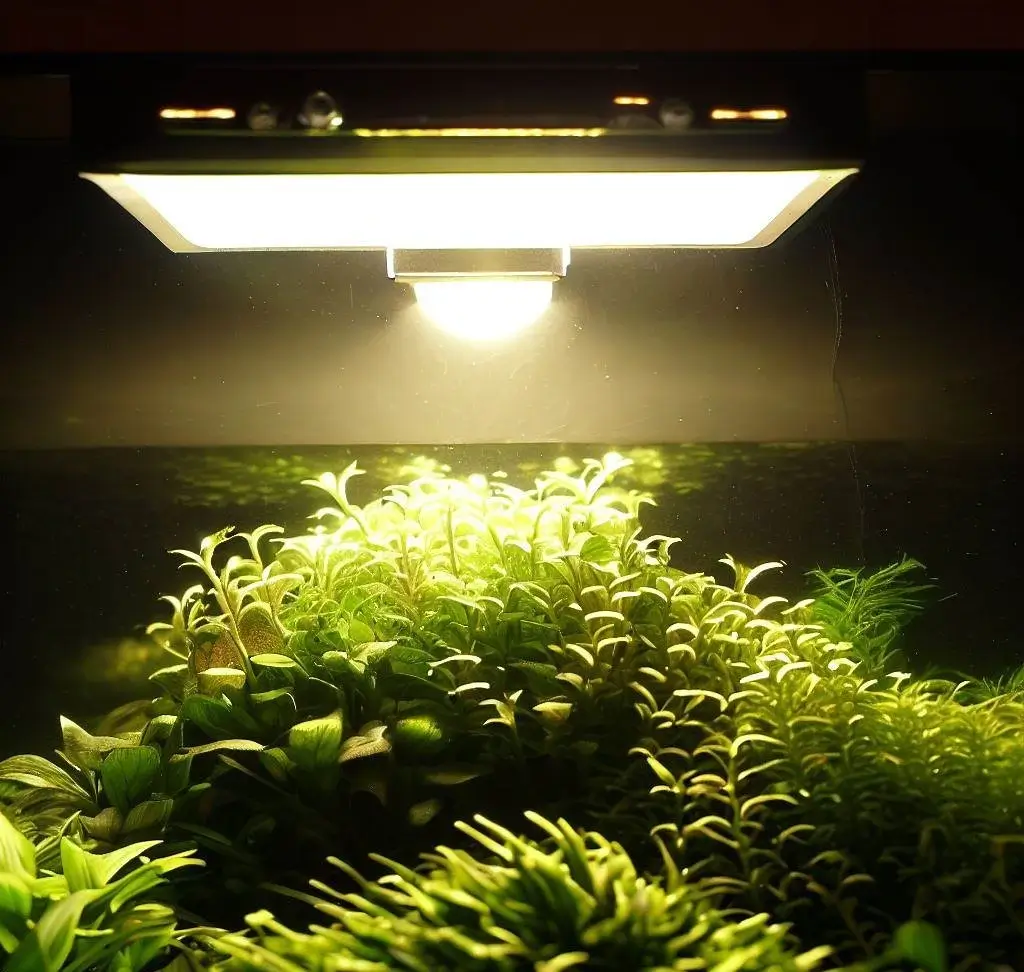

In general, most plants require around 12 to 16 hours of light each day during their growth phase. However, it’s important to note that different types of plants have varying light requirements. For instance, leafy greens and herbs may do well with 12 to 14 hours of light, while fruiting plants like tomatoes or peppers may benefit from longer durations of 14 to 16 hours. The exact duration of light should be adjusted based on the specific needs of the plants being cultivated. It’s crucial to provide a consistent duration of light each day, as abrupt changes in lighting schedules can cause stress and negatively impact plant growth.
• Most plants require around 12 to 16 hours of light each day during their growth phase.
• Leafy greens and herbs may do well with 12 to 14 hours of light.
• Fruiting plants like tomatoes or peppers may benefit from longer durations of 14 to 16 hours.
• The exact duration of light should be adjusted based on the specific needs of the plants being cultivated.
• Consistency in providing a duration of light is crucial for optimal plant growth.
Energy Efficiency of Grow Lights
Grow lights are known for their energy-efficient qualities, making them a popular choice among hydroponic growers. Unlike traditional light sources, such as incandescent bulbs, grow lights are designed to maximize energy savings while providing the necessary light spectrum for optimal plant growth. LEDs, in particular, stand out for their exceptional energy efficiency. According to a study published in the Journal of Cleaner Production, LED grow lights can reduce energy consumption by up to 50% compared to traditional lighting systems. This significant reduction in energy usage not only translates to cost savings but also minimizes the environmental impact associated with electricity consumption.
A key factor contributing to the energy efficiency of grow lights is their ability to emit light within specific wavelengths that plants can readily absorb. By tailoring the light spectrum to meet the needs of different plant stages, growers can avoid wasting energy on wavelengths that plants do not utilize effectively. This targeted lighting approach allows for efficient energy conversion, ensuring that an ample amount of light is delivered to the plants without unnecessary energy wastage. Additionally, the use of energy-efficient components, such as high-quality diodes and advanced power management systems, further enhances the overall energy efficiency of modern grow lights. This combination of optimized light spectrum and sophisticated technology makes grow lights a sustainable and cost-effective option for hydroponic systems.
• LED grow lights can reduce energy consumption by up to 50% compared to traditional lighting systems.
• Tailoring the light spectrum to meet the needs of different plant stages avoids wasting energy on unused wavelengths.
• Energy-efficient components, such as high-quality diodes and advanced power management systems, enhance overall efficiency.
• The targeted lighting approach ensures ample light delivery without unnecessary energy wastage.
• Grow lights are a sustainable and cost-effective option for hydroponic systems.
Cost Comparison: Grow Lights vs. Sunlight
In hydroponic systems, the cost comparison between using grow lights and relying on natural sunlight is an important consideration for many gardeners. While sunlight is a free and readily available resource, the use of grow lights does incur additional expenses. However, it is crucial to evaluate the long-term benefits and potential drawbacks to make an informed decision.
When comparing costs, it is essential to consider the initial investment of purchasing the necessary grow lights. High-quality grow lights can range from a few hundred to thousands of dollars, depending on the type and specifications. On the other hand, sunlight is a completely free resource; harnessing it requires minimal equipment, such as reflective materials or shades for optimizing light exposure.
Additionally, the ongoing operational expenses should be taken into account. Grow lights consume electricity, which directly impacts your electricity bill. The energy consumption varies depending on the type of grow light, wattage, and duration of use. On the contrary, sunlight doesn’t incur additional electricity costs. Nevertheless, it is worth noting that relying solely on sunlight may require adjusting the location or orientation of your hydroponic system to ensure optimal exposure throughout the day.

When considering the cost comparison between grow lights and sunlight, you must also evaluate the potential yields and productivity of your hydroponic system. Grow lights offer the advantage of providing a consistent light source, allowing for year-round cultivation and maximizing plant growth rates. Sunlight, on the other hand, is subject to seasonal variations and weather conditions, affecting the overall productivity.
Ultimately, the cost-effectiveness of grow lights versus sunlight depends on various factors such as your location, available natural light, specific plant requirements, project scale, and budget. Careful consideration and assessment of these factors will help you determine the most financially viable option for your hydroponic endeavors.
• The initial investment for purchasing grow lights can range from a few hundred to thousands of dollars, depending on the type and specifications.
• Sunlight is a completely free resource and requires minimal equipment, such as reflective materials or shades, to optimize light exposure.
• Grow lights consume electricity, resulting in additional ongoing operational expenses. Energy consumption varies based on the type of grow light, wattage, and duration of use.
• Relying solely on sunlight doesn’t incur additional electricity costs but may require adjusting the location or orientation of your hydroponic system for optimal exposure throughout the day.
• Grow lights provide a consistent light source, allowing for year-round cultivation and maximizing plant growth rates.
• Sunlight is subject to seasonal variations and weather conditions that can affect overall productivity.
• Factors such as location, available natural light, specific plant requirements, project scale, and budget should be carefully considered when determining cost-effectiveness between grow lights versus sunlight in hydroponic systems.
Heat Production and Ventilation
Heat production and ventilation are crucial factors to consider in hydroponic systems. As grow lights emit light, they also generate heat, which can affect the overall temperature of the growing environment. Maintaining proper ventilation is essential to mitigate the potential negative impact of excess heat.
Excessive heat can lead to various issues in hydroponics, including stunted growth, nutrient deficiencies, and even plant stress or death. Adequate ventilation helps dissipate heat and regulate the temperature, ensuring the optimal growing conditions for plants. It also helps to control humidity levels, preventing the development of mold or fungal diseases.
To manage heat production and ventilation effectively, hydroponic growers should consider the heat output of different types of grow lights. LED lights, for example, produce significantly less heat compared to high-intensity discharge (HID) lights. By selecting LED lights or using efficient cooling systems, growers can maintain a stable and desirable temperature range within their hydroponic systems. Remember, optimal ventilation is essential to achieve successful and healthy plant growth in hydroponics.
• Proper ventilation helps dissipate excess heat in hydroponic systems
• Excessive heat can lead to stunted growth, nutrient deficiencies, and plant stress or death
• Adequate ventilation regulates temperature and humidity levels for optimal plant growth
• LED lights produce less heat compared to high-intensity discharge (HID) lights
• Efficient cooling systems or selecting LED lights can help maintain a stable temperature range
Flexibility and Control with Grow Lights
Grow lights offer gardening enthusiasts unparalleled flexibility and control in their hydroponic systems. With the ability to adjust the spectrum, intensity, and duration of light, growers can cater to the specific needs of their plants at every stage of growth. This level of customization is particularly advantageous for those cultivating a wide variety of crops with varying light requirements.
In addition to adjusting the light parameters, growers can also manipulate the positioning and coverage of the grow lights. This allows for efficient use of space and the ability to target specific areas or plants that may require more or less light. Furthermore, the use of timers and automated systems enables growers to create precise lighting schedules, mimicking natural sunlight and optimizing plant growth. Whether it’s extending the photoperiod for vegetative growth or providing supplemental lighting during cloudy days, the flexibility provided by grow lights ensures that plants receive the ideal lighting conditions for their development.

By harnessing the power of technology, growers can achieve remarkable control over their hydroponic systems. This level of precision allows for year-round cultivation, increased crop yields, and accelerated growth rates. No longer limited by sunlight availability or weather conditions, gardeners can create optimal environments for their plants, leading to healthier and more productive harvests. With the ability to fine-tune every aspect of the lighting setup, grow lights have truly revolutionized the way we approach and practice hydroponic gardening.
• Adjusting the spectrum, intensity, and duration of light allows growers to meet the specific needs of their plants at every growth stage.
• Customization is particularly beneficial for cultivating a wide variety of crops with varying light requirements.
• Manipulating the positioning and coverage of grow lights enables efficient use of space and targeted lighting for different areas or plants.
• Timers and automated systems allow for precise lighting schedules that mimic natural sunlight, optimizing plant growth.
• Flexibility provided by grow lights ensures that plants receive ideal lighting conditions throughout their development.
• Technology-driven control over hydroponic systems enables year-round cultivation, increased crop yields, and accelerated growth rates.
• Growers are no longer limited by sunlight availability or weather conditions, leading to healthier and more productive harvests.
Potential Limitations of Sunlight for Hydroponics
Sunlight is undoubtedly a crucial factor in the growth and development of plants. However, when it comes to hydroponic systems, there are potential limitations to relying solely on sunlight. One of the main challenges is the inconsistency of natural sunlight. As the angle and intensity of sunlight changes throughout the day and with different weather conditions, it can be difficult to ensure a consistent and optimal light environment for hydroponic crops.
Moreover, indoor hydroponic systems may face limitations due to lack of access to direct sunlight. For those growing plants in basements or other enclosed spaces, the availability of sunlight may be limited or nonexistent. In such cases, relying solely on sunlight may result in stunted growth and reduced yields. To overcome these limitations, artificial grow lights can be used to provide a consistent and customizable light spectrum and intensity that meet the specific needs of the plants.
• Inconsistent and changing angle/intensity of natural sunlight throughout the day and with different weather conditions
• Difficulty in ensuring a consistent and optimal light environment for hydroponic crops
• Lack of access to direct sunlight in indoor hydroponic systems, especially in basements or enclosed spaces
• Limited or nonexistent availability of sunlight can result in stunted growth and reduced yields
• Artificial grow lights can be used to provide a consistent and customizable light spectrum and intensity that meet the specific needs of plants.
Environmental Considerations
When considering environmental factors in hydroponic systems, it is important to recognize the potential impact of grow lights on energy consumption. Traditional grow lights, such as high-intensity discharge (HID) lamps, can be energy-intensive and may contribute to higher electricity bills. However, advancements in technology have led to the development of more energy-efficient options, such as LED grow lights. LED lights not only consume less energy but also have a longer lifespan, reducing the environmental footprint of hydroponic systems.
Another aspect to consider is the heat production associated with grow lights. While natural sunlight does not generate heat within a controlled environment, artificial lights can emit a considerable amount of heat. This heat can affect the temperature and humidity levels of the growing area, potentially impacting plant health and productivity. To mitigate these effects, proper ventilation and cooling systems should be in place, ensuring optimal growing conditions and minimizing energy wastage.

In summary, when considering environmental aspects of hydroponic systems, it is crucial to consider energy consumption and heat production associated with grow lights. Opting for energy-efficient LED lights and implementing appropriate cooling measures can help reduce the environmental impact while maintaining optimal growing conditions.
• LED grow lights consume less energy and have a longer lifespan compared to traditional grow lights like HID lamps.
• Energy-efficient LED lights can help reduce electricity bills and minimize the environmental footprint of hydroponic systems.
• Artificial grow lights generate heat, which can affect temperature and humidity levels in the growing area.
• Proper ventilation and cooling systems should be implemented to maintain optimal growing conditions and minimize energy wastage.
• Considering energy consumption and heat production is crucial for reducing the environmental impact of hydroponic systems.
Choosing the Right Grow Light for Your Hydroponic System
When choosing the right grow light for your hydroponic system, there are several factors to consider in order to maximize plant growth and yield. One important factor to consider is the type of grow light technology. LED grow lights have gained popularity in recent years due to their energy efficiency and long lifespan. They are also versatile and can be used for different growth stages of plants by adjusting the light spectrum. On the other hand, fluorescent grow lights are more affordable and emit less heat, making them suitable for smaller indoor gardens. High-intensity discharge (HID) grow lights, such as metal halide and high-pressure sodium lights, are known for their high light intensity and are ideal for larger commercial operations.
Another factor to consider is the light output or intensity of the grow light. Different plants have varying light requirements, and it’s important to match the light intensity to the needs of your specific crops. Light intensity is typically measured in foot-candles or lux, and different growth stages may require different light levels. For example, seedlings and young plants require lower light levels compared to mature plants in the flowering stage. Understanding the light requirements of your plants will help you determine the appropriate light intensity for your hydroponic system.
By carefully considering the type of grow light technology and the light intensity, you can choose a grow light that meets the specific needs of your hydroponic system. Next, we will explore other important factors to consider, such as the duration of light, energy efficiency, and cost comparison between grow lights and natural sunlight. Making informed decisions about these factors will help you create an optimal growing environment for your hydroponic plants, leading to healthier and more productive harvests.
• LED grow lights are energy efficient and have a long lifespan
• Fluorescent grow lights are more affordable and emit less heat
• HID grow lights, such as metal halide and high-pressure sodium lights, have high light intensity and are ideal for larger operations
• Different plants have varying light requirements, so it’s important to match the light intensity to your specific crops
• Light intensity is typically measured in foot-candles or lux
• Seedlings and young plants require lower light levels compared to mature plants in the flowering stage
The table shows the factors need to be considered while choosing lights:
| Consideration | Key Factors to Consider |
|---|---|
| Light Type | Choose LED, Fluorescent, or HID based on energy efficiency and plant requirements. |
| Spectrum | Select a spectrum suitable for your plants’ growth stages. |
| Intensity | Ensure adequate light intensity for your crops. |
| Energy Efficiency | Opt for energy-efficient options like LED for cost savings. |
| Coverage Area | Choose lights that cover your entire growing area evenly. |
| Versatility | Select lights versatile enough for different growth stages or crops. |
\
LED Grow Lights: Advantages and Disadvantages
LED grow lights have become increasingly popular among hydroponic enthusiasts for several reasons. One advantage of LED lights is their energy efficiency. LED grow lights consume less energy compared to other types of grow lights, helping to reduce electricity costs and minimize the environmental impact. Additionally, LED lights have a longer lifespan, reducing the need for frequent replacements and further contributing to cost savings.
Another advantage of LED grow lights is their ability to emit specific wavelengths of light that are optimized for plant growth. Unlike traditional grow lights, such as fluorescent or HID lights, LED lights can be customized to emit the precise spectrum of light that plants need at different stages of growth. This targeted light spectrum promotes photosynthesis and enhances plant development. LED grow lights also produce less heat, reducing the risk of burning the plants and allowing for closer placement to achieve maximum light intensity.
• LED grow lights are energy efficient and consume less electricity compared to other types of grow lights.
• This helps in reducing electricity costs and minimizing the environmental impact.
• LED lights have a longer lifespan, reducing the need for frequent replacements and contributing to cost savings.
• They emit specific wavelengths of light that are optimized for plant growth.
• Unlike traditional grow lights, LED lights can be customized to emit the precise spectrum of light needed at different stages of growth.
• This targeted light spectrum promotes photosynthesis and enhances plant development.
• LED grow lights produce less heat, reducing the risk of burning plants and allowing for closer placement to achieve maximum light intensity.
Fluorescent Grow Lights: Pros and Cons
Fluorescent grow lights have long been popular among indoor gardeners and hydroponics enthusiasts due to their many advantages. One of the key benefits of fluorescent lights is their energy efficiency. Compared to other types of grow lights, such as High-Intensity Discharge (HID) lights, fluorescent lights consume less electricity and produce less heat. This not only helps to lower energy costs but also reduces the need for additional ventilation and cooling systems.
Another advantage of fluorescent grow lights is their versatility. These lights come in different sizes and shapes, making them suitable for a variety of growing spaces. Whether you have a small indoor garden or a larger hydroponic system, there is a fluorescent light option to fit your needs. Additionally, fluorescent lights emit a wide spectrum of light, including blue and red wavelengths that are essential for plant growth. This makes them suitable for both vegetative growth and flowering stages of plants, providing gardeners with flexibility and control over their growing cycles.
However, despite their many benefits, fluorescent grow lights also have a few limitations. One of the main drawbacks is their lower light intensity compared to other types of grow lights, such as HID or LED lights. This means that fluorescent lights may not be suitable for plants that require high light intensity or for larger growing spaces where you need to cover a larger area. Additionally, fluorescent lights tend to have a shorter lifespan compared to other types of lights, which may require more frequent replacements and maintenance. Nonetheless, with proper planning and consideration of these factors, fluorescent grow lights can still be an effective and affordable option for indoor gardening and hydroponic systems.
• Fluorescent grow lights are energy-efficient, consuming less electricity and producing less heat compared to other types of grow lights.
• Their energy efficiency helps lower energy costs and reduces the need for additional ventilation and cooling systems.
• Fluorescent grow lights come in different sizes and shapes, making them versatile and suitable for various growing spaces.
• They emit a wide spectrum of light, including essential blue and red wavelengths for plant growth, making them suitable for both vegetative growth and flowering stages.
• However, fluorescent grow lights have lower light intensity compared to HID or LED lights, which may not be suitable for plants that require high light intensity or larger growing spaces.
• They also have a shorter lifespan compared to other types of lights, requiring more frequent replacements and maintenance.
• Despite these limitations, with proper planning and consideration of factors like light intensity requirements and space size, fluorescent grow lights can still be an effective and affordable option for indoor gardening.
Here is a table that shows the pros and cons of fluorescent grow light:
| Aspect | Fluorescent Grow Lights |
|---|---|
| Pros | |
| Energy Efficiency | Relatively energy-efficient compared to some other options. |
| Cost | Initial setup cost is generally lower than some alternatives. |
| Spectrum Options | Provides a good spectrum of light for plant growth. |
| Cool Temperature | Emit less heat compared to high-intensity discharge lights. |
| Versatility | Suitable for various growth stages of plants. |
| Availability | Widely available and easy to find in stores. |
| Cons | |
| Limited Intensity | Generally lower light intensity compared to some alternatives. |
| Lifespan | Shorter lifespan compared to some other types of lights. |
| Size | Bulky and may require more space for installation. |
| Limited Coverage | May not cover a large area, leading to the need for multiple lights. |
| Environmental Impact | Contains small amounts of mercury, which can be harmful if not handled properly. |
| Spectrum Limitation | Limited spectrum options compared to some advanced LED lights. |
High-Intensity Discharge (HID) Grow Lights: Pros and Cons
High-Intensity Discharge (HID) grow lights have become increasingly popular in hydroponic systems due to their numerous advantages. One of the primary benefits of HID grow lights is their high light output. HID lights, especially metal halide (MH) and high-pressure sodium (HPS) bulbs, emit intense light that closely resembles natural sunlight. This high intensity promotes vigorous plant growth and ensures optimal photosynthesis.
Another advantage of HID grow lights is their versatility. These lights can be used throughout the entire growth cycle of plants, from seedling to flowering. By using MH bulbs during the vegetative phase and switching to HPS bulbs during the flowering phase, growers can provide plants with the specific light spectrum they need at each stage of growth. This flexibility allows for better control and customization of the lighting conditions, leading to improved plant development and higher yields.

Here is a table showing the pros and cons of grow lights:
| Aspect | Pros | Cons |
|---|---|---|
| Light Output | High light intensity, suitable for various plant stages. | Generates a significant amount of heat, requiring additional ventilation and cooling systems. |
| Spectrum Range | Provides a broad spectrum of light, suitable for plant growth. | Spectrum may not be as customizable as some other modern lighting technologies. |
| Coverage Area | Covers a large area, making them suitable for spacious grow spaces. | Size and bulkiness may limit placement options in smaller or vertically limited environments. |
| Cost | Initial equipment cost is relatively lower compared to some newer technologies. | Operating costs, including electricity and potential cooling, can be higher over the long term. |
| Lifespan | Generally, a longer lifespan compared to some other lighting options. | Over time, light intensity can decrease, and bulbs may need replacement. |
| Versatility | Suitable for various plant types and growth stages. | Bulbs can be specific to either the vegetative or flowering phase, requiring bulb changes during the growth cycle. |
| Availability | HID systems and replacement parts are widely available. | May become less popular as newer, more energy-efficient technologies emerge. |
| Penetration | Penetrates the canopy well, reaching lower leaves and branches. | Requires careful positioning to avoid excessive heat stress on plants. |
However, it’s important to consider some of the drawbacks associated with HID grow lights. One notable downside is their high energy consumption. HID bulbs tend to be less energy-efficient compared to other types of grow lights, such as LED or fluorescent lights. As a result, they can significantly increase electricity costs for indoor gardening setups. Additionally, HID lights produce a considerable amount of heat, which can lead to increased temperature levels in the growing area. Proper ventilation and cooling systems must be implemented to prevent heat stress and maintain an optimal growing environment.
While HID grow lights offer impressive performance, it is essential for growers to carefully evaluate their energy requirements and consider the potential impact of heat production in order to make an informed decision about incorporating HID lights into their hydroponic systems.
• HID grow lights have high light output, promoting vigorous plant growth and optimal photosynthesis.
• HID grow lights are versatile and can be used throughout the entire growth cycle of plants.
• MH bulbs provide the specific light spectrum needed during the vegetative phase, while HPS bulbs are ideal for flowering.
• This flexibility allows for better control and customization of lighting conditions, leading to improved plant development and higher yields.
• However, HID grow lights have high energy consumption compared to other types of grow lights.
• This can significantly increase electricity costs for indoor gardening setups.
• HID lights also produce a considerable amount of heat, which can lead to increased temperature levels in the growing area.
• Proper ventilation and cooling systems must be implemented to prevent heat stress and maintain an optimal growing environment.
Combining Natural and Artificial Light Sources
Combining natural and artificial light sources in a hydroponic system can offer numerous benefits for plant growth and productivity. By integrating both sources, gardeners can provide a more balanced and consistent light spectrum, ensuring that plants receive adequate light for photosynthesis throughout the day.
Natural sunlight is a valuable resource for plant growth, as it provides a full spectrum of light that is essential for optimal photosynthesis. However, sunlight is subject to seasonal variations, cloudy days, and shorter daylight hours, which can limit its availability and consistency. By incorporating artificial grow lights, gardeners can overcome these limitations and provide a more stable light environment for their plants.
Furthermore, combining natural and artificial light sources allows for greater flexibility and control over lighting conditions. Gardeners can supplement natural sunlight with artificial lighting during periods of low light, such as early mornings or late afternoons. This ensures that plants receive sufficient light even in challenging environmental conditions. Additionally, artificial lighting can be adjusted in terms of intensity, duration, and spectrum to meet specific plant requirements at different stages of growth, maximizing their potential for development.
Overall, the combination of natural and artificial light sources can enhance productivity, improve plant quality, and provide more consistent and controllable lighting conditions for hydroponic systems. Gardeners have the opportunity to optimize their cultivation practices by harnessing the benefits of both sources, allowing for a more efficient and effective growth environment.
• By integrating both natural and artificial light sources, gardeners can provide a more balanced and consistent light spectrum for optimal plant growth.
• Natural sunlight is valuable but subject to seasonal variations and limited availability, making artificial grow lights necessary for a stable light environment.
• Combining natural and artificial lighting allows for greater flexibility and control over lighting conditions, supplementing low light periods with artificial lighting.
• Artificial lighting can be adjusted in terms of intensity, duration, and spectrum to meet specific plant requirements at different stages of growth.
• The combination of natural and artificial light sources enhances productivity, improves plant quality, and provides more consistent and controllable lighting conditions.
Watch the video to know more about the difference between grow light and sunlight in hydroponics.
Best Practices for Using Grow Lights in Hydroponics.
When it comes to using grow lights in hydroponics, there are several best practices that can help ensure optimal plant growth and yield. One important practice is to provide the correct light intensity for each stage of plant development. Different plants have different light requirements, and it is crucial to adjust the intensity of the grow lights accordingly. This can be done by adjusting the distance between the light source and the plants or by using dimmable grow lights that allow for easy intensity control. It’s also important to regularly monitor the light intensity and make adjustments as needed to avoid overexposure or underexposure.
In addition to intensity, the duration of light exposure is another key factor to consider. Most plants require a specific amount of light exposure each day to complete their photosynthesis process and promote healthy growth. It is recommended to provide plants with a consistent light schedule that mimics natural sunlight. This can typically range from 12 to 16 hours of light per day, depending on the plant species. Monitoring and maintaining a consistent light duration is crucial for promoting healthy growth and preventing any negative effects on the plants’ metabolic processes.
• Provide the correct light intensity for each stage of plant development
• Adjust the distance between the light source and plants or use dimmable grow lights for easy intensity control
• Regularly monitor and adjust light intensity to avoid overexposure or underexposure
• Consider the duration of light exposure for optimal plant growth
• Most plants require a specific amount of light exposure each day for photosynthesis and healthy growth
• Mimic natural sunlight with a consistent light schedule ranging from 12 to 16 hours per day
• Monitor and maintain a consistent light duration to promote healthy growth and prevent negative effects on metabolic processes
What is the role of light in hydroponic systems?
Light is essential for photosynthesis, which is the process by which plants convert light energy into chemical energy to fuel their growth. In hydroponic systems, where plants are grown without soil, providing the right amount and quality of light is crucial for the plants’ overall health and productivity.
How do grow lights differ from natural sunlight?
Grow lights are artificial light sources specifically designed to provide the necessary light spectrum for plant growth. While natural sunlight contains a broad spectrum of light, grow lights can be customized to emit specific wavelengths that are most beneficial for plants. Additionally, grow lights can be controlled in terms of intensity and duration, allowing for precision in meeting the plants’ light requirements.
What is the spectrum of light and why is it important in hydroponics?
The spectrum of light refers to the range of wavelengths that light can have, including different colors. In hydroponics, plants require different wavelengths of light for various stages of growth. Blue light is crucial for vegetative growth, while red light is essential for flowering and fruiting. By providing the right spectrum of light, growers can optimize plant growth and yield.
How does the intensity of light affect hydroponic plants?
The intensity of light refers to the amount of light energy reaching the plants. It plays a vital role in determining the rate of photosynthesis and overall plant growth. Insufficient light intensity can lead to weak, leggy plants, while excessive light intensity can cause leaf burn or stunted growth. Finding the right balance is essential for optimal plant development.
Should grow lights be used for the entire duration of a day?
The duration of light, or photoperiod, varies depending on the plant species and growth stage. Some plants require longer periods of light during vegetative growth, while others need shorter periods during flowering. It’s important to understand the specific light requirements of your plants and adjust the duration accordingly to mimic their natural lighting conditions.
Are grow lights energy-efficient compared to sunlight?
Yes, grow lights are designed to be energy-efficient, especially when using technologies like LED lights. They convert a high percentage of electrical energy into usable light for plants, resulting in less wasted energy. Sunlight, on the other hand, is readily available and free, making it a more cost-effective option if the environmental conditions allow for it.
What are the potential limitations of relying solely on sunlight in hydroponics?
While natural sunlight is valuable, it has limitations in terms of consistency, quality, and availability. Relying solely on sunlight may not provide the necessary light spectrum, intensity, or duration for optimal plant growth. Moreover, in indoor hydroponic systems, sunlight may be limited or inconsistent due to factors like weather, shading, or geographical location.
What environmental considerations should be taken into account when using grow lights?
Grow lights produce heat, so proper ventilation and cooling systems are essential to maintain the ideal temperature for plant growth. Additionally, the energy consumption of grow lights should be considered, as well as the potential environmental impact of producing and disposing of the lights. Choosing energy-efficient and eco-friendly options can help minimize these concerns.
How do I choose the right grow light for my hydroponic system?
When choosing a grow light, factors such as the type of plants, growth stage, available space, budget, and energy efficiency should be considered. LED grow lights are popular for their energy efficiency and customizable spectrum, while fluorescent lights can be more affordable for smaller setups. High-intensity discharge (HID) lights offer high output but require more energy and cooling.
Can natural and artificial light sources be combined in hydroponics?
Yes, combining natural and artificial light sources can be beneficial in hydroponics. Natural sunlight can provide a broader spectrum of light and serve as a cost-effective supplement to artificial lighting. By using a combination, growers can harness the advantages of both sources and provide a more comprehensive light environment for their plants.