Growing Kale: How To Get Great Greens Harvests
Table of Contents
Understanding the Basics of Kale Cultivation
Kale, also known as Brassica oleracea, is a leafy green vegetable that has gained popularity for its numerous health benefits and versatile culinary uses. Understanding the basics of kale cultivation is essential for gardening enthusiasts who wish to grow this nutritious vegetable in their own gardens or farms.
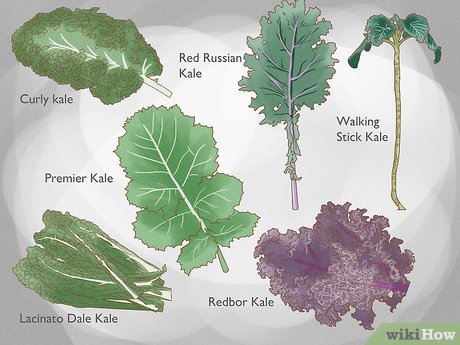
To start with, it is important to select the right kale varieties for optimal growth. There are several different types of kale, including curly kale, Red Russian kale, and Lacinato kale, each with its own unique characteristics and flavor profiles. By choosing the appropriate variety for your specific growing conditions and personal preferences, you can ensure successful cultivation.
In terms of soil preparation, kale plants thrive in well-draining soil that is rich in organic matter and nutrients. Before planting, it is recommended to amend the soil with compost or aged manure to improve its fertility and water-holding capacity. Conducting a soil test can also be beneficial to identify any nutrient deficiencies or pH imbalances that need to be addressed. By providing the right soil conditions, you can create an ideal environment for your kale plants to flourish.
Selecting the Right Kale Varieties for Optimal Growth
When it comes to selecting the right kale varieties for optimal growth, there are several factors to consider. One important aspect is the climate in which you will be growing your kale. Different varieties have different temperature and weather preferences, so it is crucial to choose varieties that are well-suited to your specific growing conditions. For example, if you live in a colder region, you may want to select kale varieties that are more cold tolerant.
Another factor to consider is your intended use for the kale. Are you planning to harvest it for its leaves or for its stems? Some varieties are better suited for leaf production, while others are bred for their ornamental stems. Additionally, different kale varieties have varying levels of flavor and texture. If you prefer a mild and tender kale, then you may want to choose a variety known for these characteristics. On the other hand, if you enjoy a more robust and sturdy kale, there are varieties available to suit your taste.
Ultimately, the key to selecting the right kale varieties for optimal growth is to do your research and experiment with different varieties to find the ones that best meet your needs and preferences. By considering factors such as climate suitability, intended use, and flavor/texture preferences, you can choose varieties that will thrive in your garden and provide you with a satisfying harvest. So take some time to explore the wide range of kale varieties available and start planting the ones that pique your interest. Happy gardening!
Essential Soil Preparation Techniques for Kale Planting
When it comes to growing healthy and vibrant kale plants, proper soil preparation is essential. The right soil conditions can provide the necessary nutrients and support for optimal growth and development. Before planting kale, it is important to ensure that the soil is well-drained and rich in organic matter. A loose and friable soil texture will allow for good root development and ensure efficient water and nutrient uptake by the plants.
To prepare the soil for kale planting, start by removing any weeds or debris from the planting area. Proper weed management is crucial to prevent competition for resources and reduce the risk of pest and disease infestations. Once the area is clear, it is recommended to perform a soil test to determine the pH levels and nutrient deficiencies, if any. This will help you tailor your soil amendment plan to the specific needs of your kale plants. Adjusting the soil pH to a slightly acidic range of 6.0-6.8 will promote nutrient availability and optimize plant growth.
After conducting a soil test, it’s time to amend the soil with organic matter. Adding well-rotted compost or aged manure will improve soil structure, enhance moisture retention, and increase the fertility of the soil. Work the organic matter into the top 6-8 inches of soil using a garden fork or a tiller, ensuring it is evenly distributed. Allow the amended soil to rest for a few days before planting kale. This will allow the organic matter to decompose further and release its beneficial nutrients, ensuring a nutrient-rich environment for the growing kale plants.
Taking the time to properly prepare the soil before planting kale will set the foundation for a successful and abundant harvest. By ensuring good drainage, amending the soil with organic matter, and providing the ideal pH levels, you will create a nutrient-rich environment that will support the growth and development of your kale plants. Stay tuned for our next article, where we will delve into the topic of providing adequate sunlight and temperature for successful kale growth.
• Proper soil preparation is essential for growing healthy and vibrant kale plants
• Well-drained and rich soil conditions provide necessary nutrients and support for optimal growth
• Clear the planting area of weeds and debris to prevent competition for resources
• Perform a soil test to determine pH levels and nutrient deficiencies
• Adjust the soil pH to a slightly acidic range of 6.0-6.8 for optimal plant growth
• Amend the soil with well-rotted compost or aged manure to improve structure, moisture retention, and fertility
• Work the organic matter into the top 6-8 inches of soil using a garden fork or tiller
• Allow amended soil to rest before planting to release beneficial nutrients
• Properly preparing the soil sets the foundation for a successful harvest
Here’s a table summarizing the essential soil preparation techniques for successful kale planting:
| Technique | Description |
|---|---|
| Soil Type | Kale can be grown in all types of free-draining soil. Ensure the soil is well-draining, open, and friable. |
| Organic Matter | Incorporate well-rotted manure and compost into the soil. These organic materials enrich the soil with nutrients and improve its structure. Consider using Seasol Liquid Compost as a no-dig option. |
| Soil pH | Aim for a soil pH level between 6.0 and 7.0. Kale prefers slightly acidic soil (around 5.5 to 6.8), but it generally tolerates slightly alkaline soil as well. If needed, add a handful of lime per square meter to adjust the pH. |
| Temperature | Kale thrives in soil with a temperature range of 60-65°F (15-18°C) during planting. Once established, it can withstand even lower temperatures. |
| Preventing Clubroot Disease | Maintaining the ideal pH range helps prevent clubroot disease, which can affect kale plants. |
Remember to follow these guidelines to create optimal conditions for your kale plants.
Providing Adequate Sunlight and Temperature for Successful Kale Growth
To ensure the successful growth of kale, it is crucial to provide the plant with the appropriate amount of sunlight and maintain optimal temperature conditions. Kale is a cool-season crop that thrives in full sun, receiving at least 6-8 hours of direct sunlight per day. Adequate sunlight is essential for photosynthesis, the process through which plants convert light energy into energy-rich sugars, enabling them to grow and develop properly.
In terms of temperature, kale performs best in cooler climates. Ideally, temperatures between 60°F and 70°F (15°C – 21°C) are recommended for optimal growth. While kale can withstand temperatures as low as 20°F (-6°C), it may suffer from stunted growth and reduced quality if exposed to prolonged periods of extreme cold. On the other hand, prolonged exposure to high temperatures above 80°F (27°C) can cause wilting and increase the risk of bolting, where the plant prematurely produces flowers and goes to seed.
Maintaining a consistent temperature throughout the growing season is important to prevent stress and ensure a successful kale harvest. Providing a well-drained soil rich in organic matter can help regulate temperature, as it retains moisture and provides insulation. Additionally, utilizing shade cloth or row covers can assist in managing excessive heat and protecting the plants during hot summer days.
By understanding the importance of sunlight and temperature in kale cultivation, you can create an ideal environment for your plants to thrive. Remember to regularly monitor and adjust these factors to ensure the best possible growth and yield.

Proper Watering and Irrigation Practices for Kale Plants
Watering and irrigation practices play a crucial role in ensuring the healthy growth and development of kale plants. As moisture-loving cruciferous vegetables, kale plants require consistent and adequate watering to thrive. When it comes to watering kale, it’s essential to strike a balance between providing enough moisture and avoiding excessive watering that can lead to root rot or other water-related diseases.
To meet the water requirements of kale plants, it is recommended to keep the soil consistently moist but not waterlogged. As a general guideline, aim to provide around 1 to 1.5 inches of water per week, including rainfall. However, it’s important to adjust this amount based on factors such as weather conditions, soil drainage, and plant age.
To maintain optimal soil moisture levels, regular monitoring is essential. One effective approach is to use a moisture meter to measure the moisture content in the soil. This can help determine when irrigation is necessary and prevent both overwatering and underwatering. Remember that kale plants generally require more water during periods of intense sunlight or high temperatures, so it’s important to adjust watering accordingly.
Fertilizing Kale: A Guide to Nutrient Requirements
When it comes to fertilizing kale, understanding its nutrient requirements is key to achieving optimal growth and a bountiful harvest. Kale is known for its voracious appetite for nutrients, so providing the right balance of essential elements is crucial.
First and foremost, kale thrives in soil that is rich in organic matter. Incorporating compost or well-rotted manure into the soil prior to planting will ensure a steady supply of nutrients throughout the growing season. Additionally, a soil pH between 6.0 and 7.5 is ideal for kale cultivation.
To meet kale’s nutrient needs, it is important to provide a well-rounded fertilizer. A balanced fertilizer with equal ratios of nitrogen (N), phosphorus (P), and potassium (K) is a good starting point. However, it is important to note that kale has specific nutrient requirements at different growth stages. During the vegetative stage, higher nitrogen levels promote leafy growth, while phosphorus and potassium play a crucial role in the development of strong root systems and overall plant vigor. As kale transitions to the reproductive stage, a fertilizer blend with higher phosphorus content will aid in the formation and maturation of seeds or flowers. Regular soil testing can help determine the exact nutrient requirements specific to your soil and kale variety, allowing you to tailor your fertilizer applications accordingly.
Providing the right balance of nutrients is just one piece of the puzzle when it comes to fertilizing kale. It is equally important to consider factors such as soil moisture, temperature, and overall plant health. By adopting a holistic approach to fertilizing kale, gardeners can ensure that their plants receive the necessary nutrients for healthy growth and an abundant harvest.
Controlling Pests and Diseases in Kale Plantations
Controlling pests and diseases is an essential aspect of maintaining the health and productivity of kale plantations. Like any crop, kale is susceptible to a variety of pests and diseases that can cause significant damage if not properly managed. By implementing effective pest control strategies and disease prevention techniques, growers can safeguard their kale plants and ensure a successful harvest.
One common pest that can affect kale plantations is the cabbage worm, also known as the cabbage white butterfly larva. These voracious feeders can quickly decimate kale plants if left unchecked. To control cabbage worms, regular monitoring is essential. Handpicking these pests from the leaves and destroying them is a simple but effective method. Alternatively, organic insecticides such as Bacillus thuringiensis can be applied to target and eliminate cabbage worms. Additionally, planting companion plants like marigolds, which repel cabbage worms, can offer an added layer of protection to your kale plants.

Effective Weed Management Strategies for Kale Growth
Weed management is a critical aspect of kale cultivation that directly impacts the plant’s growth and overall yield. The presence of weeds not only competes for essential resources such as water, sunlight, and nutrients but can also harbor pests and diseases that pose a threat to kale’s health. Therefore, implementing effective weed management strategies is crucial for successful kale growth.
One of the primary strategies for weed management in kale plantations is mulching. Mulching involves covering the soil around the kale plants with organic materials such as straw, hay, or wood chips. This protective layer acts as a physical barrier, preventing weed seeds from germinating and growing. Moreover, mulch also helps retain soil moisture, regulate soil temperature, and improve overall soil fertility. Applying a layer of mulch to a thickness of about 2 to 4 inches around the base of kale plants can significantly reduce weed growth and lessen the need for manual weeding.
Another effective weed management technique for kale cultivation is the use of pre-emergent herbicides. Pre-emergent herbicides work by inhibiting weed seed germination, thereby preventing weed growth before it even begins. These herbicides should be applied to the soil before planting or immediately after planting kale seeds. It is crucial to read and follow the manufacturer’s instructions carefully when using herbicides to ensure proper application and dosage. Additionally, it’s important to select herbicides that are specifically labeled safe for use in kale cultivation to avoid any negative impact on the plants or surrounding environment.
Implementing these weed management strategies can significantly reduce weed growth and enhance the overall health and productivity of kale plants. By employing mulching and pre-emergent herbicides, gardening enthusiasts can stay on top of weed control, enabling their kale crops to thrive and yield a bountiful harvest. Stay tuned for more expert tips on maximizing your kale cultivation!
Transplanting Kale Seedlings: Tips for a Smooth Transition
Transplanting seedlings is an important step in the kale cultivation process, as it ensures a smooth transition from the nursery to the final growing location. When transplanting kale seedlings, there are a few key tips to keep in mind for optimal success.
Firstly, it is crucial to choose the right time for transplanting. Kale seedlings should be sufficiently developed with a strong root system before being moved to their new home. Typically, seedlings should have at least four to six true leaves and be around four to six inches tall. This ensures that they have a good chance of survival and can adapt well to their new environment.
Secondly, proper preparation of the soil is essential. Before transplanting, ensure that the planting area is well-drained and free from any weeds or debris. It is recommended to loosen the soil to create a conducive environment for the seedlings to establish their roots. Additionally, incorporating organic matter, such as compost or well-rotted manure, can provide essential nutrients and enhance soil fertility for healthy kale growth.
By following these tips, gardeners can promote a smooth transition for their kale seedlings during the transplanting process. As the delicate seedlings adapt to their new surroundings, they are better positioned to thrive and produce a bountiful harvest.
Pruning and Thinning Kale Plants for Maximum Yield
Pruning and thinning are important tasks in kale cultivation that can significantly impact the yield of your plants. By properly managing the growth of your kale plants, you can promote healthier foliage, improve air circulation, and enhance sunlight penetration, all of which contribute to maximum yield.
Pruning involves the selective removal of specific plant parts, such as damaged or diseased leaves, to maintain the overall health and vitality of the kale plants. Additionally, pruning can help manage the size and shape of the plants, preventing them from becoming too sprawling or overcrowded. Regularly inspect your kale plants for any signs of disease or pest infestation and promptly remove any affected leaves or stems to prevent further spread.
Thinning, on the other hand, involves the deliberate removal of excess plants or seedlings to provide adequate space for the remaining ones to thrive. Overcrowding can lead to competition for nutrients, water, and sunlight, resulting in stunted growth and reduced yields. When thinning kale plants, carefully choose the strongest and healthiest seedlings to retain, ensuring that they have sufficient spacing between them. Removing the weaker seedlings allows the remaining ones to receive optimal resources and grow to their full potential.
Harnessing the Power of Companion Planting with Kale
Companion planting is a valuable technique that can maximize the growth and productivity of your kale plants. By strategically selecting compatible plants to grow alongside your kale, you can enhance nutrient availability, deter pests, and improve overall plant health.
One popular companion plant for kale is the marigold. Marigolds release chemicals into the soil that repel harmful pests, such as nematodes and aphids, which can often plague kale plants. Additionally, marigolds attract beneficial insects like ladybugs and hoverflies, which feed on common kale pests. Planting marigolds in close proximity to your kale can create a natural pest management system that reduces the need for pesticides.
Another beneficial companion for kale is the legume family, which includes plants like beans and peas. Legumes have the unique ability to fix nitrogen in the soil, replenishing this essential nutrient that kale requires for healthy growth. By intercropping kale with legumes, you can create a symbiotic relationship where the legumes benefit from the shade and support provided by the kale, while the kale benefits from the nitrogen-rich soil. This dynamic pairing not only improves overall kale yield but also promotes soil fertility in the long term.
Overall, taking advantage of the power of companion planting can significantly enhance the growth and productivity of your kale plants. By carefully selecting companion plants that offer pest control, nutrient enrichment, or other benefits, you can create a harmonious garden ecosystem that fosters healthy and abundant kale harvests.
Harvesting Kale: Timing and Techniques for the Best Greens
As a gardening enthusiast, you know that harvesting kale at the right time is crucial for flavorful and nutritious greens. So, when is the best time to harvest your kale? The answer depends on the variety and your personal preference.
Most kale varieties can be harvested when the leaves are young and tender, usually around 50 to 60 days after planting. However, some gardeners prefer to wait until the leaves have matured a bit more for a stronger flavor. Keep in mind that kale is a cold-hardy crop, and its flavor actually improves after exposure to frost or cold temperatures.
To harvest kale, simply choose the outer leaves and cut them at the base, leaving the inner leaves to continue growing. This method, known as selective harvesting, allows the plant to continue producing new leaves, ensuring a prolonged harvesting period. If you prefer to harvest the entire plant at once, you can cut it at the base, just above the soil level. Remember to leave at least a few inches of the plant intact so it can regrow if desired.
Storing and Preserving Freshly Harvested Kale
Once you have harvested your kale, it is important to know how to properly store and preserve it to maintain its freshness and maximize its shelf life. Proper storage techniques will help to retain the flavor, texture, and nutritional value of this nutrient-packed green leafy vegetable.
The first step in storing kale is to remove any dirt or debris from the leaves. Gently wash the kale under running water, being careful not to bruise or damage the leaves. After washing, thoroughly dry the leaves with a clean cloth or paper towel to remove excess moisture. Moisture can lead to spoilage and cause the leaves to wilt or turn mushy. Once dry, place the kale in a clean, dry container or plastic bag and seal it tightly. This will help to prevent any excess moisture from entering the container and keep the kale fresh for a longer period.
Exploring Different Culinary Uses for Kale
Kale, with its robust and leafy greens, has become increasingly popular in recent years due to its versatility and nutritional value. While commonly used in salads and smoothies, kale can go far beyond these traditional uses. Its hearty texture and earthy flavor make it an excellent addition to a variety of culinary creations.
One unique way to incorporate kale into your meals is by making kale chips. Simply toss freshly washed and dried kale leaves with a drizzle of olive oil and sprinkle them with your favorite seasonings, such as sea salt, garlic powder, or nutritional yeast. Bake them in the oven until crispy, and you’ll have a delicious and guilt-free snack that satisfies those crunchy cravings.
For those looking to boost the nutritional value of their morning routine, kale can be a fantastic addition to your breakfast repertoire. Try sautéing kale with onions and garlic for a flavorful base to your omelets or frittatas. Alternatively, blend it into your morning smoothies for a vibrant and nutrient-packed start to your day. The possibilities are endless when it comes to exploring different culinary uses for kale.
Let’s explore the various culinary uses for kale, a versatile and nutritious leafy green:
| Culinary Use | Description |
|---|---|
| Kale Chips | Baked kale chips are a healthy and crunchy snack. Simply toss kale leaves with a drizzle of olive oil and a pinch of sea salt, then bake until crispy. A great alternative to processed potato chips! |
| Indian Snacks | Kale pairs well with Indian snacks. Try making Quinoa Kale Khakhra, a nutritious and flavorful flatbread made from quinoa and kale. Perfect for satisfying hunger pangs during office hours. |
| Salads | Mix kale with other veggies and greens to create refreshing salads. For instance, the Jowar Kale Palak Salad combines jowar, kale leaves, broccoli, mushrooms, and a zesty lemon dressing. |
| Juices | Kale is nutrient-dense and can be used in juices. Try the Palak, Kale, and Apple Juice, which balances flavors and provides iron, vitamin C, and fiber. A great choice for weight-watchers. |
| Cooking Greens | Use kale as a cooking green. It pairs well with fish, chicken, and other proteins. You can also add it to soups or stews for a nutritional boost. |
| Sandwich Wraps | Use large kale leaves as a healthy alternative to tortillas or bread. Wrap your favorite fillings inside for a nutritious meal. |
| Smoothies | Add kale to your morning smoothies for an extra dose of vitamins A, C, and K. It blends well with fruits like mango, banana, and apple. |
Remember to experiment and enjoy the versatility of kale in your culinary creations!
The Health Benefits of Consuming Kale Regularly
Kale, often referred to as the “king of greens,” has gained immense popularity in recent years due to its exceptional health benefits. Packed with essential vitamins, minerals, and antioxidants, consuming kale regularly can enhance your overall well-being.
One of the standout features of kale is its high nutrient content. This leafy green is loaded with vitamins A, C, and K, which play key roles in supporting immune function, collagen production, and bone health, respectively. Additionally, kale contains important minerals such as calcium and manganese, essential for maintaining strong bones and supporting various enzymatic reactions in the body.
Furthermore, kale is a powerhouse of antioxidants, including beta-carotene, lutein, and zeaxanthin. These compounds help protect our cells from the harmful effects of free radicals, which are known to contribute to chronic diseases such as heart disease and cancer. The abundance of antioxidants in kale also makes it a valuable addition to our diet for promoting healthy skin and providing anti-aging effects.
Incorporating kale into your meals not only boosts your nutrient intake but also offers other potential health benefits. Research suggests that consuming kale may help reduce inflammation in the body, lower blood pressure, and support digestive health. With its low calorie and high fiber content, kale is an excellent choice for those looking to manage weight or improve their digestion.
When it comes to harnessing the health benefits of kale, the key lies in incorporating it into a balanced and varied diet. Whether it’s adding kale to your salads, blending it into smoothies, or sautéeing it as a side dish, the versatility of this leafy green makes it easy to enjoy its nutritional advantages. Stay tuned to discover more about the numerous culinary uses of kale and how to make the most of this nutrient-rich vegetable.

Troubleshooting Common Kale Growing Issues
Kale cultivation is generally a straightforward process, but like any other plant, kale can be susceptible to various issues that may hinder its growth and overall health. Understanding common kale growing issues can help gardeners identify and address these problems promptly, ensuring a successful harvest.
One potential problem gardeners may encounter is poor soil quality. Kale thrives in well-draining soil with a pH level range of 6.0-7.5. If the soil is too compact or has a pH outside of this range, it can negatively impact the plant’s nutrient uptake and overall growth. Conducting a soil test and amending the soil accordingly can help resolve this issue. Adding organic matter such as compost or aged manure can improve soil structure and nutrient content, providing a healthy growing environment for kale. Additionally, ensuring proper drainage by incorporating sand or perlite into the soil can prevent waterlogged conditions, reducing the risk of root rot and fungal diseases.
Please do watch video!
Why are my kale leaves turning yellow?
Yellowing leaves in kale can be a sign of nutrient deficiencies, such as nitrogen or iron. Ensure that you are providing adequate fertilization and consider conducting a soil test to determine any deficiencies.
How can I prevent pests from damaging my kale plants?
To control pests in kale plantations, you can use organic methods such as introducing beneficial insects like ladybugs or using insecticidal soaps. Regularly inspect your plants for signs of pests and take appropriate measures to control them.
Can I grow kale in containers?
Yes, kale can be successfully grown in containers. Choose a large container with good drainage and provide sufficient sunlight and water. Container-grown kale may require more frequent watering and fertilizing compared to plants in the ground.
How often should I prune my kale plants?
Pruning kale plants is not necessary unless you want to harvest the outer leaves continuously. In that case, you can regularly remove the outer leaves, starting from the bottom, to encourage new growth.
Can I freeze kale for later use?
Yes, kale can be frozen for later use. Blanch the kale leaves in boiling water for a couple of minutes, then plunge them into an ice bath. Drain the excess water, pack the leaves in airtight containers or freezer bags, and store them in the freezer for up to six months.
What are some common diseases that affect kale plants?
Common diseases that can affect kale plants include black rot, downy mildew, and powdery mildew. Proper sanitation, crop rotation, and selecting disease-resistant kale varieties can help in preventing these diseases.
How do I know when it is time to harvest my kale?
Kale leaves can be harvested when they reach a desired size, usually when they are about 8 to 10 inches long. However, young and tender leaves can be harvested earlier. Harvest from the bottom, leaving a few leaves on the plant for continued growth.
Can I grow kale alongside other vegetables?
Yes, kale can be grown alongside other vegetables using companion planting. It has been found to benefit from being planted near cabbage, carrots, onions, and herbs like dill and chamomile, while being planted away from tomatoes and strawberries.
What causes small and deformed kale leaves?
Small and deformed kale leaves can be caused by aphid infestations, nutrient deficiencies, or irregular watering. Adequate pest control, proper fertilization, and consistent watering can help prevent this issue.
How long does it take for kale seeds to germinate?
Kale seeds typically take around 7 to 14 days to germinate. The germination process can be accelerated by providing optimal temperature and moisture conditions.

Nicole Burke is a dynamic writer at SouthElMonteHydroponics, fueled by her passion for horticulture and environmental sustainability. Armed with a degree in Environmental Science from a renowned institution, Nicole’s expertise lies in hydroponic gardening, organic farming, and biodiversity conservation. Her insatiable curiosity and love for nature drive her to explore innovative techniques in hydroponics, seeking to revolutionize the way we grow crops in urban environments. Nicole’s writing reflects her deep commitment to promoting eco-conscious practices and fostering a deeper connection between humans and the natural world. Through her engaging storytelling, she inspires others to embrace sustainable living and harness the power of hydroponics for a greener future.






