The Science Behind Hydroponic Potatoes: How They Grow Faster and Bigger than Soil-Grown Potatoes
Table of Contents
The Benefits of Hydroponic Potatoes Cultivation
Hydroponic potato cultivation offers numerous benefits that make it an attractive option for gardening enthusiasts. One key advantage is the ability to grow potatoes in a controlled environment, free from the constraints of soil quality and seasonal variations. By providing essential nutrients directly to the roots through a nutrient solution, hydroponics ensures optimal growth and development of potatoes.

Another benefit of hydroponic potato cultivation is its efficiency in water usage. Compared to traditional soil-based cultivation, hydroponics requires significantly less water, making it a sustainable choice for potato growers. The carefully regulated system of water delivery in hydroponics ensures that plants receive the exact amount they need, eliminating waste and reducing water consumption.
Moreover, hydroponics allows for the efficient utilization of space. By eliminating the reliance on soil, hydroponic setups can be designed to maximize vertical or horizontal growing space, enabling gardeners to cultivate more potatoes in a smaller area. This compactness is particularly advantageous for urban gardeners or those with limited space.
The controlled environments established in hydroponic systems also play a crucial role in boosting potato growth. By providing optimal lighting conditions and controlling factors like temperature and humidity, hydroponics creates an ideal environment for potato plants to flourish. This leads to faster growth rates, higher yields, and better-quality potatoes.
In addition, hydroponic potato cultivation offers the advantage of precise control over nutrient availability. With the nutrient solution, gardeners can tailor the nutrient composition to meet the exact needs of potato plants at each stage of growth. This ensures optimal nutrient absorption, promoting healthier plants and higher crop yields.
Overall, the benefits of hydroponic potato cultivation make it an attractive method for growing potatoes. From increased control over growing conditions to efficient water usage and nutrient management, hydroponics presents a viable solution for gardening enthusiasts seeking to enhance their potato cultivation practices.
The Role of Nutrient Solution in Hydroponic Potatoes Growth
Hydroponic potato cultivation is a fascinating and innovative approach to growing potatoes. One crucial aspect of this method is the use of a nutrient solution, which plays a vital role in supporting the growth and development of the potato plants. Unlike traditional soil-based cultivation, where plants obtain nutrients from the soil, hydroponics relies on a carefully balanced nutrient solution to provide essential elements for plant growth.
The nutrient solution used in hydroponic potato cultivation contains a mixture of various minerals and macronutrients that are essential for the plants’ well-being. These nutrients include nitrogen, phosphorus, potassium, calcium, magnesium, and trace elements like iron, manganese, copper, zinc, and boron. By providing these nutrients directly to the plants in a controlled manner, hydroponics ensures that they have access to a consistent and optimal supply throughout their growth cycle.
Moreover, the nutrient solution in hydroponic potato cultivation can be tailored to suit the specific needs of the plants at different growth stages. For example, during the initial stages of growth, the solution may contain a higher concentration of nitrogen to promote leaf development. As the plants transition to the reproductive phase, the nutrient solution can be adjusted to increase the potassium and phosphorus levels, which are crucial for tuber formation and overall yield.
In conclusion, the nutrient solution plays a fundamental role in hydroponic potato cultivation by providing a readily available and perfectly balanced source of essential nutrients for the plants. This method not only allows for precise control over nutrient intake but also minimizes the risk of nutrient deficiencies or imbalances that can hinder plant growth. With the right combination of macronutrients and trace elements in the nutrient solution, hydroponic potato growers can maximize their crop yield and produce high-quality potatoes.
Understanding the Efficiency of Water Usage in Hydroponic Potatoes Cultivation
Water usage efficiency is a crucial aspect to consider in hydroponic potato cultivation. As we strive to maximize yields while minimizing resource consumption, understanding how efficiently water is utilized becomes paramount. Hydroponic systems offer a promising solution to this challenge, as they have the potential to significantly reduce water consumption compared to traditional soil-based cultivation methods.
One of the key reasons for this increased efficiency is that hydroponic systems enable precise control over the water supply. By delivering water directly to the plant roots in a closed system, we can minimize wastage through evaporation or runoff. Additionally, hydroponic systems can recirculate and reuse water, minimizing overall consumption and optimizing resource utilization. This approach stands in stark contrast to traditional soil-based cultivation, where water can easily be lost to evaporation or leaching through the soil, resulting in higher water demands.
By utilizing hydroponic systems, we can achieve a more sustainable and efficient use of water resources, reducing both our environmental impact and the strain on water supplies. However, it’s important to note that the specific water usage efficiency of a hydroponic potato cultivation system can vary depending on various factors, such as the type of hydroponic system used, the climate conditions, and the crop’s growth stage. Further research and optimization are needed to explore how we can continue to improve water usage efficiency in hydroponic potato cultivation and make this method even more environmentally friendly and economically viable.
The Impact of Controlled Environments on Hydroponic Potatoes Growth
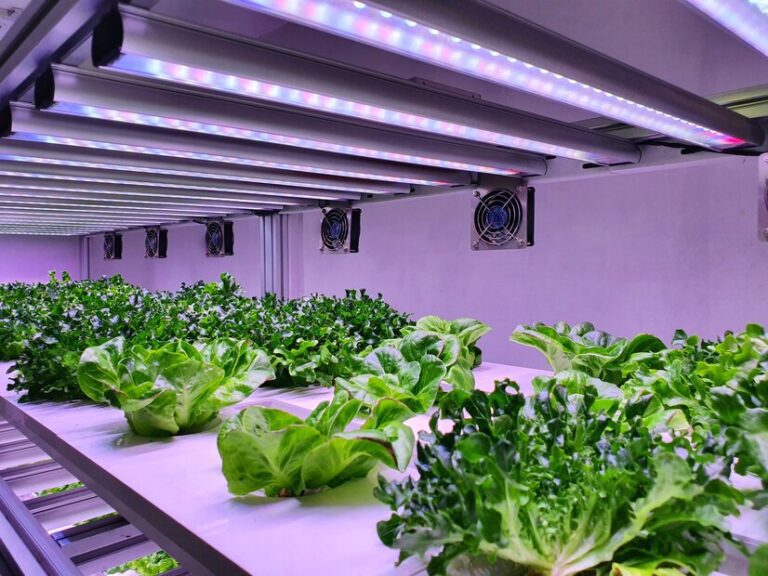
A controlled environment plays a crucial role in the growth and development of hydroponic potatoes. By carefully managing various factors such as temperature, humidity, and air quality, growers can create optimal conditions for the plants to thrive. One of the primary benefits of a controlled environment is the ability to extend the growing season, allowing for year-round cultivation irrespective of external climate conditions. This not only leads to higher yields but also provides a consistent and reliable supply of potatoes regardless of the time of year. Moreover, by controlling the environment, growers can minimize the risk of pests and diseases, reducing the need for chemical interventions and promoting healthier potato plants.

In addition to extending the growing season and mitigating pest-related challenges, a controlled environment also allows for precise control over key factors that influence potato growth. For instance, the availability and intensity of light can be regulated to ensure optimal photosynthesis and tuber formation. By adjusting the duration of light exposure and the wavelengths used, growers can manipulate the plant’s physiological responses and enhance tuber development. Similarly, by managing oxygen levels within the growing system, growers can ensure that the roots receive adequate oxygenation, promoting healthy root growth and nutrient uptake. These control mechanisms, combined with careful monitoring and adjustment of water and nutrient levels, create an environment that maximizes the potential for robust potato growth and high-quality yields.
Exploring the Role of Light in Hydroponic Potatoes Cultivation
Light is a crucial factor in the growth and development of hydroponic potatoes. In hydroponic systems, where plants are cultivated without soil, the role of light becomes even more significant. Light is essential for photosynthesis, the process by which plants convert light energy into chemical energy to fuel growth. In the case of hydroponic potatoes, light plays a vital role in promoting the production of carbohydrates, which are necessary for tuber formation. Adequate light levels are a key requirement for healthy growth, as insufficient light can lead to stunted growth, reduced yields, and poor-quality potatoes.

Different aspects of light need to be considered when cultivating potatoes hydroponically. Firstly, the intensity of light is crucial. Potatoes require a certain level of light intensity to stimulate the photosynthesis process effectively. Light intensity can be measured in terms of photosynthetic photon flux density (PPFD), which refers to the number of photons in the photosynthetically active range that reach a specific surface area per second. It is generally recommended to provide potatoes with a PPFD of around 200-400 µmol/m²/s during the vegetative growth stage and 400-600 µmol/m²/s during the reproductive stage for optimal growth.
However, it is important to note that different potato cultivars may have varying light requirements, and adjusting light intensity according to the specific cultivar is advisable. Additionally, the duration of light exposure, also known as the photoperiod, is another critical variable to consider. Most potato cultivars typically require 12-16 hours of light exposure per day for optimal growth and development. Maintaining a consistent and appropriate photoperiod is crucial to avoid disruptions in the plants’ metabolic processes and ensure a balanced growth rate.
Furthermore, the quality and spectrum of light are also important considerations in hydroponic potato cultivation. Different wavelengths of light can affect various aspects of plant growth, such as stem elongation, leaf expansion, and tuber formation. For example, blue light is known to stimulate leaf growth and overall plant development, while red light promotes both vegetative growth and tuber formation. The combination of blue and red light, often referred to as the “photosynthetic active radiation” (PAR) spectrum, is commonly used in hydroponic lighting systems to optimize potato growth.
Light-emitting diodes (LEDs) are increasingly popular in hydroponics due to their ability to provide specific wavelengths of light, which can be customized to suit the needs of different plant species. However, it is important to strike a balance and avoid excessive exposure to specific wavelengths, as this can cause stress and negatively impact the overall growth and yield of hydroponic potatoes.
In conclusion, light plays a crucial role in the hydroponic cultivation of potatoes. The intensity, duration, and quality of light are all factors that need to be carefully considered to ensure optimal growth and development. By providing the appropriate light conditions, hydroponic gardeners can promote healthy foliage, encourage tuber formation, and ultimately achieve higher yields of high-quality potatoes.
The Significance of Oxygen Levels in Hydroponic Potatoes Cultivation
Maintaining proper oxygen levels is crucial in hydroponic potato cultivation to ensure healthy growth and optimize yields. Oxygen plays a vital role in the various physiological processes of the potato plants, particularly in their root systems.
In a hydroponic system, the roots of the potato plants are suspended in a nutrient-rich solution, allowing them to directly uptake essential elements for their growth. However, unlike traditional soil-based cultivation, where roots have access to naturally occurring oxygen, hydroponic systems require additional measures to ensure an adequate oxygen supply.
Insufficient oxygen levels can lead to several issues, including root rot, nutrient deficiencies, and stunted growth. One common method to enhance oxygen availability in hydroponic systems is through the use of air pumps or air stones, which introduce oxygen into the nutrient solution. These devices create bubbles, breaking the surface tension of the solution and allowing oxygen to dissolve in water. This oxygenation process helps to promote healthy root development, nutrient absorption, and overall plant vigor.
Additionally, maintaining proper oxygenation levels is crucial during the germination stage of hydroponic potato cultivation. Oxygen aids in the germination process, allowing the tubers to sprout and establish healthy roots. It is essential to monitor oxygen levels closely, ensuring optimal conditions for the potatoes’ initial growth stages.
By prioritizing sufficient oxygen levels in hydroponic potato cultivation, gardeners can foster robust root systems, improve nutrient uptake, and ultimately achieve higher yields. Understanding and implementing appropriate measures to maintain oxygen levels is a key aspect of successful hydroponic potato cultivation.
How Hydroponic Potatoes Obtain Nutrients for Growth
Hydroponic potatoes obtain their nutrients for growth through a carefully formulated nutrient solution. In traditional soil-based cultivation, plants rely on the nutrients present in the soil. However, in a hydroponic system, these nutrients are provided directly to the plants in a water-based solution.
The nutrient solution used in hydroponic potato cultivation is specifically designed to meet the nutritional needs of the plants at each stage of their growth. It is typically composed of a balanced mix of essential macronutrients, such as nitrogen, phosphorus, and potassium, as well as micronutrients like iron, manganese, and zinc. These nutrients are dissolved in water and delivered to the plant roots through various hydroponic systems, such as nutrient film technique (NFT) or deep water culture (DWC).
The advantage of using a nutrient solution in hydroponics is that it allows for precise control over the nutrient levels and composition. This enables growers to optimize the nutrient uptake by the potatoes, leading to healthier plants and potentially higher yields. Additionally, because the plants directly absorb the nutrients in the solution, there is less risk of nutrient loss through leaching, which can occur in soil-based cultivation.
It is worth noting that the nutrient solution needs to be monitored and adjusted regularly to ensure that the potatoes receive the appropriate balance of nutrients. Growers often measure the electrical conductivity (EC) and pH levels of the solution to maintain optimal nutrient availability for the plants. By closely monitoring and adjusting the nutrient solution, hydroponic potato growers can maximize the plants’ nutrient uptake efficiency and promote vigorous growth.
Comparing the Growth Rates of Hydroponic and Soil-Grown Potatoes
When it comes to comparing the growth rates of hydroponic and soil-grown potatoes, there are several factors to consider. One of the main advantages of hydroponic potato cultivation is that it provides a controlled environment where growers can optimize the growth conditions for the plants. This includes factors such as temperature, light, and nutrient levels. By providing the plants with an ideal environment, hydroponic systems can often lead to faster growth rates compared to traditional soil cultivation.

In addition to the controlled environment, hydroponic systems also allow for precise control over nutrient delivery. Growers can tailor the nutrient solution to meet the specific needs of the plants at different growth stages, ensuring optimal nutrient uptake. This targeted approach to nutrient delivery can result in accelerated growth rates for hydroponic potatoes.
However, it is important to note that growth rates can vary depending on the specific conditions and cultivation practices used in both hydroponic and soil-based systems. Factors such as the quality of soil, nutrient content, and the health of the plant’s root system can all impact growth rates in traditional soil cultivation. Therefore, more research and experimentation are needed to fully understand and compare the growth rates of hydroponic and soil-grown potatoes.
Examining the Quality and Flavor of Hydroponic Potatoes
Hydroponic potato cultivation offers a unique opportunity to examine the quality and flavor of these versatile tubers. With a controlled environment and precise nutrient solutions, hydroponics allows for optimal growth and can lead to exceptional taste profiles.
One key factor contributing to the quality of hydroponic potatoes is the ability to manipulate the nutrient composition of the growing solution. By carefully selecting and adjusting the nutrients provided to the plants, growers can enhance specific flavors and attributes. For example, increasing potassium levels can result in sweeter potatoes, while adjusting nitrogen levels can influence starch content and texture.

Additionally, the absence of soil in hydroponic systems eliminates the risk of soil-borne diseases or contaminants that may affect the flavor of conventionally grown potatoes. This clean and controlled environment ensures that the potatoes develop their natural flavors without interference, leading to a superior taste experience for consumers.
From an aesthetic perspective, hydroponically grown potatoes can also exhibit a more uniform appearance compared to their soil-grown counterparts. The even distribution of nutrients and optimized growing conditions contribute to consistent size, shape, and coloration, enhancing the visual appeal of the tubers.
As we delve deeper into examining the quality and flavor of hydroponic potatoes, it is crucial to consider the specific cultivars used and the environmental conditions provided. Each potato variety carries its own unique taste profile, and factors such as light intensity, temperature, and humidity influence the final flavor. By fine-tuning these variables, hydroponic growers have the potential to produce potatoes that satisfy the most discerning palate.
The Environmental Sustainability of Hydroponic Potatoes Cultivation
Hydroponic potato cultivation offers numerous environmental sustainability benefits compared to traditional soil-based methods. One of the key advantages is the significant reduction in water usage. In hydroponics, water is recirculated and reused, resulting in up to 90% less water consumption compared to soil-based cultivation. This efficient use of water is particularly crucial in regions facing water scarcity or where agricultural practices can contribute to water pollution.

Furthermore, hydroponic potato cultivation minimizes the need for chemical pesticides and fertilizers. With precise control over nutrient solutions and the absence of soil-borne pests, hydroponic systems can significantly reduce or eliminate the use of harmful pesticides. This not only safeguards the quality of the crops but also minimizes environmental pollution and preserves beneficial organisms in the ecosystem. Additionally, the targeted delivery of nutrients in hydroponics ensures that plants receive the optimal amount of nutrition, reducing the overall use of fertilizers and minimizing the risk of nutrient runoff into water sources.
By adopting hydroponic techniques for potato cultivation, we have the opportunity to contribute to a more sustainable and eco-friendly future. The efficient water usage and reduced reliance on pesticides and fertilizers are key factors that promote environmental balance and safeguard our valuable natural resources. As we continue to explore and refine hydroponic methods, it becomes increasingly evident that this innovative approach holds tremendous promise for sustainable agriculture and addressing the challenges of feeding a growing global population.
Challenges and Solutions in Hydroponic Potatoes Cultivation
Hydroponic potato cultivation offers a variety of benefits, but it is not without its challenges. One of the main challenges is maintaining optimal nutrient levels in the hydroponic system. It can be tricky to achieve the right balance of nutrients that potatoes need for healthy growth, as different potato varieties and growth stages may have varying nutrient requirements. Additionally, nutrient imbalances can result in nutrient deficiencies or toxicities, which can hinder plant growth and development.
To address this challenge, it is important to regularly monitor and adjust the nutrient solution in the hydroponic system. This can be done by testing the nutrient levels and pH regularly and making necessary adjustments based on the specific requirements of the potato plants. Some hydroponic systems also incorporate automated nutrient dosing systems that help maintain proper nutrient levels consistently. By closely monitoring and managing the nutrient solution, growers can overcome this challenge and ensure that their hydroponic potatoes receive the essential nutrients they need for optimal growth.
Another challenge in hydroponic potato cultivation is disease and pest management. While hydroponic systems provide a controlled environment that minimizes the risk of soil-borne diseases and certain pests, there are still potential challenges. In particular, fungal diseases such as powdery mildew and Fusarium wilt can affect potato plants in hydroponic systems. Similarly, aphids, spider mites, and other insect pests can find their way into the controlled environment.
To mitigate these challenges, it is crucial to implement strict hygiene practices, such as regularly cleaning and disinfecting the hydroponic system and equipment. Additionally, using disease-resistant potato varieties can help minimize the risk of fungal diseases. Integrated pest management techniques, such as introducing beneficial insects or employing biological controls, can also help keep pest populations in check. By proactively managing diseases and pests, growers can ensure healthier potato plants and improve overall crop quality.
Future Prospects and Innovations in Hydroponic Potatoes Cultivation
As hydroponic potato cultivation continues to gain momentum, the future prospects and innovations in this field hold great promise for gardening enthusiasts and commercial farmers alike. With the growing demand for more sustainable and efficient food production methods, hydroponics offers a viable solution that maximizes resource usage while minimizing environmental impact.
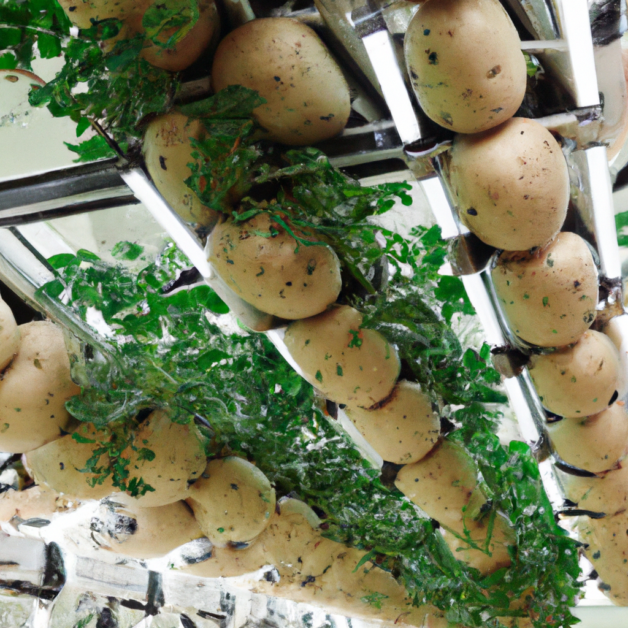

One of the key areas of innovation in hydroponic potato cultivation is the development of more advanced nutrient solutions. Researchers and experts are constantly striving to formulate nutrient solutions that not only meet the specific requirements of potato plants but also enhance their growth and yield. By meticulously balancing the essential macro and micronutrients, these advanced solutions aim to optimize the plant’s nutrient uptake and promote healthier and more robust potato growth. Additionally, the use of organic and biodegradable fertilizers in nutrient solutions is also being explored, aligning with the increasing demand for sustainable agricultural practices.
Another exciting innovation on the horizon is the integration of artificial intelligence (AI) and automation in hydroponic potato systems. AI-powered sensors and monitoring systems enable real-time data collection on key parameters such as temperature, humidity, nutrient levels, and plant health. This allows growers to have precise control over the growing environment and make real-time adjustments to optimize growth conditions. Furthermore, automated feeding and irrigation systems can ensure a consistent and precise delivery of nutrient solutions, reducing human error and labor requirements. These advancements not only enhance the efficiency of hydroponic potato cultivation but also offer a more streamlined and user-friendly approach for both experienced growers and beginners.
Learn more about it in the given video:
What are the benefits of hydroponic potato cultivation?
Hydroponic potato cultivation offers several benefits, including increased yield, faster growth rates, better control over nutrient intake, reduced water usage, and the ability to grow potatoes in areas with limited access to arable land.
How does the nutrient solution affect the growth of hydroponic potatoes?
The nutrient solution provides all the necessary nutrients for the growth of hydroponic potatoes. It contains a balanced mixture of essential nutrients such as nitrogen, phosphorus, and potassium, which are required for optimal growth and development.
What is the efficiency of water usage in hydroponic potato cultivation?
Hydroponic potato cultivation is known for its efficient water usage. Compared to traditional soil-based cultivation, hydroponics uses up to 90% less water as it recirculates the nutrient solution, minimizing water wastage.
How does a controlled environment impact the growth of hydroponic potatoes?
A controlled environment in hydroponic potato cultivation allows for precise control over temperature, humidity, and lighting conditions. This ensures optimal growth and minimizes the risk of diseases, pests, and other environmental factors that can hinder potato growth.
What is the role of light in hydroponic potato cultivation?
Light plays a crucial role in hydroponic potato cultivation as it is the primary source of energy for photosynthesis. Proper lighting, including a balanced spectrum and duration, is essential for promoting healthy plant growth and maximizing potato yields.
Why are oxygen levels significant in hydroponic potato cultivation?
Adequate oxygen levels are crucial for the roots of hydroponic potato plants. Oxygen helps in nutrient absorption, root respiration, and prevents the development of anaerobic conditions that can lead to root rot and other diseases.
How do hydroponic potatoes obtain nutrients for growth?
Hydroponic potatoes obtain nutrients for growth through the nutrient solution, which is delivered directly to the roots. The roots absorb the necessary nutrients from the solution, allowing for efficient nutrient uptake and utilization by the plants.
How do the growth rates of hydroponic potatoes compare to soil-grown potatoes?
Hydroponic potatoes generally exhibit faster growth rates compared to soil-grown potatoes. The controlled environment, optimized nutrient intake, and absence of competition from weeds contribute to the accelerated growth and development of hydroponically grown potatoes.
What is the quality and flavor of hydroponic potatoes like?
Hydroponic potatoes are known for their consistent quality and flavor. The controlled growing conditions ensure that the potatoes are free from soil-borne diseases, contaminants, and excessive use of chemical fertilizers, resulting in a clean and superior flavor.
Is hydroponic potato cultivation environmentally sustainable?
Yes, hydroponic potato cultivation is considered environmentally sustainable. It requires less water, reduces the need for pesticides and herbicides, and can be practiced in urban areas, reducing the need for transportation and minimizing the carbon footprint associated with traditional potato farming.
What are some challenges and solutions in hydroponic potato cultivation?
Challenges in hydroponic potato cultivation include maintaining proper nutrient balance, preventing disease outbreaks, and managing environmental factors. Solutions include regular monitoring and adjustment of nutrient solutions, implementing pest and disease control measures, and using advanced technology for climate control.
What are the future prospects and innovations in hydroponic potato cultivation?
Future prospects and innovations in hydroponic potato cultivation include the development of more efficient and precise nutrient delivery systems, advancements in lighting technology, the use of artificial intelligence for crop monitoring and optimization, and the integration of sustainable practices such as renewable energy sources and water recycling systems.

Pallavi Gupta is a burgeoning writer at SouthElMonteHydroponics, blending her passion for data analysis with a keen interest in biotechnology. Currently pursuing a Bachelor’s in Biotechnology at Amity University, Pallavi delves into the intricacies of life sciences while gaining hands-on experience in the exciting world of data analysis. Her unique background provides a fresh perspective on hydroponic farming, as she explores the intersection of biotechnology and sustainable agriculture. Through her writing, Pallavi aims to bridge the gap between data-driven insights and innovative farming practices, inspiring others to harness technology for a greener future.