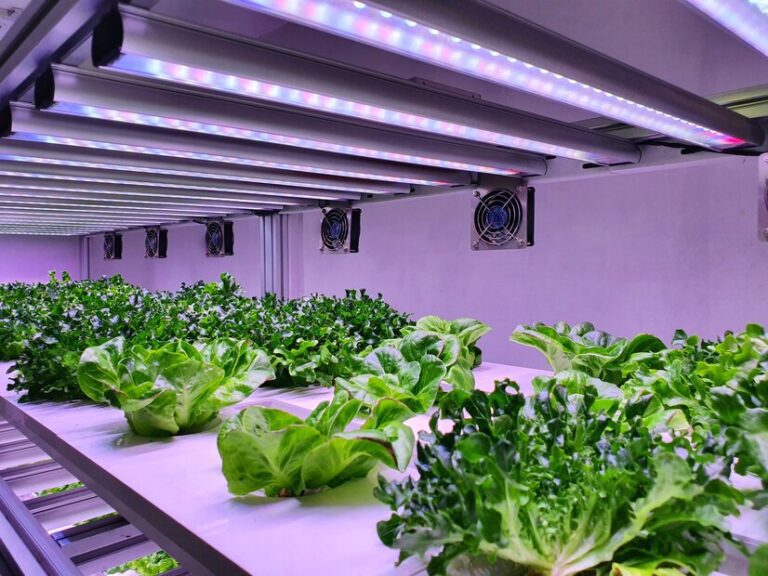
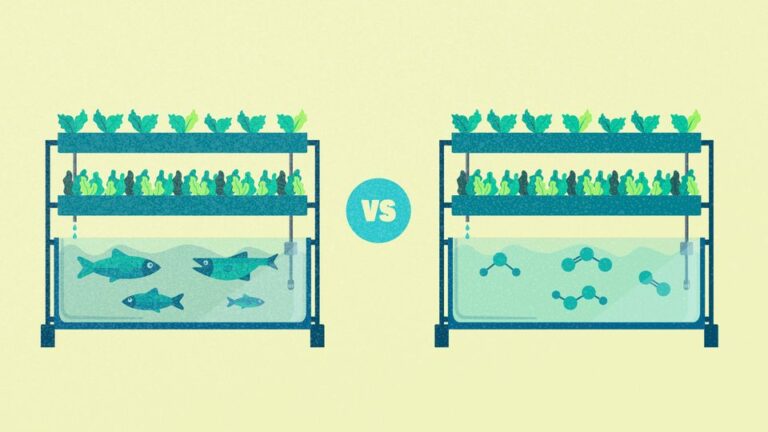
Hydroponics: A Journey Through History
Ever wondered how ancient civilizations managed to grow crops in barren lands or even in the depths of winter? Enter hydroponics—the age-old technique that’s been quietly reshaping agriculture for centuries. From the enigmatic Hanging Gardens of Babylon to the high-tech greenhouses of today, hydroponics has a rich and diverse history that’s ripe for exploration. Join us on a journey through time as we unearth the fascinating origins and evolution of hydroponics. From the Aztec’s innovative floating gardens to modern vertical farming, we’ll delve into the ingenuity of human creativity and the science behind soilless cultivation. Whether you’re a seasoned green thumb or just curious about the future of farming, buckle up for an enlightening ride. Get ready to grow your knowledge and maybe even a few veggies along the way. Let’s dive into hydroponics together!
Table of Contents
Ancient Agricultural Innovations
Ancient agricultural innovations have played a crucial role in shaping the development of farming practices we see today. From the Hanging Gardens of Babylon to the Aztec Floating Gardens, ancient civilizations demonstrated remarkable ingenuity and resourcefulness in their approach to agriculture.
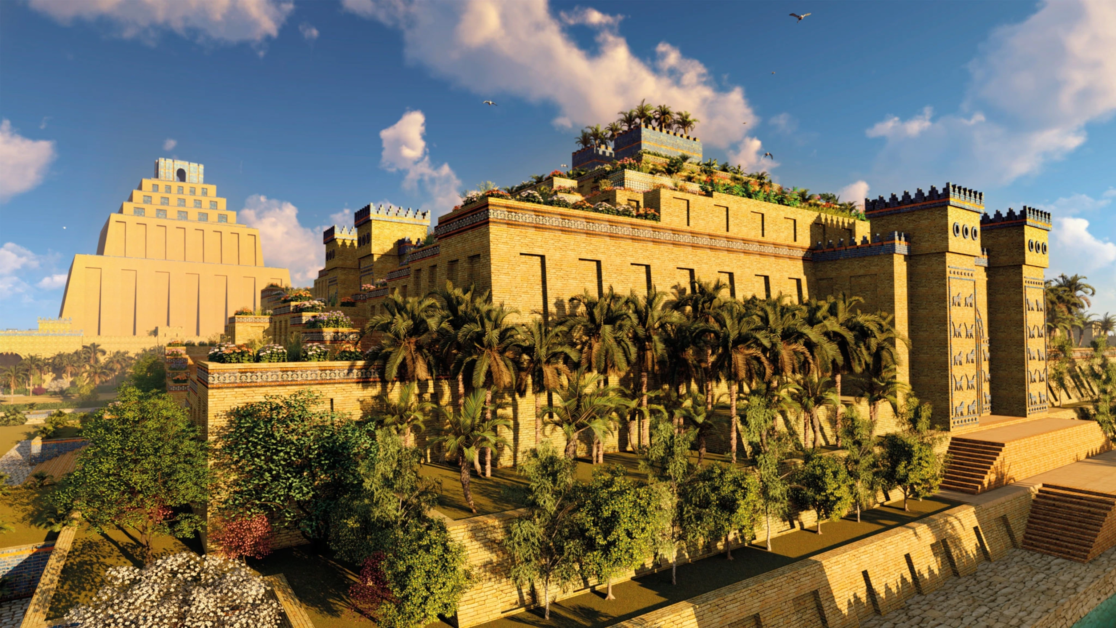

The Hanging Gardens of Babylon, often considered one of the Seven Wonders of the Ancient World, were a marvel of engineering and horticulture. Built around 600 BCE by King Nebuchadnezzar II, these terraced gardens were a feat of hydroponics, utilizing a system of pulleys and irrigation channels to bring water to the plants. It is believed that a variety of plant species, including trees and exotic flowers, were cultivated in the gardens, creating a verdant oasis in the arid region.
In ancient Egypt, another remarkable agricultural innovation took place. The Egyptians developed sophisticated irrigation systems, such as the shaduf, to bring water from the Nile River to their crops. They also practiced the art of crop rotation, alternating the cultivation of different crops to improve soil fertility. Additionally, the Egyptians utilized a form of hydroponics known as “floating gardens” or “floating pots,” where plants were placed in baskets and floated on the surface of the water, absorbing nutrients directly from the water source.
These ancient agricultural practices demonstrate the early exploration of soil-less cultivation and the utilization of water-based systems to nourish plants. The knowledge and techniques developed during these times laid the foundation for future innovations in hydroponics, ultimately leading to its modern-day applications in commercial agriculture and urban farming. As we delve further into the history of agriculture, we will uncover more remarkable advancements and the ongoing evolution of hydroponics.
The Hanging Gardens of Babylon
Nestled in ancient Mesopotamia, the Hanging Gardens of Babylon stood as a marvel of architectural ingenuity. According to lore, King Nebuchadnezzar II commissioned these opulent gardens in the 6th century BCE, a lavish tribute to his wife, Queen Amytis.
Though the gardens’ exact location remains debated among scholars, ancient texts vividly describe their splendor. It’s believed they were constructed on tiered terraces, supported by stone columns and adorned with a lush array of trees, plants, and flowers. Complex irrigation systems, powered by pumps drawing water from the nearby Euphrates River, sustained their verdant allure.
The Table here provides an overview of the descriptions and aspects of The Hanging Gardens of Babylon
| Aspect | Description |
|---|---|
| Ancient Wonder | The Hanging Gardens of Babylon, situated in ancient Mesopotamia, stood as a marvel of architectural ingenuity during the 6th century BCE. |
| Royal Tribute | Legend has it that King Nebuchadnezzar II constructed these lavish gardens as a grand gesture to please his wife, Queen Amytis. |
| Debate and Description | Despite ongoing speculation about their exact location and existence, vivid descriptions from ancient texts paint a rich picture of the gardens’ beauty. |
| Terraced Splendor | The gardens were believed to be built on tiered terraces, adorned with a diverse array of trees, plants, and flowers, supported by stone columns. |
| Innovative Irrigation | A complex system of pumps drew water from the nearby Euphrates River to irrigate the gardens, showcasing advanced irrigation techniques for the time. |
| Enduring Inspiration | The Hanging Gardens have captured imaginations throughout history, serving as a perennial source of inspiration for gardeners and architects worldwide. |
| Foundational Influence | Their innovative terraced design and advanced irrigation methods laid the groundwork for future agricultural advancements. |
| Hydroponic Precursors | As we delve into modern hydroponics and soil-less cultivation, we’re left to wonder if the Hanging Gardens were early examples of these practices. |
| Legacy of Ingenuity | While their secrets may remain elusive, the Hanging Gardens endure as a testament to human creativity and our enduring quest to nurture natural beauty. |
Across the ages, the Hanging Gardens have stirred imaginations, inspiring gardeners and architects worldwide. Their innovative terraced design and advanced irrigation techniques foreshadowed future agricultural advancements. As we delve into modern hydroponics and soil-less cultivation, we’re left to ponder: Were the Hanging Gardens precursors to these practices? While their mysteries endure, their legacy as a testament to human creativity and reverence for natural beauty remains undiminished.
Innovations in Ancient Egypt
Ancient Egypt is renowned for its remarkable innovations in agriculture, setting the stage for modern-day horticultural practices. One of the greatest achievements of the ancient Egyptians was the development of an intricate irrigation system that enabled the cultivation of crops in arid areas alongside the River Nile. The utilization of canals and dikes allowed them to control the water flow, ensuring a consistent supply to farmlands. This innovative approach not only facilitated crop cultivation but also supported the growth of a highly productive and sustainable agricultural system.

Furthermore, the ancient Egyptians were pioneers in the concept of soil fertility and its maintenance. They recognized the importance of using organic matter, such as animal manure and compost, to enrich the soil and optimize plant growth. The meticulous management of their fertile land allowed for the cultivation of a variety of crops, including cereals like wheat and barley, fruits like figs and dates, and vegetables like onions and lettuce. By employing innovative farming techniques and carefully tending to their fields, the ancient Egyptians were able to achieve high yields and ensure food security for their civilization.
Through their ingenuity and a deep understanding of the land, the ancient Egyptians demonstrated a profound appreciation for agriculture. Their advancements in irrigation systems and soil fertility continue to inspire and inform modern agricultural practices, including the revolutionary field of hydroponics, which harnesses the power of nutrient-rich water to cultivate plants. As we delve further into the world of hydroponics, we will uncover the fascinating evolution of this agricultural method and its significant contributions to sustainable food production worldwide.
The Aztec Floating Gardens
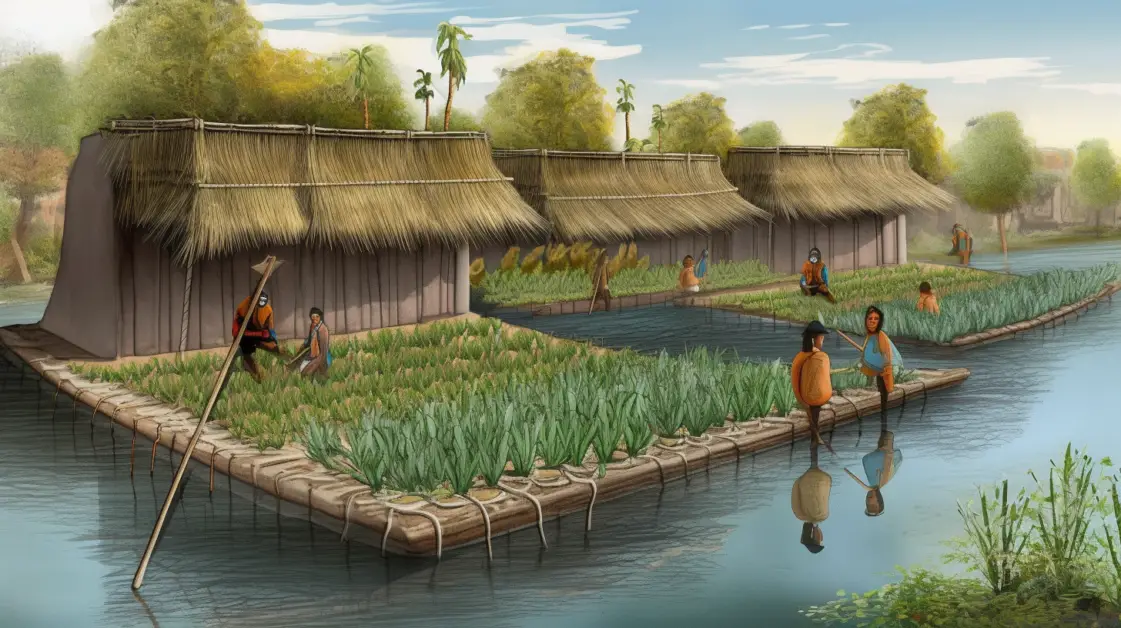

The Aztec civilization in ancient Mexico developed an ingenious agricultural system known as the floating gardens. Also called chinampas, these gardens were artificial islands created by weaving together layers of lake beds and then anchoring them with wooden poles driven into the lakebed. These floating gardens were not only a brilliant solution to the Aztecs’ need for arable land but also played a crucial role in sustaining their population.
The Aztec floating gardens were strategically designed to optimize the use of fertile soil and water resources. By constructing these floating platforms in the shallow parts of Lake Texcoco, they ensured that the gardens were constantly nourished by the nutrient-rich sediment carried by the lake’s waters. The Aztecs cultivated various crops on these chinampas, including maize, beans, squash, and different types of vegetables. This innovative farming technique allowed them to produce abundant amounts of food, contributing to the sustenance of the burgeoning Aztec population. The success of the floating gardens highlights the resourcefulness and ingenuity of the Aztec people in overcoming the challenges of limited land availability.
The Renaissance and Soil-less Cultivation
During the Renaissance period, significant advancements were made in various fields, including agriculture. One innovative practice that emerged during this time was soil-less cultivation, which revolutionized the way plants were grown. Instead of relying on traditional soil-based methods, renaissance gardeners and botanists began experimenting with alternative growing mediums to support plant growth.

One of the pioneers of soil-less cultivation during this era was Sir Francis Bacon, an English philosopher and scientist. Bacon explored the use of various substrates such as sand, gravel, and pumice as alternatives to soil. He believed that by controlling the nutrients and environmental factors, plants could thrive in these unconventional growing conditions. Bacon’s experiments laid the groundwork for modern hydroponics, as he introduced the concept of delivering nutrient solutions directly to the plants’ roots, thus eliminating the need for soil altogether.
This newfound interest in soil-less cultivation during the Renaissance opened up new possibilities for growing crops in urban environments and areas with limited access to fertile soil. The concept gained traction among gardening enthusiasts and eventually spread across Europe, leading to further experimentation and refinement of these techniques. As the Renaissance period progressed, more innovative ideas and inventions emerged, setting the stage for the future development of hydroponics and its wide-ranging applications in modern agriculture.
18th-Century Experiments with Hydroponics
In the 18th century, there was a surge of interest in experimenting with hydroponics as a means of cultivating plants without soil. Scholars and scientists delved into various methods to understand the potential of this innovative approach to agriculture.
One notable experiment from this era was conducted by English botanist Stephen Hales. In 1727, Hales successfully grew plants in a water-based solution enriched with essential nutrients. His experiment provided valuable insights into the role of minerals in plant growth, paving the way for further exploration in the field of hydroponics. Additionally, Swedish chemist Carl Wilhelm Scheele’s work in the late 1700s and early 1800s focused on the importance of oxygen in plant nutrition, which added to the growing body of knowledge on hydroponic cultivation techniques.
This Table provides the list of experiments which were conducted during 18th Century!
| Year | Experiment | Researcher(s) | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1699 | Woodward’s Water Culture | John Woodward | Woodward conducted one of the earliest documented hydroponics experiments, growing plants in water with added nutrients. |
| 1727 | Stephen Hales’ Experiment | Stephen Hales | Hales experimented with growing plants in various solutions, demonstrating the importance of water and air in plant growth. |
| 1749 | The Dutch East India Company | Dutch East India Company | The Dutch East India Company conducted experiments using hydroponics to grow plants on ships during long sea voyages, reducing the risk of scurvy among sailors. |
| 1783 | Ingenhousz’s Hydroponic Experiment | Jan Ingenhousz | Ingenhousz experimented with growing plants in water enriched with various substances, laying the groundwork for future hydroponic research. |
| 1797 | Saussure’s Experiment | Nicolas-Théodore de Saussure | Saussure conducted experiments on plant nutrition, including growing plants in water without soil to study their uptake of nutrients. |
These 18th-century experiments laid the foundation for future advancements in hydroponics, establishing it as a field of scientific study and innovation. As researchers continued to probe the potential of soil-less cultivation, they set the stage for the development of nutrient solutions and the refinement of hydroponic systems that we benefit from today. The knowledge and discoveries gained from these early experiments provide an essential building block for our current understanding of hydroponics as a sustainable and effective method of agriculture.
The Rise of Modern Hydroponics
In recent decades, hydroponics has experienced a remarkable rise as a modern agricultural practice. This innovative method of growing plants without soil has gained popularity among gardening enthusiasts, commercial farmers, and even space agencies like NASA. The rise of modern hydroponics can be attributed to numerous factors:
Overall, the rise of modern hydroponics can be attributed to advancements in technology, the demand for sustainable food production, and the advent of urban agriculture. As this innovative method continues to evolve and gain traction, it holds the potential to revolutionize the way we grow and consume food. By harnessing the power of technology and sustainable practices, hydroponics offers a glimpse into a future where agriculture can thrive in any setting, even in the most urbanized environments.
Hydroponics in the Early 20th Century
The early 20th century ushered in a period of profound exploration and innovation in the realm of hydroponics, marking a transformative era in agricultural history. During this time, a confluence of scientific curiosity, agricultural necessity, and pragmatic ingenuity converged to propel hydroponics from the margins of scientific inquiry to the forefront of agricultural advancement.
- Recognition of Potential: As agriculturalists grappled with the challenges of soil depletion, land scarcity, and food security concerns, hydroponics emerged as a beacon of hope. Visionary scientists and agricultural pioneers began to recognize the inherent potential of hydroponics to transcend the limitations imposed by traditional soil-based farming methods. The notion that plants could thrive without the need for soil challenged long-held assumptions, sparking a wave of curiosity and exploration.
- William Frederick Gericke: Among the luminaries of this era, William Frederick Gericke stood as a trailblazer in the field of hydroponics. As a professor at the University of California, Berkeley, Gericke embarked on a series of pioneering experiments in the 1920s that would forever alter the trajectory of agricultural science. By meticulously cultivating plants in nutrient-rich water solutions, Gericke demonstrated the feasibility of soil-less cultivation, effectively shattering the paradigm that soil was indispensable for plant growth.
- Experiment Success: Gericke’s groundbreaking experiments yielded astonishing results, serving as a testament to the resilience and adaptability of plant life. In meticulously controlled environments, devoid of traditional soil mediums, crops flourished under the nurturing embrace of nutrient-enriched water solutions. The success of Gericke’s experiments not only validated the viability of hydroponics but also ignited a fervent interest in its potential applications across diverse agricultural landscapes.
- Military Adoption: The practical implications of hydroponics extended far beyond the confines of academic curiosity, finding practical utility in unexpected arenas such as the military. Against the backdrop of global conflict and logistical challenges, the United States military recognized the potential of hydroponics to provide a reliable source of fresh food for troops deployed in remote and inhospitable environments. Embracing hydroponics as a means of ensuring sustenance amidst adversity, the military’s adoption of this innovative cultivation method underscored its practical efficacy and resilience.
In summation, the early 20th century marked a seminal chapter in the annals of hydroponics, characterized by bold experimentation, paradigm-shifting discoveries, and practical applications. The pioneering efforts of figures like William Frederick Gericke and the pragmatic adoption of hydroponics by institutions such as the military laid the groundwork for its enduring relevance and continued evolution in modern agriculture. As we reflect on this transformative era, we are reminded of the profound impact that ingenuity, perseverance, and scientific curiosity can wield in shaping the future of food production.
The Development of Nutrient Solutions
Nutrient solutions play a crucial role in advancing hydroponics by providing essential elements for plant growth without the need for soil. Through years of research and experimentation, precise formulations have been developed to meet specific plant requirements. These solutions contain a balanced combination of macronutrients such as nitrogen, phosphorus, and potassium, as well as micronutrients like iron, zinc, and manganese.
The table, here provides a concise and organized overview of the key aspects of nutrient solution management in hydroponic agriculture!
| Aspect | Description |
|---|---|
| Customized Formulations | Tailored nutrient solutions to meet plant needs based on type, growth stage, and environmental factors. |
| pH and EC Control | Adjustment for optimal pH and electrical conductivity (EC) to enhance nutrient absorption and plant health. |
| Hydroponic System Compatibility | Formulations tailored for different hydroponic systems’ effectiveness. |
| Supplemental Additives | Additional supplements for improved plant health and productivity. |
| Water Quality Management | Testing and treatment for water purity, preventing harmful substance buildup. |
| Recycling and Sustainability | Efforts to recycle and reuse solutions to minimize waste and promote sustainability. |
| Quality Assurance | Standards and certifications ensuring product purity and effectiveness. |
These solutions are precisely formulated to meet the unique needs of different plants, with adjustments made for pH and electrical conductivity to optimize nutrient absorption. Compatibility with various hydroponic systems ensures effectiveness, while supplemental additives enhance plant health and productivity. Water quality management is essential to maintain purity and prevent harmful substances. Efforts to recycle solutions promote sustainability, and adherence to quality assurance standards ensures product purity and effectiveness. Overall, nutrient solution management in hydroponics is a multifaceted process aimed at maximizing plant growth while minimizing environmental impact.
NASA’s Contribution to Hydroponics
NASA’s groundbreaking hydroponic research is transforming food sustainability in space missions. Traditional farming methods are impractical in space due to microgravity and limited resources. To address this, NASA has developed innovative hydroponic systems like the Veggie Plant Growth System, which uses LED lighting to optimize plant growth. This technology ensures astronauts have a reliable food supply while in space. Moreover, the knowledge gained from these experiments is being applied to terrestrial agriculture, offering solutions to challenges such as water scarcity and land limitations. By leveraging hydroponic techniques, farmers can achieve higher crop yields with less water and space, contributing to global food security. As we confront the growing challenges of population growth and climate change, NASA’s hydroponic advancements offer hope for a more sustainable future both on Earth and beyond.
NASA’s groundbreaking research in hydroponics not only propels space exploration forward but also presents a paradigm shift in sustainable agriculture practices on Earth. By addressing the unique challenges of microgravity and limited resources in space, hydroponics emerges as a crucial solution for ensuring a self-sustaining food supply during space missions. Through innovative hydroponic systems like the Veggie Plant Growth System, NASA pioneers technologies that optimize plant growth and nutritional value in controlled environments. Furthermore, the knowledge gained from space experiments informs terrestrial agriculture, leading to transformative advancements in crop cultivation techniques. With its ability to enhance crop yields, conserve water, and thrive in diverse environments, hydroponics offers a promising alternative to traditional farming methods, laying the foundation for a greener and more sustainable future for food production worldwide.
Hydroponics in Commercial Agriculture
In the dynamic landscape of commercial agriculture, hydroponics emerges as a compelling and sustainable cultivation method gaining widespread attention. Unlike traditional farming, hydroponics employs a soilless technique, nurturing plants in a nutrient-rich water solution. This innovative approach offers multifaceted benefits for commercial growers, positioning it as a favored choice in the agricultural sector.
Hydroponics excels in maximizing crop yields through meticulous control over nutrient delivery and environmental variables. Growers can finely tune these factors to optimize plant growth and enhance productivity, ensuring consistently bountiful harvests. Moreover, by circumventing the need for soil, hydroponic systems mitigate the risk of soil-borne diseases and pests, fostering healthier and more uniform crop development.
A hallmark of hydroponics lies in its remarkable efficiency in resource utilization, particularly water. Compared to conventional agriculture, hydroponic systems demand significantly less water, making them an environmentally conscientious option. This water-saving attribute not only conserves this precious resource but also reduces fertilizer usage, curbing adverse effects on the surrounding ecosystem. Overall, hydroponics embodies a sustainable and forward-thinking approach to commercial agriculture, poised to meet the demands of modern farming while minimizing environmental impact.
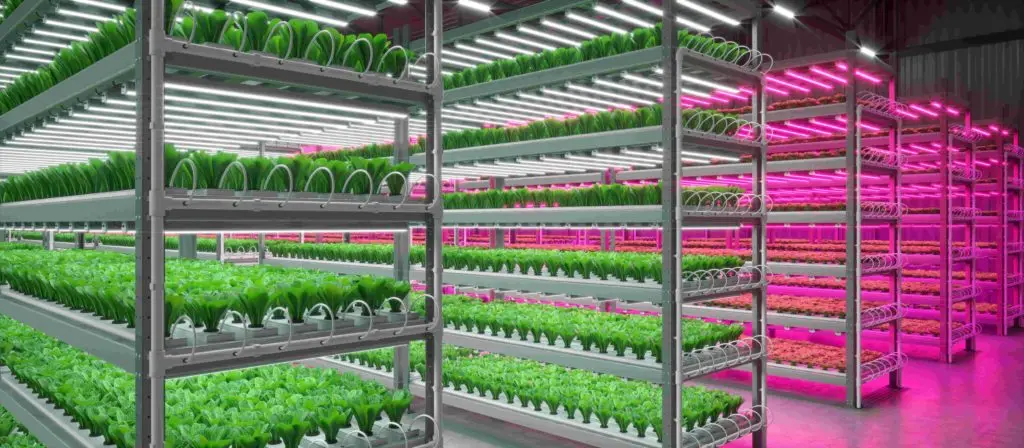
The Emergence of Vertical Farming
Vertical farming is a relatively new concept in the field of agriculture that has gained significant attention in recent years. Unlike traditional farming methods, which rely on large areas of land, vertical farming utilizes vertical space to grow crops in stacked layers. This innovative approach has the potential to revolutionize the way we produce food, particularly in urban areas where land availability is limited.
One of the key advantages of vertical farming is its ability to maximize land use efficiency. By utilizing vertical space, farmers can grow a larger quantity of crops in a smaller area. This is especially beneficial in urban environments, where land is scarce and expensive. Vertical farming also eliminates the need for extensive land preparation, such as clearing and leveling, as well as the use of fertile soil. Instead, specialized systems are used to provide the necessary nutrients, water, and lighting for plant growth, allowing crops to be grown in controlled environments year-round.
- Maximized Land Use: Vertical farming optimizes space utilization, enabling higher crop yields in smaller areas.
- Urban Adaptability: Well-suited for urban environments, vertical farms can be integrated into densely populated areas.
- Reduced Environmental Impact: Minimizes land degradation and habitat destruction associated with traditional agriculture, offering a more sustainable alternative.
- Year-Round Cultivation: Controlled indoor environments allow for consistent crop production regardless of seasonal fluctuations.
- Resource Efficiency: Precision nutrient delivery systems minimize resource wastage, conserving water and nutrients.
- High Initial Investment: Vertical farming setups often require significant upfront investment in infrastructure and technology.
- Energy Consumption: Indoor lighting and climate control systems contribute to higher energy consumption compared to traditional farming.
- Technical Complexity: Requires expertise in specialized systems and technologies, posing a learning curve for farmers.
- Limited Crop Variety: Some crops may not thrive in vertical farming environments, limiting the range of cultivable crops.
- Dependency on Supplies: Reliance on external supplies of nutrients, water, and energy can pose logistical challenges.
Hydroponics in Urban Agriculture
As urban populations burgeon, the quest for fresh, nourishing sustenance within city confines has intensified. Enter hydroponics, a beacon of hope for urban agriculture. This innovative method, eschewing soil, boasts a plethora of advantages that make it a beacon of promise in bustling urban landscapes.
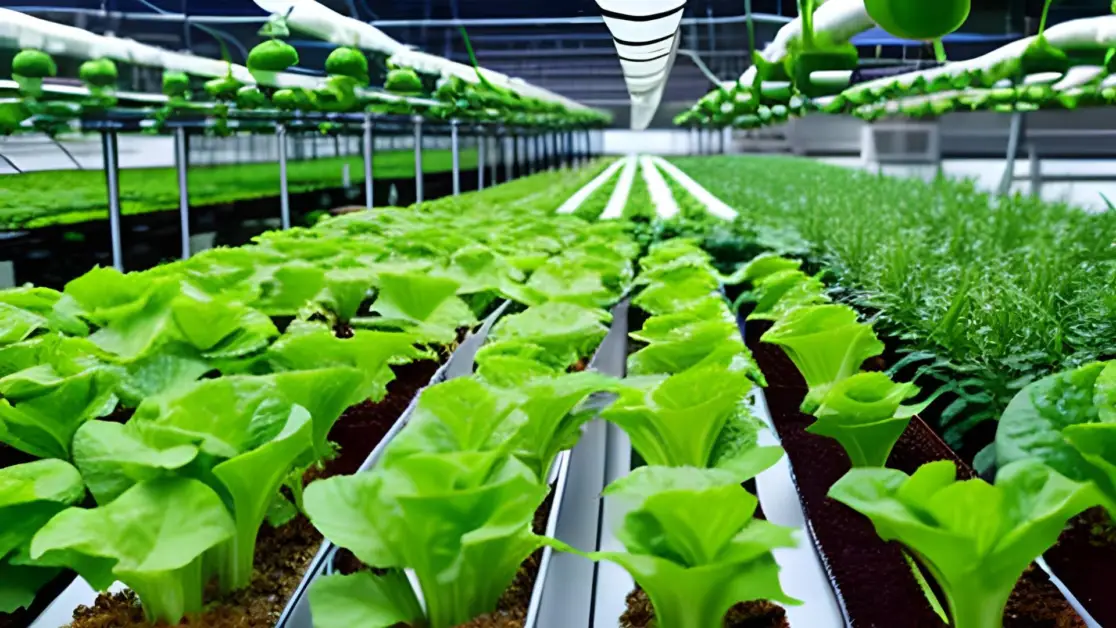

At its core, hydroponics unlocks the door to year-round crop cultivation, defying the constraints of seasons. Urban farmers wield control over every aspect of the growth environment, yielding bumper harvests in record time. Particularly in space-starved cities, hydroponic setups ascend vertically, making every inch of land count. With this ingenious system, urban farmers harness maximum productivity within a minimal footprint, heralding a shift towards sustainable, resource-efficient food production.
Furthermore, hydroponics emerges as a champion of water conservation, significantly slashing consumption compared to conventional agriculture. Through the art of recycling nutrient-rich water, hydroponic setups curtail waste, a boon for water-scarce urban locales grappling with exorbitant water costs. Not stopping there, hydroponics bids farewell to harmful pesticides and herbicides, crafting a pristine environment where pests and diseases dare not tread. The result? Healthier, safer produce for urbanites and a substantial reduction in agricultural chemical pollution.
In essence, hydroponics emerges as a beacon of hope for urban agriculture. Its prowess in optimizing space, conserving water, and curbing chemical usage paints a vivid picture of a greener, more sustainable urbanfuture. As cities navigate the tumultuous waters of food security and environmental resilience, integrating hydroponics into urban farming frameworks promises to be a pivotal stride towards a brighter, bountiful tomorrow.
Hydroponics and Sustainable Food Production
Hydroponics emerges as a beacon of sustainability in food production, offering a plethora of advantages over traditional agriculture:
- Controlled Environment: Plants thrive without soil, enabling year-round cultivation in a meticulously controlled environment.
- Water and Nutrient Efficiency: Hydroponics slashes water consumption by 90% compared to conventional farming, utilizing nutrients judiciously.
- Pesticide-Free: Protected from pests and diseases, hydroponic produce is free from harmful pesticides and herbicides, ensuring purity and safety.
- Accelerated Growth: Meticulously balanced nutrient solutions foster accelerated growth rates and bountiful harvests, yielding up to 30% more crops.
- Localized Production: Urban hydroponic farms reduce reliance on extensive transportation networks, cutting carbon emissions and bolstering food accessibility.
With its potential to fortify food security, conserve resources, and mitigate environmental footprints, hydroponics promises a sustainable, future-forward approach to food production. Ongoing research and innovation will further enhance efficiency and broaden its applications, nourishing communities and safeguarding the planet.
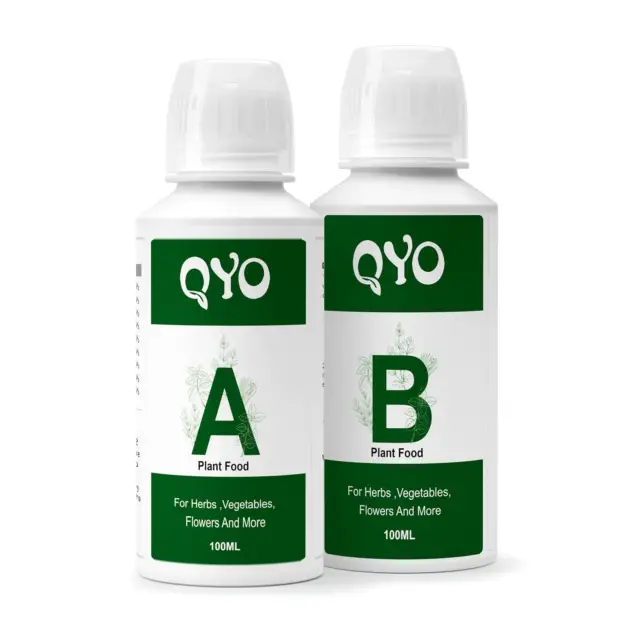
There is this one product which I want to recommend using on my personal experience is the Plant Food Hydroponic Nutrients Supplies!
Having used this hydroponic plant food nutrient solution extensively in my own setup, I can confidently attest to its effectiveness and convenience. This nutrient blend is a game-changer for hydroponic growers like myself, offering a complete package of essential nutrients necessary for robust plant growth. The hydroponic plant food nutrient solution is a specially formulated blend designed to provide all the essential nutrients required for optimal plant growth in hydroponic systems. This liquid nutrient solution offers a convenient and effective way to nourish plants without the use of soil, making it ideal for hydroponic gardening enthusiasts.
Key Features:
- Complete Nutrient Mix: Balanced blend of essential macronutrients and micronutrients for optimal plant growth.
- Liquid Formulation: Easy-to-mix liquid solution ensures rapid absorption by plant roots.
- Versatile Application: Compatible with various hydroponic setups for seamless integration.
- Enhanced Plant Performance: Promotes vigorous growth, strong roots, and abundant flowering and fruiting.
- Long-Lasting Supply: Generous quantity provides cost-effective, consistent nutrient availability for multiple growth cycles.
- Complete Nutrition: I’ve noticed a significant improvement in the health and vitality of my plants since incorporating this solution into my hydroponic system. The balanced mix of macronutrients and micronutrients ensures that my plants receive all the necessary nourishment they need to thrive.
- Ease of Use: Mixing and applying this liquid solution couldn’t be simpler. Its liquid form allows for quick and easy blending with water, saving me time and effort during my routine maintenance tasks.
- Versatility: Whether I’m using a deep water culture, nutrient film technique, or drip system, this nutrient solution performs admirably across all my hydroponic setups. Its versatility makes it a go-to choice for growers with different systems.
- Visible Results: From vibrant foliage to abundant fruiting, the results speak for themselves. My plants have shown remarkable growth and productivity since I started using this solution, yielding higher yields and healthier crops.
- Storage Sensitivity: To maintain potency and efficacy, proper storage is essential. Storing it in a cool, dark place away from direct sunlight and extreme temperatures ensures optimal performance.
- Accurate Measurement: Achieving the right nutrient concentration requires precise measuring tools. Over or under-application can affect plant health, so it’s crucial to measure carefully.
- Availability Concerns: Depending on location, availability may be limited, posing a challenge for some growers to access this product easily.
In conclusion, my experience with this hydroponic plant food nutrient solution has been overwhelmingly positive. It has become a staple in my hydroponic gardening routine, delivering consistent and impressive results. While there are some considerations to keep in mind, the benefits far outweigh any drawbacks. I highly recommend this product to fellow hydroponic enthusiasts looking to optimize their plant growth and maximize their yields.
- High-Quality Nutrients
- Convenient Packaging
- Versatility
- Easy to Use
- Shelf Life
- Storage Space
The Benefits of Hydroponics
Hydroponics, the method of growing plants without soil, has garnered popularity among gardening enthusiasts for its array of benefits. This innovative approach not only maximizes space utilization but also offers precise control over nutrient delivery and significant water conservation advantages.
Key Points:
- Maximized Space Utilization:
- Unlike traditional soil-based gardening, hydroponics eliminates the need for extensive soil volume, allowing for the cultivation of more plants in a smaller area.
- Ideal for urban farming and space-constrained environments, hydroponic systems optimize land usage while increasing crop yield potential.
- Precise Nutrient Control:
- Hydroponics enables meticulous control over nutrient delivery, ensuring plants receive an optimal blend of macronutrients, micronutrients, and water.
- This targeted approach to plant nutrition fosters rapid growth, enhances crop quality, and boosts overall productivity while minimizing nutrient waste.
- Water Conservation:
- Traditional soil-based gardening often results in water wastage through evaporation, inefficient irrigation, and runoff.
- In contrast, hydroponic systems use up to 90% less water by directly delivering the nutrient solution to plant roots, reducing water loss and promoting sustainability.
In summary, hydroponics offers a host of advantages, from maximizing space utilization to precise nutrient control and water conservation. Whether you’re an urban farmer, a gardening enthusiast seeking efficient space optimization, or simply intrigued by innovative agricultural practices, hydroponics presents an exciting solution for cultivating a diverse range of plants sustainably and effectively.
Exploring the Future of Hydroponics
Hydroponics, the soil-less cultivation method for plants, has witnessed a surge in popularity in recent years, offering a glimpse into an innovative future of agriculture. As we delve into the potential advancements of this technique, several exciting possibilities emerge.
One avenue of progress involves the fusion of technology with hydroponic systems. The integration of smart sensors and automated controls empowers growers to finely tune environmental variables such as temperature, humidity, pH levels, and nutrient delivery. This precision not only enhances efficiency but also ensures the ideal conditions for robust plant growth. Furthermore, leveraging artificial intelligence (AI) algorithms enables the analysis of vast datasets to optimize cultivation practices, leading to increased yields and reduced resource consumption. The amalgamation of technology and hydroponics holds tremendous potential for transforming the landscape of plant cultivation in the years to come.
Another frontier in the evolution of hydroponics is the exploration of new and unconventional crops suitable for this innovative growing approach. Traditionally associated with leafy greens and herbs, hydroponics is now expanding its horizons. Ongoing experiments aim to broaden the spectrum of plants capable of thriving in hydroponic environments. From fruits like strawberries and tomatoes to crops such as root vegetables and grains, researchers are continually pushing boundaries. The future may witness hydroponics not only diversifying the range of cultivable crops but also addressing the escalating demand for sustainable food production in an efficient manner.
FAQS
What are the benefits of hydroponics?
Hydroponics offers several benefits, including increased crop yields, faster growth rates, and the ability to grow plants in areas with limited access to fertile soil. It also requires less water and eliminates the need for pesticides.
How does hydroponics contribute to sustainable food production?
Hydroponics promotes sustainable food production by using less land and water compared to traditional agriculture. It also eliminates soil erosion and reduces the need for chemical fertilizers and pesticides, making it an environmentally friendly farming method.
What role did NASA play in the development of hydroponics?
NASA’s research in hydroponics aimed to find sustainable food production methods for space missions. Their experiments led to the development of nutrient solutions and advanced hydroponic systems, which have now been adopted for use on Earth.
How does hydroponics fit into urban agriculture?
Hydroponics is well-suited for urban agriculture as it allows plants to be grown vertically and in controlled environments. This enables cultivation in small spaces such as rooftops, balconies, or even indoor settings, making it ideal for urban areas with limited land availability.
What is the concept of vertical farming?
Vertical farming is a farming technique that utilizes vertical space to grow crops in stacked layers, often in urban environments. Hydroponics plays a crucial role in vertical farming as it enables efficient use of space and resources, allowing for year-round production of fresh, local produce.
How has hydroponics evolved over time?
Hydroponics has evolved from ancient agricultural innovations such as the Hanging Gardens of Babylon to modern-day commercial agriculture and sustainable food production practices. Throughout history, advancements in technology and scientific understanding have led to the development of more efficient and sophisticated hydroponic systems.
How does hydroponics help in areas with poor soil quality?
Hydroponics eliminates the need for fertile soil as it allows plants to grow in nutrient-rich water solutions. This makes it ideal for areas with poor soil quality or contaminated land, where traditional farming methods may not be feasible.
Can hydroponics be used for organic farming?
Yes, hydroponics can be used for organic farming. While the use of synthetic fertilizers is common in hydroponics, organic nutrient solutions and natural pest control methods can be employed to meet the standards of organic farming.
What are some examples of ancient hydroponic practices?
Ancient hydroponic practices include the Hanging Gardens of Babylon, where plants were cultivated using a form of hydroponics, and the Aztec Floating Gardens, where crops were grown on rafts floating on water.
How does hydroponics contribute to water conservation?
Hydroponics consumes significantly less water compared to traditional soil-based farming. The water used in hydroponic systems is recirculated and reused, reducing water wastage and helping conserve this precious resource.

Pallavi Gupta is a burgeoning writer at SouthElMonteHydroponics, blending her passion for data analysis with a keen interest in biotechnology. Currently pursuing a Bachelor’s in Biotechnology at Amity University, Pallavi delves into the intricacies of life sciences while gaining hands-on experience in the exciting world of data analysis. Her unique background provides a fresh perspective on hydroponic farming, as she explores the intersection of biotechnology and sustainable agriculture. Through her writing, Pallavi aims to bridge the gap between data-driven insights and innovative farming practices, inspiring others to harness technology for a greener future.