Harvesting Potatoes: Unearthing Tasty Tubers
Preparing the Soil for Potato Harvesting
Preparing the soil for potato harvesting is a crucial step in ensuring a successful and bountiful crop. The quality of the soil directly impacts the growth and development of potatoes, as it provides the necessary nutrients, drainage, and structure for optimal root growth. Therefore, proper soil preparation is essential for maximizing yield and minimizing the risk of disease.
One of the first steps in preparing the soil for potato harvesting is conducting a soil test. This will help determine the pH level, nutrient content, and overall fertility of the soil. Based on the results, necessary amendments can be made to ensure the soil is balanced and suitable for potato cultivation. Adding organic matter, such as compost or well-rotted manure, can improve the soil’s structure and increase its ability to retain moisture and nutrients, promoting healthy root development. It is also important to remove any weeds or debris from the soil, as they can compete with potato plants for resources and harbor pests and diseases.

In addition to soil amendments, proper drainage is essential for growing healthy potatoes. Excessive moisture can lead to diseases like rot and fungal infections, which can significantly reduce crop yield. Therefore, it is important to ensure proper drainage by incorporating organic matter into heavy clay soils or installing drainage systems in areas prone to waterlogging. Additionally, hilling or ridging the soil around potato plants can help improve drainage and prevent tubers from sitting in waterlogged soil.
By taking the time to prepare the soil adequately before potato planting, gardeners and farmers can create an ideal growing environment that will support the development of healthy and productive potato plants. Whether you are cultivating a small backyard plot or managing a large-scale potato farm, investing in soil preparation is an essential step towards a successful potato harvest.
Choosing the Right Potato Varieties for Optimal Harvest
When it comes to choosing the right potato varieties for optimal harvest, there are several factors to consider. Each variety has unique characteristics that can affect its yield, taste, and overall suitability for different growing conditions. It is important to select varieties that are well-suited to your specific region and climate, as this can greatly impact their growth and productivity.
One key consideration is the maturity period of the potato variety. Some varieties are early maturing, meaning they reach harvestable size relatively quickly, while others are late maturing and take longer to reach their full potential. The choice between early and late maturing varieties will depend on various factors, such as your desired harvesting timeframe, local weather patterns, and the availability of storage facilities.
Another factor to consider is the intended use of the harvested potatoes. Certain varieties are better suited for specific culinary purposes, such as baking, boiling, or making into french fries. Understanding the end use of your potatoes can help you select the varieties that will deliver the desired taste and texture.
Furthermore, it is important to assess the disease resistance and overall health of different potato varieties. Some varieties are naturally more resistant to common potato diseases, such as blight or scab, which can greatly impact the quality and yield of your harvest. By selecting disease-resistant varieties, you can minimize the risk of crop loss and ensure a successful harvest.
In conclusion, choosing the right potato varieties for optimal harvest requires careful consideration of factors such as maturity period, culinary suitability, and disease resistance. By selecting varieties that align with your specific growing conditions and intended use, you can maximize the productivity and quality of your potato harvest. Consult with local experts, reference reliable sources, and consider past experiences to make informed decisions that will lead to successful potato cultivation.
Understanding the Different Stages of Potato Growth
Potatoes, a staple in many diets around the world, go through several distinct stages of growth before they are ready to be harvested. Understanding these stages is key to ensuring a successful potato harvest.
The first stage of potato growth is known as the sprouting or sprout emergence stage. At this point, small shoots begin to emerge from the seed potatoes planted in the soil. These shoots, commonly referred to as sprouts or eyes, are a sign that the potato plant is beginning to grow. As the sprouts continue to develop, they will eventually emerge from the soil surface.
The next stage is the vegetative stage, during which the potato plant focuses on building a strong foliage and root system. This stage is crucial for the plant’s ability to photosynthesize and gather energy from the sun. During this time, the potato plants will grow large, lush leaves and establish a network of roots beneath the soil surface.
Following the vegetative stage is the flowering stage, where the potato plants produce clusters of small, white or purple flowers. While not all potato varieties produce flowers, this stage is often considered a marker for the plant’s progression towards maturity.
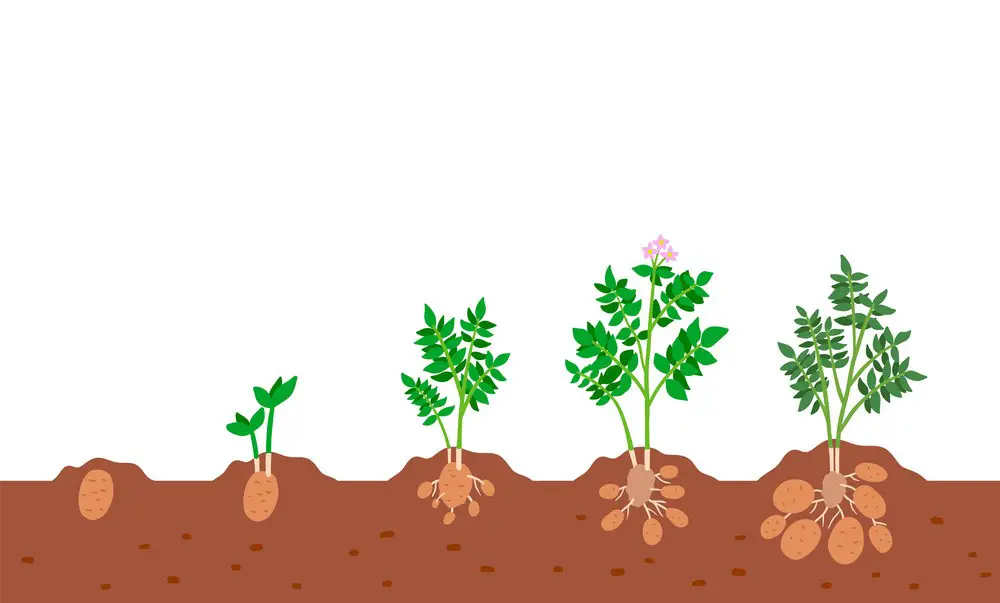

Finally, we reach the last stage, known as the maturity or tuberization stage. It is during this stage that the potatoes themselves begin to develop and grow underground. As the plant continues to draw nutrients from the soil, tubers begin to form and grow in size. Monitoring the maturity stage is crucial, as harvesting too early can result in underdeveloped potatoes, while harvesting too late may lead to excessive growth and oversized tubers.
Understanding the different stages of potato growth allows gardeners and farmers to time the harvest perfectly, ensuring a bountiful yield of high-quality potatoes. By correctly identifying the stages and employing appropriate care and maintenance practices, the journey from seed to harvest can be a rewarding and successful endeavor.
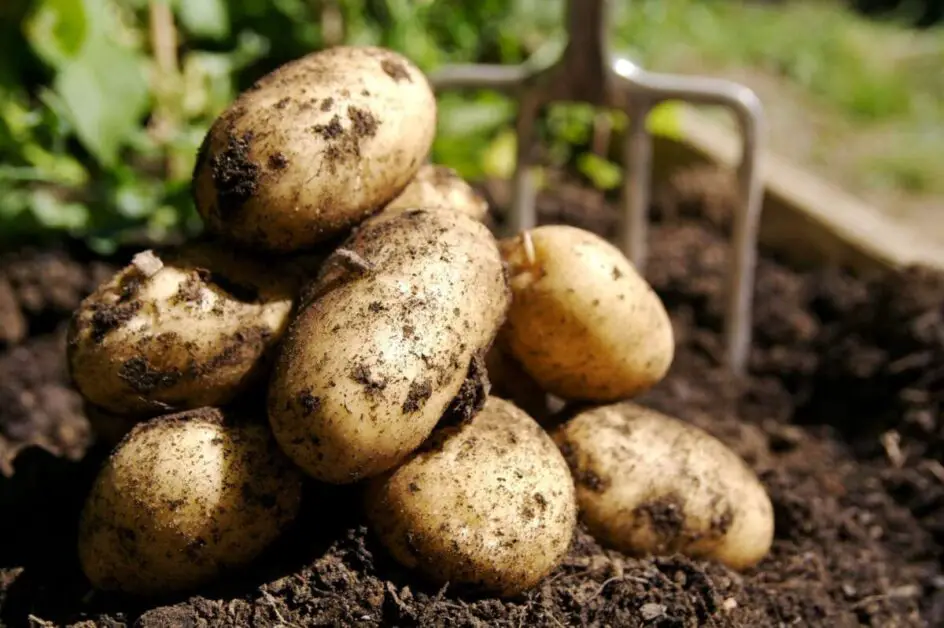
Signs That Potatoes Are Ready for Harvest
Determining the optimal time for potato harvesting is crucial to ensure a bountiful yield of high-quality tubers. Knowing the signs that potatoes are ready for harvest can help gardeners make informed decisions and maximize their crop.
One of the key indicators that potatoes are ready for harvest is the appearance of the foliage. Once the foliage starts to yellow and die back, it is a clear sign that the tubers have reached maturity. This is because the process of senescence, or the natural aging and deterioration of the plant, signifies that the potatoes have finished growing and have developed their full flavor and nutritional content.
Another important sign to look out for is the skin texture of the potatoes. When the skins become firm and set, not easily punctured or damaged, it is a clear indication that the tubers are ready for harvest. This firmness indicates that the potatoes have developed a protective skin layer, which helps to preserve their quality during storage. Additionally, the skin color of the potatoes can also provide valuable information. For most varieties, a healthy, vibrant color signals that the tubers are mature and ready to be harvested.
By paying close attention to the foliage and skin characteristics of the plants, gardeners can accurately determine when their potatoes are ready for harvest. Harvesting at the right time ensures that the tubers have reached their peak flavor and nutritional value, making the effort and hard work of potato cultivation truly rewarding. In the following sections, we will discuss the tools and equipment needed for potato harvesting as well as the steps for digging up and properly handling the freshly harvested tubers.
Here is a table that shows the signs of potato harvest:
| Sign | Description |
|---|---|
| Flowering | Potato plants typically flower before tubers are ready for harvest. This is an early indicator, but not definitive. |
| Foliage Browning | The foliage of potato plants will start to turn yellow and then brown as the tubers mature beneath the soil. |
| Skin Set | The skins of mature potatoes will become firm and set, making them more resistant to damage during harvesting. |
| Size | Mature potatoes will have reached their full size and will no longer be growing larger. They should be a suitable size for the variety you planted. |
| Skin Texture | Mature potatoes will have a relatively thick skin that is undamaged and smooth, rather than thin and easily damaged. |
| Digging Test | You can carefully dig up one or two test plants to check the size and quality of the potatoes. If they meet your expectations, it’s likely time to harvest the rest. |
Tools and Equipment Needed for Potato Harvesting
When it comes to harvesting potatoes, having the right tools and equipment is essential in ensuring a smooth and efficient process. Here are some of the key tools and equipment needed for potato harvesting:
1. Harvesting Fork: A harvesting fork, also known as a potato fork, is a must-have tool for lifting potatoes out of the ground. It features sturdy tines that penetrate the soil easily and minimize damage to the tubers.
2. Garden Shovel: A garden shovel is useful for digging up rows of potatoes and creating trenches for planting. Look for a shovel with a sharp edge and a comfortable grip to make the task easier.
3. Basket or Bucket: Once the potatoes are lifted from the ground, they need a place to be stored. A basket or bucket with a handle is ideal for collecting and transporting harvested potatoes.
4. Wheelbarrow: If you have a large potato harvest, a wheelbarrow can be a lifesaver. It allows you to easily transport a large quantity of potatoes from the garden to the storage area.
5. Gloves: Don’t forget to protect your hands with a good pair of gardening gloves. This will prevent blisters and keep your hands clean as you handle the soil and potatoes.

Remember, having the right tools and equipment can make all the difference in achieving a successful potato harvest. Investing in quality tools will not only save you time and effort but also contribute to the overall health and quality of your potatoes.
Steps for Digging Up Potatoes
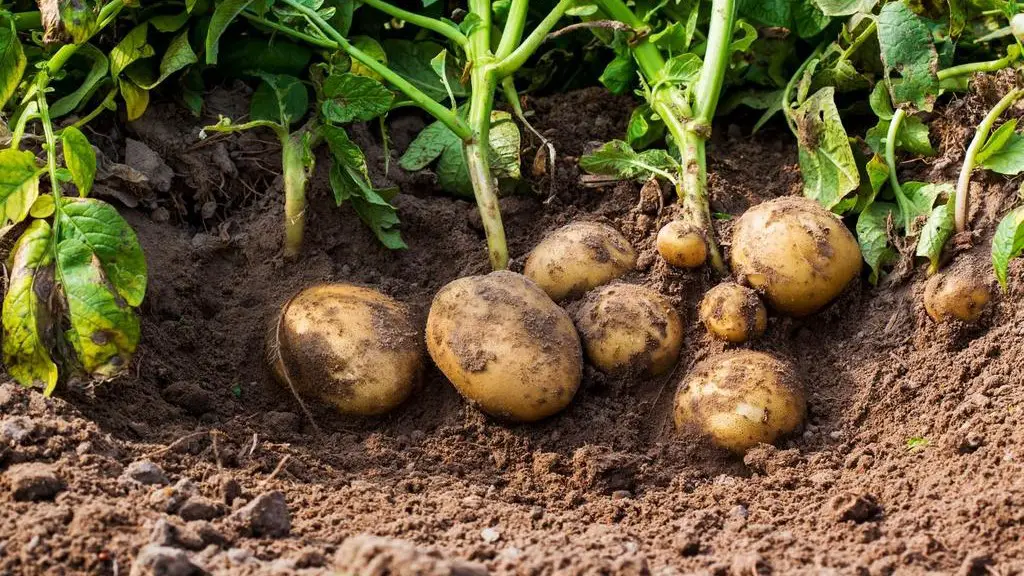
To ensure a successful potato harvest, it is important to properly dig up the potatoes when they are ready for harvest. This process requires some attention to detail, as mishandling can result in damage to the tubers. Here are the steps for digging up potatoes:
1. Prepare the area: Before digging up the potatoes, gently remove any weeds or debris from the soil surface around the plants. This will help prevent dirt and contaminants from getting mixed in with the harvested potatoes.
2. Loosen the soil: Starting a few inches away from the base of the plant, carefully insert a garden fork or a spade into the soil. Gently lift the tool to loosen the soil, being cautious not to damage the potatoes. Work your way around the plant, gradually moving closer to the base and lifting the soil as needed.
3. Lift the plants: Once the soil is loosened, carefully lift the entire plant out of the ground. Hold the plant by the stem or foliage, avoiding the tubers. If the potatoes are clustered close together, gently separate the plants to avoid any damage.
4. Inspect the harvest: Take a moment to inspect the potatoes you have just harvested. Remove any damaged or diseased tubers, as they can spoil the entire harvest. Set aside any potatoes with blemishes or wounds for immediate use, as they have a shorter storage life.
5. Cure the potatoes: After harvesting, it is important to allow the potatoes to cure for a short period. Place them in a well-ventilated area with temperatures between 45-60°F (7-15°C) and a humidity level of around 85%. This process helps to toughen the skin and prevent rot during storage.
Remember, the process of digging up potatoes requires gentleness and care to preserve the quality of the harvest. Following these steps will help ensure a successful potato harvest and allow you to enjoy the fruits of your labor.
Handling and Storing Freshly Harvested Potatoes
Handling and storing freshly harvested potatoes requires careful attention to ensure their longevity and quality. After digging up the potatoes from the soil, it is essential to handle them gently to avoid any damage and bruises. Rough handling can lead to the development of wounds, which can become entry points for bacteria and fungi, causing rot and spoilage.
Once the potatoes have been carefully handled, it is crucial to store them in optimal conditions to maintain their freshness and flavor. Potatoes are best stored in a cool, dark, and dry environment with proper ventilation. Exposing potatoes to light can cause them to turn green, indicating the presence of solanine, a naturally occurring toxic compound. This undesired green tint affects both the taste and quality of the potatoes. Additionally, excessive moisture can promote the growth of mold and mildew, leading to deterioration. Therefore, finding a balance between humidity levels and ventilation is essential for preserving the potatoes’ quality.
Tips for Cleaning and Curing Potatoes After Harvest
After the potatoes have been harvested, proper cleaning and curing techniques are crucial to ensure their long-term storage and maintain their quality. Here are some tips to help you effectively clean and cure your freshly harvested potatoes.
First, gently brush off any excess soil from the potatoes. It’s essential to be cautious and avoid damaging the skin, as this can lead to spoilage during the curing process. A soft-bristle brush or your hands can be used for this task.
Next, allow the potatoes to dry naturally for a few hours in a well-ventilated area. This step helps to remove any moisture on the surface and prevent the growth of bacteria or fungi.

Once the potatoes are dry, transfer them to a dark and cool place for the curing process. Curing involves storing the potatoes at a temperature range of 45-60°F (7-15°C) with high humidity for about two weeks. This allows the skin of the potatoes to thicken and heal, which aids in extending their shelf life and improving their flavor.
Proper air circulation is crucial during the curing process. Avoid overcrowding the potatoes and ensure there is enough space between them. It is best to place them in a single layer, allowing air to freely circulate and minimizing the risk of rotting or sprouting.
By following these tips for cleaning and curing your harvested potatoes, you can enhance their storage life and maintain their quality. Properly cured potatoes will stay fresh and flavorful for an extended period, allowing you to enjoy the fruits of your labor throughout the year.
How to Determine the Quality of Harvested Potatoes
Determining the quality of harvested potatoes is essential to ensure that you have a bountiful yield of delicious and nutritious tubers. There are a few key factors to consider when assessing the quality of your potatoes.
Firstly, you need to examine the skin of the potatoes. A healthy potato should have smooth, unblemished skin. Look out for any signs of damage, such as cuts, bruises, or discoloration, as these can indicate rot or disease. Additionally, take note of the color of the skin. While certain varieties may naturally have different skin colors, vibrant and consistent hues are generally a positive sign.
Next, it’s time to check the texture and firmness of the potatoes. Gently squeeze the tubers to ensure that they are firm and free from any soft or mushy areas. Soft pockets or sponginess may indicate decay or spoilage.
Another important aspect to consider is the size and shape of the potatoes. Depending on the variety, potatoes may come in various sizes and shapes. However, aim for uniformity within a batch. Large variations in size can indicate irregular growth or uneven conditions during cultivation.
Remember, the quality of harvested potatoes can greatly affect their taste, texture, and storability. By carefully evaluating the skin, texture, and size of the potatoes, you can ensure that you have a high-quality harvest that will bring joy to your culinary adventures.
Common Challenges and Solutions in Potato Harvesting
Potato harvesting can be a rewarding process for gardeners and farmers alike. However, it is not without its challenges. One common challenge in potato harvesting is dealing with potato diseases and pests. Potatoes are susceptible to a variety of diseases, such as late blight, early blight, and blackleg. These diseases can greatly reduce the yield and quality of the harvested potatoes. Similarly, pests like Colorado potato beetles and wireworms can cause significant damage to the crops.
To overcome these challenges, it is important to implement preventive measures and adopt integrated pest management strategies. Crop rotation is an effective practice that helps reduce the risk of diseases and pests. By rotating potatoes with other crops, such as legumes or grains, the buildup of specific pathogens and pests can be minimized. Additionally, regular inspection and monitoring of the potato plants for signs of diseases or pests can help in early detection and prompt action. Using organic pest control methods, such as introducing beneficial insects, using insecticidal soaps, or applying neem oil, can also help manage pests without harmful effects on the environment.
Another challenge in potato harvesting is the issue of storage and proper handling of freshly harvested potatoes. Potatoes are living organisms and are prone to deterioration if not stored correctly. Factors such as temperature, humidity, and light exposure can greatly affect their quality and shelf life. One common issue is the formation of sprouts, which can lead to an undesirable texture and taste. To address this, it is important to store potatoes in a cool, dark, and well-ventilated area. It is recommended to keep the temperature between 45 to 50 degrees Fahrenheit (7 to 10 degrees Celsius) and humidity between 85 to 90 percent to inhibit sprouting.
Additionally, sorting and handling potatoes carefully during harvesting and storage is crucial. Damaged or bruised potatoes should be separated and used promptly to prevent the spread of rot. Regularly inspecting stored potatoes and removing any spoiled or infected ones can help maintain the quality of the remaining crop. By understanding the common challenges in potato harvesting and implementing effective solutions, gardeners and farmers can ensure a successful and bountiful harvest of this versatile and nutritious crop.
The table below shows us some of the challenges that can be seen in potato harvesting:
| Challenge | Description |
|---|---|
| Soil Conditions | Wet or compacted soil can make it difficult to dig up potatoes without damaging them or the plants. It may also cause tubers to rot if left in damp conditions for too long. |
| Pest Damage | Pests such as wireworms, slugs, and potato beetles can damage potato plants and tubers, reducing yield and quality. |
| Disease | Diseases such as late blight, early blight, and blackleg can affect potato plants and tubers, leading to reduced yields and increased susceptibility to rot during storage. |
| Storage Challenges | Potatoes need to be stored in cool, dark, and well-ventilated conditions to prevent sprouting, rot, and disease. Improper storage can lead to significant losses. |
| Mechanical Damage | Mechanical harvesters or digging tools can cause damage to potato tubers if used improperly or in unsuitable conditions, leading to reduced quality and yield. |
| Greening | Exposure to sunlight can cause potatoes to develop green spots, which contain toxic compounds called solanine. Green potatoes should not be consumed. |
| Size and Shape Variation | Harvesting potatoes with consistent size and shape can be challenging, especially with irregularly shaped tubers or when using mechanical equipment. |
| Timing | Harvesting too early can result in underdeveloped potatoes, while waiting too long may lead to tubers becoming oversized, woody, or susceptible to disease and pests. |
| Labor Intensive | Harvesting potatoes can be labor-intensive, especially on larger scales or when using traditional hand methods, requiring significant time and effort. |
| Storage Rot and Sprouting | Improper storage conditions, such as high humidity or temperature fluctuations, can lead to rotting or premature sprouting of potatoes, reducing their shelf life. |
The Role of Crop Rotation in Potato Harvesting
Crop rotation plays a crucial role in potato harvesting, as it is a key practice that helps maintain soil health and prevent the buildup of pests and diseases. Rotating the potato crops with other non-related crops can help break the cycle of pests and diseases that specifically target potatoes. By introducing different crop varieties into the rotation, the balance of nutrients in the soil can be maintained, reducing the risk of nutrient imbalances and depletion.
One of the primary benefits of crop rotation in potato harvesting is the reduction in pest and disease pressure. Certain pests and diseases have a specific host range, and by rotating potatoes with other crops, the breeding grounds and food sources for these pests and diseases are interrupted. This can help minimize the need for chemical interventions and promote a healthier, more sustainable approach to potato cultivation.
Additionally, crop rotation can also have a positive impact on soil fertility. Different crops have different root structures and nutrient requirements. By rotating potatoes with crops that have different root depths and nutrient needs, the soil can be replenished with a more diverse range of nutrients. This helps prevent nutrient imbalances and promotes a healthier, more fertile soil, ultimately leading to improved potato yields.
In conclusion, incorporating crop rotation practices into potato harvesting can have a significant impact on the overall success of the crop. By reducing pest and disease pressure and maintaining soil fertility, growers can optimize their potato production while minimizing the need for chemical interventions and promoting sustainable farming practices.
Sustainable Practices for Potato Harvesting
In order to ensure sustainable practices for potato harvesting, it is important to take into consideration factors such as soil health, water conservation, and reduced chemical usage. One approach is to focus on building and maintaining healthy soil through the use of organic matter and cover crops. Adding compost or manure to the soil helps improve its structure, fertility, and water-holding capacity, enabling optimal growth for potato plants. Additionally, intercropping with nitrogen-fixing plants like legumes can help reduce the need for synthetic fertilizers, as these plants naturally add nitrogen back into the soil.
Water conservation plays a vital role in sustainable potato harvesting. Efficient irrigation techniques, such as drip irrigation or using moisture sensors, can minimize water waste and ensure that potatoes receive just the right amount of moisture they need. By employing these methods, growers can reduce water consumption and ultimately contribute towards preserving water resources. Furthermore, incorporating mulching techniques can help retain soil moisture, suppress weed growth, and improve soil temperature regulation, resulting in healthier potato plants and increased water efficiency.
Creative Recipes and Ideas for Cooking Freshly Harvested Potatoes
Cooking freshly harvested potatoes provides a world of culinary possibilities. The earthy flavor and creamy texture of these spuds make them a versatile ingredient that can be used in a variety of dishes. One popular way to enjoy these potatoes is by simply boiling or roasting them and serving them as a side dish with a sprinkle of salt and a pat of butter. This allows the natural flavors of the potatoes to shine and pairs well with a wide range of main courses.
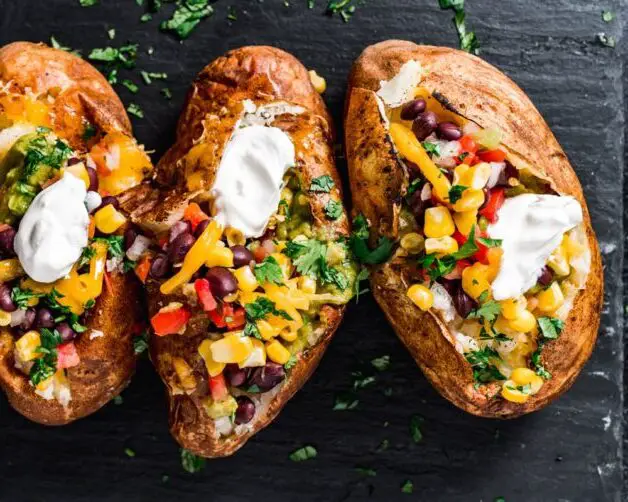
For those looking to get a bit more creative in the kitchen, there are plenty of other delicious recipes to try. How about some crispy potato wedges seasoned with herbs and spices, or a cheesy potato gratin layered with creamy sauce? If you’re in the mood for something comforting, a classic potato soup or a hearty potato and leek stew will hit the spot. For a more exotic twist, you can make a batch of spicy potato samosas or whip up some crispy potato croquettes. The possibilities are truly endless when it comes to cooking with freshly harvested potatoes.
The Health Benefits of Potatoes and How They Are Enhanced by Proper Harvesting
Potatoes, a staple in many cuisines around the world, offer a multitude of health benefits when harvested and consumed properly. These nutrient-rich tubers are an excellent source of carbohydrates, vitamins, and minerals. They are also low in fat and calories, making them a healthy option for those looking to maintain or lose weight.
One of the key factors in enhancing the health benefits of potatoes lies in their proper harvesting. Harvesting potatoes at the right time ensures that they retain their nutritional value and taste. When potatoes are harvested immature, they may lack in flavor and nutrients. On the other hand, if potatoes are left in the ground for too long, they can become overripe and lose their desired texture and taste.
Proper harvesting involves closely monitoring the growth stages of potatoes and determining the optimal time for harvest. This can be determined by observing the foliage and the maturity of the tubers. Potatoes should be harvested when the tops of the plants start to turn yellow and wither, indicating that they have reached their full potential. Additionally, the skin of the tubers should be firm and easily separable from the flesh. Harvesting at this stage ensures that the potatoes have developed the right balance of starches and sugars, resulting in a flavorful and nutritious harvest.
Watch this video to learn more about potato harvesting in your garden.
The Economic Significance of Potato Harvesting in Agriculture
Potato harvesting holds immense economic significance in the field of agriculture. Potatoes are one of the world’s most widely grown and consumed crops, contributing significantly to global food security and economic prosperity. The economic impact of potato harvesting can be witnessed through multiple lenses, including job creation, market value, and export opportunities.
One of the key economic drivers of potato harvesting is job creation. Potatoes require manual labor at various stages, from planting to harvesting, providing employment opportunities for a large number of people. In regions heavily reliant on agriculture, the potato industry plays a vital role in sustaining livelihoods and boosting local economies. Additionally, the demand for potato-related products, such as processed foods, snacks, and starch, further drives employment in various sectors of the food industry.
Moreover, the market value of potatoes cannot be underestimated. Potatoes are a staple food in many parts of the world and their steady demand ensures a consistent market for farmers. The economic significance is not limited to fresh potatoes alone; the processing industry, which transforms potatoes into value-added products like chips and fries, contributes substantially to the overall economic impact. The versatile nature of potatoes allows for the development of various consumer goods, creating a diverse and robust market for farmers and manufacturers alike.
Furthermore, the potato industry plays a significant role in international trade, driving economic growth through exports. Many countries rely on potato exports to generate revenue and strengthen their trade relationships. The global demand for potatoes, combined with their long shelf life and ease of transportation, makes them an attractive commodity for export. This not only contributes to the economic well-being of potato-producing regions but also fosters collaboration and cooperation between nations.
In conclusion, the economic significance of potato harvesting in agriculture cannot be overlooked. Its contribution to job creation, market value, and international trade highlights its importance as a vital crop with immense economic potential. As we delve further into this topic, we will explore the various aspects of potato harvesting and uncover the strategies and practices employed to maximize its economic benefits.
Case Studies and Success Stories in Potato Harvesting Techniques.
In the field of potato harvesting techniques, case studies and success stories serve as valuable resources that offer practical insights into effective methods and innovative approaches. These real-world examples highlight the application of scientific principles and the successful implementation of strategies, providing inspiration and guidance for gardening enthusiasts looking to improve their potato harvests.
One notable case study comes from a potato farm in the highlands of Idaho, where a combination of precision planting and careful management practices led to a significant increase in yield. By utilizing state-of-the-art planting machinery that ensured consistent seed spacing and depth, the farm achieved more uniform plant growth and reduced the competition for nutrients and water. Additionally, employing advanced irrigation and nutrient management techniques, such as drip irrigation and fertigation, allowed for precise control over the water and nutrient supply, resulting in healthier plants and higher tuber production.
Another success story originates from a small-scale organic operation located in Vermont. Facing the challenge of limited space and a desire to promote sustainable practices, the farm adopted a vertical gardening system for their potato crop. By utilizing vertical towers with multiple layers, they maximized their land use efficiency while still providing optimal growing conditions for the plants. This innovative approach not only increased their harvest yield but also minimized pest and disease issues, as the plants’ upward growth reduced contact with soil-borne pathogens.
These case studies exemplify the diverse range of strategies and techniques employed by potato farmers to enhance their harvests. By learning from these success stories, gardening enthusiasts can adapt and implement similar approaches in their own gardens, improving their chances of a bountiful potato harvest.
How long does it take for potatoes to mature before harvest?
The time it takes for potatoes to mature before harvest can vary depending on the variety and growing conditions. On average, it takes about 70 to 120 days from planting to harvesting.
Are there specific signs to look for to determine if potatoes are ready for harvest?
Yes, there are several signs that indicate potatoes are ready for harvest. These include the plant foliage turning yellow and dying back, the skin of the potatoes becoming firm, and the potatoes reaching their desired size.
What tools and equipment are needed for potato harvesting?
Some common tools and equipment needed for potato harvesting include a digging fork or shovel, a potato fork or rake, buckets or containers for collecting the harvested potatoes, and a storage area or bins for storing the harvested potatoes.
How should freshly harvested potatoes be handled and stored?
Freshly harvested potatoes should be handled with care to avoid damage. They should be stored in a cool, dark, and well-ventilated area to prevent sprouting and spoilage. It is best to store them in containers or bags that allow for air circulation.
What are some common challenges in potato harvesting and their solutions?
Common challenges in potato harvesting include damage from pests and diseases, mechanical or weather-related damage during harvesting, and storage issues. Solutions include implementing pest control measures, using proper harvesting techniques, and ensuring proper storage conditions.
What is the role of crop rotation in potato harvesting?
Crop rotation is important in potato harvesting as it helps prevent the buildup of pests and diseases in the soil. By rotating potatoes with other crops, the risk of soilborne pathogens and pests affecting the potato harvest is reduced.
Can you provide some sustainable practices for potato harvesting?
Some sustainable practices for potato harvesting include using organic fertilizers and pesticides, practicing water conservation, implementing integrated pest management strategies, and adopting crop rotation techniques.
What are some creative recipes and ideas for cooking freshly harvested potatoes?
There are numerous creative recipes and ideas for cooking freshly harvested potatoes. Some popular options include roasted potatoes, mashed potatoes, potato salads, potato soups, and potato gnocchi.
What are the health benefits of potatoes and how are they enhanced by proper harvesting?
Potatoes are a good source of carbohydrates, fiber, and various vitamins and minerals. Proper harvesting ensures that the potatoes retain their nutritional value and taste, enhancing their health benefits.
What is the economic significance of potato harvesting in agriculture?
Potato harvesting is economically significant in agriculture as potatoes are a widely consumed and versatile crop. They contribute to the agricultural industry by providing income for farmers, creating job opportunities, and contributing to the overall economy through trade and export.







