Powdery Mildew Treatment And Prevention with 10 steps
Table of Contents
1) Introduction to the Fungal Disease: powdery mildew
Powdery mildew is a common fungal disease that affects a wide range of plants, including ornamentals, fruits, and vegetables. This disease is caused by various species of fungi belonging to the order Erysiphales. It is characterized by the appearance of a white or grayish powdery substance on the leaves, stems, and sometimes even the flowers of infected plants.
Powdery mildew can cause significant damage to affected plants, resulting in reduced growth, yield, and overall plant health. Additionally, it can negatively impact the aesthetic appeal of ornamental plants, making them less desirable for landscaping purposes. It is essential for gardeners and plant enthusiasts to have a good understanding of this disease and its management strategies in order to minimize its impact and maintain healthy plants.
In the following sections, we will delve into the identification of powdery mildew, the environmental factors that contribute to outbreaks, cultural practices to prevent its occurrence, as well as organic and chemical methods for control. By implementing these strategies, we can effectively manage powdery mildew and help our plants thrive.

2) Identifying Powdery Mildew: Recognizing Symptoms and Affected Plants
Powdery mildew is a common fungal disease that affects a wide range of plants, including ornamentals, vegetables, and fruit trees. It is characterized by the appearance of a white powdery coating on the leaves, stems, and sometimes even the flowers of affected plants. This coating is actually a mass of fungal spores that spread easily and can quickly infect nearby plants.
One of the key symptoms of powdery mildew is the presence of white, powdery spots or patches on the leaves. These spots can start off small but progressively increase in size as the fungal infection spreads. The leaves may also become distorted or stunted, and in severe cases, they may turn yellow or brown and eventually wither. It’s important to note that the appearance of powdery mildew can vary depending on the plant species, so it’s essential to familiarize yourself with the specific symptoms associated with the plants you are dealing with.
Affected plants may include a wide variety of species, and some are more susceptible to powdery mildew than others. Common plants that are often affected by this fungal disease include roses, cucumbers, squash, zucchini, melons, beans, and many ornamental flowers. Powdery mildew can thrive in both humid and dry environments, making it a persistent threat regardless of the climate. In order to effectively manage and prevent powdery mildew outbreaks, it is crucial to recognize the symptoms and affected plants early on, as this will allow for prompt and targeted intervention measures.
3) Environmental Factors Contributing to Powdery Mildew Outbreaks
Environmental factors play a crucial role in influencing the outbreaks of powdery mildew, a common fungal disease that affects many plants. One contributing factor to the prevalence of powdery mildew is high humidity levels. Fungi thrive in environments with moisture, and a humid climate provides the ideal conditions for their growth and reproduction. The spores of powdery mildew can easily spread through the air in such conditions, increasing the risk of infection for susceptible plants. Additionally, poor air circulation in gardens or greenhouses can exacerbate the problem by trapping the moisture and preventing it from dissipating.
Another environmental factor that contributes to powdery mildew outbreaks is inadequate sunlight. Powdery mildew tends to flourish in shaded areas where plants receive little direct sunlight. The lack of sunlight hampers the plant’s ability to dry out and create an unfavorable environment for fungal growth. This is especially true for plants that are densely packed together or located under overhanging vegetation, as they are more likely to experience restricted sunlight exposure. Furthermore, plants that are grown in areas with insufficient light may have weakened immune systems, making them more vulnerable to powdery mildew infections.
Understanding these environmental factors is crucial in preventing and managing powdery mildew outbreaks. By addressing issues related to humidity and sunlight, gardeners can create an environment that is less favorable for powdery mildew development. Additionally, implementing cultural practices and integrated pest management strategies (discussed in subsequent sections) can further mitigate the impact of these environmental factors on the occurrence of powdery mildew.
4) Cultural Practices to Prevent Powdery Mildew: Maintaining Healthy Plants
Cultural practices play a crucial role in preventing and managing powdery mildew outbreaks in plants. By maintaining healthy plants, gardeners can significantly reduce the risk of infection and promote overall plant vigor. One essential cultural practice is regular monitoring of plants, especially during periods of high humidity and temperature. This allows gardeners to promptly identify any signs of powdery mildew and take appropriate action.
Another important aspect of maintaining healthy plants is ensuring proper air circulation. Powdery mildew thrives in still, stagnant air, so it is recommended to space plants adequately to allow for good airflow. This can be achieved by pruning branches and thinning out crowded areas. Additionally, avoiding excessive use of nitrogen-rich fertilizers can help prevent the rapid growth of susceptible plant tissues, making them less vulnerable to powdery mildew. By implementing these cultural practices, gardeners can create an environment that discourages powdery mildew growth and promotes the overall well-being of their plants.
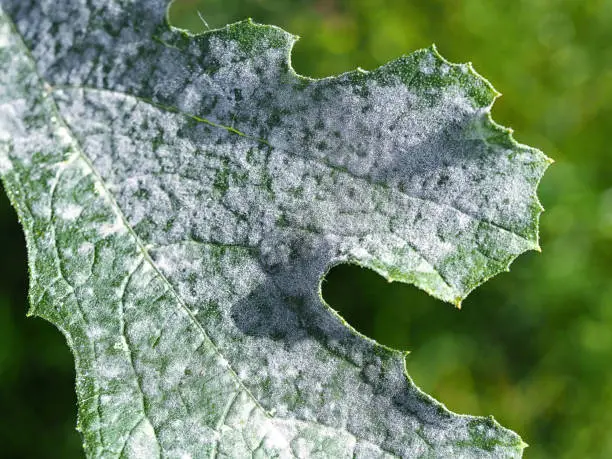

5) Proper Plant Selection and Placement to Minimize Powdery Mildew Risk
Proper plant selection and placement play a crucial role in minimizing the risk of powdery mildew. When choosing plants for your garden or landscape, it is important to consider their susceptibility to powdery mildew. Some plant species are naturally more resistant to the disease, while others are highly susceptible. By opting for resistant varieties, you can significantly reduce the likelihood of powdery mildew outbreaks.
Additionally, the placement of plants in your garden can impact their susceptibility to the disease. Proper spacing is key, as it allows for better air circulation and sunlight penetration, which can help prevent the growth and spread of powdery mildew. Avoid overcrowding plants, as this can create favorable conditions for the disease to thrive. Similarly, consider placing plants in areas with adequate sunlight exposure, as powdery mildew tends to be more prevalent in shaded or poorly ventilated locations.
When making plant selections and deciding on their placement, consult with local extension offices, nurseries, or gardening experts. They can provide valuable insight into the powdery mildew resistance of different plant varieties and offer specific recommendations based on your region’s climate and environmental conditions. Taking the time to carefully choose and position plants can go a long way in minimizing the risk of powdery mildew and helping you maintain a vibrant and healthy garden.

6) Irrigation and Watering Techniques to Reduce Powdery Mildew Infection
Irrigation and watering techniques play a crucial role in reducing the risk of powdery mildew infection in plants. Proper moisture management is essential to create an environment less favorable for the growth and spread of this fungal disease. Overhead irrigation, such as sprinklers, should be avoided as it can create a humid microclimate on the foliage, promoting the development of powdery mildew. Instead, drip irrigation or soaker hoses can be used to deliver water directly to the root zone, minimizing moisture on the leaves.
Another important consideration is the timing of watering. It is recommended to water plants in the morning so that the foliage has enough time to dry during the day. Moist leaves for an extended period can become a breeding ground for powdery mildew spores. Additionally, watering should be done at the base of the plants, keeping the foliage as dry as possible. By following these irrigation and watering practices, gardeners can significantly reduce the risk of powdery mildew infection and maintain healthier plants.
7) Organic Approaches for Powdery Mildew Control: Natural Remedies
Organic approaches for powdery mildew control offer gardeners a natural and environmentally friendly alternative to chemical treatments. These natural remedies focus on preventing and managing powdery mildew outbreaks using substances derived from plants and other organic materials. One effective natural remedy is neem oil, which is extracted from the seeds of the neem tree. Neem oil has been shown to have antifungal properties that can inhibit the growth and spread of powdery mildew on plants. It works by disrupting the life cycle of the fungus, preventing spore germination and reducing further infection. Neem oil can be easily mixed with water and sprayed onto the affected plants, providing an effective and safe solution.
Another natural remedy that has gained popularity in powdery mildew control is a mixture of baking soda and water. Baking soda has been shown to have fungicidal properties, making it an effective treatment for powdery mildew. By altering the pH on the leaf surface, baking soda creates an environment that is unfavorable for the growth and development of the fungus. To prepare the mixture, simply dissolve one tablespoon of baking soda in one gallon of water and spray it onto the affected plants. It is important to note that this remedy should not be used too frequently, as excessive use of baking soda can lead to leaf burn.
8) Chemical Methods for Powdery Mildew Management: Fungicides and Their Application
Fungicides play a crucial role in the management of powdery mildew, a fungal disease that can wreak havoc on plants. These chemical compounds are specifically designed to target and eradicate the culprit fungi that cause powdery mildew. When applied correctly, fungicides can effectively control and prevent the spread of the disease, leading to healthier and more productive plant growth.
There are various types of fungicides available in the market, each with its own mode of action and application method. Contact fungicides, for instance, work by coming into direct contact with the fungal spores, inhibiting their growth and development. On the other hand, systemic fungicides are absorbed by the plant, allowing the chemical to circulate within its tissues, thereby providing extended protection against powdery mildew. Selecting the appropriate fungicide and understanding its mode of action are critical in ensuring successful powdery mildew management. Furthermore, proper application techniques are essential to maximize the effectiveness of the fungicide and minimize potential harm to the environment.
9) Integrated Pest Management Strategies for Long-Term Powdery Mildew Prevention
Integrated Pest Management (IPM) strategies play a vital role in preventing and managing powdery mildew in the long term. By combining various techniques, gardeners and farmers can effectively minimize the impact of this fungal disease on their plants. One essential aspect of IPM is regular monitoring and scouting for signs of powdery mildew infestation. This involves inspecting plants regularly and identifying the characteristic white, powdery patches on leaves, stems, and flowers.
Once powdery mildew is detected, it is important to promptly take action to prevent its further spread. A key component of IPM is cultural practices that promote plant health and reduce conditions favorable for powdery mildew development. Proper pruning techniques, such as thinning overcrowded foliage and removing infected plant parts, can help improve air circulation and reduce humidity levels, which are conducive to the growth of powdery mildew. Additionally, practicing good sanitation, including removing fallen leaves and debris, can further prevent the disease from spreading and overwintering.
10) Seasonal Powdery Mildew Prevention: Precautions for Different Times of the Year.
Seasonal Powdery Mildew Prevention: Precautions for Different Times of the Year
Managing powdery mildew requires a proactive approach that takes into account the changing seasons. By understanding the specific precautions for each time of the year, gardeners can minimize the risk of powdery mildew outbreaks and keep their plants healthy and vibrant.
During the spring, when temperatures start to rise and plants begin to emerge from their winter dormancy, it is crucial to focus on preventative measures. Regularly inspecting plants for early signs of powdery mildew, such as white powdery spots on leaves or stems, is essential. Pruning and removing any infected plant parts can help prevent the disease from spreading. Additionally, ensuring optimal air circulation by spacing plants appropriately can reduce humidity levels, which inhibits the growth and spread of powdery mildew spores. Gradually increasing irrigation frequency while avoiding overhead watering can also contribute to a healthier growing environment.
As the summer months approach and temperatures soar, gardeners must be vigilant in their powdery mildew prevention efforts. Providing adequate shading and mulching can help regulate soil temperatures, preventing excessive heat stress on plants and reducing the chances of powdery mildew outbreaks. Regularly monitoring moisture levels in the soil and adjusting watering practices accordingly is crucial during this time, with a focus on promoting deep root growth rather than surface moisture. Removing any fallen leaves or debris from the garden bed can also discourage powdery mildew spores from finding suitable breeding grounds. Lastly, being mindful of overcrowding plants and promoting proper air circulation can prevent the humid microenvironments that powdery mildew thrives in.
Remaining mindful of the changing seasons and tailoring preventative measures accordingly is key to effective powdery mildew management. In the next section, we will explore additional strategies and techniques that gardeners can implement to keep their plants protected from this common fungal disease.
What is powdery mildew?
Powdery mildew is a fungal disease that affects a wide range of plants, characterized by a white powdery coating on the leaves, stems, and flowers.
How can I identify powdery mildew on my plants?
Look for symptoms such as white powdery patches, distorted growth, yellowing or browning of leaves, and premature leaf drop.
What environmental factors contribute to powdery mildew outbreaks?
Powdery mildew thrives in areas with high humidity, low air circulation, and moderate temperatures. Overcrowding of plants and poor sunlight exposure can also contribute to outbreaks.
What cultural practices can help prevent powdery mildew?
Maintaining good plant hygiene, such as removing infected plant material and debris, promoting proper air circulation, and avoiding overhead watering, can help prevent powdery mildew.
How can plant selection and placement minimize the risk of powdery mildew?
Choosing powdery mildew-resistant plant varieties and placing them in areas with optimal sunlight exposure can reduce the risk of infection.
What irrigation and watering techniques can reduce powdery mildew infection?
Watering plants at the base rather than overhead, using drip irrigation or soaker hoses, and watering early in the day to allow foliage to dry can help minimize powdery mildew infection.
Are there any organic remedies for powdery mildew control?
Yes, organic approaches such as neem oil, baking soda, sulfur, and milk solutions can be used as natural remedies to control powdery mildew.
What are the chemical methods for powdery mildew management?
Fungicides specifically formulated to target powdery mildew can be used as a chemical method for managing the disease. Follow the instructions and safety precautions provided by the manufacturer.
What is integrated pest management for long-term powdery mildew prevention?
Integrated pest management involves combining various preventive measures, cultural practices, organic remedies, and chemical methods in a holistic approach to control and prevent powdery mildew in the long term.
What precautions should be taken for seasonal powdery mildew prevention?
Different times of the year may require specific precautions for preventing powdery mildew. These can include adjusting cultural practices, increasing air circulation, and implementing preventative treatments based on the specific needs of the season.

Beck Wakeford is a dedicated writer at SouthElMonteHydroponics, with a fervent enthusiasm for agriculture and technological innovation. Armed with a degree in Agricultural Engineering from a leading university, Beck specializes in hydroponic systems design, automation, and optimization. Their passion for merging traditional farming with cutting-edge technology drives them to explore novel solutions for sustainable food production. Beck’s expertise and keen interest in the intersection of engineering and agriculture make them a valuable asset in the quest for efficient and eco-friendly farming practices. Through their writing, Beck aims to inspire others to embrace the potential of hydroponics in shaping a more sustainable future.