Southern Staple: Growing Collard Greens
Did you know that collard greens have been a staple in Southern cuisine for centuries? These leafy greens are not only delicious, but they’re also packed with nutrients like vitamin K, vitamin A, and calcium. But have you ever tried growing your own collard greens? It’s easier than you might think!
In this blog post, we’ll take a closer look at how to grow collard greens in your own backyard. We’ll cover everything from the best time to plant them to how to care for them once they’ve sprouted. Whether you’re a seasoned gardener or just starting out, this guide will provide you with the knowledge and expertise you need to grow healthy and delicious collard greens.
Not only is growing your own collard greens a fun and rewarding experience, but it’s also a great way to ensure that you’re eating fresh and healthy produce. Plus, you’ll be able to impress your friends and family with your gardening skills!
So, are you ready to become a collard green growing expert? Let’s get started!
Table of Contents
The History of Collard Greens in the Southern United States
Collard greens have long been an integral part of the culinary and cultural heritage of the Southern United States.
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/how-to-grow-collard-greens-4125810-4-847bc13d938642278653de04a6071358.jpg)
- Historical Roots: Collard greens have a rich history dating back to the arrival of African slaves in America, with their culinary tradition believed to originate from West African cooking practices.
- Survival and Sustenance: During the era of slavery, collard greens served as a crucial source of sustenance for African-American families. Enslaved individuals cultivated collard greens in their gardens to ensure a reliable source of nutrition for themselves and their families.
- Post-Emancipation Tradition: After emancipation, the tradition of growing and cooking collard greens persisted among African-American communities in the South. They remained an affordable and easily accessible food, contributing to the cultural and culinary heritage of the region.
- Southern Culinary Staple: Collard greens became deeply ingrained in Southern culinary traditions, transcending racial boundaries to become a beloved staple in Southern cuisine.
- Versatile Preparation: Collard greens are prepared in various ways, including braised with ham hocks, simmered with onions and garlic, or combined with other greens, showcasing their versatility and adaptability in Southern cooking.
Overall, collard greens symbolize resilience, cultural heritage, and the enduring legacy of African-American culinary traditions in the American South.
Understanding the Nutritional Value of Collard Greens
Collard greens are not only a delicious addition to your plate, but they also offer numerous health benefits. Packed with essential vitamins and minerals, collard greens are a nutritional powerhouse that can contribute to your overall well-being.

- High Vitamin C Content: Collard greens are packed with vitamin C, boasting over 42 milligrams per cup when cooked. This amount provides more than 70% of the daily recommended intake for adults. Vitamin C is renowned for its immune-boosting properties, helping to shield the body against illnesses and infections.
- Vitamin K Powerhouse: Just one cup of cooked collard greens contains a remarkable 1028 micrograms of vitamin K, nearly 1300% of the recommended daily intake for adults. Vitamin K is essential for blood clotting and bone health, playing a vital role in maintaining overall bodily function.
- Rich in Essential Nutrients: Collard greens offer an array of other crucial nutrients, including vitamin A, calcium, and fiber. Vitamin A supports healthy vision and skin, while calcium promotes strong bones and teeth. The fiber content aids digestion and helps regulate cholesterol levels.
Incorporating collard greens into your diet is a smart and nutritious choice. Whether you choose to enjoy them steamed, sautéed, or as an ingredient in your favorite recipes, you can savor the taste while reaping the many nutritional benefits they offer.
Selecting the Right Variety of Collard Greens for Your Garden
When selecting the right variety of collard greens for your garden, it is important to consider factors such as climate, soil conditions, and personal preferences. Collard greens come in various cultivars, each offering unique characteristics and benefits. Some popular varieties include Georgia Southern, Vates, Champion, and Morris Heading.
| Variety | Advantages | Characteristics |
|---|---|---|
| Champion | – High yields. – Slow to bolt. – Large, dark blue-green leaves. – Good post-harvest storage. | – Matures in about 75 days. – Height: 24-36 inches. – Spread: About 30 inches. |
| Ellen Felton Dark | – Heirloom variety with tender and flavorful dark green leaves. – Passed down through generations. | – Matures in 60-80 days. – Height: 15-22 inches. – Spread: 22-35 inches. |
| Georgia | – Tolerant of both heat and cold. – Flavor improves with light frost. | – Matures in 65-70 days. – Height: 24-36 inches. – Smooth, slightly wrinkled dark blue-green leaves. |
| Morris Heading | – Bolt-resistant. – Grows relatively quickly. | – Characteristics not specified. |
| Old Timey Blue | – None listed. | – Characteristics not specified. |
| Tiger Hybrid | – None listed. | – Characteristics not specified. |
| Vates | – None listed. | – Characteristics not specified. |
As you determine the best variety for your garden, consider factors such as your local climate, available space, and desired taste. Additionally, consult with local nurseries, agricultural extension offices, or fellow gardeners for recommendations specific to your region. By selecting the right variety, you can ensure a successful and bountiful harvest of collard greens in your garden.
Preparing the Soil for Growing Collard Greens
Preparing the soil is a crucial step in successfully growing collard greens. This leafy vegetable thrives in well-drained, nutrient-rich soil, so it’s important to create the right conditions for optimal growth. Start by clearing the area of any debris or weeds, ensuring that the soil is free from competing vegetation. This will prevent any unwanted competition for nutrients and water.

By adequately preparing the soil and creating an optimum environment, you will set the stage for successful collard green cultivation. The nutrient-rich soil will provide the necessary foundation for healthy plants, ensuring their ability to flourish and produce an abundant harvest.
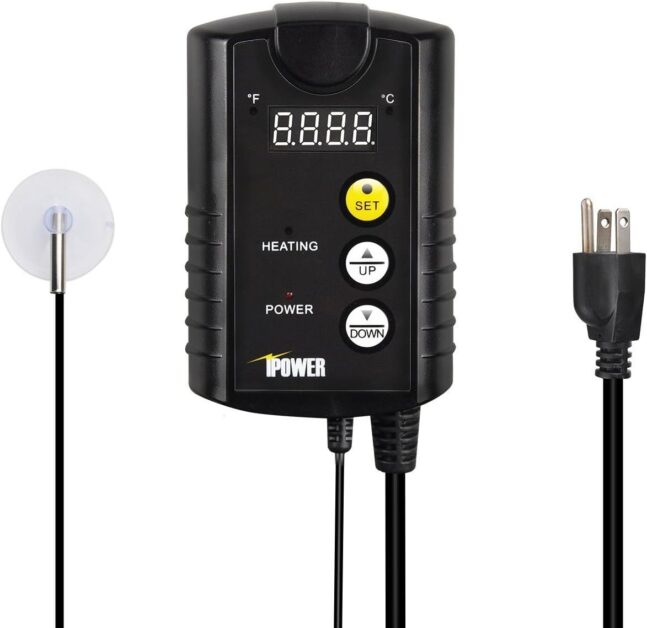
I recently purchased the iPower Digital Heat Mat Thermostat to enhance my indoor gardening setup, and I must say, it’s been a game-changer. With its precise temperature control and easy-to-use interface, I can now effortlessly maintain the ideal growing conditions for my plants. The wide temperature range allows me to cater to the specific needs of different plant species, ensuring optimal growth and development.
Its durability gives me confidence in its long-term performance, and while it may have a slightly higher price point, the benefits far outweigh the cost. Overall, I highly recommend the iPower Digital Heat Mat Thermostat to any gardener looking to take their indoor gardening to the next level.
✅ Wide Temperature Range: It has a wide temperature range from 40 to 108 degrees Fahrenheit (5 to 42 degrees Celsius), providing flexibility to accommodate various plant species’ temperature requirements.
✅ Easy-to-Use Interface: The thermostat features a user-friendly interface with easy-to-read digital displays, making it simple to set and monitor the temperature.
✅ Versatility: This thermostat can be used for various applications beyond seed germination, such as controlling temperature in reptile terrariums, brewing setups, and fermentation chambers.
✅ Durable Construction: The iPower thermostat is built with durable materials, ensuring longevity and reliability in maintaining consistent temperatures.
❌ Limited Compatibility: Although versatile, this thermostat is specifically designed for use with heat mats and may not be compatible with all heating devices or systems.
❌ External Probe: The thermostat requires an external probe to accurately measure the temperature, which may add complexity to the setup and increase the risk of damage if not handled carefully.
❌ No Battery Backup: In case of power outages, the thermostat does not have a built-in battery backup feature, potentially disrupting temperature control and affecting plants’ health.
❌ Single Outlet: It provides control for a single heating device, which may be insufficient for users with multiple heat mats or heating systems in their setup.
Planting Collard Greens: Best Practices and Timing
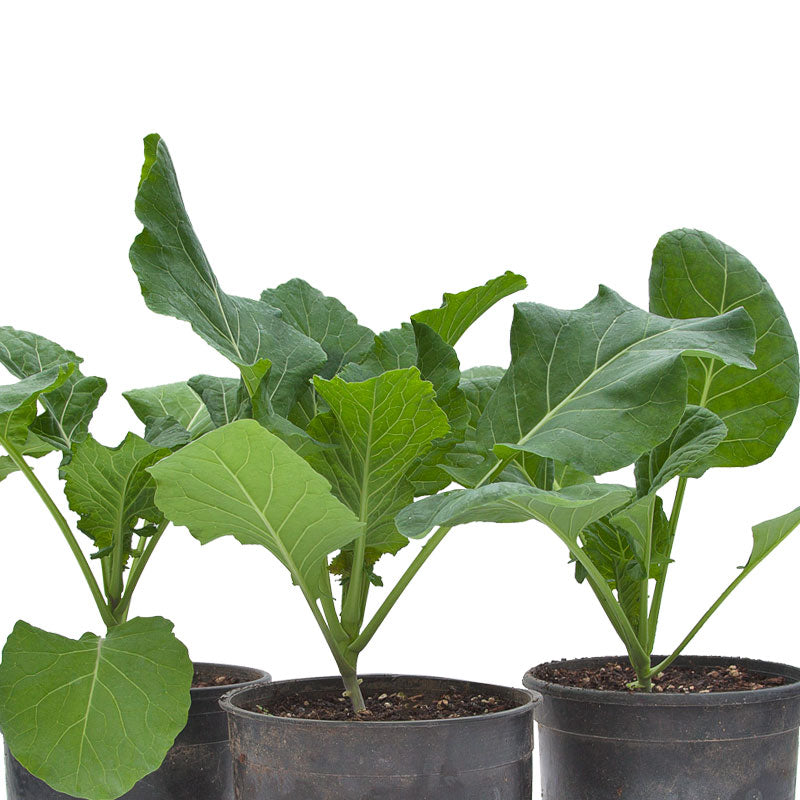

Planting collard greens requires careful consideration of best practices and timing to ensure successful growth and a bountiful harvest. Before planting, it is important to select a variety of collard greens that suits your specific needs and growing conditions. Varieties such as Georgia Southern and Vates are popular choices due to their reliable performance and excellent flavor.
- Optimal Timing: Collard greens are cool-season crops and thrive in temperatures between 45°F to 75°F.
- Ideal Seasons: The best times for planting collard greens are early spring and fall when temperatures are within the favorable range.
- Temperature Sensitivity: Extreme temperatures should be avoided as they can adversely affect germination and growth of collard greens.
- Direct Sowing: Collard green seeds should be sown directly into well-prepared soil that is rich in organic matter to ensure successful growth.
- Soil Preparation: Performing a soil test is recommended to assess pH levels and nutrient content. Collard greens prefer slightly acidic soil with a pH of 6.0 to 6.5.
By following these best practices and carefully considering the timing of your plantings, you can set your collard greens up for success. With proper care and attention, you will be rewarded with healthy, nutrient-rich greens that can be enjoyed in a variety of delicious dishes.
Providing Adequate Sunlight and Water for Collard Greens
Collard greens, like any other plant, require adequate sunlight and water to thrive and produce a bountiful harvest. As a gardener, it is essential to provide the right conditions to ensure the success of your collard greens.
- Sunlight Requirements: Collard greens thrive in both full sun and partial shade. Ideally, they should receive a minimum of six hours of direct sunlight daily for optimal growth and development. Position them strategically in your garden to maximize sun exposure.
- Watering Needs: Consistent moisture is essential for collard greens. During dry spells or hot summer months, ensure regular watering to keep the soil moist. Avoid overwatering to prevent root rot and other issues. Aim for evenly moist soil without saturation.
- Mulching: Mulching around collard greens helps retain soil moisture, reducing the need for frequent watering. Monitor soil moisture levels regularly and adjust your watering schedule as needed to maintain the ideal growing conditions for your collard greens.
Fertilizing Collard Greens: What You Need to Know

When it comes to fertilizing collard greens, there are a few key factors to consider in order to achieve optimal growth and yield. Collard greens are heavy feeders, meaning they require a significant amount of nutrients to thrive.
Here are the essential steps for preparing the soil and fertilizing collard greens in your garden:
- Soil Preparation:
- Incorporate organic matter: Before planting, work well-rotted manure or compost into the soil. This enriches the soil with nutrients and improves its structure.
- Ensure proper drainage: Collard greens prefer well-draining soil. If your soil tends to retain water, consider adding sand or perlite to improve drainage.
- Planting Collard Greens:
- Choose a sunny location: Collard greens thrive in full sun.
- Space the plants: Plant collard greens about 18 to 24 inches apart to allow for healthy growth.
- Sow seeds or transplant seedlings: You can directly sow seeds or start with young seedlings.
- Fertilization:
- Nitrogen (N) is crucial for foliage development. Collard greens benefit from regular nitrogen applications.
- Use a balanced fertilizer: Look for a fertilizer with an N-P-K ratio such as 10-10-10 or 14-14-14.
- Apply according to packaging instructions: Follow the recommended rates for your specific fertilizer.
- Fertilize at planting: Mix the fertilizer into the soil when planting.
- Side-dress during growth: Apply additional fertilizer around the base of the plants as they grow.
- Avoid over-fertilization: Too much nitrogen can lead to excessive leafy growth and reduced flavor.
The following table explains about the fertilizing collard greens:
| Nutrient Type | Application Rate (per 100 square feet) |
|---|---|
| Nitrogen (N) | 1-2 pounds |
| Phosphorus (P) | 0.5-1 pound |
| Potassium (K) | 1-2 pounds |
| Calcium (Ca) | 1-2 pounds |
| Magnesium (Mg) | 0.5-1 pound |
It is advisable to divide the total amount of fertilizer into multiple applications, spreading them out over the growing season. This helps prevent nutrient burn and promotes consistent growth. Additionally, periodic applications of a slow-release organic fertilizer can provide a steady supply of nutrients over an extended period of time. By following these guidelines, gardeners can ensure that their collard greens receive the necessary nutrients for vigorous and healthy growth.
Managing Pests and Diseases in Collard Greens
Pests and diseases can pose a significant threat to the health and productivity of collard greens. It is essential for gardeners to be proactive in managing these potential issues to ensure a successful harvest.
| Pest/Disease | Symptoms | Treatment | Effects on Plant |
|---|---|---|---|
| Pests | |||
| Aphids | Cluster of pale, translucent insects on the undersides of leaves. | Use insecticidal soap or neem oil. | Suck out tender leaves’ juices. |
| Harlequin Bug | Feeding damage on collard plants. | Insecticidal soap or neem oil. | Damage to leaves. |
| Cabbage Worms | Chewing damage by larvae on leaves. | Insecticidal soap or other pesticides. | Significant leaf damage. |
| Armyworms | Common when planting collard. | Use diatomite or insecticidal soap. | Potential leaf destruction. |
| Maggots | Significant damage to collard plants. | Investigate methods to get rid of maggots. | Harm to plant health. |
| Loopers | Common collard pests. | Learn how to control caterpillars and loopers. | Leaf damage due to feeding. |
| Moths | Population on collard plants. | Spray with neem oil or use insecticidal soap. | Potential harm to leaves. |
| Cutworms | Attempt to feed on collard. | Explore ways to control cutworms. | Damage to young plants. |
| Flea Beetles | Slow down plant growth. | Use insecticidal soap from the garden center. | Reduced growth due to feeding. |
| Nematodes | Root damage. | Diatomite or insecticidal soap to get rid of nematodes. | Impact on root health. |
| Thrips | Significant damage to collard plants. | Research tips and tricks for controlling thrips. | Leaf damage and potential stunted growth. |
| Diseases | |||
| Black Rot | Serious plant disease. No cure once present. | Remove infested collard plants to prevent spread. | Severe damage to plant health. |
| Leaf Spot | Common problem on collard plants. | Learn how to get rid of leaf spot. | Spots on leaves affect overall plant appearance. |
| Anthracnose | Occurs sometimes on collard plants. | Use fungicides available at the garden center. | Fungal infection affecting plant health. |
| Downy Mildew | Common on collard plants. | Spray vinegar onto leaves. | Fuzzy growth on leaves. |
| Damping Off | Occurs due to poor germination conditions. | Provide high-quality soil and avoid overwatering. | Seedlings fail to thrive. |
| Mold | Presence of plant mold. | Water plants less frequently and ensure good air circulation. | Mold growth affects overall plant health. |
By implementing proactive measures such as regular monitoring, using appropriate pest control methods, and practicing good sanitation, gardeners can effectively manage pests and diseases in collard greens, promoting healthy growth and a bountiful harvest. Stay tuned for more helpful tips in our ongoing series on growing collard greens.
Pruning and Harvesting Collard Greens for Continued Growth
When it comes to pruning and harvesting collard greens for continued growth, there are a few key practices to keep in mind. Pruning can help promote healthier and bushier growth, while harvesting should be done strategically to ensure the plant keeps producing.
Pruning Guidelines:
- Regularly remove yellow or damaged leaves to redirect the plant’s energy towards new growth and prevent disease spread.
- Pruning can stimulate branching and promote a fuller plant appearance.
- Use clean and sharp garden shears to avoid damaging the plant during pruning.
- Optimal timing for pruning is when collard greens are six to eight weeks old.
- Leave at least two to three healthy leaves on the plant to sustain photosynthesis and support continued growth.
Harvesting Techniques:
- Begin harvesting collard greens once they reach a desirable size.
- Start with the outer leaves, which are larger and more mature, offering a stronger flavor.
- To harvest, grip the base of the leaf near the stem and gently pull downwards for natural detachment.
- Harvest from the bottom of the plant upwards to ensure ongoing growth and production.
It’s important to avoid completely stripping the plant of its leaves, as this can hinder further growth. By practicing proper pruning and harvesting techniques, you can enjoy a continuous supply of fresh collard greens throughout the growing season.
Cooking and Preserving Collard Greens: Traditional Southern Recipes
Collard greens have a rich history in Southern cuisine, and traditional recipes have been passed down through generations. These recipes showcase the delicious flavors and textures of collard greens while honoring the cultural heritage of the South.
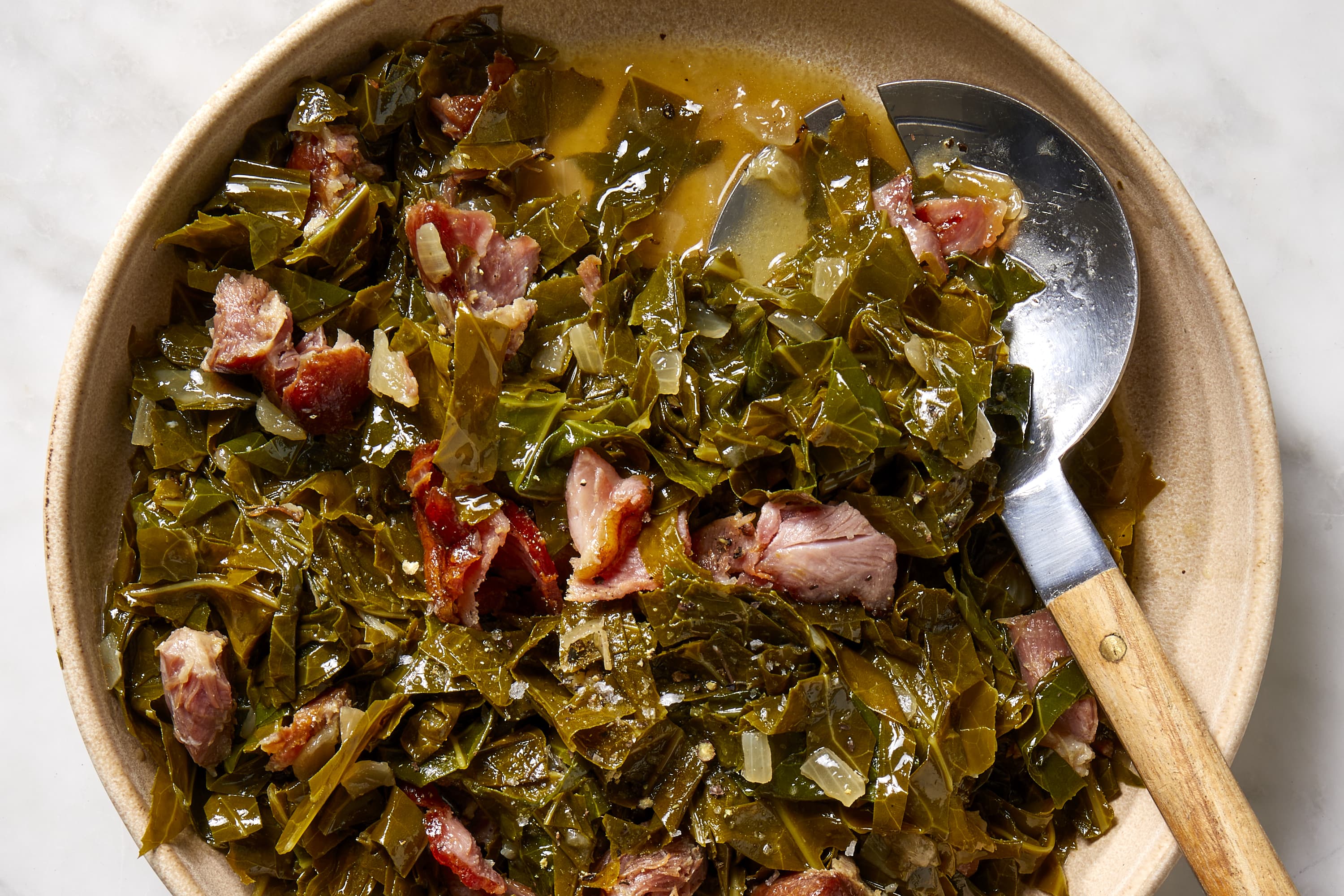

- Low and Slow Cooking Method: Collard greens are traditionally prepared by simmering them with smoked meats such as ham hocks or bacon for hours until they become tender and flavorful.
- Flavor Infusion: This cookingmethod allows the collard greens to absorb the smoky and savory essence of the meats, resulting in a comforting and satisfying dish.
- Sautéed Flavor Combination: Another classic Southern recipe involves sautéing onions, garlic, and a touch of vinegar to provide a tangy contrast to the earthy greens.
- Balanced Flavors: The addition of brown sugar or honey adds a hint of sweetness to balance out the flavors, while crushed red pepper flakes provide a spicy kick.
- Harmonious Blend: This combination of flavors creates a harmonious blend that enhances the natural taste of the collard greens, resulting in a delicious side dish or main course.
By utilizing these cooking methods and flavor combinations, you can create delectable collard greens that are sure to be enjoyed by all.
Collard Greens: Traditional Southern Recipe
Ingredients:
- 2 pounds washed and chopped collard greens
- 3 quarts water
- 1 smoked ham hock
- 3 chicken bouillon cubes
- 8 slices bacon, chopped
- 1 medium onion, finely chopped
- 3 cloves garlic
- 1 lb collard greens, washed, trimmed, and cut
- 3 cups chicken broth
- 1 teaspoon red pepper flakes
- 1 large smoked turkey leg, fully cooked
- Salt & pepper
- Hot sauce
- Olive oil
Instructions:
Preparing Collard Greens:
- Wash the collard greens thoroughly to remove any dirt or debris.
- Remove the stems and chop the greens into bite-sized pieces.
Cooking:
- In a large deep skillet or pot, heat olive oil on medium heat.
- Add chopped bacon and cook until almost crisp.
- Add finely diced onions and cook until tender.
- Stir in minced garlic and cook until fragrant.
- Add chicken broth, red pepper flakes, and smoked turkey leg.
- Bring to a boil, then reduce heat and simmer for 20-30 minutes.
- Remove the turkey leg, let it cool, then remove the meat from the bone and cut it into bite-size pieces.
- Return the meat and skin to the pot.
- Add the collard greens, pushing them down if needed.
- Cover and simmer for up to 60 minutes or until desired tenderness is reached, stirring occasionally.
- Season with salt and pepper as desired.
Serving:
- Plate the collard greens and drizzle with a few drops of hot sauce.
- Serve hot as a delicious and traditional Southern side dish.
This recipe captures the essence of traditional Southern collard greens, slow-cooked to perfection with flavorful ingredients like bacon, smoked turkey, and a blend of seasonings. Enjoy the rich, savory taste of this classic dish that pairs perfectly with a variety of Southern meals.
Exploring Different Culinary Uses for Collard Greens
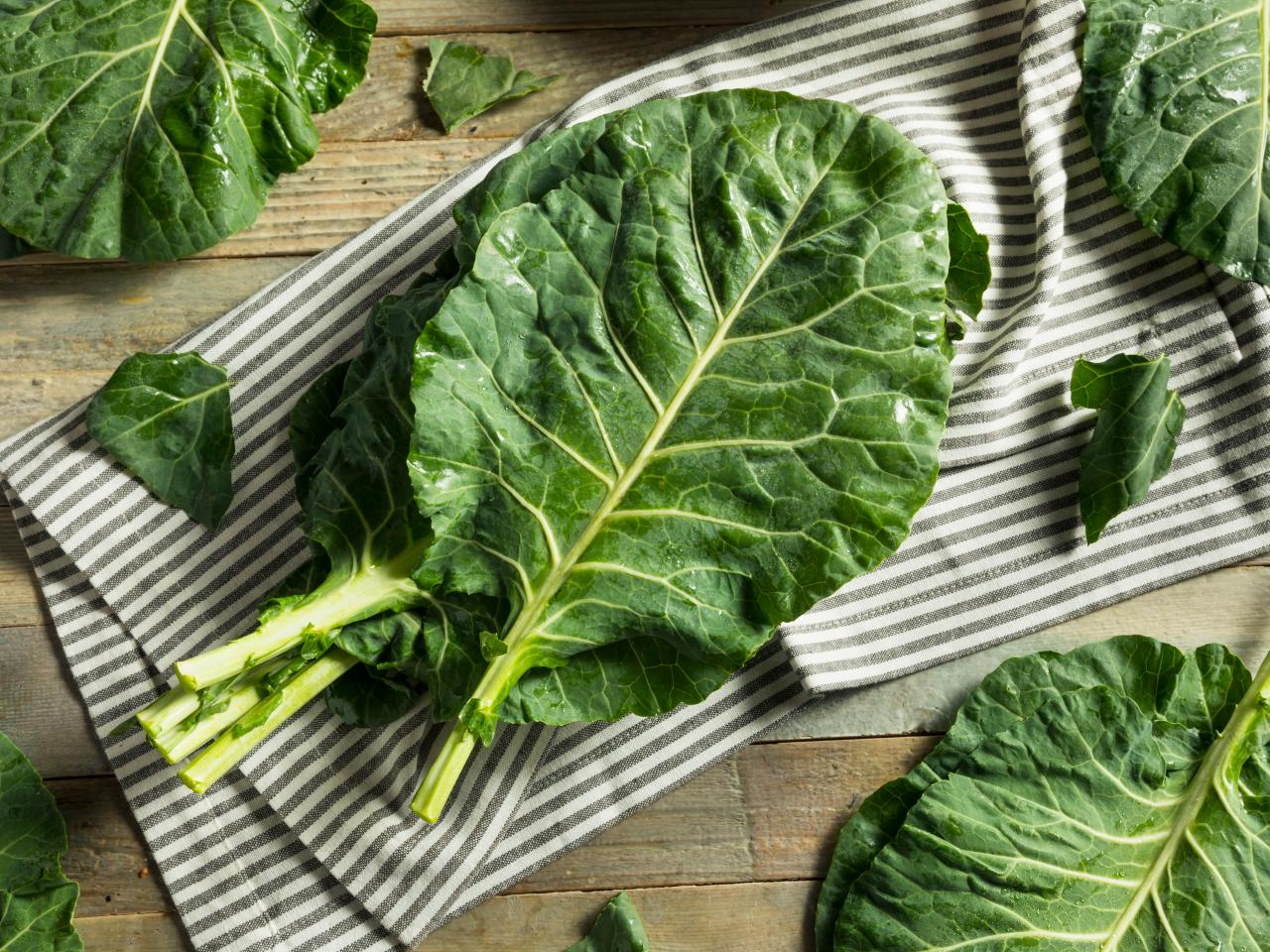

Collard greens are a versatile leafy green vegetable that can be cooked in a variety of ways, offering a range of flavors and textures. Here are some culinary uses for collard greens, along with brief descriptions:
- Traditional Southern Dishes:
- Collard greens are a staple in Southern cuisine. They pair wonderfully with smoky and rich flavors, making them an essential component in dishes like collard greens with ham hocks or black-eyed peas. The slightly bitter taste of collard greens balances well with these hearty dishes.
- Salads and Wraps:
- The large, sturdy leaves of collard greens serve as excellent vessels for creating wraps. Here’s how:
- Blanch the leaves: Briefly blanch the leaves to soften them.
- Wrap fillings: Use collard leaves to wrap around ingredients such as roasted vegetables, grilled chicken, or tofu. This results in a nutritious and flavorful meal option.
- Chopped or shredded: Add chopped or shredded collard greens to salads for an extra boost of vitamins and minerals.
- The large, sturdy leaves of collard greens serve as excellent vessels for creating wraps. Here’s how:
- Incorporation into Soups, Stews, and Stir-Fries:
- Collard greens can be added to various cooked dishes:
- Soups and stews: Add collard greens towards the end of the cooking process. They wilt quickly and contribute to the overall flavor.
- Stir-fries: Their robust texture holds up well during longer cooking times. Whether in a hearty vegetable soup or a spicy Asian stir-fry, collard greens enhance the dish’s nutritional value.
- Collard greens can be added to various cooked dishes:
Collard greens truly are a versatile vegetable, offering numerous culinary possibilities. Whether used in traditional Southern dishes, salads and wraps, or in various cooked preparations, collard greens provide a healthy and delicious addition to any meal.
So why not expand your culinary repertoire and explore the diverse ways to incorporate collard greens into your cooking? From tangy and spicy to mild and comforting, the flavors of collard greens are waiting to be discovered and enjoyed.
Having delved into “Collards: A Southern Tradition from Seed to Table,” I found it to be an enriching journey into the heart of Southern cuisine. From its insightful exploration of collard greens’ cultural significance to its practical gardening tips and mouthwatering recipes, this book offers a comprehensive and delightful experience for anyone interested in this iconic vegetable. Whether you’re a seasoned gardener, a culinary enthusiast, or simply curious about Southern traditions, “Collards” serves as a valuable resource, imparting knowledge and inspiration with every turn of the page.
- Comprehensive Coverage: The book offers a comprehensive exploration of collard greens, covering everything from their history and cultural significance to practical tips for growing and cooking them.
- Cultural Insight: It provides valuable insight into the Southern tradition of collard greens, including their role in Southern cuisine and their significance in African American culinary heritage.
- Growing Tips: Readers can benefit from the practical advice and tips for growing collard greens, making it a useful resource for gardeners interested in cultivating this nutritious vegetable.
- Recipes: The book likely includes a collection of recipes showcasing various ways to prepare and enjoy collard greens, offering readers inspiration for incorporating this versatile vegetable into their meals.
- Beautiful Presentation: It may feature stunning photography or illustrations that enhance the reading experience and make the book visually appealing.
- Limited Focus: While the book may offer in-depth information about collard greens, its narrow focus on this specific vegetable may limit its appeal to readers interested in broader topics related to gardening or Southern cuisine.
- Subjective Taste: The recipes and cooking techniques presented in the book may cater to specific tastes or preferences, which may not resonate with all readers.
- Price: Depending on the reader’s budget, the price of the book may be considered a drawback, especially if they are looking for a more affordable or budget-friendly resource on collard greens.
Health Benefits of Including Collard Greens in Your Diet
Collard greens are not only a delicious addition to your meals, but they also offer a plethora of health benefits that make them a valuable addition to your diet. Packed with essential nutrients, vitamins, and minerals, collard greens can contribute to maintaining overall wellness and preventing various health conditions.

High Fiber Content:
- Collard greens are rich in dietary fiber, which plays a vital role in maintaining a healthy digestive system and regulating bowel movements.
- The fiber content in collard greens promotes proper digestion, prevents constipation, and aids in weight management by inducing a feeling of fullness.
Antioxidant-Rich:
- Collard greens contain antioxidants like vitamin C and beta-carotene, which help protect the body against harmful free radicals and reduce inflammation.
- These antioxidants contribute to a strengthened immune system, fighting off infections and supporting overall immune function.
Heart Health Benefits:
- The fiber in collard greens can help lower cholesterol levels, reducing the risk of heart disease and promoting cardiovascular health.
Potential Anti-Cancer Properties:
- Studies suggest that the antioxidants found in collard greens may have potential anti-cancer properties, aiding in the prevention of certain types of cancer.
By incorporating collard greens into your diet, you can enjoy these various health benefits and support your overall well-being. Whether added to salads, sautéed with your favorite vegetables, or included in hearty soups and stews, collard greens offer a versatile and nutritious addition to any meal. So why not make the most of their health benefits and indulge in the deliciousness of collard greens?
Collard Greens as a Sustainable and Environmentally Friendly Crop
Collard greens are renowned for their sustainability and environmentally friendly nature, making them an excellent choice for gardeners looking to reduce their ecological footprint. These leafy greens have a remarkable ability to grow in various environments and climates, requiring minimal resources compared to other crops.

- Nutritional Value: Collard greens are packed with nutrients, including high amounts of antioxidants, vitamin A, and vitamin K. These nutrients contribute to maintaining night vision, preventing cataracts and macular degeneration, and improving bone health.
- Cultural Significance: Collard greens have a rich cultural history, particularly in the American South and African diaspora. They are a staple in traditional dishes like feijoada in Brazil, caldo verde in Portugal, and haakh in Kashmir.
- Sustainability: Collard greens are a sustainable crop due to their ability to thrive in cooler temperatures, making them suitable for various climates. They are also a part of the cabbage family, which includes other nutrient-rich and sustainable crops like broccoli and cauliflower.
- Pesticide Use: Conventionally grown collards have been identified as a cause for concern due to pesticide use, making organic production and consumption a more sustainable choice.
- Environmental Impact: Sustainable agricultural systems, such as intercropping, can help reduce greenhouse gas emissions and carbon footprint associated with collard green production. A study in Southeast Brazil found that intercropping collard greens with spinach or chicory resulted in approximately 31% lower greenhouse gas emissions compared to monoculture systems.
- Certifications: Products containing at least 95% organic material are recognized by trusted certifications, ensuring a more sustainable choice for consumers
In conclusion, collard greens are a nutritious, culturally significant, and sustainable crop that can contribute to environmentally friendly food production when grown using sustainable practices like intercropping and organic farming. By choosing organic and sustainably produced collard greens, consumers can support a more environmentally friendly food system.
Sharing Collard Greens: Community Gardens and Food Security
Community gardens play a vital role in addressing food security and promoting sustainability by providing individuals and communities with the opportunity to grow their own food and share the harvest with others.
Collard greens are an excellent choice for community gardens due to their nutritional value and versatility in cooking, offering vitamins A, C, and K, fiber, and various minerals.
Sharing collard greens from community gardens promotes healthy eating habits and provides nutritious food to individuals and families who may not have access to fresh produce, thereby addressing food insecurity.
Community gardens offer opportunities for education and skill-building in sustainable gardening practices, crop rotation, pest management, and composting, fostering a deeper connection to food and the environment.
Community gardens promote a sense of community ownership and pride, creating a supportive environment where individuals can share gardening expertise, cultural traditions, and experiences associated with collard greens.
By cultivating collard greens in community gardens, we not only enhance access to nutritious food but also create spaces for learning, collaboration, and community building, ultimately contributing to a healthier and more sustainable future.
Collard Greens in Southern Culture and Cuisine
Collard greens hold a special place in the heart of Southern culture and cuisine. With their rich history and distinct flavors, they have become a staple in many traditional Southern dishes.
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/27434_Special-Sides_-364_3-da9a967beca34e3eba367fbf9ee63ba7.jpg)
- Traditional Southern Dishes:
- Collard greens are a cornerstone of Southern cuisine. They feature prominently in classic dishes like collard greens with smoked ham hocks and savory cornbread stuffed with collard greens.
- The hearty and slightly bitter flavor of collard greens pairs exceptionally well with other iconic Southern foods, creating comforting and satisfying meals.
- Special Occasions and Family Gatherings:
- During family gatherings and special occasions, collard greens often take center stage on Southern tables.
- They are commonly served alongside dishes like fried chicken, black-eyed peas, and cornbread.
- The communal aspect of sharing collard greens reflects the joy of coming together, celebrating heritage, and enjoying a meal with loved ones.
- Symbol of Resilience and Resourcefulness:
- Historically, collard greens were abundant and widely available, especially for African Americans during challenging times of hardship and segregation.
- Their role as a nutritious and accessible food source symbolizes resilience and resourcefulness within the Southern community.
- Culinary Heritage:
- Collard greens remain a cherished ingredient in Southern cooking, passed down through generations.
- Whether prepared traditionally or incorporated into innovative dishes, they continue to evoke flavors and traditions that define Southern cuisine.
So, the next time you savor a plate of perfectly seasoned collard greens, remember the cultural significance and culinary heritage they represent! 🌿🥬
Resources and References for Growing Collard Greens
Looking to delve deeper into the world of collard greens and enhance your practices for growing them? Here are some valuable resources and references to help you expand your knowledge and achieve optimal results in your gardening endeavors.
1. Books:
– “The Vegetable Gardener’s Bible” by Edward C. Smith: This comprehensive guide provides invaluable insights into growing a wide range of vegetables, including collard greens. It covers everything from soil preparation to harvesting, making it an essential resource for both beginner and experienced gardeners.
– “The New Organic Grower” by Eliot Coleman: A revered reference for organic gardening, this book offers strategies to maximize yields and maintain crop health, with a section dedicated to growing greens like collards. Coleman’s expertise in sustainable practices can greatly enhance your understanding of environmentally friendly approaches.
2. Online Sources:
– The National Gardening Association (NGA) website: NGA provides a wealth of information on various aspects of gardening, including collard greens. Their online resources offer guidance on planting, caring for, and harvesting collards, as well as troubleshooting common issues.
– Agricultural Extension websites: Many university agricultural extensions publish informative articles and fact sheets on collard greens. These sources provide research-based recommendations tailored to specific regions, helping you adapt the cultivation practices to your local conditions.
Remember to critically evaluate the credibility and reliability of online sources, ensuring they are from reputable organizations or experts in the field. By exploring these resources, you can take your collard green cultivation to new heights and achieve the best possible outcomes in your garden.
Watch video for more information:
fAQ
How long does it take for collard greens to grow?
The time it takes for collard greens to grow can vary depending on the variety and growing conditions. On average, collard greens take about 60-80 days to reach maturity.
Can I grow collard greens in containers?
Yes, collard greens can be grown in containers as long as the container is large enough to accommodate their root system. Choose a container that is at least 12 inches deep and wide.
Do collard greens need full sun to grow?
Collard greens thrive in full sun but can tolerate partial shade. However, they will grow best and produce more abundant foliage if given at least 6-8 hours of direct sunlight per day.
How often should I water my collard greens?
Collard greens require regular watering to keep the soil consistently moist. Water deeply once or twice a week, depending on the weather and soil conditions.
What are common pests and diseases that affect collard greens?
Common pests that may affect collard greens include aphids, cabbage worms, and flea beetles. Diseases such as clubroot and downy mildew can also be a concern. Implementing proper pest and disease management practices can help mitigate these issues.
Can I harvest collard greens more than once?
Yes, collard greens are a cut-and-come-again crop, meaning you can harvest the outer leaves while allowing the inner leaves to continue growing. This allows for multiple harvests from the same plant.
Are collard greens high in nutrients?
Yes, collard greens are highly nutritious. They are rich in vitamins.
How can I preserve collard greens for later use?
Collard greens can be preserved by blanching and freezing them. Simply blanch the leaves in boiling water for a few minutes, then transfer them to an ice bath to cool. Drain and freeze in airtight containers or freezer bags.
What are some traditional Southern recipes that use collard greens?
Traditional Southern recipes using collard greens include dishes like collard greens with bacon, Hoppin’ John, and collard greens stew. These recipes often incorporate ingredients like smoked ham hocks or onions for added flavor.
Are community gardens a good way to share collard greens and promote food security?
Yes, community gardens can play a crucial role in sharing collard greens and other fresh produce within a community. They provide access to nutritious food, promote food security, and foster a sense of community and cooperation among participants.

Studied Agricultural Engineering-Plant Protection at University of California, Davis.
Head of Content writing team at Southelmontehydroponics.com