How To Grow Rice For A Sustainable Supply
Table of Contents
The Importance of Rice as a Staple Food Crop
Rice, scientifically known as Oryza sativa, is one of the most important staple food crops in the world. With its origins in Asia, this cereal grain has been cultivated for thousands of years and has played a vital role in providing sustenance for billions of people. The significance of rice as a staple food can be attributed to several key factors.
Firstly, rice is highly nutritious and serves as a valuable source of carbohydrates, providing energy to fuel the body. It contains essential amino acids and is relatively low in fat, making it a healthy choice for individuals seeking a balanced diet. Additionally, rice is gluten-free, making it suitable for those with gluten intolerance or celiac disease.
Furthermore, rice is incredibly versatile and can be consumed in various ways. It can be boiled, steamed, or fried, and is a key ingredient in numerous dishes across different cultures. Whether it is the base of a hearty stir-fry, the main component of sushi, or the foundation of a comforting rice pudding, this grain has a remarkable ability to adapt and complement a wide array of flavors.
Moreover, rice is a highly sustainable crop, capable of producing high yields on relatively small areas of land. Its adaptability to different climatic conditions, such as wet, tropical environments or dry, upland regions, makes it an ideal choice for cultivation in many parts of the world. The crop’s ability to thrive in submerged conditions gives rise to the practice of paddy rice farming, which takes advantage of flooded fields to suppress weeds and increase yields.
In conclusion, the importance of rice as a staple food crop cannot be overstated. Its nutritional value, versatility, and sustainability make it a crucial component of global food security. From providing sustenance for billions of people to supporting the livelihoods of countless farmers worldwide, rice continues to play a vital role in nourishing communities and shaping cultures.
Understanding the Environmental Impact of Rice Production
Rice is one of the most important staple food crops in the world, providing sustenance to over half of the global population. However, it is crucial to understand the environmental impact of rice production in order to ensure its sustainability for future generations.
One of the main environmental concerns associated with rice production is the emission of greenhouse gases, particularly methane. The submerged conditions required for rice cultivation create an anaerobic environment where methane-producing microorganisms thrive. These emissions contribute to global warming and the depletion of the ozone layer. Additionally, the use of chemical fertilizers and pesticides in rice cultivation can result in water pollution and the loss of biodiversity in surrounding ecosystems.
To mitigate these environmental impacts, various approaches have been developed. One such approach is the adoption of alternate wetting and drying (AWD) irrigation techniques, which reduce water usage and methane emissions compared to traditional continuous flooding methods. Another strategy is the implementation of integrated pest management (IPM) practices, which involve the use of natural predators and resistant rice varieties to control pests, thus minimizing the need for chemical interventions. Furthermore, the use of organic fertilizers and the promotion of crop rotation can enhance soil health, reduce chemical runoff, and support a more sustainable rice production system.
Understanding the environmental impact of rice production is essential for the development of sustainable practices that can mitigate its negative effects. By adopting innovative techniques and promoting environmentally friendly approaches, we can strive towards a future where rice production is not only abundant, but also ecologically responsible.
• Rice production has a significant environmental impact, particularly in terms of greenhouse gas emissions and water pollution.
• Methane emissions from rice cultivation contribute to global warming and ozone depletion.
• The use of chemical fertilizers and pesticides can result in water pollution and loss of biodiversity.
• Alternate wetting and drying (AWD) irrigation techniques can reduce water usage and methane emissions compared to continuous flooding methods.
• Integrated pest management (IPM) practices involve the use of natural predators and resistant rice varieties to control pests, reducing the need for chemical interventions.
• Organic fertilizers and crop rotation can improve soil health, reduce chemical runoff, and support sustainable rice production.
• Understanding the environmental impact is crucial for developing sustainable practices in rice production.
Selecting the Ideal Rice Varieties for Sustainable Cultivation
Selecting the ideal rice varieties is crucial for sustainable cultivation practices. With a wide variety of options available, it is important to consider several factors before making a decision. One key factor to evaluate is the climate and growing conditions in your specific region. Different rice varieties have varying tolerance to temperature, rainfall, and soil conditions. Therefore, selecting a variety that flourishes in your local climate will greatly enhance the chances of a successful harvest.
Another important consideration is the desired characteristics of the rice variety. Factors such as yield potential, grain quality, disease resistance, and tolerance to pests should all be taken into account. For example, if you are looking for higher yields, you may choose a high-yielding variety that has been proven to perform well in your area. On the other hand, if you prioritize grain quality, you might opt for a variety known for its excellent taste and texture.
It is also essential to stay updated on the latest research and advancements in rice breeding. Scientists and researchers are constantly developing new rice varieties that are more resistant to diseases, pests, and environmental stress. By staying informed about these developments, you can make informed decisions about the best rice varieties for sustainable cultivation.

Preparing the Soil for Rice Planting
Preparing the soil for rice planting is a crucial step in ensuring a successful and bountiful harvest. The quality of the soil directly impacts the growth and development of rice crops, as well as their ability to withstand environmental stressors. To achieve optimal soil conditions, several factors must be considered.
First and foremost, soil fertility plays a key role in rice cultivation. The soil should be rich in essential nutrients such as nitrogen, phosphorus, and potassium, which are vital for the plant’s growth. Conducting soil tests to determine its nutrient composition can help you identify any deficiencies and allow for targeted fertilization. This will not only improve crop yield but also contribute to sustainable farming practices by ensuring that fertilizers are applied in optimum quantities.
Next, proper soil preparation is essential for creating an ideal seedbed for rice planting. This involves removing any weeds, rocks, or debris that may hinder the plant’s growth or interfere with the mechanized planting process. The soil should be plowed, followed by harrowing or tilling to break up clumps and create a fine, level seedbed. This facilitates uniform germination and emergence of rice seedlings, leading to more consistent crop growth and easier weed control.
In addition to cultivating a healthy seedbed, ensuring proper water management is crucial for successful rice cultivation. Rice is a semi-aquatic plant that thrives in flooded conditions, making the establishment of an effective irrigation system vital. Controlling the amount of water, both during the initial flooding and subsequent stages of growth, helps to prevent waterlogging and optimize nutrient availability to the plants.
In conclusion, preparing the soil for rice planting is a multifaceted process that requires careful attention to soil fertility, seedbed quality, and water management. By addressing these vital components, farmers can create an environment conducive to optimum crop growth and ultimately achieve higher yields. Implementing these practices not only contributes to sustainable rice farming but also supports global food security by ensuring a steady and reliable supply of this vital staple crop.

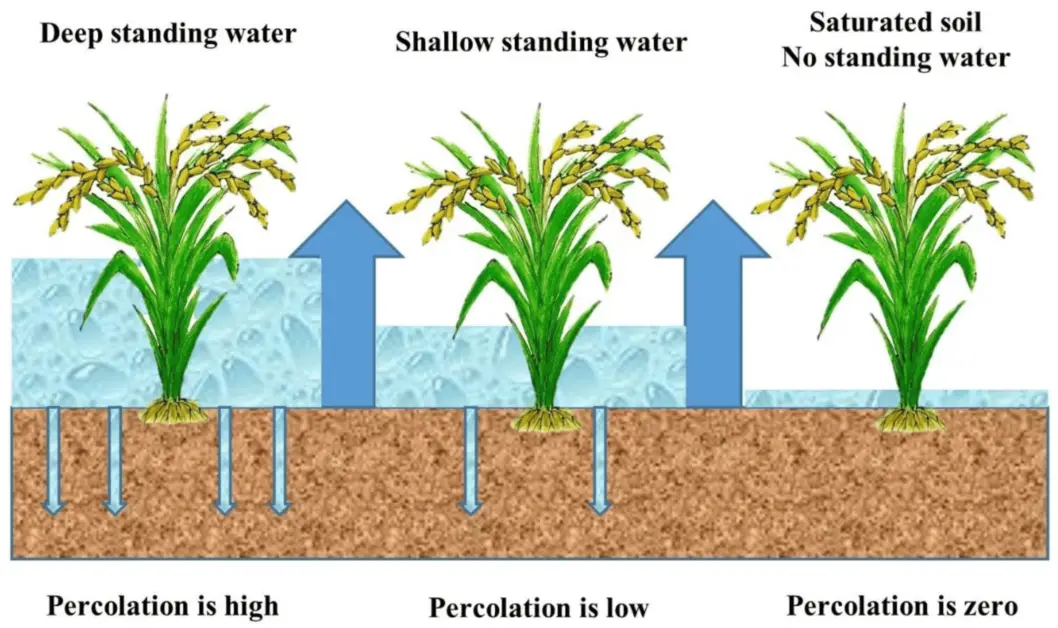
Optimal Water Management Techniques for Rice Cultivation
Optimal water management techniques are crucial for successful rice cultivation. Rice is a semi-aquatic crop that requires a consistent water supply throughout its growth stages. Adequate water management not only ensures proper plant growth and development but also contributes to the overall sustainability of the rice farming system.
One key technique in water management is the practice of intermittent flooding. This involves periodically flooding and draining the rice fields to provide the necessary balance of water and oxygen for the plants. By periodically submerging the rice plants, the growth of undesirable weeds is suppressed, while the rice plants can efficiently absorb nutrients from the soil. It is important to note that the duration and frequency of flooding should be carefully determined based on factors such as soil type, weather conditions, and rice variety. A well-designed irrigation system with adjustable water levels and effective drainage is essential for implementing intermittent flooding effectively.
Another important aspect of water management in rice cultivation is avoiding excessive or wasteful use of water. Over-irrigation not only leads to water wastage but also increases the leaching of nutrients, resulting in environmental pollution. Employing water-saving techniques such as alternate wetting and drying (AWD) can significantly reduce water consumption while maintaining optimal growing conditions for the rice plants. AWD involves allowing the soil to dry out partially between irrigation cycles, mimicking the natural wet and dry cycles that rice plants experience in their natural habitat. This practice not only conserves water but also helps in controlling weed growth and reducing greenhouse gas emissions. Proper monitoring of soil moisture levels, through the use of moisture sensors or visual indicators, can aid in implementing AWD effectively.
Implementing these optimal water management techniques in rice cultivation can lead to increased water-use efficiency, reduced environmental impact, and improved yields. By adopting practices such as intermittent flooding and alternate wetting and drying, rice farmers can ensure the sustainable production of this vital staple crop.
Implementing Integrated Pest Management Strategies in Rice Fields
Integrated Pest Management (IPM) is a crucial approach in addressing the various pest challenges faced in rice fields. By combining different strategies and techniques, farmers can effectively manage pests while minimizing the negative impact on the environment and human health. One of the key components of IPM is the use of biological control agents, such as natural predators and parasites, to regulate pest populations. These beneficial organisms help maintain a balance in the ecosystem by preying on pests, reducing the need for chemical pesticides.
In addition to biological control, cultural and physical control methods can also be employed in rice fields. Cultural control involves implementing practices that disrupt the lifecycle of pests and create unfavorable conditions for their survival. For example, farmers can adjust their planting schedules to avoid peak pest populations or choose rice varieties that are resistant to common pests. Physical control methods include the use of physical barriers, like nets or traps, to prevent pests from infesting the rice plants. These approaches can be highly effective in reducing pest damage while minimizing the reliance on chemical pesticides.
Fertilizer Application Methods for Sustainable Rice Growth
Fertilizer application methods play a crucial role in ensuring sustainable growth and productivity of rice crops. The proper application of fertilizers not only helps meet the nutrient requirements of the plants but also minimizes environmental impact. When it comes to rice cultivation, there are various fertilizer application techniques that can be employed to achieve sustainable and efficient results.
One widely used method is the split application of fertilizers, where nutrients are applied in multiple doses throughout the crop growth cycle. This technique allows for better absorption and utilization of nutrients by the plants, reducing the risk of nutrient runoff and leaching. By supplying the right amount of fertilizers at different growth stages, farmers can optimize nutrient uptake and minimize losses, leading to improved yields and reduced environmental impact.
Another effective method is the use of slow-release fertilizers, which release nutrients gradually over an extended period. These fertilizers provide a steady supply of nutrients to the rice plants, ensuring that they are available when needed and reducing the risk of nutrient wastage. Slow-release fertilizers not only promote sustainable growth but also minimize the risk of nutrient imbalances and environmental pollution.
In addition to these techniques, precision fertilization can be employed to apply fertilizers with utmost accuracy. By using advanced technologies such as soil testing and crop sensors, farmers can determine the precise nutrient requirements of their rice crops and adjust fertilizer application accordingly. This targeted approach ensures that nutrients are applied only where and when they are needed, reducing waste and optimizing nutrient use efficiency.
Overall, by selecting the appropriate fertilizer application methods, rice farmers can promote sustainable growth, optimize nutrient use, and minimize environmental impact. It is essential for farmers to understand the specific needs of their rice crops and adopt the most suitable techniques to achieve sustainable and efficient fertilizer application.
Certainly! Here’s a table outlining Fertilizer Application Methods for Sustainable Rice Growth:
| Method | Description |
|---|---|
| 1. Balanced Fertilization | Use a combination of inorganic and organic nutrient sources to provide essential elements like nitrogen (N), phosphorus (P), and potassium (K). Proper nutrient balance ensures healthy rice growth. |
| 2. Need-Based Rate of Fertilizer Application | Apply fertilizers based on the specific nutrient requirements of rice crops. Soil testing can help estimate location-specific fertilizer needs. |
| 3. Appropriate Methods and Timing | Consider different application methods such as broadcasting, band placement, or foliar spraying. Timing matters—apply fertilizers during critical growth stages to maximize nutrient uptake. |
| 4. Water Management | Proper water management affects nutrient availability. Maintain consistent soil moisture levels to optimize nutrient absorption by rice plants. |
| 5. Soil pH Management | Adjust soil pH to the optimal range (usually 6.0 to 7.5) for efficient nutrient uptake. Lime application can help correct acidic soils. |
| 6. High-Yielding Cultivars | Choose rice varieties adapted to local conditions. High-yielding cultivars respond better to proper nutrient management. |
Implementing these practices can enhance nutrient use efficiency, promote sustainable rice production, and protect the environment!
Efficient Weed Control Measures for Rice Farming
Weed control is a vital aspect of rice farming, as it directly affects the productivity and quality of the crop. Efficient weed management not only reduces competition for resources such as light, water, and nutrients but also minimizes the risk of yield loss due to weed infestation.
One of the most commonly employed and effective weed control measures in rice farming is the use of herbicides. Selective herbicides, specifically designed for rice cultivation, can effectively target and eliminate unwanted weeds without causing harm to the rice plants. These herbicides are applied either pre-emergence or post-emergence, depending on the growth stage of the weeds and rice. Careful selection and application of herbicides, based on factors such as weed species, growth stage, and application timing, play a crucial role in achieving successful weed control. Additionally, it is important to follow the recommended dosage and safety guidelines provided by agricultural authorities to minimize any negative impacts on the environment.
Certainly! Here’s a table outlining Efficient Weed Control Measures for Rice Farming:
| Method | Description |
|---|---|
| 1. Land Preparation | Start land preparation 3-4 weeks before planting. Plowing destroys weeds and remaining stubble from the previous crop. Allow weeds to grow before the next cultivation. A level field helps retain a constant water level that controls weeds. |
| 2. Wet Seeded Rice | Plow and harrow several times before planting. Depending on weed population, perform three or more operations. Allow weeds to emerge for at least 2 weeks, then kill them with another shallow tillage. This reduces weed seeds in the soil and greatly reduces subsequent crop weeds. |
| 3. Dry Seeded Rice | Allow weeds to emerge within 1-2 weeks, then kill them with either a non-selective herbicide or light cultivation. Spray herbicides and perform manual and/or mechanical weeding. |
| 4. Stale Seedbed Technique | Effective for irrigated, dry direct-seeded rice. Allows weeds to emerge before planting, followed by herbicide application or light cultivation. |
| 5. Herbicides | Use herbicides, especially where labor is scarce and wage rates are high. Proper herbicide application is crucial13. |
| 6. Manual and Mechanical Weeding | Control weeds through manual hand-weeding and mechanical methods using implements like push weeders and interrow cultivation weeders. |
Implementing these measures ensures effective weed control and promotes healthy rice growth!
Choosing the Right Planting Method for Rice Production
When it comes to rice production, choosing the right planting method is crucial for achieving optimal yields and ensuring sustainable farming practices. There are several factors to consider when selecting the planting method, such as the soil type, water availability, climate conditions, and the desired yield quantity and quality.
One commonly used technique is the transplanting method, where rice seedlings are grown in a nursery and then transplanted into the main field. This method allows for more precise spacing between plants, resulting in better air circulation and reduced competition for resources. Transplanting also helps control weeds more effectively and can lead to higher yields compared to direct seeding. However, it requires more labor and time for transplanting the seedlings, as well as maintaining the nursery beds.
Another planting method is direct seeding, where rice seeds are directly sown into the field without prior nursery cultivation. This method is less labor-intensive and time-consuming compared to transplanting. It is suitable for areas with limited labor availability and water resources. Direct seeding can also lead to higher weed infestation, which needs to be managed through proper weed control measures. However, with the use of improved seed varieties and appropriate weed management practices, direct seeding can be an efficient and cost-effective planting method.
Overall, the choice of planting method in rice production depends on various factors, including the farmer’s resources, agroecological conditions, and production goals. It is important for farmers and agronomists to assess these factors and select the most suitable planting method to ensure sustainable rice cultivation and maximize yields.
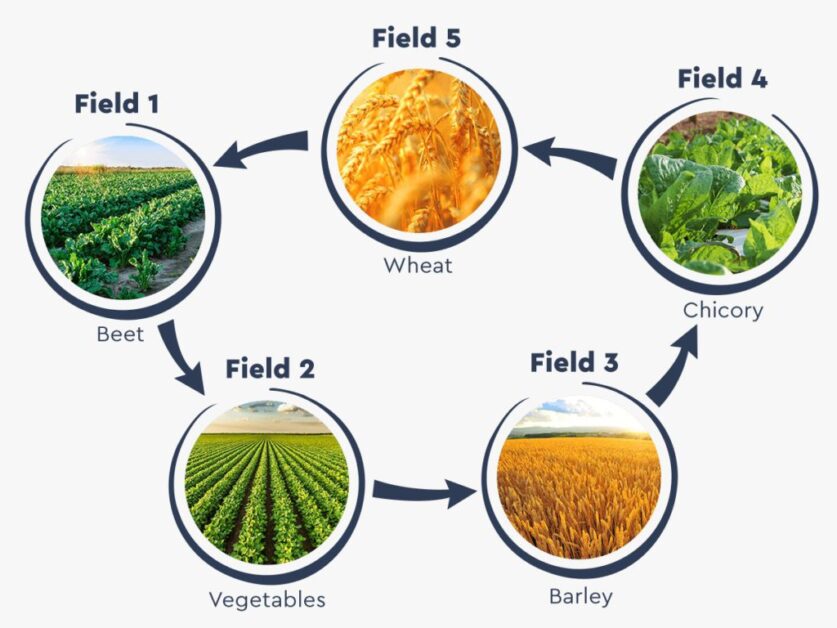
Essential Crop Rotation Practices for Sustainable Rice Supply
Crop rotation is a vital practice in achieving a sustainable rice supply. By systematically alternating crops in a specific sequence, farmers can effectively manage pests, diseases, and nutrient depletion in their rice fields. Additionally, crop rotation enhances soil health, improves water retention, and promotes overall ecosystem balance.
Rotating rice with leguminous crops, such as soybeans or mung beans, can offer several benefits. Legumes have the unique ability to fix nitrogen from the atmosphere and convert it into a usable form for plants. This natural nitrogen fixation reduces the need for synthetic fertilizers and helps replenish soil fertility. Furthermore, leguminous crops can suppress weeds, break pest cycles, and reduce the incidence of soil-borne diseases. By integrating legumes into the crop rotation plan, farmers can achieve sustainable rice production while improving the long-term health of their fields.
Another effective rotation strategy involves alternating rice with deep-rooted crops, such as sweet potatoes or wheat. These crops help break up compacted soil layers, improve aeration, and enhance water infiltration. By reducing soil compaction, farmers can increase root development and nutrient uptake in subsequent rice crops. Additionally, deep-rooted crops can scavenge nutrients from lower soil layers, preventing nutrient leaching and making them available for the following rice crop. This practice not only improves soil structure but also minimizes nutrient loss, ultimately contributing to sustainable rice cultivation.
In conclusion, implementing essential crop rotation practices is crucial for maintaining a sustainable rice supply. By incorporating leguminous crops and deep-rooted plants into the rotation plan, farmers can effectively manage pests and diseases, improve soil health, and enhance overall rice production. By adopting these practices, we can ensure a sustainable future for rice farming while safeguarding the environment and preserving the long-term viability of our agricultural systems.
Managing Diseases and Disorders in Rice Plants
Managing diseases and disorders in rice plants is crucial for ensuring a healthy and productive crop. Rice plants are susceptible to various pests, diseases, and environmental factors that can hinder their growth and reduce overall yield. Implementing effective disease management strategies is essential in minimizing crop damage and maximizing rice production.
One common disease that affects rice plants is rice blast, caused by the fungus Magnaporthe grisea. This disease can cause devastating yield losses and can spread rapidly under favorable environmental conditions. To manage rice blast, it is important to choose resistant rice varieties and practice proper field sanitation. Additionally, applying fungicides at the appropriate time and frequency can help control the spread of the disease. Regular scouting and monitoring of the rice crop is also crucial to detect any signs of infection early on, allowing for timely intervention.
Another significant disease in rice plants is bacterial leaf blight, caused by the bacterium Xanthomonas oryzae pv. oryzae. This disease can result in leaf discoloration, lesions, and considerable yield losses. Effective management of bacterial leaf blight involves selecting resistant rice varieties and implementing cultural practices that promote plant health, such as proper spacing and avoiding waterlogged conditions. Applying copper-based bactericides can provide some control, but monitoring and early detection remain essential for effectively managing this disease.
In conclusion, managing diseases and disorders in rice plants requires a proactive and integrated approach. By selecting resistant varieties, practicing good field sanitation, and adopting appropriate pesticide or bactericide applications, rice growers can minimize the impact of diseases on their crops. Regular monitoring and early detection are vital to promptly implement control measures and safeguard the health and productivity of rice plants.
Harvesting and Post-Harvest Handling Techniques for Rice
Harvesting and post-harvest handling techniques are crucial for preserving the quality and value of rice grains. When it comes to harvesting rice, the timing is of utmost importance. It is essential to harvest the crop at the right stage of maturity to ensure optimal grain yield and quality. Typically, rice is harvested when the grains have reached physiological maturity, which is indicated by a change in color from green to golden yellow. Harvesting too early can result in low grain quality, while delaying the harvest may lead to shattering and yield losses.
Once the rice crop is harvested, it undergoes a series of post-harvest handling processes to maintain its quality and prevent spoilage. Threshing is the initial step, where the grains are separated from the rest of the plant material. Traditionally, threshing was done manually, but mechanized methods such as combine harvesting have become more prevalent, improving efficiency and reducing labor. After threshing, the grains are typically dried to remove excess moisture, as high moisture content can lead to mold growth and deterioration during storage. Drying can be achieved through sun drying or using mechanical dryers, depending on the resources available and the desired quality standards. Proper drying is crucial to prevent grain spoilage and ensure long-term storage quality.
Effective Storage and Preservation Methods for Rice Grains
Effective storage and preservation methods are crucial in maintaining the quality and nutritional value of rice grains. By implementing the right techniques, farmers and consumers can ensure that their rice remains fresh and free from pests or contaminants for extended periods.
One of the key considerations in rice storage is the moisture content. Rice grains should be dried to a moisture level of around 12-14% before storing to prevent fungal growth and insect infestation. This can be achieved by allowing the freshly-harvested rice to air dry on mats or other suitable surfaces. Once the desired moisture level is reached, the grains can be transferred to storage containers such as bins or silos.
Additionally, proper ventilation is essential to prevent moisture buildup and maintain the quality of stored rice. Adequate airflow helps prevent the formation of molds and reduces the risk of spoilage. It is recommended to store rice grains in well-ventilated areas with good air circulation. Regular monitoring of the storage environment, including temperature and humidity levels, is also advisable to ensure optimal conditions for rice preservation.
To further protect rice grains from pests, various methods can be employed. These include the use of hermetic storage techniques, such as sealed containers or bags, which create an oxygen-deficient environment, suffocating pests and inhibiting their reproduction. Alternatively, natural insect repellents, such as neem leaves or essential oils, can be introduced during storage to deter pests without compromising the quality of the rice.
By employing effective storage and preservation methods, rice farmers and consumers can extend the shelf life of rice grains while ensuring that they retain their nutritional value. These practices not only contribute to food security but also reduce post-harvest losses, ultimately promoting sustainability in rice farming and consumption.
Promoting Sustainable Rice Farming through Organic Practices
Promoting Sustainable Rice Farming through Organic Practices
Organic farming practices have gained momentum in recent years, with more farmers opting for eco-friendly methods to cultivate rice. This shift towards organic practices is driven by the urgent need to protect the environment, maintain soil health, and ensure the sustainability of rice farming for future generations. By embracing organic practices, farmers can reduce the reliance on synthetic fertilizers and pesticides, reduce water pollution, and minimize the carbon footprint associated with rice production.
One of the key advantages of organic rice farming is the preservation of soil health. Instead of relying on chemical inputs, organic farmers focus on building a fertile soil ecosystem that supports the growth and development of rice plants. Practices such as crop rotation, cover cropping, and the use of organic compost or manure help to enrich the soil with essential nutrients and improve its structure. This not only enhances the productivity of rice crops but also reduces soil erosion and supports beneficial soil microorganisms that contribute to plant health.
Moreover, organic rice farming promotes biodiversity, creating a more resilient and ecologically balanced farming system. By avoiding the use of chemical pesticides, organic farmers encourage natural pest control mechanisms and provide habitats for beneficial insects, birds, and other wildlife. This integrated approach to pest management helps to reduce crop losses caused by pests while preserving the natural balance of the ecosystem.
In conclusion, organic farming practices offer a sustainable solution for rice production, aligning agricultural activities with environmental stewardship. By adopting organic practices, farmers can contribute to the conservation of soil health, biodiversity preservation, and reduction of pollution. Encouraging and promoting sustainable rice farming through organic practices is essential to ensure the long-term viability of rice production and secure food security in a changing climate.
Enhancing Rice Yields and Quality through Modern Technologies
Modern technologies have revolutionized agriculture, and the rice industry has not been left behind. Through the application of cutting-edge techniques, farmers can now enhance rice yields and improve the overall quality of their crops. One such technology is precision agriculture, which utilizes advanced sensors and remote monitoring systems to gather data on soil moisture levels, nutrient content, and even crop health. By precisely analyzing this information, farmers can make informed decisions regarding irrigation, fertilizer application, and disease management, thereby maximizing yields and minimizing wastage.
In addition to precision agriculture, genetic engineering has also played a significant role in enhancing rice production. Scientists have been able to develop genetically modified (GM) rice varieties that offer increased resistance to pests, diseases, and adverse climate conditions. These stress-tolerant varieties have the potential to significantly improve yields, as they are better equipped to withstand challenging environmental factors. Moreover, GM rice has also been engineered with enhanced nutritional value, such as increased iron and vitamin A content, addressing important public health concerns in regions where rice forms a significant portion of the diet. With the help of modern biotechnology, rice farmers can now grow crops that are better adapted to their specific farming conditions, thus ensuring a more sustainable and productive agricultural system.
Collaborating with Local Communities for a Sustainable Rice Supply
Collaborating with local communities is crucial for ensuring a sustainable rice supply. By involving and engaging the people who live and work in the areas where rice is cultivated, we can foster a sense of ownership and responsibility towards the environment and the crop. This collaboration allows for the exchange of knowledge, expertise, and traditional farming practices that have been passed down through generations.
One way to collaborate with local communities is through participatory research and development projects. By involving farmers, researchers, and extension workers in the decision-making processes, we can create solutions that are responsive to the needs and aspirations of the community. For example, identifying and addressing specific challenges faced by farmers in the region can help develop tailored strategies for sustainable rice cultivation. This collaborative approach ensures that the solutions are not only scientifically sound but also culturally and socially relevant.
Furthermore, collaborating with local communities enables the sharing of resources and technologies that can enhance productivity and reduce environmental impact. By providing training and access to modern farming techniques, we can empower farmers to adopt more sustainable practices. Additionally, this collaborative effort can help establish efficient rice supply chains, where farmers, processors, and retailers work together to ensure a fair and transparent market for rice products.
In conclusion, collaborating with local communities is a fundamental pillar for achieving a sustainable rice supply. By engaging farmers, researchers, and other stakeholders, we can harness collective knowledge and expertise to develop innovative solutions that benefit both the environment and the community. This collaborative approach fosters a sense of ownership and responsibility, ensuring the long-term viability of rice cultivation and the well-being of all those involved.
For better understanding watch the below video.
Why is rice considered a staple food crop?
Rice is considered a staple food crop because it provides a significant source of calories and nutrients for a large portion of the world’s population, particularly in Asian countries.
What are some of the environmental impacts associated with rice production?
Some environmental impacts associated with rice production include water pollution from fertilizer and pesticide runoff, methane emissions from flooded rice fields, and loss of biodiversity due to land conversion for rice cultivation.
How do farmers select the ideal rice varieties for sustainable cultivation?
Farmers select rice varieties for sustainable cultivation based on factors such as adaptability to local growing conditions, resistance to pests and diseases, high yield potential, and nutritional quality.
What are optimal water management techniques for rice cultivation?
Optimal water management techniques for rice cultivation include practices such as intermittent flooding, alternate wetting and drying, and the use of water-saving technologies like drip irrigation.
How can integrated pest management strategies be implemented in rice fields?
Integrated pest management strategies in rice fields involve using a combination of cultural, biological, and chemical control methods to manage pests while minimizing the environmental impact. This may include practices like crop rotation, biological pest control, and judicious use of pesticides.
What are efficient weed control measures for rice farming?
Efficient weed control measures for rice farming include using techniques such as manual weeding, herbicide application, mulching, and the use of weed-resistant rice varieties.
What are some essential crop rotation practices for sustainable rice supply?
Some essential crop rotation practices for sustainable rice supply include incorporating leguminous crops that fix nitrogen into the rotation, growing non-rice crops to break pest and disease cycles, and practicing fallow periods to improve soil fertility.
How can diseases and disorders in rice plants be effectively managed?
Diseases and disorders in rice plants can be effectively managed through practices such as planting disease-resistant varieties, practicing crop rotation, adopting good sanitation practices, and timely application of appropriate fungicides or treatments.
What are some effective storage and preservation methods for rice grains?
Effective storage and preservation methods for rice grains include proper drying before storage, using airtight containers to prevent insect infestation, and storing rice in cool and dry conditions to prevent moisture absorption and mold growth.
How can local communities collaborate for a sustainable rice supply?
Local communities can collaborate for a sustainable rice supply by participating in farmer cooperatives, implementing community-based water management systems, sharing knowledge and best practices, and supporting initiatives for sustainable rice farming through local government programs or non-governmental organizations.

Nicole Burke is a dynamic writer at SouthElMonteHydroponics, fueled by her passion for horticulture and environmental sustainability. Armed with a degree in Environmental Science from a renowned institution, Nicole’s expertise lies in hydroponic gardening, organic farming, and biodiversity conservation. Her insatiable curiosity and love for nature drive her to explore innovative techniques in hydroponics, seeking to revolutionize the way we grow crops in urban environments. Nicole’s writing reflects her deep commitment to promoting eco-conscious practices and fostering a deeper connection between humans and the natural world. Through her engaging storytelling, she inspires others to embrace sustainable living and harness the power of hydroponics for a greener future.






